Lors de la spécification des contacteurs pour les systèmes électriques, il est essentiel de comprendre la différence entre CEI 61095 et IEC 60947-4-1 les normes pour garantir la sécurité, la performance et la conformité. Ces deux normes de la Commission Électrotechnique Internationale (CEI) régissent la conception et l'application des contacteurs, mais elles desservent des marchés distincts. La CEI 61095 concerne les applications domestiques et similaires, tandis que la CEI 60947-4-1 couvre le contrôle des moteurs industriels et la commutation intensive. Choisir la mauvaise norme peut entraîner une défaillance prématurée, des risques pour la sécurité et des temps d'arrêt coûteux du système.
Ce guide complet examine les différences techniques, les exigences d'application et les critères de sélection pour les deux normes, aidant ainsi les ingénieurs électriciens, les tableautiers et les professionnels de l'approvisionnement à prendre des décisions éclairées.

Comprendre les fondamentaux
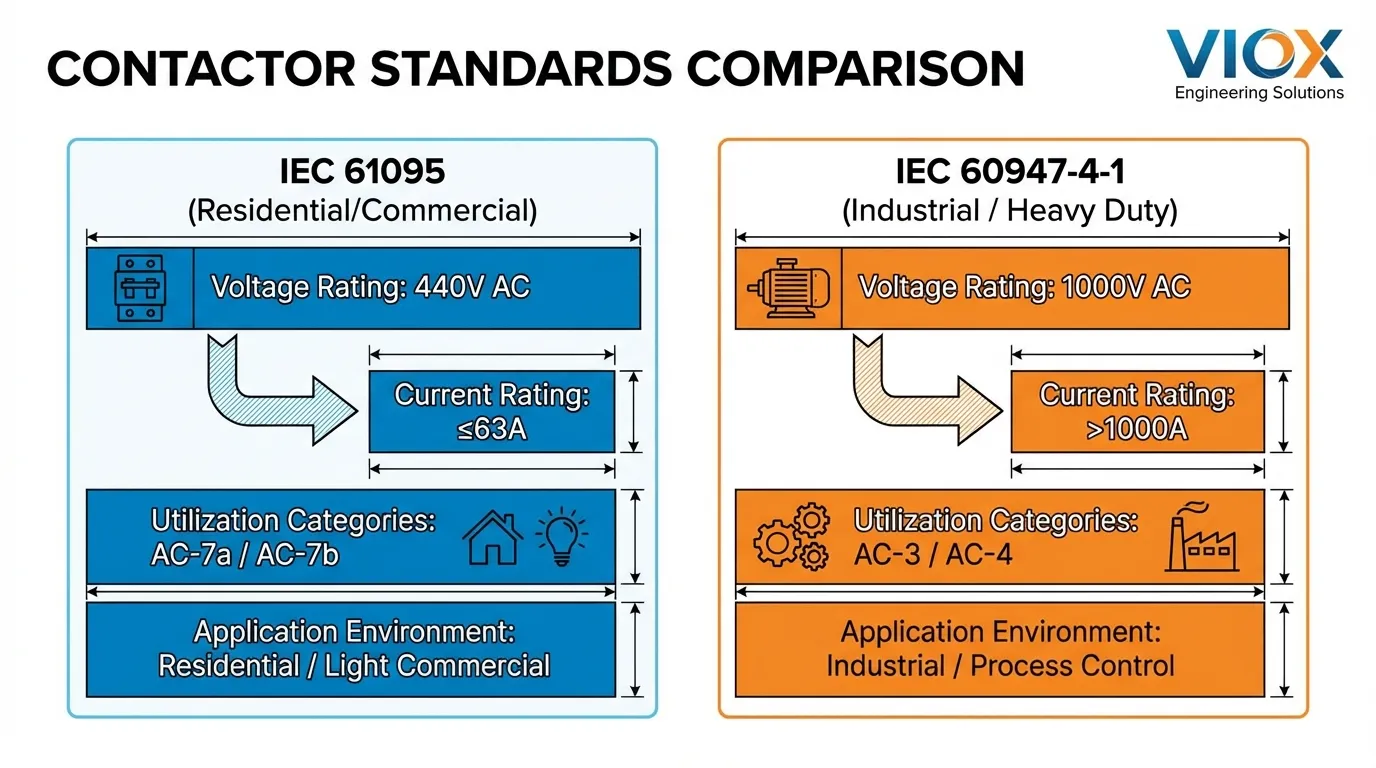
CEI 61095 s'applique aux contacteurs électromécaniques à coupure dans l'air conçus pour des usages domestiques et similaires. Ces contacteurs sont conçus pour des circuits allant jusqu'à 440V AC avec des courants de fonctionnement ne dépassant généralement pas 63A pour la catégorie d'utilisation AC-7a et 32A pour les catégories AC-7b, AC-7c et AC-7d. La norme traite spécifiquement des applications où la fréquence de commutation est modérée et les charges relativement prévisibles, telles que le contrôle de l'éclairage résidentiel, les systèmes HVAC et les petites applications de moteurs.
