Respuesta Directa: Un interruptor automático interrumpe automáticamente la corriente eléctrica durante condiciones de falla y puede operar bajo carga, mientras que un seccionador (aislador) proporciona aislamiento visible para fines de mantenimiento y solo debe operar cuando los circuitos están desenergizados. Los interruptores automáticos ofrecen protección; los seccionadores proporcionan aislamiento.
Comprender la diferencia entre los interruptores automáticos y los seccionadores es fundamental para la seguridad eléctrica, el diseño adecuado del sistema y el cumplimiento de los códigos. Ambos dispositivos controlan los circuitos eléctricos, pero cumplen propósitos fundamentalmente diferentes en los sistemas eléctricos.
Definiciones clave: Interruptores automáticos vs. Seccionadores
¿Qué es un disyuntor?

Un interruptor de circuito es un dispositivo de conmutación eléctrica automático diseñado para proteger los circuitos eléctricos interrumpiendo el flujo de corriente cuando se producen condiciones de falla. Puede establecer, transportar e interrumpir corrientes en condiciones normales y anormales (de falla).
Características principales:
- Operación automática durante fallas
- La extinción del arco capacidad
- Puede operar en condiciones de plena carga
- Proporciona protección contra sobrecorriente y cortocircuito
- Reiniciable después de dispararse
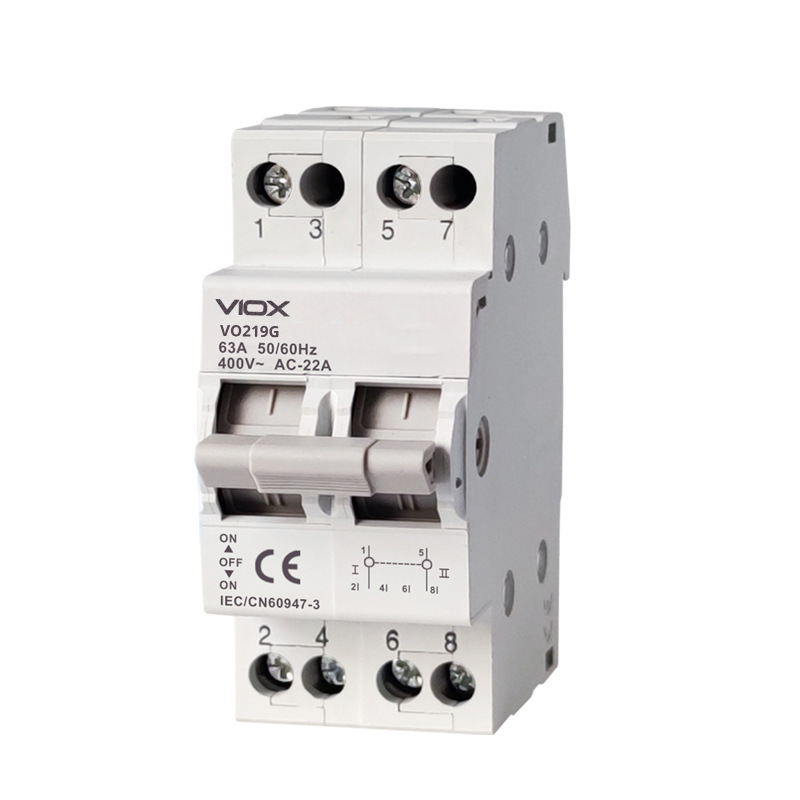
¿Qué es un seccionador (aislador)?
Un seccionador, también llamado aislador, es un dispositivo de conmutación mecánica que proporciona aislamiento de los circuitos para fines de mantenimiento y seguridad. Crea un espacio visible entre los contactos eléctricos cuando está abierto.
