Choosing the right control voltage for your timer relay—12V, 24V, 120V, or 230V—directly impacts system safety, compatibility, and reliability. While 24V DC has become the modern standard for industrial automation due to its safety advantages and PLC compatibility, 12V suits mobile and battery-powered applications, and 120V/230V AC options remain essential for high-power equipment and regional mains-powered systems. This guide provides decision frameworks, comparison tables, and application-specific recommendations to help engineers, system integrators, and procurement specialists specify the optimal timer relay voltage for any control system.
Timer relays are fundamental control components enabling precise, time-based automation across industrial, commercial, and residential applications. The control voltage you specify determines system compatibility, installation safety, and long-term reliability.

Understanding Timer Relay Control Voltages
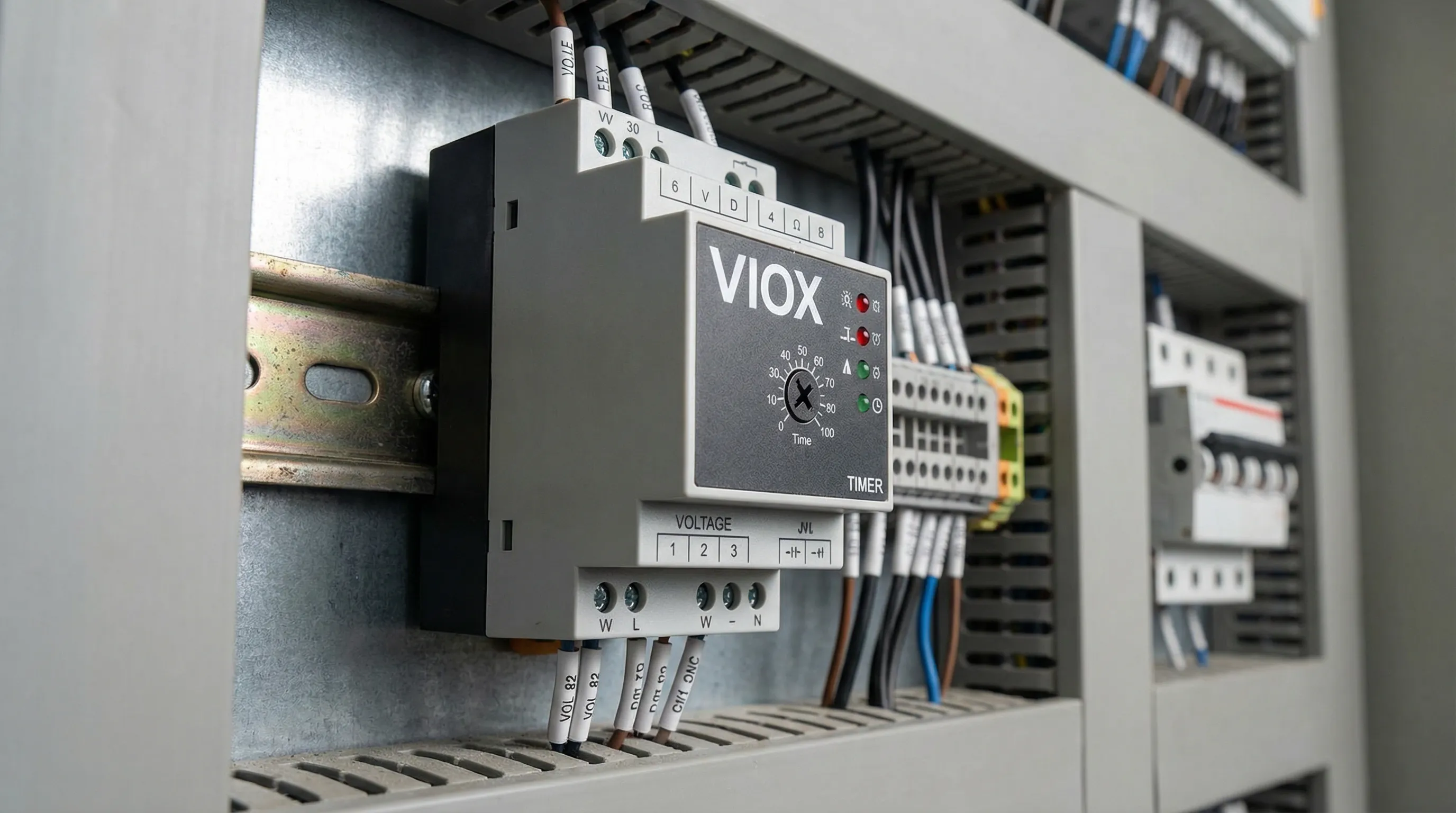
The control voltage (also called coil voltage or operating voltage) is the electrical signal required to energize the timer relay’s internal coil and activate its switching mechanism. This voltage powers the relay’s timing circuit and electromagnet, enabling the device to measure time intervals and control output contacts that may switch much higher voltages and currents.
