What is an MCB and Why Switch Position Matters
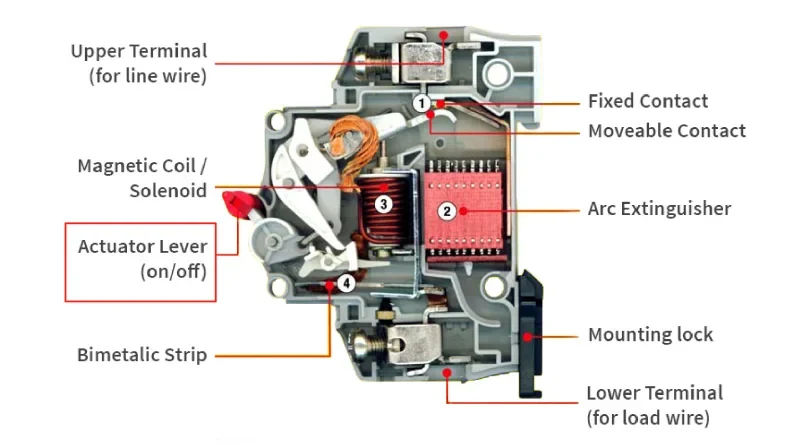
A Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB) is an automatic electrical switch designed to protect electrical circuits from overload and short circuit conditions. The switch position directly controls whether electricity flows through your circuits, making proper understanding essential for safety and functionality.
⚠️ SAFETY WARNING: Always turn off main power before working with MCBs. Electrical work should be performed by qualified electricians when required by local codes.
MCB Switch Positions: Complete Visual Guide
| Position | Status | Handle Direction | Current Flow | Visual Indicator |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ON | Circuit Active | UP ⬆️ | Power Flowing | Handle pointing upward |
| OFF | Circuit Inactive | DOWN ⬇️ | No Power | Handle pointing downward |
| TRIPPED | Fault Detected | MIDDLE ↔️ | No Power | Handle in center position |
Key Differences Between MCB Positions
ON Position (UP):
- Handle points upward toward the “1” or “ON” marking
- Circuit is energized and power flows normally
- All connected devices receive electricity
- Green or blue indicator may be visible (brand dependent)
OFF Position (DOWN):
- Handle points downward toward the “0” or “OFF” marking
- Circuit is de-energized with no power flow
- Connected devices do not receive electricity
- Red indicator may be visible (brand dependent)
TRIPPED Position (MIDDLE):
- Handle sits between ON and OFF positions
- Indicates automatic disconnection due to fault
- Must be reset before normal operation
- Often accompanied by a visible indicator flag
How to Properly Operate an MCB Switch
Turning MCB ON (Energizing Circuit):
- Verify safety: Ensure area is dry and you’re not touching metal parts
- Check position: Confirm handle is in DOWN (OFF) position
- Firm upward push: Press handle firmly upward until it clicks into place
- Verify connection: Handle should be fully UP with no resistance
- Test operation: Check that connected devices receive power
Turning MCB OFF (De-energizing Circuit):
- Identify correct breaker: Verify you’re switching the intended circuit
- Firm downward push: Press handle firmly downward until it clicks
- Confirm position: Handle should be fully DOWN in OFF position
- Verify disconnection: Check that connected devices have no power
Resetting a Tripped MCB:
- Identify the fault: Determine what caused the trip (overload/short circuit)
- Address the problem: Disconnect faulty appliances or resolve wiring issues
- Reset sequence: First push handle fully DOWN, then push UP to ON position
- Monitor operation: Watch for immediate re-tripping indicating ongoing faults
💡 EXPERT TIP: If an MCB repeatedly trips after reset, stop attempting to reset it and contact a qualified electrician immediately.
