When a project engineer at a European industrial equipment manufacturer specified time delay relays for a new control panel, the manufacturer’s procurement team pushed back—”Do these meet IEC 61812-1?” Without the right certification documentation, the project stalled. The relay supplier claimed “CE compliance,” but CE marking without IEC 61812-1 testing meant nothing for time relay functional requirements.
This scenario plays out daily. IEC 61812-1 isn’t just a compliance checkbox—it’s the international framework that defines what “reliable time relay” means in measurable, testable terms. Engineers specifying components, procurement managers evaluating suppliers, and quality teams maintaining certification all face the same question: how do you know a time relay will perform as claimed? The standard provides the answer.
Three things make IEC 61812-1 matter: it establishes global performance baselines for timing accuracy and repeatability, verifies safety under electrical stress and environmental conditions, and provides a common language for comparing products across manufacturers. In the European market, it’s effectively mandatory for CE marking. Even in North America, where UL and NEMA frameworks dominate, IEC 61812-1 certification signals a manufacturer’s commitment to international quality benchmarks.

What Is IEC 61812-1? Overview and Purpose
IEC 61812-1 is the international standard titled “Time relays and coupling relays for industrial and residential use – Part 1: Requirements and tests.” Published by the International Electrotechnical Commission, it defines the performance, safety, and electromagnetic compatibility requirements for time delay relays used in control circuits, automation systems, and industrial equipment.
The standard’s current version is IEC 61812-1:2023 Edition 3.0, published in June 2023. This edition superseded the 2011 second edition and introduced significant updates including explicit coverage of coupling relays, cybersecurity requirements for industrial automation and control systems (IACS), environmental information mandates, and expanded routine testing protocols.
Think of IEC 61812-1 as the technical rulebook that answers: “What does a properly designed time relay look like?” It covers both electromechanical and solid-state relay technologies, addresses devices with DIN-rail mounting and plug-in socket configurations, and spans voltage ranges from low-voltage DC circuits to 240VAC industrial control applications.
The standard serves two audiences simultaneously. For manufacturers, it provides a structured testing and documentation framework that, once certified, opens global market access—particularly for EMEA, where it’s regionally adopted as EN IEC 61812-1:2024 and is effectively required for CE marking. For engineers and procurement professionals, it creates a common specification language; when a datasheet claims “IEC 61812-1 compliant,” you know exactly what that relay has been tested for and what performance documentation should exist.
Scope and Applicable Products: What the Standard Covers
IEC 61812-1 applies to time relays and coupling relays used in two broad application environments: industrial applications (control, automation, signal, and industrial equipment) and automatic electrical controls for residential and similar-use equipment. This dual scope makes the standard relevant whether you’re specifying relays for a factory automation panel or a residential HVAC control system.
What’s included: The standard covers all common time relay functions—on-delay (delay-on-energization), off-delay (delay-on-de-energization), interval timing, pulse output, flasher/cyclic operation, star-delta motor starting sequences, and multifunction programmable timing modes. It applies to both electromechanical relay outputs and solid-state switching outputs. Devices using voltage-dependent timing circuits, current-dependent timing, electronic timing circuits, pneumatic timing mechanisms, or hybrid technologies all fall within scope.
What’s excluded: Measuring relays are explicitly outside the standard’s scope. IEC 61812-1 focuses on functional time relays where timing is the primary control function, not relays that measure electrical parameters (voltage, current, frequency) and provide time-delayed responses based on measurement thresholds.
The standard defines device classifications across multiple dimensions: switching element type (electromechanical vs. solid-state), construction and housing type, mounting method (DIN-rail, plug-in socket, PCB mount, panel mount), connection method, and environmental suitability. This classification system ensures the requirements adapt to different relay technologies and installation scenarios rather than forcing a one-size-fits-all approach.
For procurement specifications, understanding scope matters when reading supplier datasheets. If a relay datasheet claims IEC 61812-1 compliance, you can expect documentation covering the device’s timing function type, classification category, rated operational parameters, and environmental limits—all defined within the standard’s framework.