IEC 60947-4-1 régit les contacteurs et les démarreurs de moteurs pour les applications industrielles, couvrant les équipements avec des tensions nominales allant jusqu'à 1000V AC ou 1500V DC. Cette norme traite des exigences exigeantes des environnements industriels où les contacteurs doivent gérer de lourdes charges inductives, des cycles de commutation fréquents (souvent des millions d'opérations) et des conditions de fonctionnement difficiles, notamment des températures extrêmes, des vibrations et de la contamination.
La distinction fondamentale réside dans leur philosophie de conception : la CEI 61095 privilégie la rentabilité et la simplicité pour les applications résidentielles, tandis que la CEI 60947-4-1 met l'accent sur la robustesse, l'endurance et les fonctions de protection avancées pour les applications industrielles.
Comparaison technique complète
| Paramètre | CEI 61095 (Domestique) | CEI 60947-4-1 (Industriel) |
|---|---|---|
| Tension nominale | ≤ 440V AC (entre phases) | ≤ 1000V AC, ≤ 1500V DC |
| Note Actuelle | ≤ 63A (AC-7a), ≤ 32A (AC-7b/c/d) | Jusqu'à plusieurs milliers d'ampères |
| Application principale | Résidentiel, commercial léger | Contrôle de moteurs industriels, machinerie lourde |
| Catégories d'utilisation | AC-1, AC-7a, AC-7b, AC-7c, AC-7d | AC-1, AC-2, AC-3, AC-4, DC-1, DC-3, DC-5 |
| Pouvoir de coupure | ≤ 6 kA conditionnel | Jusqu'à 100 kA+ (selon le type) |
| Fréquence de commutation | Modérée (fonctionnement occasionnel) | Élevée (cycles fréquents, millions d'opérations) |
| Tests d'endurance | Durée de vie électrique/mécanique de base | Endurance complète dans les conditions nominales |
| Coordination de court-circuit | Coordination de type 1 requise | Options de coordination de type 1 et de type 2 |
| Protection de l'environnement | Degré de pollution 2 (typique) | Protection améliorée pour les environnements industriels |
| Extinction d'arc | Conception de base à coupure dans l'air | Systèmes avancés de trempe à l'arc |
| Montage | Rail DIN (conception modulaire) | Montage sur panneau, rail DIN ou enfichable |
| Contacts auxiliaires | Contacts auxiliaires limités | Options de contacts auxiliaires multiples |
| Commande de bobine | Commande standard ou électronique | Standard, électronique ou à courant continu |
| Exigences en matière de tests | Procédures de test simplifiées | Tests complets par catégorie d'utilisation |
| Installation typique | Unités de consommation, tableaux de distribution | Centres de commande de moteurs (CCM), panneaux industriels |
Principales différences techniques expliquées
1. Tensions et courants nominaux
La différence la plus fondamentale réside dans les valeurs nominales électriques. Les contacteurs CEI 61095 sont conçus pour les applications résidentielles basse tension jusqu'à 440 V AC avec des courants nominaux généralement plafonnés à 63 A. Cela les rend idéaux pour contrôler les circuits d'éclairage domestique, les petits équipements HVAC et les appareils électroménagers résidentiels.
En revanche, les contacteurs CEI 60947-4-1 gèrent des tensions beaucoup plus élevées (jusqu'à 1000 V AC ou 1500 V DC) et des courants allant de quelques ampères à plusieurs milliers d'ampères. Ces valeurs nominales sont nécessaires pour contrôler les grands moteurs industriels, les machines lourdes et les charges industrielles de forte puissance. Par exemple, un démarreur de moteur industriel typique peut contrôler un moteur de 200 HP consommant 250 A à 480 V, ce qui dépasse de loin les capacités des contacteurs domestiques.
