電気におけるMCBの正式名称
MCBの正式名称は「“小型サーキットブレーカー“ – 過電流、短絡、または故障状態が検出されたときに、電気回路を自動的に遮断する重要な電気安全装置。MCBの正式名称は、現代の電気設備において最も重要な保護装置の一つを表しています。.
迅速に回答: MCBはMiniature Circuit Breaker(小型回路遮断器)の略で、危険な電気状態が発生した場合に自動的に電力を遮断し、電気回路を損傷から保護します。.
MCBの正式名称とその用途を理解することは、住宅、商業、および産業用途における電気安全、法規遵守、および適切な回路保護にとって非常に重要です。.
MCBの正式名称の説明:MCBは何の略ですか?
MCBの正式名称であるMiniature Circuit Breaker(小型回路遮断器)は、このデバイスが何をするかを正確に示しています。
- Miniature(小型): より大型の回路遮断器と比較してコンパクトなサイズ
- 回路: 電気回路と経路を保護します
- Breaker(遮断器): 故障時に電気の流れを遮断または中断します
その他の一般的なMCBの正式名称のバリエーション
| 略語 | フルフォーム | コンテキスト |
|---|---|---|
| MCB | 小型サーキットブレーカー | 標準的な電気用語 |
| MCB | Motor Circuit Breaker(モーター回路遮断器) | モーター保護アプリケーション |
| MCB | Magnetic Circuit Breaker(電磁式回路遮断器) | 電磁トリップ機構を強調 |
電気システムにおけるMCBとは?
小型回路遮断器(MCB)は、短絡や過負荷状態を含む過電流状態によって引き起こされる損傷から電気回路を保護するように設計された、自動的に作動する電気開閉装置です。動作後に交換が必要な従来のヒューズとは異なり、MCBはリセットして何度も再利用できます。.
主な機能: MCBは異常な電気状態を検出し、機器の損傷、電気火災、および潜在的な感電の危険を防ぐために、回路を直ちに遮断します。.
MCBと他の回路保護デバイス:完全な比較
| 特徴 | MCB(ミニチュアサーキットブレーカー) | MCCB(モールドケース回路遮断器) | ヒューズ | RCD/GFCI(漏電遮断器/地絡遮断器) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 現在の評価 | 0.5A~125A | 100A~2500A | 1A~800A | 25A~100A |
| 定格電圧 | 最大400V AC | 最大1000V AC | いろいろ | 最大500V AC |
| 遮断容量 | 6kA~25kA | 25kA~200kA | 10kA~200kA | 6kA~25kA |
| 応答時間 | 0.02~0.05秒 | 0.02~0.1秒 | 0.001~1秒 | 0.025~0.04秒 |
| 再利用性 | はい(トリップ後にリセット) | はい(トリップ後にリセット) | いいえ(溶断後に交換) | はい(トリップ後にリセット) |
| 保護タイプ | 過電流および短絡 | 過電流および短絡 | 過電流および短絡 | 地絡および残留電流 |
| コスト | 低~中 | 中~高 | 非常に低い | 中 |
| メンテナンス | 最小限 | 定期的な点検が必要 | 交換のみ | 定期的なテストが必要 |
| の応用 | 住宅および軽商業 | 産業および重商業 | すべてのアプリケーション | 安全保護のみ |
