
Direct Answer
When facing aging switchgear, facility managers have three primary options: retrofit (upgrading internal components like circuit breakers while keeping the existing structure), refurbish (comprehensive maintenance and repair of existing equipment), or complete replacement (removing old equipment and installing new systems). The optimal choice depends on equipment age, condition, budget constraints, and operational requirements. Retrofitting typically saves 40-70% compared to full replacement while extending equipment life by 15-30 years, refurbishment costs 20-40% of replacement but offers shorter-term benefits (5-10 years), and complete replacement provides the longest service life (25-40 years) with the highest upfront investment but lowest long-term maintenance costs.
Key Takeaways
- Retrofit solutions can save $500,000+ in equipment costs and reduce project timelines from 60 weeks to 25-30 weeks compared to complete replacement
- Refurbishment extends switchgear life by 5-10 years at 20-40% of replacement cost, ideal for equipment under 20 years old with good structural integrity
- Complete replacement is necessary when equipment exceeds 30-40 years, has obsolete components, or fails to meet current safety standards
- Hidden costs including downtime, labor, conduit modifications, and cable replacements can exceed equipment costs by 200-300%
- Decision framework should evaluate equipment age, spare parts availability, maintenance costs, safety compliance, and facility expansion plans
Understanding Your Three Options
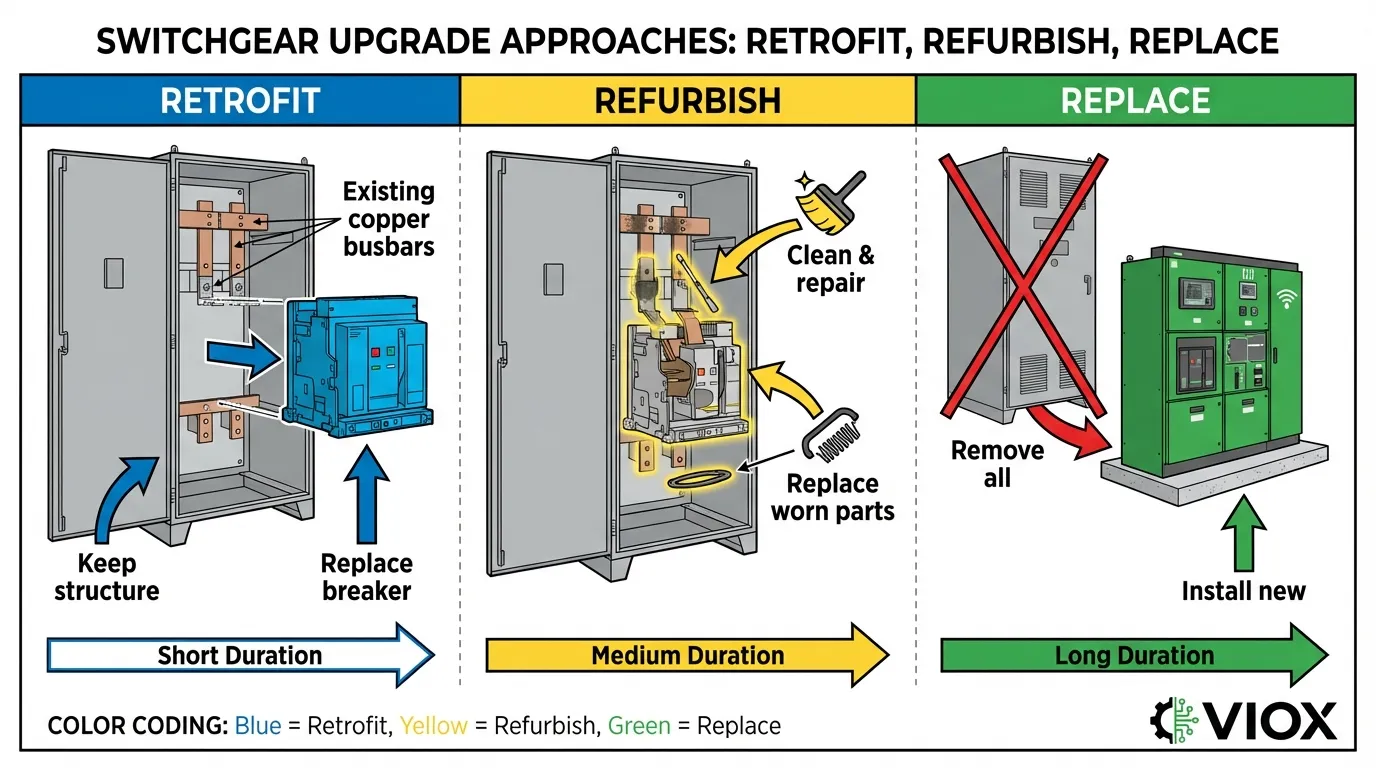
What Is Switchgear Retrofit?