2. Catégories d'utilisation : Domestique vs. Industriel
Catégories d'utilisation CEI 61095 :
- AC-1: Charges non inductives ou légèrement inductives (chauffage résistif, éclairage incandescent)
- AC-7a: Charges de moteurs pour appareils électroménagers (machines à laver, lave-vaisselle)
- AC-7b: Charges de moteurs pour les équipements de climatisation et de réfrigération
- AC-7c: Commutation de commande de lampe à décharge électrique compensée
- AC-7d: Commutation de lampes LED et d'appareils de commande de LED (ajouté dans l'édition 2023)
Catégories d'utilisation CEI 60947-4-1 :
- AC-1: Charges non inductives ou légèrement inductives
- CA-2: Démarrage de moteurs à bagues et coupure pendant le fonctionnement
- AC-3: Démarrage de moteurs à cage d'écureuil, coupure pendant le fonctionnement (catégorie industrielle la plus courante)
- AC-4: Démarrage, freinage par contre-courant, fonctionnement par à-coups et approche lente des moteurs à cage d'écureuil
- DC-1, DC-3, DC-5: Diverses applications de commande de moteurs à courant continu
La catégorie AC-3 est la plus largement utilisée dans les environnements industriels, conçue pour les contacteurs qui démarrent les moteurs à cage d'écureuil et les arrêtent en cours de fonctionnement. Ces contacteurs doivent supporter des courants d'appel 5 à 8 fois supérieurs au courant nominal du moteur pendant le démarrage. En savoir plus sur les catégories d'utilisation des contacteurs.
3. Exigences en matière d'endurance et de fiabilité
Les applications industrielles exigent une endurance nettement supérieure. Les contacteurs IEC 60947-4-1 sont soumis à des tests d'endurance rigoureux impliquant des millions de cycles de fonctionnement dans des conditions nominales. Un contacteur typique de catégorie AC-3 peut être testé pour 1 à 8 millions d'opérations, en fonction du courant nominal et de l'application.
Les contacteurs IEC 61095, bien que toujours fiables, sont conçus pour des cycles de service modérés typiques des applications résidentielles, peut-être quelques milliers à quelques dizaines de milliers d'opérations au cours de leur durée de vie. Cette différence dans les exigences d'endurance a un impact direct sur la sélection des matériaux de contact, la conception des ressorts et les mécanismes de coupure d'arc.
4. Coordination en court-circuit
Les deux normes exigent une coordination avec les dispositifs de protection contre les courts-circuits (SCPD), mais la norme IEC 60947-4-1 propose deux types de coordination distincts :