Why Control Voltage Matters
Specifying the correct control voltage is critical for three primary reasons:
System Compatibility: The timer relay must match your existing control system voltage. A PLC outputting 24V DC signals cannot directly drive a 120V AC relay without additional interface equipment. Mismatched voltages prevent operation or require costly converters.
Safety: Lower DC voltages (12V, 24V) are classified as Safety Extra-Low Voltage (SELV) under IEC 61140, minimizing electric shock risk to personnel during installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting. Higher AC voltages (120V, 230V) require additional safety precautions and qualified personnel.
Reliability and Noise Immunity: DC control voltages, particularly 24V, offer superior noise immunity in electrically harsh industrial environments. AC voltages may be preferred for longer cable runs due to lower voltage drop characteristics.
DC vs AC Control Voltages
Timer relays are available with both DC and AC control voltages, each with distinct advantages:
| Characteristic | DC Control (12V, 24V) | AC Control (120V, 230V) |
| Safety | SELV classification, minimal shock risk | Requires electrical safety precautions |
| Noise Immunity | Excellent, resistant to EMI/RFI | Susceptible to electrical noise |
| Power Availability | Requires power supply; common in modern automation | Direct from mains supply |
| Typical Applications | PLC systems, sensors, modern automation | Traditional control panels, high-power systems |
| Voltage Stability | Consistent output from regulated power supplies | Subject to mains voltage fluctuations |
| Distance | Higher voltage drop over long cable runs | Better suited for long-distance transmission |
Key Consideration: Many modern VIOX timer relays feature universal voltage inputs (e.g., 24-240V AC/DC), eliminating the need to choose between AC and DC and providing global compatibility. These multi-voltage models detect the input voltage type automatically and adjust operation accordingly.
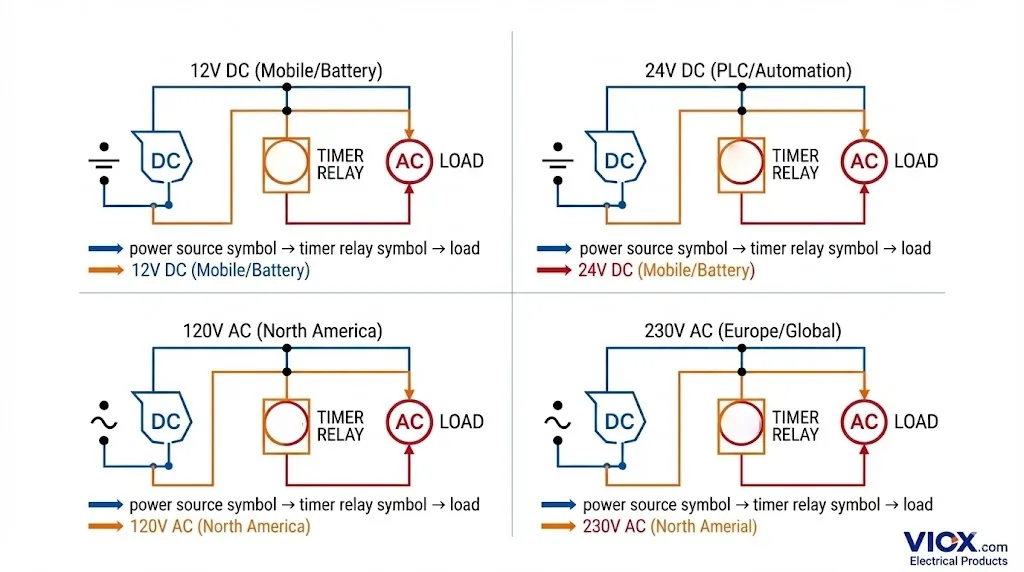
12V vs 24V vs 120V vs 230V: Complete Comparison
Detailed Voltage Specifications
Each control voltage option serves distinct applications based on power requirements, safety needs, and system architecture:
| Voltage | Type | Typical Tolerance | Safety Classification | Primary Use Cases | Geographic Preference |
| 12V DC | DC | ±10-15% | SELV (Safe) | Automotive, mobile equipment, battery systems | Global |
| 24V DC | DC | ±10-20% | SELV (Safe) | PLC systems, industrial automation, sensors | Global (Standard) |