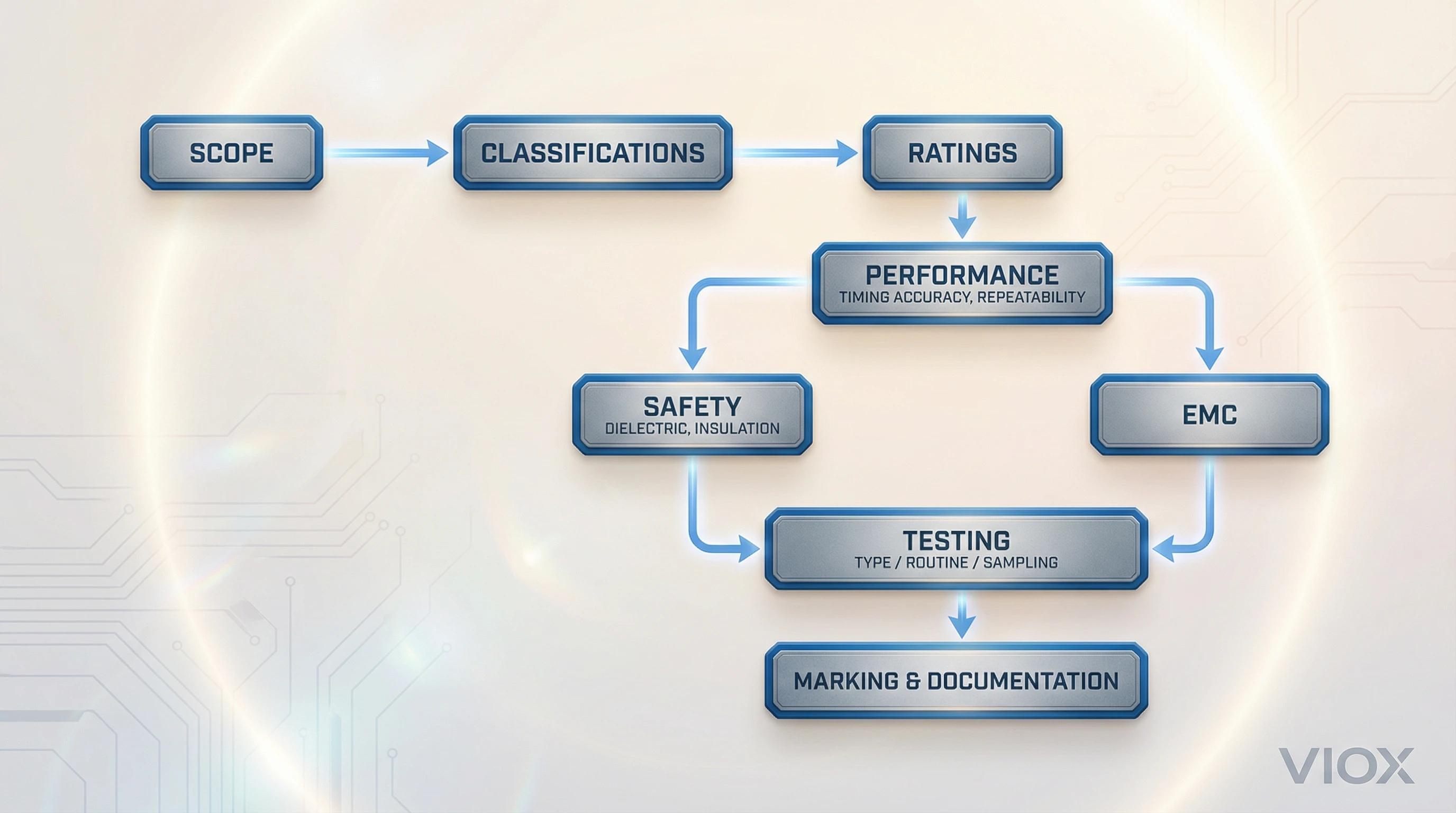
Key Technical Requirements Explained
IEC 61812-1 structures its requirements into distinct categories, each addressing a specific aspect of relay performance, safety, or durability. These requirements translate into testable criteria that manufacturers must meet and engineers should look for in datasheets.
Classifications and Ratings
Every compliant relay must declare its classification and ratings, which define its operational boundaries. Rated input voltage and frequency specify the control voltage range at which the relay operates (e.g., 24VDC, 120VAC 50/60Hz, universal input 12-240VAC/DC). Release voltage defines the point below which the relay de-energizes, typically 10-20% of rated voltage. Power consumption indicates input power drawn by the timing circuit during operation.
Output circuit ratings vary by technology. Electromechanical outputs include contact ratings (voltage, current, load type) and mechanical/electrical endurance. Solid-state outputs specify switching voltage/current limits and leakage current. Conditional short-circuit current rating defines the maximum prospective short-circuit current the relay can handle when protected by a specified overcurrent device. Environmental ratings cover operating/storage/transport temperature ranges, humidity limits, pollution degree (I-IV per IEC 60664-1), and altitude rating.