- Coordination de type 1: En cas de court-circuit, le contacteur ou le démarreur peut subir des dommages, mais ne doit pas présenter de danger pour les personnes ou l'installation. Le contacteur doit être remplacé ou réparé avant de pouvoir être remis en service. Ceci est similaire à la coordination requise par la norme IEC 61095.
- Coordination de type 2: En cas de court-circuit, aucun effet dangereux n'est autorisé et le contacteur doit pouvoir être réutilisé après l'élimination du défaut. Seule une soudure mineure des contacts est acceptable et l'équipement ne doit pas nécessiter de maintenance importante. Ce niveau de coordination plus élevé est essentiel pour les applications industrielles où les temps d'arrêt sont coûteux.
Il est essentiel de comprendre la coordination en court-circuit lors de la sélection des MCCB pour les applications de panneaux.
5. Coupure d'arc et conception des contacts
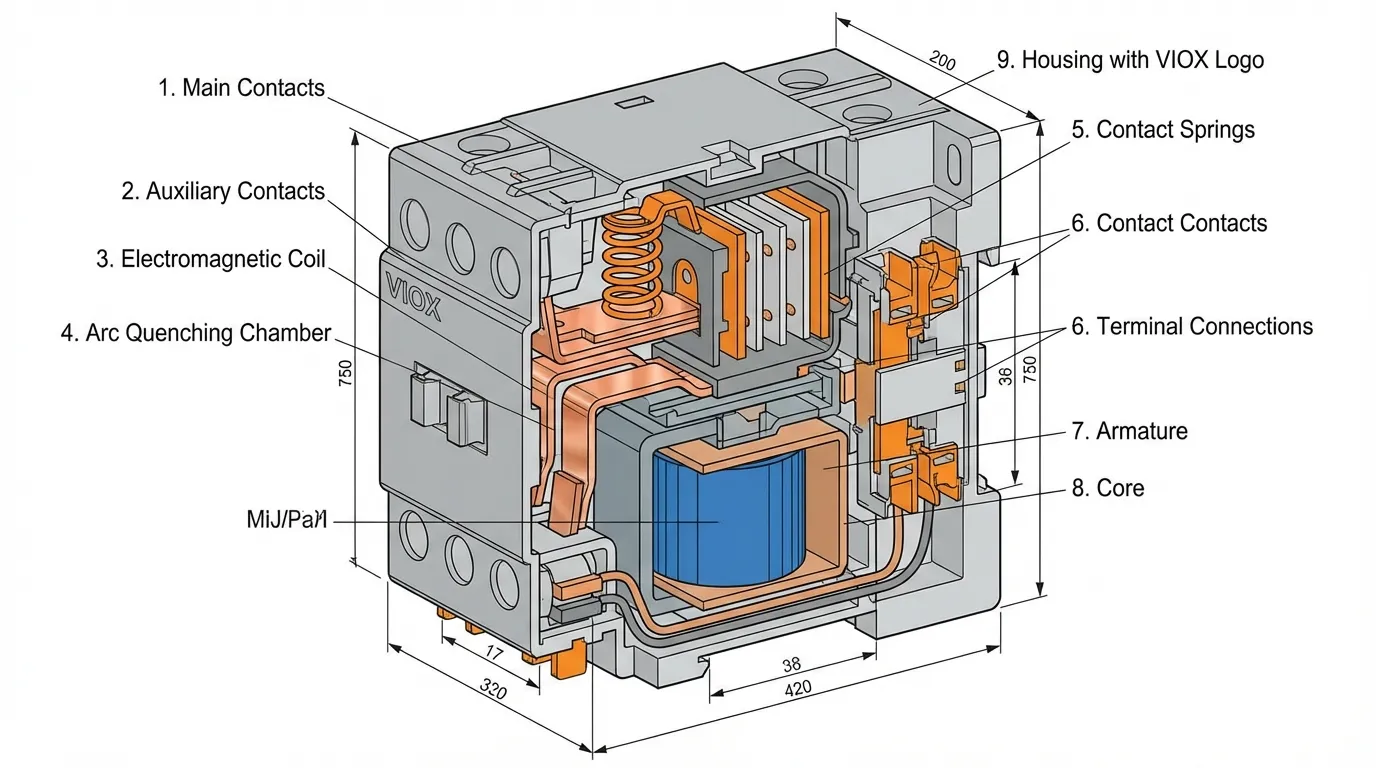
Les contacteurs industriels utilisent des systèmes sophistiqués de coupure d'arc pour interrompre en toute sécurité les courants élevés, en particulier sous des charges inductives. Ceux-ci peuvent inclure :
- Bobines d'extinction magnétique pour entraîner les arcs dans les chambres d'extinction
- Plusieurs plaques de séparation d'arc pour diviser et refroidir les arcs
- Matériaux de contact améliorés (alliages d'argent, argent-tungstène)
- Espacements de contact plus importants et pression de contact plus élevée
Les contacteurs domestiques utilisent des conceptions de coupure à air plus simples, adaptées à leurs courants nominaux inférieurs et à leurs cycles de service moins exigeants. Comprendre les composants internes du contacteur permet d'expliquer ces différences de conception.
Lignes directrices d'application
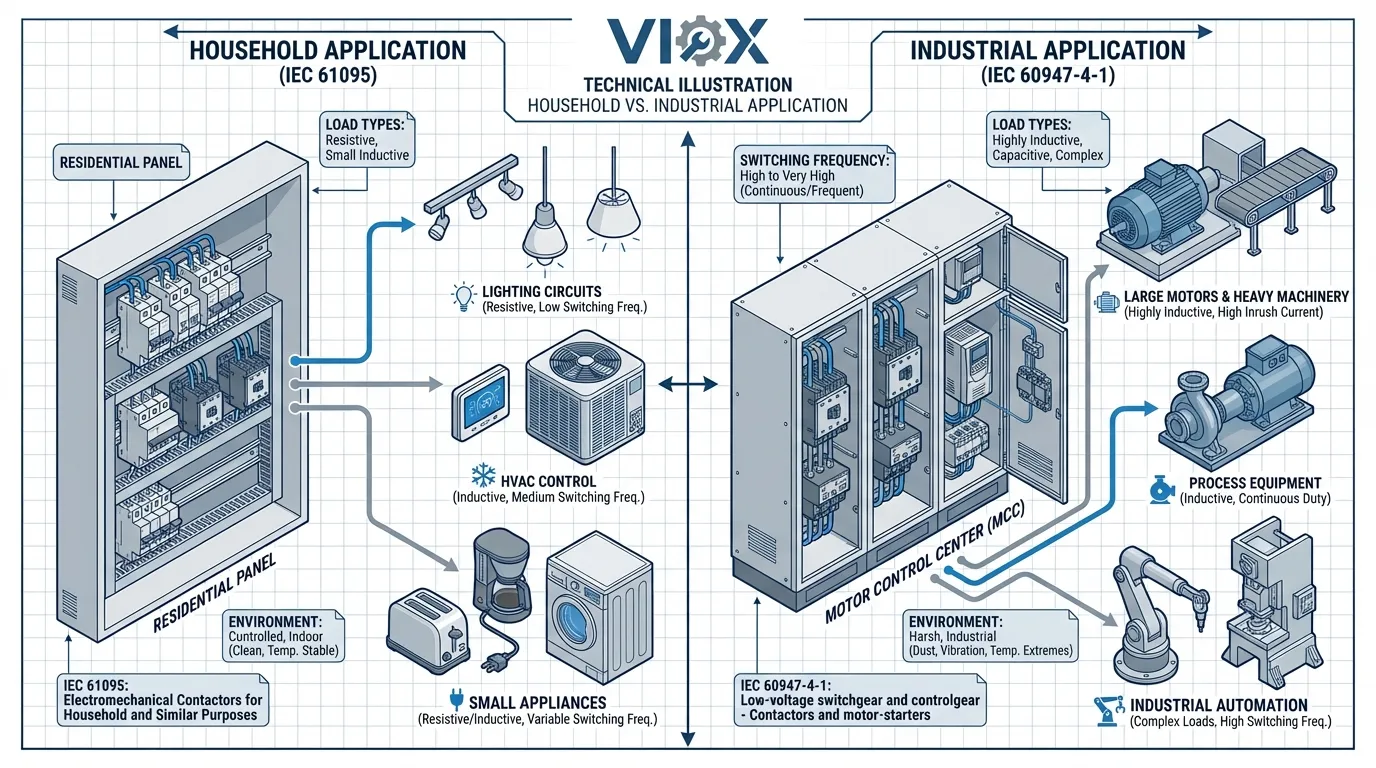
Quand spécifier les contacteurs IEC 61095
- Panneaux électriques résidentiels et les unités de consommation
- Systèmes d'automatisation des bâtiments (commande d'éclairage, programmation CVC)
- Applications commerciales légères (éclairage de vente au détail, CVC de petits bureaux)
- Applications de contacteurs modulaires nécessitant un montage sur rail DIN
- Intégration de la maison intelligente avec des circuits de commande électroniques
- Commande d'éclairage LED (catégorie d'utilisation AC-7d)
- Applications avec courant ≤ 63A et tension ≤ 440V AC
Les contacteurs IEC 61095 excellent dans les applications où la rentabilité, la taille compacte et le montage sur rail DIN sont des priorités. Les contacteurs modulaires sont particulièrement populaires dans les systèmes modernes de gestion de bâtiments.