Common MCB Applications and Use Cases
Residential Applications:
- Lighting circuits: Control power to room lighting systems
- Power outlets: Manage electricity to wall outlets and receptacles
- Appliance circuits: Dedicated circuits for major appliances
- HVAC systems: Protection for heating and cooling equipment
Commercial Applications:
- Office equipment: Computer and technology circuit protection
- Industrial machinery: Motor and equipment circuit control
- Emergency systems: Critical system isolation and protection
- Maintenance isolation: Safe work area disconnection
MCB Safety Requirements and Best Practices
🔒 Critical Safety Rules:
| Safety Requirement | Why It Matters | Professional Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| Dry hands only | Prevents electrical shock | Use insulated tools when possible |
| Turn off main power | Eliminates energized work | Required for panel modifications |
| Visual verification | Confirms switch position | Double-check before assuming status |
| Professional help | Complex issues need expertise | Call electrician for recurring trips |
Code Compliance Considerations:
- NEC Article 240: Circuit breaker requirements and applications
- Local electrical codes: Municipality-specific regulations
- Installation standards: Proper mounting and accessibility requirements
- Inspection requirements: Professional verification for safety compliance
Troubleshooting MCB Position Issues
Problem: MCB Won’t Stay in ON Position
Possible Causes:
- Circuit overload condition
- Short circuit in connected wiring
- Faulty MCB mechanism
- Improper installation
Solutions:
- Reduce connected load and try reset
- Inspect for damaged wiring or appliances
- Replace MCB if mechanism is faulty
- Have professional verify installation
Problem: MCB Won’t Turn OFF
Possible Causes:
- Mechanical binding in switch mechanism
- Corrosion or debris in contacts
- Worn or damaged switch assembly
Solutions:
- Apply firm, consistent pressure
- Check for physical obstructions
- Replace MCB if mechanism fails
- Contact electrician for panel issues
Problem: Unclear Switch Position
Possible Causes:
- Worn position markings
- Intermediate switch position
- Damaged position indicators
Solutions:
- Compare with adjacent MCBs for reference
- Use non-contact voltage tester to verify status
- Replace MCB with unclear markings
- Have electrician verify circuit status
How to Choose the Right MCB for Your Needs
Selection Criteria:
Current Rating:
- Match MCB amperage to circuit requirements
- Common ratings: 6A, 10A, 16A, 20A, 25A, 32A
- Never exceed wire capacity ratings
Breaking Capacity:
- Minimum 6kA for residential applications
- 10kA or higher for commercial installations
- Match to electrical system fault levels
Curve Type:
- Type B: Resistive loads (lighting, heating)
- Type C: Mixed loads (motors, transformers)
- Type D: High inrush current applications
Number of Poles:
- Single pole: 120V/230V circuits
- Double pole: 240V/400V circuits
- Three pole: Three-phase applications
Professional Installation and Maintenance Guidelines
When to Call a Professional:
- New MCB installation: Requires electrical permits and inspection
- Panel modifications: Adding circuits or upgrading service
- Recurring trips: Indicates underlying electrical problems
- Code compliance: Meeting local electrical requirements
⚠️ SAFETY WARNING
: MCB installation and electrical panel work must comply with local electrical codes and may require professional installation by licensed electricians.
Maintenance Schedule:
- Monthly: Visual inspection of switch positions and indicators
- Quarterly: Test operation by switching OFF and ON
- Annually: Professional electrical system inspection
- As needed: Reset after trips and investigate causes
Quick Reference Guide
MCB Position Memory Aid:
- UP = ON (Power flows UP through the circuit)
- DOWN = OFF (Power flows DOWN to ground/neutral)
- MIDDLE = TRIPPED (Automatic safety disconnection)
Emergency Procedures:
- Electrical emergency: Turn main breaker OFF immediately
- Sparking or burning smell: Disconnect power and call electrician
- Repeated tripping: Stop resetting and seek professional help
- Unclear positions: Use voltage tester to verify circuit status
Frequently Asked Questions
Which direction is ON for an MCB switch?
The ON position for an MCB is when the handle points UP toward the top of the electrical panel. This position allows current to flow through the circuit and power connected devices.
How can you tell if an MCB is ON or OFF?
You can tell MCB position by the handle direction: UP means ON with power flowing, DOWN means OFF with no power. Many MCBs also have “1” (ON) and “0” (OFF) markings, plus colored indicators.
What does it mean when an MCB is in the middle position?
When an MCB handle is in the middle position, it has automatically TRIPPED due to an overload or short circuit. The circuit has no power, and you must reset the breaker by pushing it fully DOWN then UP to restore operation.
Is it safe to reset a tripped MCB yourself?
Yes, resetting a tripped MCB is generally safe if you follow proper procedures: ensure the area is dry, identify and address the cause of the trip, push the handle fully DOWN then UP, and monitor for immediate re-tripping. However, call an electrician if the MCB repeatedly trips.
Why won’t my MCB stay in the ON position?
If an MCB won’t stay ON, there’s likely an ongoing fault condition such as circuit overload, short circuit, or damaged wiring. First reduce the electrical load and try resetting. If the problem persists, disconnect suspected faulty devices and contact an electrician.
Can MCB position affect electrical safety?
Absolutely. Incorrect MCB positions can leave circuits energized when you expect them to be OFF, creating serious shock and electrocution hazards. Always verify MCB position visually and use a non-contact voltage tester when safety is critical.
How often should you test MCB switch operation?
Test MCB operation quarterly by switching from ON to OFF and back to ON, ensuring smooth operation and proper positioning. Never test under load – turn off connected devices first. Schedule annual professional inspection for complete electrical system safety.
What’s the difference between MCB OFF and tripped positions?
OFF position (DOWN) is intentional user control with the handle fully down. TRIPPED position (MIDDLE) is automatic safety disconnection with the handle between UP and DOWN. Tripped MCBs require manual reset by pushing DOWN then UP to restore operation.
💡 Expert Recommendation: Understanding MCB positions is fundamental to electrical safety. When in doubt about circuit status, always use a non-contact voltage tester and consult with qualified electricians for complex electrical issues. Proper MCB operation protects both your electrical system and personal safety.
Remember: Electrical work beyond basic MCB operation should be performed by licensed electricians in compliance with local electrical codes and safety requirements.
Related
How to Know If Circuit Breaker is Bad
Circuit Breakers vs Miniature Circuit Breakers: Complete Comparison Guide
How to Choose the Right Miniature Circuit Breaker: Complete Technical Guide