Timing Performance Specifications
This is where IEC 61812-1 earns its relevance for time relays. The standard defines how timing accuracy must be measured and documented:
- Setting accuracy: The tolerance between the set timing value and the actual measured timing value at reference conditions (typically 23°C, rated voltage). Example: A 10-second timer with ±5% accuracy triggers between 9.5-10.5 seconds.
- تکراری قابلیت: How consistently the relay hits the same timing value across multiple operations. Lower repeatability values mean more consistent performance.
- Recovery time: The minimum interval required between operations before the relay can accurately time again
- Minimum control impulse: The shortest pulse duration needed to reliably trigger timing
- Influence quantities: How timing performance degrades under varying voltage (±15% typical) and temperature extremes (operating range limits)
Annex A of the standard provides calculation methods for determining these values, which manufacturers use to generate the timing specifications you see in datasheets.
Safety and Dielectric Requirements
Electrical safety requirements ensure the relay won’t create shock hazards or fail catastrophically:
- Heating limits: Terminal and accessible surface temperatures must stay within defined limits during continuous operation and overload conditions. A ball pressure test verifies that plastic housings don’t deform under heat.
- ڈائی الیکٹرک طاقت: The relay must withstand power-frequency voltage tests (50/60Hz AC test voltage applied between isolated circuits) and impulse withstand voltage tests (1.2/50μs surge impulses simulating lightning or switching transients) without breakdown. Test levels are tabulated based on voltage rating and insulation category.
- Clearances and creepage distances118: موصل حصوں کے درمیان جسمانی فاصلہ IEC 60664-1 کے مطابق کم از کم فاصلوں پر پورا اترنا چاہیے، جو کام کرنے والے وولٹیج، آلودگی کی ڈگری اور موصلیت کی قسم سے طے ہوتا ہے۔.
- بجلی کے جھٹکے سے تحفظ120: موصلیت کے نظاموں کو خطرناک لائیو حصوں تک رسائی کو روکنا چاہیے اور عام اور غلط حالات میں سالمیت کو برقرار رکھنا چاہیے۔.
121: EMC اور ماحولیاتی تقاضے
122: جدید کنٹرول پینل برقی طور پر شور والے ماحول میں کام کرتے ہیں۔ IEC 61812-1 اس بات کو یقینی بناتا ہے کہ ٹائم ریلے برقی مقناطیسی مداخلت کے باوجود کارکردگی کو برقرار رکھیں۔
- 123: قوت مدافعت کے تقاضے124: ریلے کو مخصوص سطح کے منعقدہ خلل (وولٹیج ڈپس، سرجز، تیز ٹرانزینٹس)، ریڈی ایٹڈ آر ایف فیلڈز، الیکٹرو اسٹاٹک ڈسچارج اور مقناطیسی فیلڈز کا غلط ٹرگرنگ یا ٹائمنگ کی غلطیوں کے بغیر مقابلہ کرنا چاہیے۔ صنعتی ماحول بمقابلہ رہائشی/ہلکی صنعتی ترتیبات کے لیے علیحدہ جدولیں ٹیسٹ کی سطحوں کی وضاحت کرتی ہیں۔.
- 125: خارج شدہ خلل126: ریلے کے سوئچنگ اور ٹائمنگ سرکٹس کو ضرورت سے زیادہ برقی مقناطیسی اخراج پیدا نہیں کرنا چاہیے جو قریبی آلات میں مداخلت کریں۔
- 127: ارتعاش اور جھٹکا128: مکینیکل مضبوطی کے ٹیسٹ اس بات کی تصدیق کرتے ہیں کہ ریلے ارتعاش (سائنوسائیڈل سویپ، رینڈم وائبریشن) اور مکینیکل شاک (ہاف سائن پلس ایکسلریشن) کے تحت برقی تسلسل اور ٹائمنگ کی درستگی کو برقرار رکھتی ہے۔
129: ایڈیشن 3.0 شامل کیا گیا 130: سائبر سیکیورٹی کے تقاضے 131: صنعتی آٹومیشن نیٹ ورکس (IACS ماحول) سے منسلک ریلے کے لیے اور 132: ماحولیاتی معلومات 133: مینوفیکچررز کو مواد، ری سائیکلنگ ڈیٹا اور ماحولیاتی طور پر باشعور ڈیزائن کے عمل کو دستاویزی شکل دینے کی ضرورت ہے۔.