Quand spécifier les contacteurs IEC 60947-4-1
- Centres de commande de moteurs industriels (MCC)
- Machines lourdes et les équipements de production
- Stations de pompage et de compression
- Systèmes CVC dans les grands bâtiments commerciaux
- Exploitation minière, pétrochimie et fabrication installations
- Applications nécessitant une coordination de type 2
- Commutation à haute fréquence opérations (à-coups, freinage par contre-courant)
- Grands démarreurs de moteur (>10 HP / 7,5 kW)
- Environnements industriels difficiles (températures extrêmes, vibrations, contamination)
Pour les applications industrielles critiques, contacteurs de sécurité avec contacts à guidage forcé peuvent être nécessaires pour répondre aux normes de sécurité des machines.

Critères de sélection et bonnes pratiques
Analyse de charge
Avant de sélectionner un contacteur, effectuez une analyse approfondie de la charge :
- Courant en régime permanent: Courant continu que le contacteur doit supporter
- Courant d'appel: Courant de crête pendant le démarrage du moteur ou la commutation de la lampe
- Cycle de service: Fréquence et durée des opérations de commutation
- Facteur de puissance de la charge: Affecte l'énergie de l'arc et l'usure des contacts
- Conditions environnementales: Température, humidité, altitude, degré de pollution
Considérations sur la tension
Assurez-vous que la tension nominale de fonctionnement (Ue) du contacteur correspond ou dépasse la tension du circuit. Pour les systèmes triphasés, la tension est mesurée entre les phases. Vérifiez également :
- Tension nominale d'isolation (Ui): Doit dépasser la tension du circuit
- Tension nominale de tenue aux chocs (Uimp): Généralement 4 kV pour la norme IEC 61095, plus élevée pour les applications industrielles
- Tension du circuit de commande: Doit correspondre à l'alimentation de commande disponible
Sélection de la cote actuelle
Pour les contacteurs IEC 61095, sélectionnez en fonction de la catégorie d'utilisation appropriée :
- Calibre AC-7a pour les charges de moteur
- Calibre AC-1 pour les charges résistives (généralement plus élevé que AC-7a)
Pour les contacteurs IEC 60947-4-1, le calibre AC-3 est le plus courant pour les applications de moteur. Appliquez toujours les facteurs de réduction appropriés pour :
- Température ambiante supérieure à 40 °C
- Altitude supérieure à 2000 m
- Groupement de plusieurs contacteurs dans des boîtiers
Comprendre les facteurs de réduction de puissance électrique est essentiel pour un dimensionnement correct.