Switchgear retrofit involves upgrading the internal active components—primarily circuit breakers, protective relays, and control systems—while retaining the existing switchgear structure, cabinet, buswork, and enclosures. This approach modernizes outdated systems without the extensive demolition and reconstruction required for complete replacement.
Key characteristics of retrofit:
- Replaces the “heart” of the system (circuit breakers) with modern vacuum or SF6 technology
- Maintains existing footprint and structural components
- Minimal modifications to buswork and secondary wiring
- Typically completed in hours to days rather than weeks
- Extends equipment life by 15-30 years
Modern retrofit solutions include direct replacement circuit breakers designed to fit existing cubicles with plug-and-play compatibility, and retrofill solutions that modify the internal circuit breaker cell to accept new equipment. Both approaches significantly reduce downtime compared to full replacement while delivering current technology benefits.

What Is Switchgear Refurbishment?
Refurbishment involves comprehensive maintenance, inspection, cleaning, testing, and selective repair or replacement of worn components within the existing switchgear system. This process restores equipment to near-original performance specifications without fundamental design changes.
Refurbishment typically includes:
- Detailed inspection and diagnostic testing of all components
- Cleaning and lubrication of mechanical parts
- Replacement of worn contacts, springs, and insulation materials
- Recalibration of protective relays and trip settings
- Testing to relevant ANSI/IEC standards
- Repainting and cosmetic restoration
Refurbishment works best for switchgear that is structurally sound but showing signs of wear, typically equipment 15-25 years old that has been properly maintained. The process can restore 80-90% of original performance at a fraction of replacement cost, extending service life by 5-10 years.
What Is Complete Replacement?
Complete replacement involves removing all existing switchgear equipment and installing entirely new systems with current technology, updated safety features, and modern monitoring capabilities. This approach provides the longest service life but requires the highest capital investment and most extensive facility modifications.
Replacement considerations:
- New equipment typically smaller than legacy systems
- Requires conduit relocation and cable modifications
- Involves extensive engineering, design, and commissioning
- Provides latest safety features including arc flash mitigation
- Enables integration with digital monitoring and SCADA systems
- Delivers 25-40 years of reliable service life
Replacement becomes necessary when equipment has reached end-of-life (typically 30-40 years), critical components are obsolete with no retrofit options available, or facility expansion requires significantly increased capacity that cannot be achieved through upgrades.
Comprehensive Cost-Benefit Comparison
| Factor | Retrofit | Refurbish | Replace |
|---|---|---|---|
| Upfront Cost | 30-60% of replacement | 20-40% of replacement | 100% (baseline) |
| Project Duration | 25-30 weeks | 8-16 weeks | 52-60 weeks |
| Downtime Required | Hours to days | Days to weeks | Weeks to months |
| Equipment Life Extension | 15-30 years | 5-10 years | 25-40 years (new) |
| Energy Efficiency Improvement | 20-30% | 5-10% | 30-40% |
| Maintenance Cost Reduction | 40-50% | 15-25% | 60-70% |
| Safety Feature Updates | Modern protection | Limited updates | Latest technology |
| Digital Integration | Possible with smart breakers | Limited capability | Full IoT/SCADA ready |
| Environmental Impact | 40 tons CO₂ saved | 15-20 tons CO₂ saved | Highest carbon footprint |
| Spare Parts Availability | 20-30 years guaranteed | Depends on OEM | 30+ years guaranteed |
Hidden Cost Analysis
Beyond equipment purchase prices, facility managers must account for substantial hidden costs that can dramatically impact total project investment:
Labor and Installation Costs:
- Retrofit: $50,000-$150,000 (minimal modifications)
- Refurbish: $75,000-$200,000 (component-level work)
- Replace: $250,000-$750,000 (complete installation)
Infrastructure Modifications:
- Conduit relocation and resizing: $30,000-$100,000
- Cable replacement or splicing: $50,000-$200,000
- Structural modifications (pads, walls, doors): $40,000-$150,000
- Fire suppression and HVAC updates: $25,000-$75,000
Operational Impact Costs:
- Production downtime: $50,000-$2.3M per hour (industry dependent)
- Temporary power solutions: $15,000-$50,000
- Expedited shipping for critical components: $10,000-$30,000
- Additional testing and commissioning: $20,000-$60,000
Compliance and Engineering:
- Design and engineering services: $40,000-$120,000
- Arc flash studies and labeling: $15,000-$40,000
- Permit fees and inspections: $5,000-$20,000
- Updated documentation and training: $10,000-$25,000
These hidden costs often equal or exceed the equipment purchase price, making comprehensive cost-benefit analysis essential for accurate decision-making.