| 120V AC | AC | ±10% | Hazardous voltage | North American control panels, legacy systems | North America |
| 230V AC | AC | ±10% | Hazardous voltage | European machinery, mains-powered systems | Europe, Asia, Global |
12V DC Timer Relays
- Widely available in automotive and mobile applications
- Compatible with standard 12V battery systems (vehicles, boats, RVs)
- Lowest power consumption among common voltages
- Readily available power supplies
- Less common in industrial automation (24V is preferred)
- Higher current draw for equivalent power compared to 24V
- Limited availability in industrial-grade timer relay models
Typical Applications:
- Automotive aftermarket controls
- Marine and RV systems
- Solar battery charging controllers
- Portable equipment and generators
- Agricultural mobile machinery
24V DC Timer Relays
- Industry standard for modern PLC and automation systems
- SELV safety classification reduces electrical hazards
- Excellent noise immunity in industrial environments
- Wide availability from all major manufacturers
- Compatible with industrial sensors, actuators, and field devices
- Lower current requirements than 12V for same power
- Requires dedicated 24V power supply (adds cost if not already present)
- Voltage drop can be significant over long cable runs (>100m)
Typical Applications:
- PLC-controlled automation systems
- Factory assembly lines and process control
- Building automation and HVAC controls
- Safety circuits and emergency stop systems
- Industrial machinery and robots
- Packaging and material handling equipment
Market Position: 24V DC is the dominant standard in new industrial installations worldwide.
120V AC Timer Relays
- Direct connection to North American mains power (no power supply needed)
- Suitable for high-power applications
- Lower voltage drop over long distances compared to 24V DC
- Well-established in existing installations
- Hazardous voltage requires qualified electricians for installation
- Not SELV-rated; higher shock risk during troubleshooting
- Less compatible with modern PLC systems (requires interface relays)
- Subject to mains voltage fluctuations
Typical Applications:
- North American commercial HVAC systems
- Lighting control in buildings
- Older industrial control panels
- Pump and motor controls
- Building equipment (exhaust fans, heaters)
230V AC Timer Relays
- Direct connection to European/international mains (230V/240V)
- No power supply required in regions with 230V mains
- Efficient for controlling high-power equipment
- Suitable for long-distance control signal transmission
- Hazardous voltage classification