Coordination de la protection contre les courts-circuits
Vérifiez que le contacteur est correctement coordonné avec le dispositif de protection contre les courts-circuits (SCPD) sélectionné (disjoncteur ou fusible). Les fabricants fournissent des tableaux de coordination spécifiant :
- Courant nominal de court-circuit maximal
- Type et calibre de SCPD recommandés
- Type de coordination atteint (Type 1 ou Type 2)
Pour les applications industrielles, la coordination de Type 2 est préférable pour minimiser les temps d'arrêt après des conditions de défaut.
Différences d'installation et d'entretien
Installation IEC 61095
- Standard Montage sur rail DIN de 35 mm (selon IEC 60715)
- Largeur modulaire typiquement 2-4 modules (1 module = 18 mm)
- Bornes à vis ou à ressort pour le raccordement des fils
- Protection environnementale minimale requise
- Installation dans des unités de consommation ou des tableaux de distribution standard
Installation IEC 60947-4-1
- Montage sur panneau avec connexions boulonnées pour les grands contacteurs
- Montage sur rail DIN pour les petits contacteurs industriels
- Terminaison de câble professionnelle avec cosses de câble
- Étanchéité environnementale selon les besoins (indices IP)
- Installation dans des centres de commande de moteur avec des dégagements appropriés
- Prise en compte de la dissipation thermique et de la ventilation
Les Exigences De Maintenance
Contacteurs IEC 61095: Maintenance minimale requise dans les applications résidentielles typiques. Inspection périodique pour :
- État des contacts (inspection visuelle)
- Etanchéité des bornes
- Fonctionnement mécanique
Contacteurs IEC 60947-4-1: Programmes de maintenance réguliers basés sur les cycles de fonctionnement :
- Inspection et remplacement des contacts
- Nettoyage des chambres de coupure
- Lubrification des composants mécaniques
- Vérification des contacts auxiliaires
- Essai de résistance d'isolation
Les listes de contrôle de la maintenance des contacteurs industriels fournissent des conseils détaillés pour les programmes de maintenance préventive.
Idées reçues
Mythe 1 : “ Les contacteurs domestiques peuvent gérer des charges industrielles s'ils sont surdimensionnés ”
Réalité: Même les contacteurs IEC 61095 surdimensionnés n'ont pas la capacité d'extinction d'arc, l'endurance et la coordination de court-circuit requises pour les applications industrielles. L'utilisation de contacteurs domestiques dans des environnements industriels viole les normes de sécurité et crée des risques de responsabilité.
Mythe 2 : “ Les contacteurs industriels sont toujours de meilleure qualité ”
Réalité: Les contacteurs IEC 60947-4-1 sont conçus pour des exigences différentes, pas nécessairement de “ meilleure ” qualité. Pour les applications résidentielles, les contacteurs IEC 61095 offrent un rapport coût-performance optimal avec des caractéristiques de sécurité appropriées.
Mythe 3 : “ Tous les contacteurs ayant le même courant nominal sont interchangeables ”
Réalité: Les courants nominaux sont spécifiques aux catégories d'utilisation. Un contacteur IEC 61095 de 32 A (AC-7b) ne peut pas remplacer un contacteur IEC 60947-4-1 de 32 A (AC-3) car les caractéristiques de charge et les cycles de service diffèrent considérablement.
Mythe 4 : “ Le pouvoir de coupure en court-circuit n'a pas d'importance s'il y a un disjoncteur ”
Réalité: Le contacteur doit être correctement coordonné avec le SCPD. Un contacteur dont le pouvoir de coupure est inadéquat peut exploser ou provoquer un arc électrique même avec une protection contre les surintensités appropriée.
Mises à jour récentes des normes
IEC 61095:2023 Édition
La dernière édition comprend des mises à jour importantes :
- Catégorie AC-7d: Nouvelle catégorie d'utilisation pour les lampes LED et les appareillages de commande de LED, répondant au marché croissant de l'éclairage LED
- Circuits de commande électroniques: Exigences pour les contacteurs avec électroaimants à commande électronique
- Exigences de marquage améliorées: Étiquetage amélioré pour une installation et une maintenance plus sûres
- Essais environnementaux: Procédures de test d'humidité et de température mises à jour
IEC 60947-4-1:2023 Édition
Les changements récents incluent :
- Adoption de l'AC-7d: Intégré à partir de la CEI 61095 pour les applications LED industrielles
- Dispositifs de commutation de protection instantanée du moteur (IMPSD): Nouvelles exigences pour la protection rapide du moteur
- Aspects environnementaux: Référence à la CEI TS 63058 pour les considérations de durabilité
- Compatibilité des modules d'entraînement en aval: Exigences pour les contacteurs utilisés avec des variateurs de fréquence
Considérations sur les coûts
Coût initial
Les contacteurs IEC 61095 coûtent généralement $15-$150 selon l'intensité nominale et les caractéristiques. Les contacteurs IEC 60947-4-1 varient de $50-$5,000+ pour les grandes unités industrielles.