Características principales:
- Solo operación manual
- Espacio de aislamiento visible
- Opera solo cuando los circuitos están desenergizados
- Sin capacidad de interrupción de fallas
- Evita la energización accidental durante el mantenimiento
Tabla comparativa completa
| Característica | Interruptor automático | Seccionador (aislador) |
|---|---|---|
| Propósito principal | Protección contra fallas | Aislamiento para mantenimiento |
| La operación | Automático y manual | Sólo manual |
| La Extinción Del Arco | Sí (SF6, vacío, aceite, aire) | No – mínimo o ninguno |
| Interrupción de carga | Sí – capacidad de plena carga | No – operación solo sin carga |
| Corriente de falla | Interrumpe las corrientes de falla | No se pueden interrumpir corrientes de falla |
| Espacio visible | No es necesario | Requerido por seguridad |
| Normas | IEC 62271-100, IEEE C37 | IEC 62271-102, IEEE C37.30 |
| Voltaje típico | Todos los niveles (BT a EAT) | Media a alta tensión |
| Coste de instalación | Más alto | Baja |
| Mantenimiento | Mecanismo complejo | Mecanismo simple |
Diferencias críticas explicadas
1. Capacidad de interrupción de fallas
Interruptores automáticos:
- Diseñado para interrumpir corrientes de falla hasta su capacidad nominal
- Utiliza medios de extinción de arco (gas SF6, vacío, aceite o aire)
- Puede interrumpir corrientes muchas veces su clasificación normal durante las fallas
- Esencial para la protección del sistema
Seccionadores:
- No puede interrumpir las corrientes de falla de forma segura
- Puede crear arcos peligrosos si se abre bajo carga
- Se utiliza solo después de que el circuito es desenergizado por otros medios
- Principalmente aislamiento, no interrupción
2. Condiciones de operación
Interruptores automáticos:
- Opera en condiciones normales y de falla
- Puede establecer e interrumpir corrientes de plena carga
- Funciona automáticamente durante condiciones anormales
- Adecuado para operación frecuente
Seccionadores:
- Opera solo en condiciones sin carga o con carga mínima
- Requiere que el circuito se desenergice antes de la operación
- Operación manual con indicación de posición visible
- Operación infrecuente para fines de mantenimiento
⚠️ De Advertencia De Seguridad: Nunca opere un seccionador bajo condiciones de carga. Esto puede causar arcos peligrosos, daños al equipo y graves riesgos de seguridad.
Aplicaciones y Casos de Uso
Cuándo usar interruptores automáticos
Aplicaciones industriales:
- Protección y control de motores
- Protección de alimentadores en sistemas de distribución
- Protección de generadores y transformadores
- Interrupción de corriente de falla en sistemas de energía
Aplicaciones comerciales:
- Protección de desconexión del servicio principal
- Protección de circuito derivado
- Aplicaciones de centro de carga
- Integración del interruptor de transferencia automática
Aplicaciones residenciales:
- Protección del panel eléctrico principal
- Protección de circuito individual
- Protección GFCI y AFCI
- Integración de protección contra sobretensiones para toda la casa
Cuándo usar seccionadores
Aplicaciones de subestaciones:
- Seccionamiento de barras
- Aislamiento de equipos para mantenimiento
- Requisitos de aislamiento visible
- Conmutación de líneas en sistemas de transmisión
Aplicaciones industriales:
- Interruptores de desconexión de motor
- Aislamiento de equipos
- Aislamiento de seguridad para mantenimiento
- Puntos de desconexión de emergencia
Aplicaciones de Mantenimiento:
- Creación de zonas de trabajo seguras
- Procedimientos de bloqueo y etiquetado
- Aislamiento para el servicio de equipos
- Confirmación visual de la desenergización
Criterios de Selección y Guías Expertas
Selección de Interruptores Automáticos
Factores Clave a Considerar:
- Corriente Nominal: Debe exceder la corriente de operación normal
- Capacidad de Ruptura: Debe exceder la máxima corriente de falla
- Tensión Nominal: Debe coincidir o exceder la tensión del sistema
- Tipo de Carga: Consideraciones de motor, resistiva, capacitiva
- Condiciones Ambientales: Interior/exterior, temperatura, contaminación
Consejo De Expertos: Siempre consulte estudios de corriente de falla al seleccionar interruptores automáticos. La capacidad de ruptura debe exceder la máxima corriente de falla disponible en el punto de instalación.