MCBの種類と用途
電流特性による分類
タイプB MCB(定格電流の3~5倍)
- アプリケーション 住宅用照明および一般電源回路
- トリップ範囲: 3In~5In(In = 定格電流)
- 使用例: LED照明、シーリングファン、一般コンセント
- プロテクション: 中程度の突入電流アプリケーション
タイプC MCB(定格電流の5~10倍)
- アプリケーション 商業および軽工業アプリケーション
- トリップ範囲: 5In~10In
- 使用例: モーター、変圧器、蛍光灯
- プロテクション: より高い突入電流耐性
タイプD MCB(定格電流の10~20倍)
- アプリケーション 産業用モーターおよび高突入電流機器
- トリップ範囲: 10In~20In
- 使用例: 大型モーター、溶接機器、X線装置
- プロテクション: 非常に高い突入電流アプリケーション
極数による分類
| MCBタイプ | 説明 | の応用 | 定格電圧 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 単極(1P) | 1本の活線を遮断 | 単相AC回路 | AC240V |
| 2極 (2P) | 電流線と中性線を遮断 | 中性線保護付き単相 | AC240V |
| 3極 (3P) | 3本の電流線を遮断 | 三相AC回路 | 415V AC |
| 四極(4P) | 3本の電流線 + 中性線を遮断 | 三相中性線付き | 415V AC |
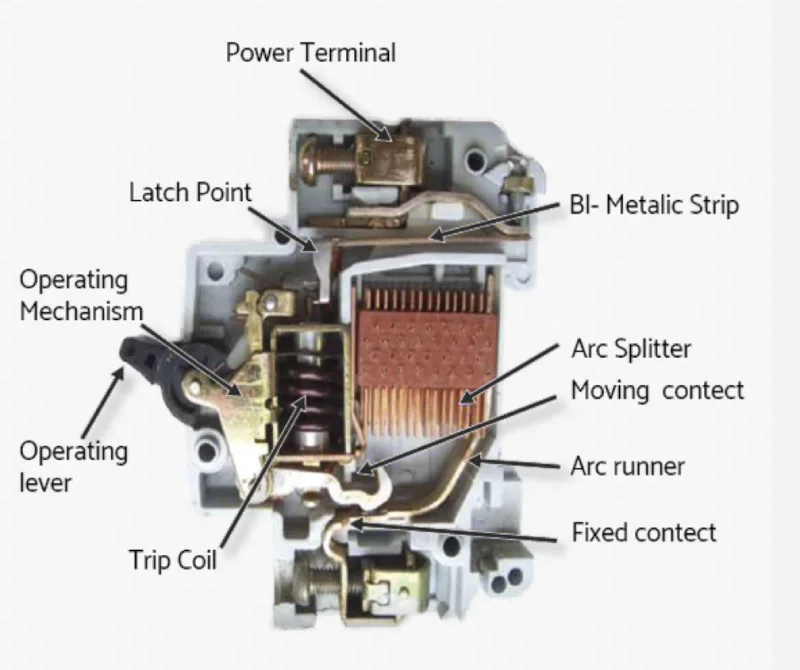
MCBの仕組み:技術的な動作
操作メカニズム
1. 熱保護(過負荷)
- バイメタルストリップは持続的な過電流により加熱される
- ストリップが曲がり、トリップ機構を作動
- 応答時間:過負荷レベルに応じて1秒から数分
2. 磁気保護(短絡)
- 電磁コイルは高電流時に磁場を発生する
- 磁力がトリップ機構を瞬時に引っ張る
- 応答時間:0.02~0.05秒
3. アーク消弧
- 負荷がかかった状態で接点が分離するとアークが発生
- アークシュートシステムがアークを安全に消弧
- 高度なモデルではSF6ガスまたは真空チャンバーを使用
⚠️安全警告
MCBの設置作業を行う前に、必ず電源が完全に遮断されていることを確認してください。電気工事規定および安全基準への準拠を確実にするため、資格のある電気技師のみがMCBの設置または交換を行う必要があります。.
MCB選定基準:専門家ガイド
現在の評価の選択
ステップ1:負荷電流の計算
負荷電流 = 総電力 (W) ÷ 電圧 (V)
ステップ2: ディレーティング係数を適用する
- 周囲温度によるディレーティング:0.8~1.0
- グルーピング係数:0.8~0.95
- ケーブルのディレーティング:ケーブルメーカーの仕様による
ステップ3:MCB定格の選択
- MCB定格は、計算された負荷電流の≥ 125%である必要があります。
- ケーブルの許容電流を超えてはならない
- 将来の負荷拡張を考慮する(通常20~30%)
破断容量の選択
| 設置タイプ | 最小遮断容量 |
|---|---|
| 住宅 | 6kA |
| コマーシャル | 10kA |
| 産業 | 25kA |
| 重工業 | 50kA+ |
💡専門家の先端
故障レベルの計算または測定を使用して、設置場所での予想短絡電流を常に確認してください。MCBの遮断容量は、最大故障電流を少なくとも25%の安全マージンで超える必要があります。.