- Requires compliance with local electrical codes
- Less compatible with low-voltage control systems
- Installation restricted to licensed electricians in many regions
Typical Applications:
- European industrial machinery
- International commercial equipment
- High-power motor control
- HVAC systems in 230V regions
- Building services (pumps, compressors, ventilation)
Universal Voltage Timer Relays (24-240V AC/DC)
Modern VIOX timer relays increasingly offer universal voltage inputs that accept a wide range:
- Single model serves global markets
- Simplified inventory and procurement
- Flexible installation across different voltage systems
- Future-proof for facility voltage changes
- Reduced engineering specification complexity
Considerations:
- Typically 10-20% higher cost than single-voltage models
- Verify actual voltage range covers your requirements
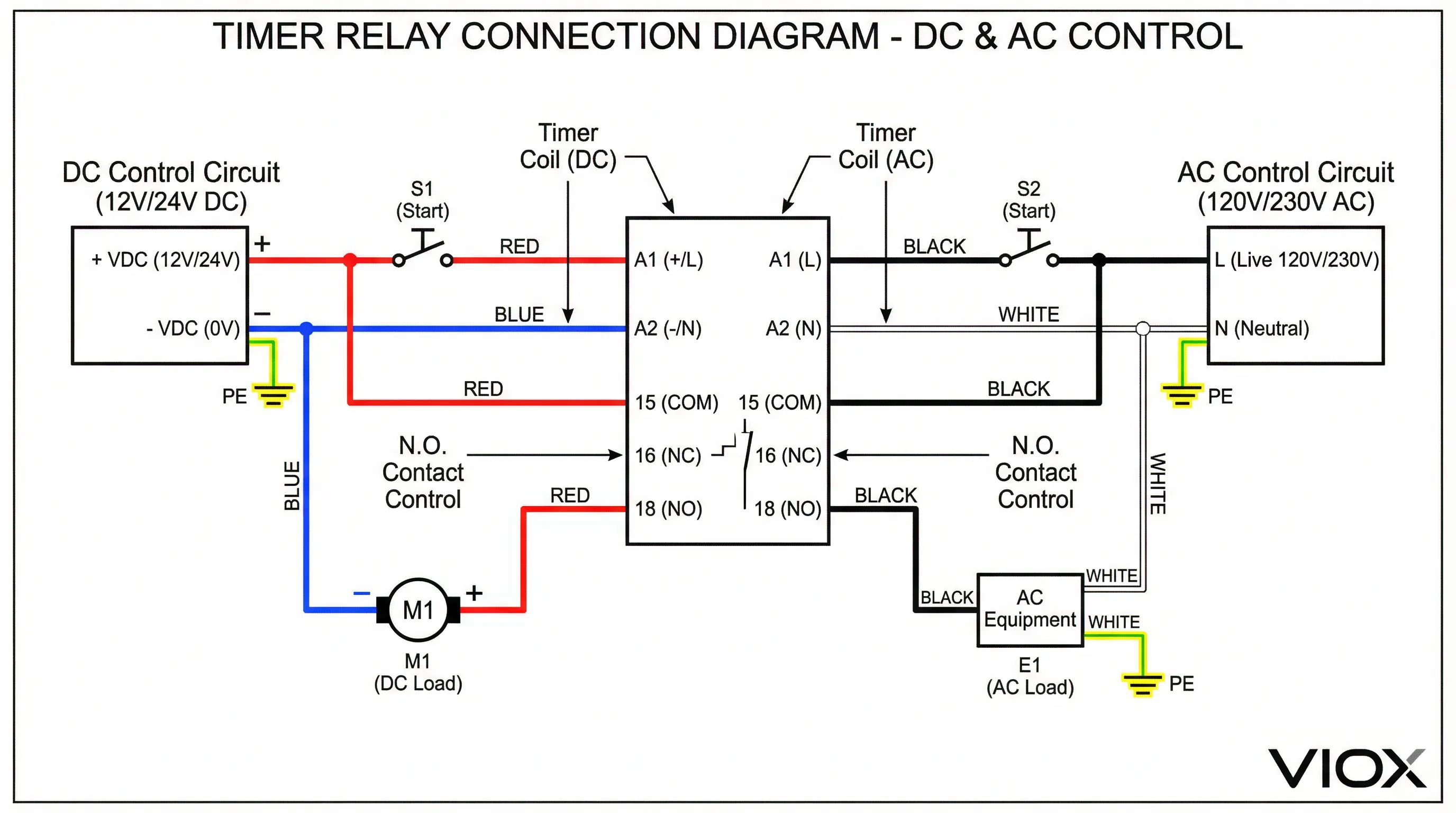
Selection Criteria by Application Type
Decision Framework
Use this systematic approach to select the optimal timer relay control voltage:
| Priority Factor | Recommended Voltage | Reasoning |
| Existing PLC/control system | Match system voltage | Ensures direct compatibility; 24V DC for most modern PLCs |
| Safety-critical applications | 12V or 24V DC (SELV) | Minimizes shock hazard during maintenance and troubleshooting |
| Mobile/battery-powered | 12V DC | Standard automotive/marine battery voltage |
| No existing control system | 24V DC (future-proof) | Industry standard; maximum flexibility for expansion |
| Retrofit to existing AC system | Match existing (120V or 230V) | Minimizes installation cost and complexity |
| Global equipment | Universal 24-240V AC/DC | Single specification for worldwide deployment |
| Long cable runs (>100m) | 120V or 230V AC | Lower voltage drop over distance |
| Noisy electrical environment | 24V DC | Superior EMI/RFI immunity |
Application-Specific Recommendations
Industrial Automation and Manufacturing
Recommended: 24V DC
- PLC input/output modules
- Industrial sensors (proximity, photoelectric, pressure)
- Pneumatic valve solenoids
- Panel indicators and push buttons
- Safety relays and emergency stop circuits
- 120V/230V AC: Legacy equipment or standalone motor starters without PLC control
- Universal voltage: Equipment supplied to multiple global facilities
Building Automation and HVAC
Recommended: 24V AC or 24V DC
Building management systems typically operate on 24V AC (North America) or 24V DC (Europe). Timer relays control fan delay-off, compressor time delays, ventilation purge cycles, and lighting sequences.