Selección de Seccionadores
Factores Clave a Considerar:
- Requisitos de Aislamiento: Especificaciones de espacio visible
- Resistencia Mecánica: Ciclos de operación esperados
- Clasificación Ambiental: Resistencia a la intemperie para unidades exteriores
- Requisitos de Enclavamiento: Enclavamientos de seguridad con otros equipos
- Accesibilidad: Facilidad de operación y acceso para mantenimiento
Consejo De Expertos: Especifique seccionadores con contactos auxiliares para indicación remota de posición. Esto mejora la seguridad y la conciencia operativa.
Seguridad y cumplimiento del código
Código nacional Eléctrico (NEC) de los Requisitos de
Artículo 240 – Protección De Sobrecorriente:
- Los interruptores automáticos deben proporcionar protección contra sobrecorriente
- Coordinación adecuada con los dispositivos de protección aguas arriba
- Requisitos de protección contra fallas de arco y fallas a tierra
Artículo 430 – Motores:
- Protección contra cortocircuitos del circuito derivado del motor
- Requisitos de desconexión del motor a la vista
- Especificaciones de los arrancadores de motor combinados
Cumplimiento de las Normas IEEE
Normas de la Serie IEEE C37:
- C37.04: Norma para la estructura de clasificación de los interruptores automáticos
- C37.06: Normas para interruptores automáticos de alta tensión de CA
- C37.30: Normas para interruptores de desconexión
Puntos clave de cumplimiento:
- Aplicación adecuada dentro de las clasificaciones
- Pruebas de calificación ambiental
- Cualificación sísmica cuando sea necesario
- Requisitos de compatibilidad electromagnética
⚠️ Recomendación Profesional: Siempre consulte con ingenieros eléctricos autorizados para aplicaciones de media y alta tensión. Una selección incorrecta puede provocar fallas catastróficas.
Consideraciones sobre la instalación y el mantenimiento
Mejores Prácticas para la Instalación de Interruptores Automáticos
Step-by-Step Installation Process:
- Planificación previa a la instalación
- Verifique que las clasificaciones eléctricas coincidan con la aplicación
- Confirme los niveles de corriente de falla disponibles
- Verificar las condiciones ambientales
- Instalación Física
- Siga las especificaciones de torque del fabricante
- Asegure la terminación adecuada del conductor
- Verifique las holguras mecánicas
- Pruebas y Puesta en servicio
- Pruebas de inyección primaria para relés de protección
- Prueba de funcionamiento mecánico
- Pruebas de tiempo y resistencia de contacto
Mejores Prácticas para la Instalación de Seccionadores
Step-by-Step Installation Process:
- Preparación del Sitio
- Verifique los requisitos de la cimentación
- Compruebe la distancia a las partes activas
- Asegure la accesibilidad para la operación
- Instalación mecánica
- Siga los procedimientos de alineación del fabricante
- Verifique la función del mecanismo de operación
- Pruebe los sistemas de enclavamiento
- Conexión eléctrica
- Utilice métodos adecuados de terminación de conductores
- Aplique la presión de contacto especificada
- Verifique las conexiones del circuito auxiliar
Solución De Problemas Problemas Comunes
Problemas del Interruptor Automático
Síntoma: El Interruptor No Cierra
- Verificar la fuente de alimentación de control
- Verificar el mecanismo de carga del resorte
- Inspeccionar los enclavamientos mecánicos
- Probar la continuidad de la bobina de cierre
Síntoma: Disparo intempestivo
- Analizar los perfiles de corriente de carga
- Compruebe si hay conexiones sueltas
- Verificar la coordinación tiempo-corriente adecuada
- Considerar los factores medioambientales
Problemas del seccionador
Síntoma: Operación difícil
- Inspeccionar la lubricación del mecanismo de operación
- Comprobación de la unión mecánica
- Verificar el ajuste adecuado
- Examinar el desgaste de los contactos
Síntoma: Rendimiento deficiente de los contactos
- Verificar los ajustes de presión de los contactos
- Inspeccionar en busca de contaminación
- Verificar la alineación adecuada
- Considerar la compatibilidad del material de los contactos
Guía De Referencia Rápida
Datos rápidos del interruptor automático
- Función principal: Protección automática contra fallas
- Puede operar: Bajo condiciones de carga y falla
- Extinción del arco: Sí, múltiples tecnologías disponibles
- Aplicaciones típicas: Protección e interrupción
- Referencias de código: Artículo 240 del NEC, serie IEEE C37
Datos rápidos del seccionador
- Función principal: Aislamiento para mantenimiento
- Puede operar: Solo cuando está desenergizado
- Extinción del arco: No, depende del espacio de aire
- Aplicaciones típicas: Aislamiento y desconexión visible
- Referencias de código: Artículo 430.102 del NEC, IEEE C37.30
Preguntas Frecuentes
¿Puede un seccionador reemplazar a un interruptor automático?