Decision-Making Framework: Which Option Is Right for You?
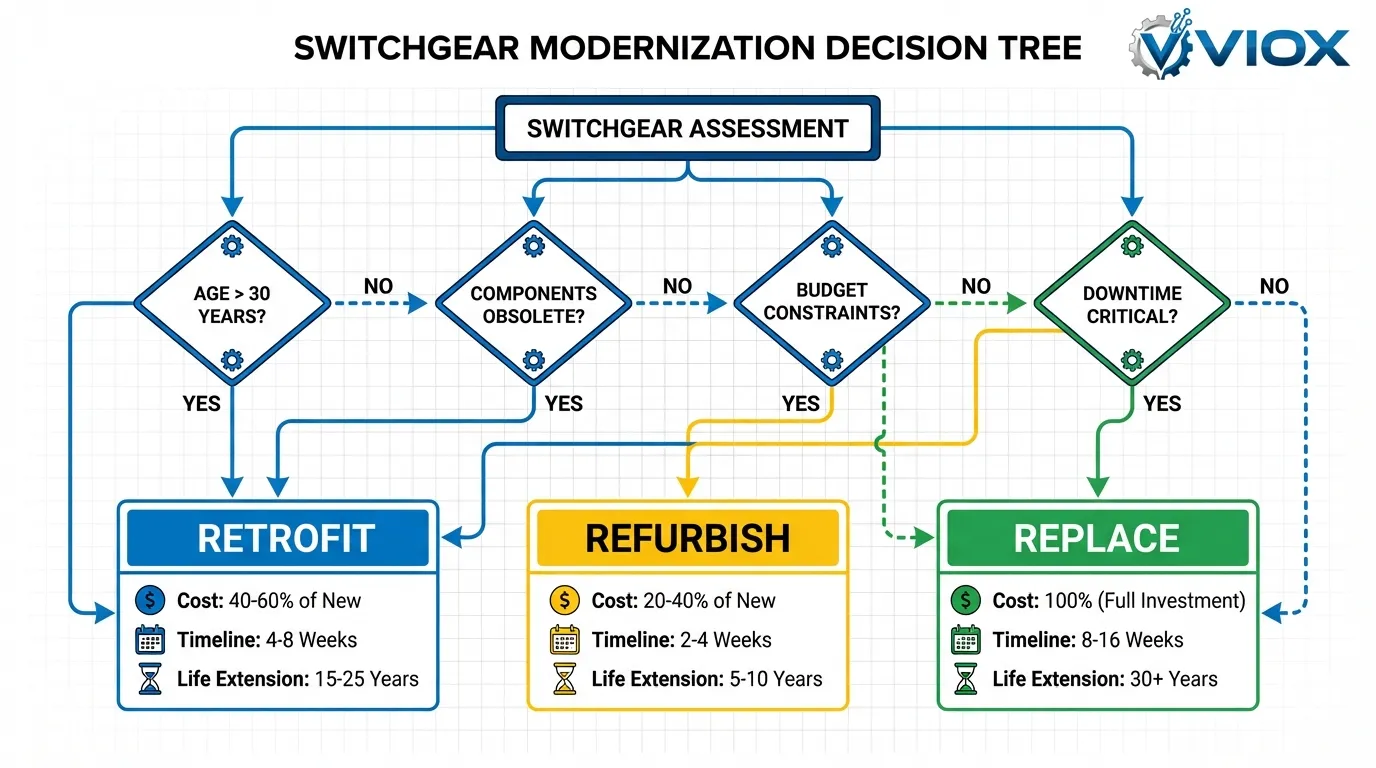
When to Choose Retrofit
Optimal conditions for retrofit:
- Equipment age: 15-30 years with sound structural components
- Primary issue: Obsolete circuit breakers or outdated protection systems
- Budget constraints: Limited capital but need for modernization
- Downtime sensitivity: Critical operations requiring minimal interruption
- Spare parts: Difficulty sourcing components for aging breakers
- Compliance needs: Must meet current safety standards without full replacement
Retrofit advantages:
- Saves 40-70% compared to complete replacement
- Reduces project timeline by 50-60%
- Minimizes facility disruption and production downtime
- Maintains existing footprint and infrastructure
- Provides modern safety features and digital capabilities
- Significantly reduces environmental impact
Retrofit limitations:
- Not suitable for severely deteriorated equipment
- May not address all obsolescence issues
- Limited capacity expansion capabilities
- Requires compatible retrofit solutions from manufacturers
When to Choose Refurbishment
Optimal conditions for refurbishment:
- Equipment age: 10-25 years with regular maintenance history
- Condition: Structurally sound with component-level wear
- Budget: Moderate investment for life extension
- Spare parts: Components still available from OEM or aftermarket
- Performance: Equipment meeting most operational requirements
- Timeline: Planned maintenance windows available
Refurbishment advantages:
- Lowest upfront cost option
- Restores equipment to near-original performance
- Extends life by 5-10 years cost-effectively
- Can be performed in stages to minimize disruption
- Preserves existing system knowledge and documentation
- Ideal for well-maintained equipment
Refurbishment limitations:
- Shorter life extension compared to retrofit or replacement
- May not address fundamental design limitations
- Cannot upgrade to latest safety or digital features
- Increasing maintenance costs as equipment continues aging
- Risk of repeated failures if underlying issues not resolved
When to Choose Complete Replacement
Optimal conditions for replacement:
- Equipment age: 30-40+ years approaching end-of-life
- Condition: Significant deterioration or repeated failures
- Obsolescence: No retrofit options available for critical components
- Capacity needs: Facility expansion requiring increased electrical capacity
- Safety concerns: Equipment lacking modern arc flash protection
- Long-term planning: 25-40 year investment horizon