- 120V/230V AC: Direct control of line-voltage equipment without contactor
- 12V DC: Battery backup systems for emergency operation
Motor Control and Power Distribution
Recommended: Varies by motor size and control architecture
| Motor Application | Control Voltage | Typical Use Case |
| Small motors (<2 HP) with starter | 24V DC | PLC-controlled conveyor, pump sequencing |
| Medium motors (2-50 HP) | 120V AC | Contactor coil control in North America |
| Large motors (>50 HP) | 230V AC | High-power industrial equipment |
| Star-delta starters | 24V DC or 120V | Timing transition between star and delta windings |
Agricultural and Mobile Equipment
Recommended: 12V DC
Tractors, irrigation systems, and mobile machinery use 12V battery systems. Timer relays control irrigation zone timing, equipment startup delays, and auxiliary system timing (lights, heaters, blowers).
- 24V DC: Larger commercial agricultural equipment with 24V systems
- 230V AC: Stationary equipment with mains power (packing sheds, storage facilities)
Safety and Emergency Systems
Recommended: 24V DC (with battery backup)
Safety circuits should use SELV voltages with uninterruptible power for emergency lighting, evacuation systems, fire suppression, and safety interlocks (per ISO 13849).
Critical requirement: Safety-related timer relays must meet applicable functional safety standards (SIL rating per IEC 61508 or Performance Level per ISO 13849).
Standards and Compliance
Timer relay control voltage selection must comply with applicable international and regional standards to ensure safety, performance, and legal compliance.
Key International Standards
| Standard | Scope | Relevance to Voltage Selection |
| IEC 61812-1 | Time relays for industrial use | Defines performance requirements, accuracy, and safety under electrical stress |
| IEC 60255 | Measuring relays and protection | Covers relay construction and testing methods |
| IEC 61140 | Protection against electric shock | Defines SELV (≤50V AC/≤120V DC) safety classification |
| IEC 60664-1 | Insulation coordination | Specifies clearances and creepage distances by voltage |
| UL 508 | Industrial Control Equipment (North America) | Safety standard for control devices including timer relays |
| IEC/UL 61810-1 | Electromechanical elementary relays | Harmonized standard replacing UL 508 for relays |
Safety Classifications
- Applies to 12V and 24V DC systems
- IEC 61140 defines SELV as ≤50V AC or ≤120V DC
- Minimal electric shock risk
- Permits non-isolated touchable parts under certain conditions
- Preferred for personnel-accessible control circuits
- Require electrical isolation and protective barriers
- Installation by qualified electricians mandated in most jurisdictions
- Additional safety documentation and labeling required
- Must meet local electrical codes (NEC, IEC 60364, etc.)