134: مکینیکل طاقت اور برداشت
135: ٹرمینلز، ساکٹس اور ماؤنٹنگ سسٹمز کو تنصیب اور آپریشن کے دوران مکینیکل تناؤ کا سامنا کرنا پڑتا ہے:
- 136: ٹرمینل ٹارک اور پل آؤٹ ٹیسٹ137: سکرو ٹرمینلز کو نقصان کے بغیر ریٹیڈ ٹائٹننگ ٹارک کو برداشت کرنا چاہیے۔ وائر پل آؤٹ ٹیسٹ برقرار رکھنے کی تصدیق کرتے ہیں۔
- 138: برقی برداشت139: رابطوں (الیکٹرو مکینیکل آؤٹ پٹس کے لیے) کو مختلف قسم کے بوجھ کے تحت مخصوص تعداد میں آپریشن مکمل کرنے چاہئیں—مزاحمتی، انڈکٹیو (پاور فیکٹر کے ساتھ) اور کم توانائی والے ڈی سی بوجھ۔ سالڈ اسٹیٹ آؤٹ پٹس مساوی سوئچنگ سائیکل ٹیسٹنگ سے گزرتے ہیں۔.
- 140: مشروط شارٹ سرکٹ کرنٹ ٹیسٹ141: ایک مخصوص اوور کرنٹ پروٹیکٹیو ڈیوائس کے ساتھ، ریلے کو آگ یا برقی جھٹکے کے خطرات پیدا کیے بغیر متوقع شارٹ سرکٹ کے حالات سے بچنا چاہیے۔
142: یہ تقاضے ایک نظام کے طور پر مل کر کام کرتے ہیں۔ ایک ٹائم ریلے میں لیب کے حالات میں ٹائمنگ کی درستگی کامل ہو سکتی ہے لیکن اگر اس کی EMC قوت مدافعت ناکافی ہو یا اس کے ٹرمینلز ارتعاش کے تحت ڈھیلے ہو جائیں تو یہ فیلڈ میں ناکام ہو سکتی ہے۔ IEC 61812-1 کا جامع دائرہ کار مکمل آپریشنل حقیقت کو حل کرتا ہے۔.
143: جانچ اور سرٹیفیکیشن کے طریقہ کار
144: IEC 61812-1 تین ٹیسٹ زمروں کی وضاحت کرتا ہے، ہر ایک مختلف معیار کی یقین دہانی کے مقصد کو پورا کرتا ہے:
145: قسم کے ٹیسٹ 146: ڈیزائن کی تعمیل کی تصدیق کریں۔ مینوفیکچررز ان کو نمائندہ نمونوں پر اس بات کو ثابت کرنے کے لیے کرتے ہیں کہ پروڈکٹ ڈیزائن تمام معیاری تقاضوں کو پورا کرتا ہے۔ قسم کے ٹیسٹوں میں مکمل بیٹری شامل ہے: حرارت، حوالہ اور اثر و رسوخ کے حالات میں بنیادی آپریشن، ٹائمنگ کی درستگی اور تکرار، ڈائی الیکٹرک طاقت، موصلیت کی مزاحمت، کلیئرنس/کریپیج، برقی برداشت، مشروط شارٹ سرکٹ کرنٹ، مکینیکل طاقت، EMC قوت مدافعت اور اخراج، ارتعاش، جھٹکا، گلو وائر اور دستاویزات کی تکمیل۔ قسم کی جانچ پڑتال شدید ہے—ایک واحد ریلے ماڈل کو لیب کے وقت کے ہفتوں اور درجنوں نمونوں کی ضرورت پڑ سکتی ہے۔.
147: ایک بار جب قسم کے ٹیسٹ پاس ہو جاتے ہیں، تو مینوفیکچرر انہیں ہر پروڈکشن یونٹ کے لیے نہیں دہراتا ہے۔ یہ وہ جگہ ہے جہاں دیگر زمرے آتے ہیں۔.
148: معمول کے ٹیسٹ 149: پروڈکشن کے 100% پر لاگو کریں۔ فیکٹری چھوڑنے والا ہر ایک ریلے ان مختصر جانچ پڑتال سے گزرتا ہے: بنیادی فعال آپریشن (کیا یہ درست طریقے سے وقت دیتا ہے؟)، کم وولٹیج پر ڈائی الیکٹرک طاقت (اچھے یونٹوں کو نقصان پہنچائے بغیر موصلیت کے نقائص کو پکڑنے کے لیے) اور، ایڈیشن 3.0 کے لیے، مخصوص ٹائمنگ کی تصدیق سمیت معمول کی جانچ پڑتال میں توسیع۔ معمول کے ٹیسٹ مکمل قسم کے ٹیسٹ پروگرام کی ضرورت کے بغیر مینوفیکچرنگ کے نقائص کو پکڑتے ہیں۔.