No, un seccionador no puede reemplazar a un interruptor automático. Los seccionadores carecen de capacidad de interrupción de fallas y no pueden proporcionar la protección contra sobrecorriente requerida por los códigos eléctricos.
¿Cuándo se deben usar ambos dispositivos juntos?
Ambos dispositivos se utilizan comúnmente juntos en aplicaciones de media y alta tensión donde las funciones de protección (interruptor automático) y aislamiento (seccionador) son necesarias para una operación y mantenimiento seguros.
¿Qué sucede si opera un seccionador bajo carga?
Operar un seccionador bajo carga puede causar arcos peligrosos, daños al equipo, riesgos de incendio y posibles lesiones. Esta práctica viola los códigos de seguridad y las recomendaciones del fabricante.
¿Hay dispositivos combinados disponibles?
Sí, algunos fabricantes ofrecen dispositivos combinados de interruptor automático-seccionador, particularmente para aplicaciones de motores. Estos dispositivos proporcionan protección y aislamiento visible en una sola unidad.
¿Cómo se determina la secuencia de operación adecuada?
Para sistemas con ambos dispositivos, siempre opere primero el interruptor automático para interrumpir la corriente, luego opere el seccionador para aislamiento. Invierta esta secuencia al volver a energizar.
¿Cuáles son los intervalos de mantenimiento típicos?
Los interruptores automáticos generalmente requieren mantenimiento cada 5-10 años, dependiendo de la aplicación y las recomendaciones del fabricante. Los seccionadores pueden requerir mantenimiento cada 10-15 años debido a sus mecanismos más simples.
¿Se pueden automatizar los seccionadores?
Sí, los seccionadores pueden equiparse con operadores de motor para control remoto, pero aún así solo deben operar en condiciones sin carga y generalmente requieren enclavamientos de seguridad adicionales.
¿Cuáles son los diferentes tipos de tecnologías de interruptores automáticos?
Los tipos principales incluyen interruptores automáticos de aire (ACB), interruptores automáticos de vacío (VCB), interruptores automáticos de gas SF6 e interruptores automáticos de aceite, cada uno adecuado para diferentes niveles de voltaje y aplicaciones.
Recomendación Profesional: Para cualquier instalación o modificación eléctrica que involucre interruptores automáticos o seccionadores, consulte con un ingeniero eléctrico con licencia o un electricista certificado. La aplicación adecuada de estos dispositivos es fundamental para la seguridad, el cumplimiento de los códigos y el funcionamiento confiable.
Recuerde: Los interruptores automáticos protegen su sistema eléctrico de fallas, mientras que los seccionadores lo protegen durante el mantenimiento. Ambos son componentes esenciales de un diseño eléctrico seguro, pero sirven para propósitos claramente diferentes y nunca deben confundirse o aplicarse incorrectamente.