Regional Compliance Considerations
- UL or CSA certification typically required for commercial installations
- NEC (National Electrical Code) governs installation practices
- 120V AC is standard control voltage for legacy systems
- Transition toward 24V DC in new automation projects
- CE marking required (compliance with Low Voltage Directive, EMC Directive)
- IEC 61812-1 is the primary functional standard
- 230V AC standard for mains-derived control
- 24V DC standard for automation and PLC systems
- Varied requirements; IEC standards widely accepted
- Many regions accept UL or CE certification
- Voltage standardization varies by country (230V dominant, some 220V/240V)
Practical Selection Guidelines
Quick Selection Decision Tree
Start Here: Do you have an existing control system?
→ YES: Match the control voltage of your PLC, DCS, or control panel
- PLC system → typically 24V DC
- Older relay panel → 120V AC (North America) or 230V AC (Europe)
- Building automation → 24V AC/DC
- Mobile equipment → 12V DC
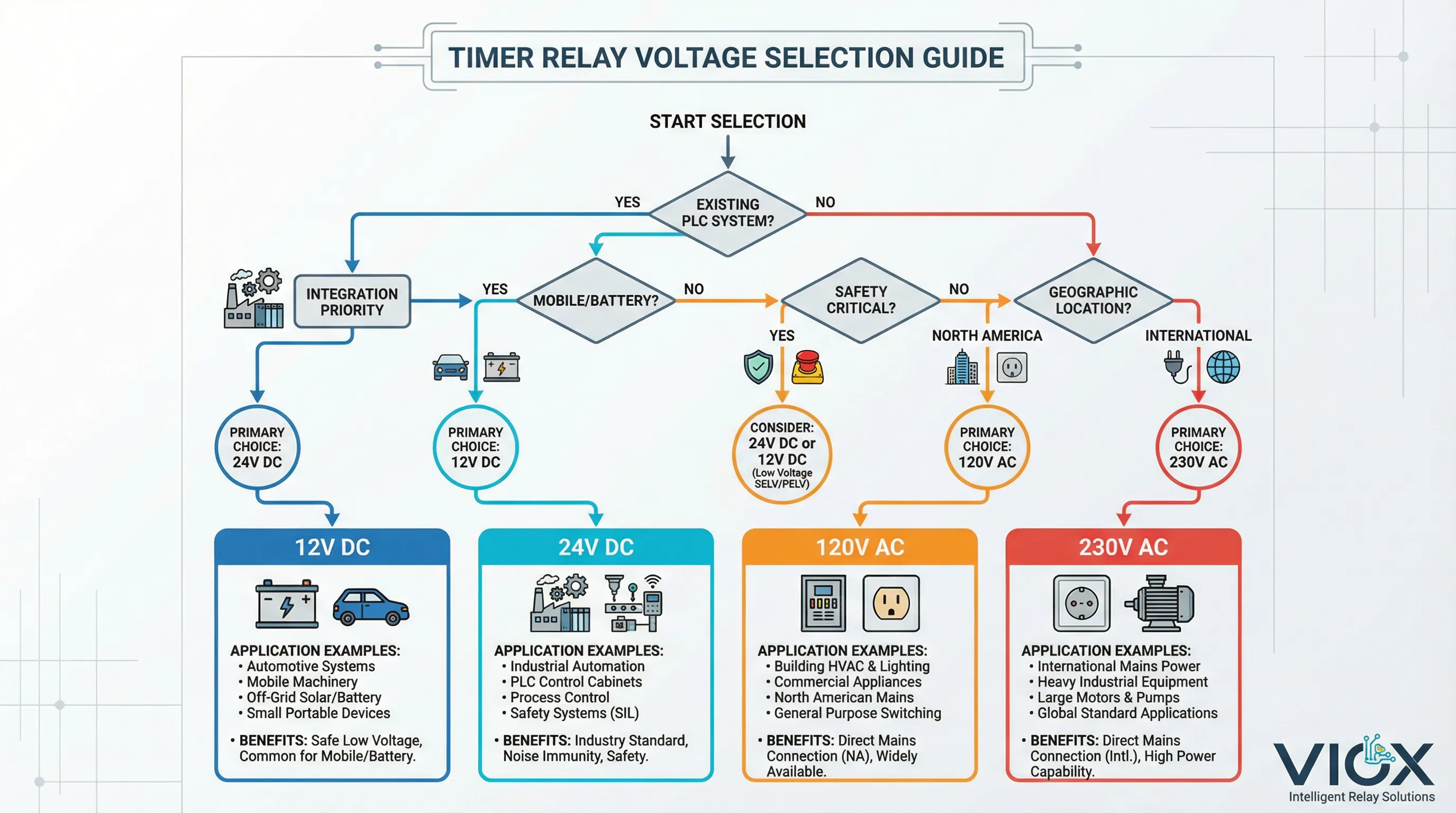
→ NO (New Design): Choose 24V DC
- Industry standard, maximum flexibility
- Best safety profile (SELV)
- Widest product availability
- Future expansion compatibility
Exception: If mains-powered equipment with no control system infrastructure, use 120V/230V AC (regional) to eliminate power supply cost.