Coût total de possession
Tenir compte des coûts du cycle de vie :
- Coûts de maintenance: Les contacteurs industriels nécessitent une maintenance plus fréquente mais offrent une durée de vie plus longue
- Coûts des temps d'arrêt: La coordination de type 2 réduit les temps d'arrêt dans les environnements industriels
- Efficacité énergétique: Les contacteurs modernes à faible consommation d'énergie de la bobine réduisent les coûts d'exploitation
- Coûts de remplacement: L'utilisation de la norme appropriée évite les défaillances prématurées et les remplacements coûteux
Pour les applications résidentielles rentables, contacteurs modulaires vs contacteurs traditionnels La comparaison aide à optimiser la sélection.
Résolution Des Problèmes Courants
Problèmes de contacteur IEC 61095
- Bruit de bourdonnement: Souvent causé par une faible tension de bobine ou une contamination
- Défaut de fermeture: Vérifier la tension de la bobine et les obstructions mécaniques
- Soudure des contacts: Peut indiquer des conditions de surcharge ou de court-circuit
Guide de dépannage des contacteurs fournit des procédures de diagnostic détaillées.
Problèmes de contacteur IEC 60947-4-1
- Usure excessive des contacts: Vérifier la sélection appropriée de la catégorie d'utilisation
- Dommages à la chambre d'arc: Indique des événements de court-circuit ou une coordination incorrecte
- Surchauffe de la bobine: Vérifier la surtension ou la température ambiante excessive
Section FAQ
Q1 : Puis-je utiliser un contacteur IEC 61095 pour contrôler un moteur industriel de 10 HP ?
R : Non. Les contacteurs IEC 61095 sont conçus pour les applications domestiques avec des courants nominaux jusqu'à 63 A et n'ont pas l'endurance, la capacité de coupure d'arc et la coordination de court-circuit requises pour la commande de moteurs industriels. Utilisez toujours des contacteurs IEC 60947-4-1 pour les moteurs industriels.
Q2 : Quel est le principal avantage de la coordination de type 2 IEC 60947-4-1 ?
R : La coordination de type 2 garantit qu'après un défaut de court-circuit, le contacteur reste apte à être utilisé sans remplacement. Cela minimise les temps d'arrêt et les coûts de maintenance dans les applications industrielles où la disponibilité des équipements est essentielle.
Q3 : Les contacteurs IEC 60947-4-1 peuvent-ils être utilisés dans des applications résidentielles ?
R : Oui, techniquement, ils peuvent fonctionner dans des applications résidentielles, mais ils sont inutilement coûteux et surdimensionnés. Les contacteurs IEC 61095 sont spécifiquement optimisés pour un usage résidentiel, offrant un meilleur rapport coût-performance pour les applications domestiques.
Q4 : Comment puis-je identifier la norme suivie par un contacteur ?
R : Vérifiez la plaque signalétique ou la documentation du produit. La référence de la norme (IEC 61095 ou IEC 60947-4-1) doit être clairement indiquée avec les catégories d'utilisation, la tension nominale et les courants nominaux.
Q5 : Quelle est la signification de la catégorie d'utilisation AC-7d ?
R : AC-7d est une nouvelle catégorie (ajoutée en 2023) spécifiquement pour la commutation de lampes LED et d'appareillages de commande de LED. Les charges LED ont des caractéristiques d'appel de courant uniques qui diffèrent des lampes à incandescence ou à décharge traditionnelles, nécessitant des considérations spécifiques de conception de contacteur.
Q6 : Les deux normes exigent-elles les mêmes tests environnementaux ?
R : Non. Bien que les deux normes incluent des tests environnementaux, la CEI 60947-4-1 exige généralement des tests plus complets pour les environnements industriels, y compris des plages de température améliorées, une résistance aux vibrations et des considérations sur le degré de pollution.
Q7 : Puis-je remplacer un contacteur IEC 61095 défaillant par une unité IEC 60947-4-1 ?