150: نمونے لینے کے ٹیسٹ 151: قسم اور معمول کے ٹیسٹوں کے درمیان بیٹھیں۔ مینوفیکچررز وقتاً فوقتاً پروڈکشن کے نمونے کھینچتے ہیں اور پروڈکشن کی مستقل مزاجی کی تصدیق کے لیے ٹیسٹوں کا ایک متعین ذیلی سیٹ چلاتے ہیں۔ یہ جاری نگرانی مینوفیکچرنگ کے عمل میں بتدریج تبدیلی کو فیلڈ کی ناکامیوں کے پیدا ہونے سے پہلے پکڑتی ہے۔.
152: معیار بھی متعین کرتا ہے۔ 153: مارکنگ اور دستاویزات کے تقاضے 154: شق 8 اور جدول 7 میں۔ تعمیل کرنے والے ریلے پر مستقل نشانات ہونے چاہئیں جن میں مینوفیکچرر کی شناخت، ماڈل/قسم کا عہدہ، ریٹیڈ ان پٹ وولٹیج اور فریکوئنسی، آؤٹ پٹ ریٹنگز، متعلقہ معیاری حوالہ جات (IEC 61812-1) اور CE مارکنگ جہاں قابل اطلاق ہو۔ تکنیکی دستاویزات میں تمام ریٹیڈ اقدار، ٹائمنگ کی وضاحتیں (درستگی، تکرار، ریکوری ٹائم)، ماحولیاتی حدود، کنکشن ڈایاگرام اور تنصیب کی ہدایات فراہم کی جانی چاہئیں۔.
155: یورپی مارکیٹ میں سرٹیفیکیشن کے لیے، مینوفیکچررز عام طور پر اس کے ساتھ کام کرتے ہیں۔ 156: مطلع شدہ ادارے157: —EU کے مطابقت کے اعلانات جاری کرنے کے لیے مجاز تسلیم شدہ جانچ کی لیبارٹریاں۔ اس عمل میں تکنیکی فائلیں جمع کرانا، قسم کی جانچ کے لیے نمونے فراہم کرنا، پروڈکشن کوالٹی سسٹمز کی تصدیق کے لیے فیکٹری آڈٹ اور جاری نگرانی شامل ہے۔ ایک بار تصدیق ہونے کے بعد، مینوفیکچرر CE مارک لگا سکتا ہے اور اس پروڈکٹ کے لیے EU کے مطابقت کا اعلان جاری کر سکتا ہے۔.