Replacement advantages:
- Longest service life (25-40 years)
- Latest technology including IoT and predictive maintenance
- Highest energy efficiency and lowest operating costs
- Comprehensive warranty and manufacturer support
- Full compliance with current codes and standards
- Opportunity to right-size equipment for actual loads
Replacement limitations:
- Highest upfront capital investment
- Longest project timeline (52-60 weeks typical)
- Most extensive facility disruption
- Requires comprehensive engineering and design
- Highest environmental impact from disposal and manufacturing
Real-World Cost Scenarios
Scenario 1: Medium-Voltage Industrial Facility (15 kV, 1600A)
Equipment: 25-year-old air circuit breaker switchgear, 12 cubicles
Option A – Retrofit:
- Equipment cost: $420,000
- Installation labor: $85,000
- Engineering and testing: $35,000
- Downtime cost (3 days): $150,000
- Total: $690,000
- Life extension: 20-25 years
Option B – Refurbish:
- Refurbishment services: $180,000
- Component replacement: $95,000
- Testing and commissioning: $25,000
- Downtime cost (1 week): $350,000
- Total: $650,000
- Life extension: 7-10 years
Option C – Complete Replacement:
- New switchgear equipment: $1,200,000
- Installation and modifications: $450,000
- Engineering and design: $120,000
- Downtime cost (6 weeks): $2,100,000
- Total: $3,870,000
- Service life: 30-35 years
Analysis: Retrofit provides the best cost-benefit ratio, delivering 80% of replacement service life at 18% of total cost. Refurbishment appears attractive initially but offers poor value when downtime costs are included.
Scenario 2: Commercial Building Low-Voltage Distribution (480V, 2000A)
Equipment: 18-year-old molded case circuit breaker panelboard, 8 sections
Option A – Retrofit:
- Direct replacement breakers: $85,000
- Installation and testing: $28,000
- Minimal downtime (1 day): $15,000
- Total: $128,000
- Life extension: 15-20 years
Option B – Refurbish:
- Breaker reconditioning: $35,000
- Component replacement: $22,000
- Testing: $8,000
- Downtime (3 days): $45,000
- Total: $110,000
- Life extension: 5-8 years
Option C – Complete Replacement:
- New panelboard system: $180,000
- Installation and modifications: $95,000
- Engineering: $25,000
- Downtime (3 weeks): $315,000
- Total: $615,000
- Service life: 25-30 years
Analysis: Retrofit offers optimal balance of cost and performance. Refurbishment provides short-term savings but poor long-term value with only 5-8 years extension. Replacement justified only if facility expansion planned.