Installation Considerations
| Factor | 12V/24V DC | 120V/230V AC |
| Power supply required | Yes (adds $50-200) | No (direct from mains) |
| Wiring | Smaller gauge acceptable | Larger gauge, conduit often required |
| Installation labor | Lower skill level acceptable | Licensed electrician typically required |
| Troubleshooting | Safe for technicians with basic training | Requires electrical safety precautions |
| Voltage drop concern | Significant over >100m runs | Minimal |
| EMI susceptibility | DC more immune (especially 24V) | AC susceptible to noise |
Cost-Benefit Analysis
- 12V/24V DC: Relay + power supply ($50-200) = Higher upfront cost
- 120V/230V AC: Relay only = Lower upfront cost
- 24V DC: Lower maintenance (safer troubleshooting), easier expansion, better reliability in noisy environments
- 120V/230V AC: Higher risk of nuisance trips from voltage fluctuations, requires electrician for modifications
VIOX Recommendation: For new industrial installations, the long-term benefits of 24V DC systems outweigh the modest additional upfront cost. The improved safety, reliability, and expansion flexibility provide superior total cost of ownership.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I use a 24V timer relay with a 12V control signal?
No, not directly. A 24V relay requires approximately 24V to energize its coil reliably. Applying only 12V will result in insufficient coil current, preventing the relay from switching. You must either use a 12V-rated timer relay or add a voltage converter. Some universal voltage timer relays (e.g., 12-48V DC range) can accommodate both voltages.
What happens if I connect a 120V AC timer relay to 230V AC?
The relay will be severely damaged or destroyed immediately. Excessive voltage causes coil overheating, insulation breakdown, and potential fire hazard. Always verify the voltage rating matches your supply exactly. If you need multi-voltage capability, specify a universal voltage model rated for your full voltage range.
Can I control a 230V load with a 24V DC timer relay?
Yes, absolutely. The control voltage (24V DC) is independent of the contact rating. Timer relay contacts are rated separately for switching capacity, commonly 5A to 16A at 250V AC. Verify the contact rating meets or exceeds your load requirements. The 24V DC only energizes the relay coil; the contacts can switch much higher voltages safely.
Is 24V AC the same as 24V DC for timer relays?
No, these are different. Some timer relays accept only AC, only DC, or both. AC relays use different coil designs than DC relays. Always verify the relay specification indicates “AC,” “DC,” or “AC/DC.” Universal voltage VIOX timer relays typically accept both 24V AC and 24V DC interchangeably, automatically detecting the input type.
Why is 24V DC preferred over 12V DC in industrial applications?
Two primary reasons: (1) Lower current draw—24V requires half the current of 12V for same power; (2) Better noise immunity. Additionally, 24V is the established PLC standard.
Do I need a special power supply for 24V DC timer relays?
Yes, you need a regulated 24V DC power supply (DIN rail mount switching power supply rated 24V DC, 1-10A depending on load). Industrial power supplies convert 120V or 230V AC mains to stable 24V DC. Size the power supply for all connected devices with 20% margin. VIOX offers compatible DIN rail power supplies.
Choosing the correct timer relay control voltage impacts safety, compatibility, and reliability. While 24V DC is the global standard for modern automation, 12V DC serves mobile applications, and 120V/230V AC remain essential for mains-powered equipment. VIOX Electric offers timer relays across all voltage options with universal voltage models for maximum flexibility.