158: خریداروں کو یہ سمجھنا چاہیے کہ “IEC 61812-1 کے مطابق” کا مطلب تصدیق کی سطح کے لحاظ سے مختلف چیزیں ہو سکتی ہیں۔ مکمل تھرڈ پارٹی سرٹیفیکیشن (مطلع شدہ ادارے کی شمولیت کے ساتھ) بغیر کسی آزاد ٹیسٹ رپورٹس کے خود اعلان کردہ تعمیل سے زیادہ وزن رکھتا ہے۔ سپلائرز کا جائزہ لیتے وقت، صرف دعووں کے بجائے ٹیسٹ رپورٹس دیکھنے کے لیے کہیں۔.
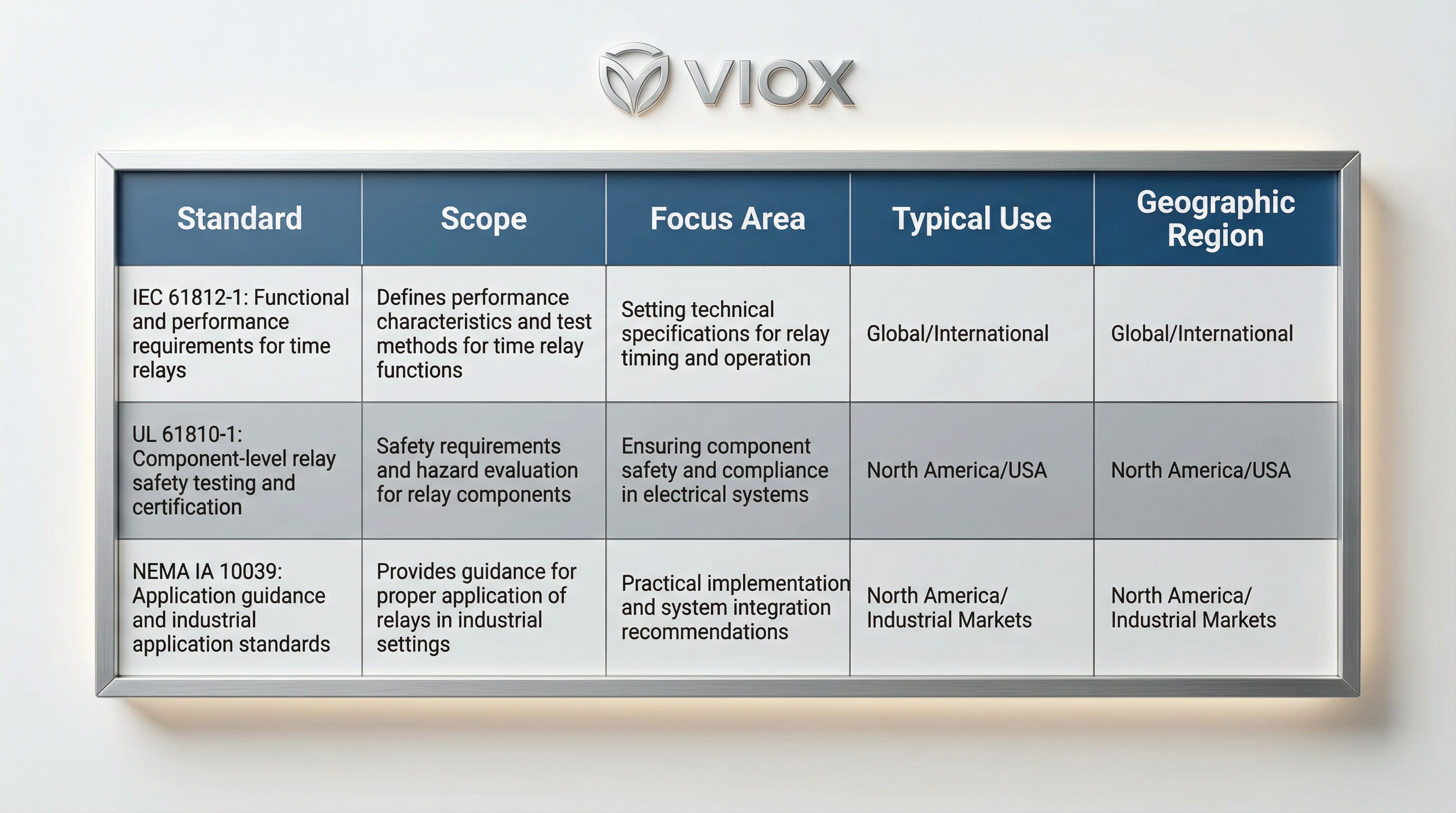
160: IEC 61812-1 بمقابلہ شمالی امریکی معیارات (UL, NEMA)
161: شمالی امریکہ اور بین الاقوامی مارکیٹوں میں کام کرنے والے انجینئرز اکثر پوچھتے ہیں: “IEC 61812-1 کا UL 508 یا NEMA معیارات سے کیا تعلق ہے جن سے میں واقف ہوں؟” فریم ورک تکمیلی ہیں لیکن پروڈکٹ کے درجہ بندی کے مختلف درجوں کو حل کرتے ہیں۔.
360: IEC 61812-1 163: خاص طور پر ٹائم ریلے اور کپلنگ ریلے کے لیے فعال تقاضوں پر توجہ مرکوز کرتا ہے۔ یہ ٹائمنگ کی کارکردگی، درجہ بندی، ماحولیاتی ریٹنگز، EMC اور ایپلیکیشن لیول ٹیسٹنگ کی وضاحت کرتا ہے۔ اسے “ٹائم ریلے فنکشنل اسپیسیفیکیشن اسٹینڈرڈ” کے طور پر سوچیں۔”
164: UL 61810-1 165: (سابقہ طور پر UL 508 کے تحت احاطہ کیا گیا) جزو کی سطح پر الیکٹرو مکینیکل ابتدائی ریلے کو حل کرتا ہے۔ یہ بنیادی ریلے کی حفاظت کی تصدیق کرتا ہے—موصلیت کے نظام، رابطے کی ریٹنگز، درجہ حرارت میں اضافہ، برداشت—اس سے قطع نظر کہ ریلے میں ٹائمنگ کے افعال ہیں یا نہیں۔ اگر آپ الیکٹرو مکینیکل ٹائم ریلے استعمال کر رہے ہیں، تو دونوں معیارات متعلقہ ہیں: UL 61810-1 اس بات کو یقینی بناتا ہے کہ بنیادی ریلے کے رابطے اور موصلیت محفوظ ہیں، جبکہ IEC 61812-1 اس بات کی تصدیق کرتا ہے کہ ٹائمنگ سرکٹ درست طریقے سے کام کرتا ہے۔.