設置-配線ガイドライン
標準配線の実践
単極MCBの接続:
- 入力側の電流線をMCBの入力端子に接続
- 出力側の電流線をMCBの出力端子に接続
- 中性線はMCBをバイパス(配電盤に直接接続)
- アース線はアースバーに直接接続
三極MCBの接続:
- 3本の相線をすべて、それぞれのMCB入力端子に接続
- 負荷側の相線をMCB出力端子に接続
- 適切な相順(R-Y-B)を維持
- 各相に適切なケーブルサイズを使用
⚠️ 法令遵守要件
IEC 60898規格:
- MCBは、ACアプリケーションに関するIEC 60898-1に準拠する必要があります。
- 必須の短絡および過負荷試験
- 温度上昇制限および絶縁要件
国立電気コード(NEC)の要件:
- 第240条:過電流保護要件
- 第240.4項:電線の保護
- 第240.6項:標準アンペア定格
設置基準:
- 最小クリアランス:全方向に50mm
- 周囲温度定格:-25°C~+70°C
- 屋内使用のためのIP20以上の保護等級
よくある問題とトラブルシューティング
MCBの頻繁なトリップに関する問題
問題:
MCBがリセット直後にトリップする
原因:
下流配線の短絡
【解決
- 回路からすべての負荷を切り離す
- メガーを使用して絶縁抵抗をテスト
- 短絡箇所を特定して修理
- 必要に応じて損傷したケーブルを交換
問題:
MCBが負荷がかかった状態でしばらくするとトリップする
原因:
過負荷状態または接続の緩み
【解決
- 実際の負荷とMCB定格を比較して計算
- すべての端子接続の締め付けを確認
- 負荷に対するケーブルサイズの妥当性を確認する
- 必要に応じて負荷を再配分するか、MCBの定格をアップグレードする
問題:
MCBが故障時にトリップしない
原因:
MCBの故障または不適切な定格
【解決
- 適切な試験装置を使用してMCBを試験する
- 故障している場合はMCBを交換する
- 遮断容量が設置に適していることを確認する
🔧 専門家の推薦
MCBの試験は、商業施設では毎年、住宅では3年ごとに、校正された試験装置を使用して実施する必要があります。指定された時間-電流特性内でトリップしないMCBは、直ちに交換する必要があります。.
MCBの仕様と規格
技術仕様表
| パラメータ | 値の範囲 | 標準の基準 |
|---|---|---|
| 定格電流 | 0.5A~125A | IEC 60898-1 |
| 定格電圧 | 230V~400V AC | IEC 60898-1 |
| 頻度 | 50Hz~60Hz | IEC 60898-1 |
| 遮断容量 | 6kA~25kA | IEC 60898-1 |
| 電気的寿命 | 10,000回 | IEC 60898-1 |
| 機械的寿命 | 20,000回 | IEC 60898-1 |
| 温度範囲 | -25°C ~ +70°C | IEC 60898-1 |
| 絶縁電圧 | 500V AC(1分間) | IEC 60898-1 |
マーキングと識別
必須マーキング:
- 製造業者名または商標
- タイプ指定およびモデル番号
- 定格電流および電圧
- 遮断容量
- トリップ特性(B、C、またはD)
- 規格準拠(IEC 60898)
安全に関する考慮事項とベストプラクティス
設置の安全性
設置前:
- 承認された電圧テスターを使用して電源の絶縁を確認する
- MCBと既存の機器との互換性を確認する
- 設置に適した遮断容量を確保する
- 周囲温度定格を確認する
インストール中:
- 適切な個人用保護具(PPE)を使用する
- ロックアウト/タグアウトの手順に従ってください
- 端子接続部に適切なトルクを維持する
- 正しいケーブルサイズと配線を確認する
インストール後:
- 適切な試験装置を使用してMCBの動作を試験する
- 正しいラベル表示と回路識別を確認する
- 設置の詳細と試験結果を文書化する
- エンドユーザーに操作手順を提供する
⚠️臨界安全の注意
MCBは過電流状態に対する保護を提供しますが、感電や地絡に対する保護は提供しません。包括的な電気安全保護のために、RCD(残留電流デバイス)を設置してください。.
コスト分析と選択要因
初期コストの比較
| MCBタイプ | 価格帯(USD) | アプリケーションの適合性 | ライフサイクルコスト |
|---|---|---|---|
| 標準MCB | $5 – $25 | 基本的な住宅/商業用 | 低 |
| 高い破断能力 | $15 – $50 | 産業用途 | 中 |
| 電子MCB | $50 – $200 | 精密なアプリケーション | 初期費用は高いが、メンテナンスは少ない |
| スマートMCB | $100 – $500 | IoTおよび監視システム | 初期費用は高いが、ダウンタイムが短縮される |
💰 コスト最適化のヒント
- 適切な遮断容量を選択する(過剰な仕様にしない)
- 複数の設置のために一括購入を検討する
- 長期的な信頼性とメンテナンスコストを考慮する
- クリティカルなアプリケーションに対するスマートMCBの利点を評価する
将来のトレンドとテクノロジー
スマートMCBテクノロジー
- リモート監視のためのIoT接続
- 予測メンテナンス機能
- エネルギー測定とレポート
- リアルタイムステータス用のモバイルアプリ統合
高度な保護機能
- アーク故障の検出と遮断
- 地絡保護の統合
- 通信プロトコル(Modbus、BACnet)
- データロギングと分析機能
クイックリファレンスガイド
MCB定格選択チェックリスト
- [ ] 最大負荷電流を計算する
- [ ] 適切なディレーティング係数を適用する
- [ ] MCB定格を負荷電流の≥ 125%に選択する
- [ ] ケーブル容量がMCB定格を超えていることを確認する
- [ ] 設置に適した遮断容量を確認する
- [ ] タイプ特性の確認(B、C、またはD)
- [ ] 電圧および周波数定格の検証
- [ ] 将来の負荷拡張の検討
緊急時の手順
- MCBがリセットしない場合: 短絡の確認、すべての負荷の取り外し、配線の点検
- 頻繁なトリップ: 負荷計算の検証、接続の確認、絶縁のテスト
- リセット後に電源が入らない場合: 下流の接続の確認、MCBの動作の検証
- 焦げ臭い匂い: 直ちに電源を切断し、損傷の有無を点検し、必要に応じて交換
MCBの正式名称に関するよくある質問
電気におけるMCBの正式名称は何ですか?