R : Bien que cela soit électriquement possible si les valeurs nominales correspondent, ce n'est pas recommandé en raison des différences de montage, des contraintes de taille et du coût. Remplacez-le par la même norme, sauf si vous mettez à niveau l'ensemble de l'installation.
Q8 : Quelle est la différence de durée de vie typique entre les contacteurs domestiques et industriels ?
R : Les contacteurs IEC 61095 réalisent généralement 10 000 à 100 000 opérations en service résidentiel. Les contacteurs IEC 60947-4-1 sont conçus pour 1 à 8 millions d'opérations selon le courant nominal et la catégorie d'utilisation.
Principaux enseignements
- Normes spécifiques à l'application: IEC 61095 et IEC 60947-4-1 desservent des marchés fondamentalement différents - applications domestiques/commerciales légères par rapport aux applications industrielles - avec des caractéristiques de performance adaptées à chaque environnement.
- Hiérarchie de tension et de courant: Les contacteurs industriels (IEC 60947-4-1) offrent des tensions nominales nettement plus élevées (jusqu'à 1000 V CA contre 440 V CA) et des capacités de courant (jusqu'à des milliers d'ampères contre 63 A maximum), ce qui reflète leurs applications lourdes.
- Les catégories d'utilisation sont importantes: Sélectionnez toujours les contacteurs en fonction de la catégorie d'utilisation appropriée (AC-7a/b pour les applications domestiques, AC-3/AC-4 pour les moteurs industriels) plutôt que simplement les courants nominaux, car les caractéristiques de charge diffèrent considérablement.
- Endurance et Fiabilité: Les contacteurs IEC 60947-4-1 sont conçus pour des millions d'opérations dans des environnements industriels exigeants, tandis que les contacteurs IEC 61095 sont optimisés pour des cycles de service modérés dans des environnements résidentiels.
- Coordination de court-circuit: Les applications industrielles bénéficient d'une coordination de Type 2 (le contacteur reste opérationnel après des défauts), tandis que les applications domestiques utilisent généralement une coordination de Type 1 (le contacteur peut nécessiter un remplacement après des défauts).
- Équilibre Coût-Performance: L'utilisation de la norme appropriée garantit une rentabilité optimale : IEC 61095 pour des solutions résidentielles abordables, IEC 60947-4-1 pour des performances industrielles robustes où les coûts d'arrêt justifient un investissement initial plus élevé.
- Conformité en matière de sécurité: Les deux normes accordent la priorité à la sécurité, mais la norme IEC 60947-4-1 comprend des fonctions de sécurité améliorées (extinction d'arc avancée, contacts à guidage forcé, étanchéité hermétique) essentielles pour les environnements industriels où une défaillance de l'équipement pourrait avoir de graves conséquences.
- Mises à jour récentes: Les éditions 2023 des deux normes ont introduit la catégorie AC-7d pour le contrôle de l'éclairage LED, reflétant l'évolution de l'industrie vers la technologie LED dans les applications résidentielles et industrielles.
- Sélection professionnelle: Lors de la spécification des contacteurs, effectuez une analyse approfondie de la charge, y compris le courant en régime permanent, les caractéristiques d'appel de courant, le cycle de service et les conditions environnementales. Consultez des ingénieurs électriciens ou des spécialistes des contacteurs pour les applications critiques.
- Considérations relatives au cycle de vie: Le coût total de possession comprend non seulement le prix d'achat initial, mais aussi les exigences de maintenance, la durée de vie prévue, l'efficacité énergétique et les coûts d'arrêt potentiels, des facteurs qui varient considérablement entre les contacteurs domestiques et industriels.
À propos de VIOX Electric
VIOX Electric est un fabricant B2B leader d'équipements électriques, spécialisé dans les contacteurs, les disjoncteurs et les composants de distribution électrique de haute qualité. Nos produits sont conformes aux normes internationales, notamment IEC 61095 et IEC 60947-4-1, garantissant la sécurité, la fiabilité et la performance pour les applications résidentielles et industrielles. Contactez VIOX dès aujourd'hui pour : pour obtenir des conseils d'experts sur la sélection des contacteurs pour votre application spécifique.
Liens internes sélectionnés pour le référencement
- Comment choisir un contacteur modulaire CA CC
- Logique de conception des composants internes des contacteurs AC
- Guide des contacteurs de sécurité par rapport aux contacteurs standard
- Guide de dépannage des contacteurs
- Contacteur vs Démarreur de moteur
- Normes électriques pour les contacteurs - Catégories d'utilisation
- Liste de contrôle de l'inspection de la maintenance des contacteurs industriels
- Contacteur modulaire et contacteur traditionnel
- Contacteurs vs Relais - Comprendre les principales différences
- Guide des facteurs de déclassement électrique