166: UL 508A 167: مکمل اسمبلیوں کے طور پر صنعتی کنٹرول پینلز کا احاطہ کرتا ہے۔ UL 508A پینلز میں نصب ٹائم ریلے کو جزو کی سطح کے تقاضوں (الیکٹرو مکینیکل اقسام کے لیے UL 61810-1، سالڈ اسٹیٹ ڈیوائسز کے لیے UL 508 باب 38) کو پورا کرنا چاہیے، لیکن پینل سرٹیفیکیشن کا عمل ریلے سرٹیفیکیشن سے الگ ہے۔.
168: NEMA IA 10039 (formerly NEMA ICS 5) provides application guidance, installation practices, and selection criteria for control-circuit and pilot devices, including time relays. It’s not a certification standard—it’s more like an application handbook. NEMA IA 10039 complements IEC 61812-1 by offering practical recommendations for relay selection, sizing, and installation that go beyond the IEC standard’s test requirements.
Practical implications: For EMEA projects, IEC 61812-1 certification is effectively mandatory; CE marking requires it. For North American projects, UL recognition (typically UL 508 or UL 61810-1) is the primary requirement, though IEC 61812-1 certification doesn’t hurt and may signal higher quality standards. Manufacturers serving global markets often pursue both IEC and UL certifications on the same product line. If you’re specifying for both markets, look for relays carrying both IEC 61812-1 and UL recognition—VIOX time delay relays, for example, maintain both certifications to serve global customers without requiring separate product lines.
Benefits of IEC 61812-1 Compliance
Beyond regulatory checkbox-ticking, IEC 61812-1 certification delivers tangible value to multiple stakeholders:
For manufacturers, it’s market access and competitive differentiation. EMEA markets effectively require EN IEC 61812-1:2024 for CE marking, so compliance unlocks European sales. The certification process also forces design discipline—products must meet defined performance benchmarks, not just “work well enough.” Manufacturers with IEC 61812-1 certification can credibly claim their timing accuracy, repeatability, and EMC performance have been independently verified.
For engineers specifying components, IEC compliance provides comparable performance data. When comparing time relays from different suppliers, IEC 61812-1 datasheets use standardized specifications measured under identical test conditions. Setting accuracy, repeatability, and influence-quantity performance become apples-to-apples comparisons rather than guesswork. You can specify “timing accuracy ±5% per IEC 61812-1” and know exactly what you’re getting.
For procurement and supply chain teams, certification reduces supplier qualification burden. A supplier claiming IEC 61812-1 compliance should have test reports, type test certificates, and declarations of conformity on file. Verifying compliance becomes a documentation check rather than requiring your own testing program. It also reduces risk—components failing IEC testing would likely cause field failures, warranty claims, and project delays costing far more than any upfront savings from non-certified alternatives.
For quality assurance and regulatory teams, IEC 61812-1 certification simplifies end-product compliance. If you’re building industrial control equipment requiring CE marking, using IEC-certified components streamlines your technical file preparation. The component’s test data becomes supporting evidence for your system-level compliance.
For system integrators and panel builders, certified components mean fewer surprises. Time relays meeting IEC EMC immunity requirements are less likely to false-trigger from VFD noise or nearby radio transmitters. Relays meeting IEC endurance and short-circuit requirements are less likely to fail prematurely in demanding applications. Fewer field callbacks translating directly to lower support costs and better reputation.
The standard also drives continuous improvement. Edition 3.0’s addition of cybersecurity and environmental information requirements reflects evolving industry needs. Manufacturers maintaining IEC certification must keep pace with these updates, ensuring their products stay relevant as industrial requirements advance.
How to Verify Supplier Compliance Claims
Not all “IEC 61812-1 compliant” claims are created equal. Here’s how to verify supplier claims without needing your own test lab:
Request the Declaration of Conformity (DoC). For CE-marked products sold in Europe, the manufacturer must provide an EU Declaration of Conformity stating which directives and harmonized standards the product meets. IEC 61812-1 (or EN IEC 61812-1:2024) should be explicitly listed. The DoC should include product identification, manufacturer details, and the name/signature of the person authorized to issue it. No DoC? Red flag.
Ask for test reports or certificates. Manufacturers who have actually conducted IEC 61812-1 testing possess test reports from accredited laboratories. These reports document which tests were performed, test conditions, results, and pass/fail status. Full test reports may be confidential, but summary certificates showing test scope and pass status should be available. If a supplier can’t produce any test documentation, their compliance claim is unsupported.
Check physical markings. IEC 61812-1 Clause 8 requires permanent markings on the relay itself. Look for the manufacturer’s mark, model/type designation, rated voltage and frequency, and the IEC 61812-1 reference. CE marks (for European market) should be visible and properly sized. Missing or incomplete markings suggest non-compliance or poor quality control.