MCBの正式名称はMiniature Circuit Breaker(小型回路遮断器)です。これは、短絡や過負荷を含む過電流状態によって引き起こされる損傷から電気回路を保護するように設計された自動電気スイッチです。.
電気工学において、MCBは何の略ですか?
電気工学において、MCBはMiniature Circuit Breaker(小型回路遮断器)の略です。これは、従来のヒューズとは異なり、過電流保護と、動作後にリセットして再利用できる機能を組み合わせた保護デバイスです。.
MCBの正式名称と他の回路遮断器の違いは何ですか?
MCBはMiniature Circuit Breaker(小型回路遮断器)(より小規模なアプリケーション向け)の略であり、MCCBはMolded Case Circuit Breaker(モールドケース回路遮断器)(より大規模な産業用アプリケーション向け)の略であり、ACBはAir Circuit Breaker(空気遮断器)(非常に高い電流アプリケーション向け)の略です。.
なぜ小型回路遮断器と呼ばれるのですか?
MCBの正式名称の「小型」とは、より大型の産業用回路遮断器と比較してコンパクトなサイズを指し、スペースが限られている住宅および軽商業アプリケーションに最適です。.
MCBとMCCBの違いは何ですか?
MCBは、より低い電流定格(最大125A)および住宅/軽商業用途向けに設計されていますが、MCCBは、産業用アプリケーション向けにより高い電流(100A〜2500A)を処理します。MCCBは、調整可能なトリップ設定とより高い遮断容量も提供します。.
MCBが故障しているかどうかをどのように知ることができますか?
MCBの故障の兆候には、過負荷時のトリップの失敗、トリップ後のリセット不能、物理的な損傷または焦げ跡、緩んだまたは腐食した端子、および一貫性のない動作が含まれます。検証には専門的なテストをお勧めします。.
MCBをより高い定格のものと交換できますか?
下流の配線とコンポーネントが増加した電流を安全に処理できる場合にのみ可能です。ケーブルの許容電流は、新しいMCBの定格を超える必要があり、適切な負荷計算を実行する必要があります。.
MCBはどのくらいの頻度でテストする必要がありますか?
住宅設備:3年ごと。商業設備:毎年。産業設備:6か月ごと、またはメンテナンススケジュールに従って。重要なアプリケーションでは、より頻繁なテストが必要になる場合があります。.
MCBが頻繁にトリップする原因は何ですか?
一般的な原因には、実際の過負荷状態、緩んだ端子接続、損傷したケーブル、湿気の侵入、周囲温度の問題、およびMCBの摩耗または故障が含まれます。.
MCB は感電から保護しますか?
いいえ、標準のMCBは過電流および短絡のみを保護します。感電保護には、RCD(残留電流デバイス)またはコンビネーションRCBOユニットを取り付けてください。.
結論:MCBの正式名称とアプリケーションの理解
MCBの正式名称であるMiniature Circuit Breaker(小型回路遮断器)は、最新の設備において最も重要な電気安全デバイスの1つです。MCBが何を意味するのか、およびこれらのデバイスがどのように機能するかを理解することで、電気の安全性、法規遵守、および信頼性の高い回路保護が保証されます。.
MCBの正式名称に関する重要なポイント:
- MCBはMiniature Circuit Breaker(小型回路遮断器)の略で、電気保護に不可欠です。
- 「小型」という指定は、住宅/商業用途向けのコンパクトなサイズを指します。
- MCBの正式名称には、自動過電流および短絡保護が含まれます。
- 専門家による設置と定期的なテストにより、最適なMCBパフォーマンスが保証されます。
- MCBとRCDを組み合わせることで、包括的な電気保護が提供されます。
複雑な電気設備やMCBの正式名称アプリケーションに関する質問については、常に資格のある電気エンジニアまたは認定電気技師に相談して、安全性と法規遵守を確保してください。.
専門家の推奨事項: MCBの正式名称を理解することは始まりにすぎません。小型回路遮断器の適切な選択、設置、およびメンテナンスには、最適な電気システム保護のために、電気規則、負荷計算、および安全基準に関する詳細な知識が必要です。.