Review datasheet completeness. IEC 61812-1 Table 7 lists required relay information. A compliant datasheet should document: timing function types, setting ranges, accuracy and repeatability values, rated input voltage/frequency, release voltage, output circuit ratings (contact type, voltage, current, endurance), environmental ratings (temperature, humidity, pollution degree), EMC environment suitability, and connection diagrams. Vague or missing specifications indicate the supplier either didn’t test or failed testing.
Verify notified body involvement (for CE marking). In Europe, certain product categories require third-party conformity assessment. While time relays typically allow self-certification under the Low Voltage Directive, manufacturers using notified bodies for voluntary certification demonstrate higher confidence. Ask if a notified body was involved and request their identification number.
Cross-check with similar products. If specifications seem too good to be true (±1% timing accuracy across -40°C to +85°C with no voltage influence, for example), they probably are. Compare claimed performance against established manufacturers’ datasheets for reality-checking.
Ask about Edition 3.0 updates. Since IEC 61812-1:2023 Edition 3.0 is the current version, ask whether the supplier’s certification is to the 2023 edition or the older 2011 edition. Edition 3.0 added cybersecurity and environmental requirements, so recent certification carries more weight.
When working with VIOX, customers receive complete documentation packages: EU Declaration of Conformity, type test reports from accredited laboratories, full datasheet specifications per Table 7, and product markings meeting Clause 8 requirements. Our certifications are maintained to the current Edition 3.0 standard, ensuring you’re specifying components tested to the latest requirements.
VIOX Time Delay Relays: IEC 61812-1 Certified
VIOX Electric maintains IEC 61812-1:2023 Edition 3.0 certification across our time relay product line, covering on-delay, off-delay, multifunction, and star-delta timing functions. Our certification scope includes both DIN-rail mounted and plug-in socket configurations, with voltage ranges from 12VDC to 240VAC.
Our certification process involves accredited third-party laboratories conducting full type testing per the standard’s requirements: timing accuracy and repeatability verification across temperature and voltage ranges, dielectric strength and insulation resistance testing, EMC immunity testing for industrial environments (per IEC 61812-1 Annex C industrial test levels), electrical endurance testing under resistive and inductive loads, and mechanical robustness verification including vibration and shock testing.
Every VIOX time relay ships with permanent markings per Clause 8, including IEC 61812-1 reference, CE marking (for European market), rated voltage and frequency, output contact ratings, and full model identification. Technical datasheets document all Table 7 required information, and customers receive EU Declarations of Conformity upon request.
For engineers specifying time relays for global projects, VIOX products carry both IEC 61812-1 and UL recognition, eliminating the need for separate component sourcing for EMEA and North American markets. Our compliance documentation streamlines your end-product certification process, whether you’re building control panels, automation systems, HVAC equipment, or industrial machinery.
Visit our product pages for detailed specifications, application notes, and compliance documentation for specific VIOX time relay models.
Conclusion: Standards Compliance as Quality Assurance
IEC 61812-1 represents more than a regulatory formality. It’s a structured framework that translates “this time relay works” into measurable, testable criteria covering timing performance, electrical safety, environmental robustness, and electromagnetic compatibility. For manufacturers, it’s a design and quality discipline. For specifiers, it’s a common language for comparing products. For procurement teams, it’s a verification tool that reduces supplier risk.
The 2023 Edition 3.0 keeps the standard relevant by adding cybersecurity and environmental requirements reflecting contemporary industrial priorities. As automation systems become more connected and sustainability pressures increase, these additions ensure IEC 61812-1 certification remains meaningful rather than becoming a legacy checkbox.
When evaluating time delay relays, don’t stop at “compliant” claims. Verify declarations of conformity, request test reports, check datasheet completeness, and inspect physical markings. The documentation trail matters as much as the certification itself—it’s your evidence that compliance is real, not just marketing language.
Standards compliance won’t prevent every field failure, but it stacks the odds in your favor. A relay tested to IEC 61812-1’s timing accuracy requirements is statistically more likely to perform reliably than an untested alternative. A relay meeting EMC immunity levels is less likely to false-trigger from electrical noise. A relay with documented endurance testing is less likely to fail prematurely under load. Compliance is insurance—you pay upfront (in component cost and specification effort) to reduce much larger downstream costs from failures, recalls, and reputation damage.
For your next project requiring time delay relays, make IEC 61812-1 certification a specification requirement, not an optional preference. The engineering work has already been done to define what “reliable” means. Use it.