Critical Evaluation Factors
Equipment Age and Condition Assessment
Conduct comprehensive evaluation including:
Visual Inspection:
- Evidence of overheating (discoloration, melted components)
- Corrosion on contacts, terminals, and enclosures
- Physical damage to insulation or mechanical components
- Oil leaks (for oil-filled equipment)
- Loose connections or worn hardware
Diagnostic Testing:
- Insulation resistance testing (megohmmeter)
- Contact resistance measurement (micro-ohmmeter)
- Partial discharge detection
- Timing and travel analysis for circuit breakers
- Thermographic imaging under load conditions
Performance History:
- Frequency of nuisance trips or failures
- Maintenance cost trends over past 5 years
- Spare parts availability and lead times
- Comparison to manufacturer’s expected service life
Spare Parts and Obsolescence Risk
Critical assessment questions:
- Are original manufacturer parts still available?
- What is the lead time for critical components?
- Are aftermarket or refurbished parts acceptable?
- Has the manufacturer discontinued the product line?
- Are there compatible retrofit solutions available?
Equipment with obsolete components faces escalating risks: extended downtime during failures, increasing maintenance costs, reduced reliability, and potential safety hazards. When critical components become unavailable, retrofit or replacement becomes necessary regardless of equipment age.
Safety and Compliance Requirements
Modern electrical codes and standards have evolved significantly, introducing enhanced safety requirements that older equipment may not meet:
Arc Flash Protection:
- Current incident energy levels and arc flash boundaries
- Availability of arc-resistant designs or retrofits
- Compliance with NFPA 70E and IEEE 1584 standards
- Personal protective equipment (PPE) requirements for maintenance
Regulatory Compliance:
- UL 891 and ANSI standards for switchgear
- OSHA workplace safety requirements
- Insurance carrier specifications
- Local electrical code updates
Safety Feature Upgrades:
- Ground fault protection systems
- Shunt trip capabilities for emergency shutdown
- Improved interlocking mechanisms
- Remote racking and operation capabilities
Non-compliant equipment exposes facilities to increased liability, denied insurance claims, regulatory penalties, and most critically, personnel safety risks.
Facility Growth and Future Needs
Strategic considerations:
- Planned facility expansions requiring increased capacity
- New equipment or processes with higher electrical demands
- Integration with renewable energy sources (solar, wind)
- Digital transformation and monitoring requirements
- Energy efficiency and sustainability goals
Facilities planning significant expansion within 5-10 years should strongly consider replacement over retrofit, as capacity limitations may necessitate premature re-investment. Conversely, facilities with stable or declining electrical demands benefit most from retrofit or refurbishment approaches.
Implementation Best Practices
Retrofit Project Execution
Phase 1: Assessment and Planning (4-6 weeks)
- Comprehensive equipment evaluation and testing
- Identification of compatible retrofit solutions
- Engineering design and one-line diagram updates
- Procurement of replacement circuit breakers and components
- Coordination with NRTL for certification requirements
Phase 2: Preparation (2-4 weeks)
- Temporary power arrangements if required
- Pre-staging of equipment and tools
- Safety planning and arc flash analysis
- Personnel training on new equipment
- Communication with affected operations
Phase 3: Installation (1-3 days per cubicle)
- De-energization and lockout/tagout procedures
- Removal of existing circuit breakers
- Installation of retrofit or retrofill solutions
- Connection verification and torque checks
- Secondary wiring modifications as needed
Phase 4: Testing and Commissioning (1-2 weeks)
- Insulation resistance and high-potential testing
- Contact resistance and timing tests
- Protective relay calibration and settings
- Integrated system testing
- Documentation and training
Refurbishment Project Execution
Assessment Phase:
- Detailed component-by-component inspection
- Diagnostic testing to establish baseline conditions
- Identification of components requiring replacement
- Development of refurbishment scope and specifications
Refurbishment Phase:
- Disassembly and cleaning of circuit breakers
- Replacement of worn contacts, springs, and bearings
- Insulation system restoration or replacement
- Mechanical adjustment and lubrication
- Reassembly with new hardware and fasteners
Testing Phase:
- Factory-level testing to ANSI/IEC standards
- Verification of mechanical and electrical performance
- Protective device calibration
- Final inspection and quality assurance
Replacement Project Execution
Design Phase (8-12 weeks):
- Load analysis and equipment sizing
- One-line and three-line diagram development
- Arc flash study and coordination analysis
- Specification development and bid process
- Long-lead equipment procurement
Preparation Phase (4-8 weeks):
- Temporary power system design and installation
- Demolition planning and waste disposal arrangements
- Site preparation including structural modifications
- Coordination with utility for service interruptions
Installation Phase (6-12 weeks):
- Removal and disposal of existing equipment
- Installation of new switchgear and associated equipment
- Primary and secondary wiring
- Integration with existing systems
- Extensive testing and commissioning
Maximizing Return on Investment
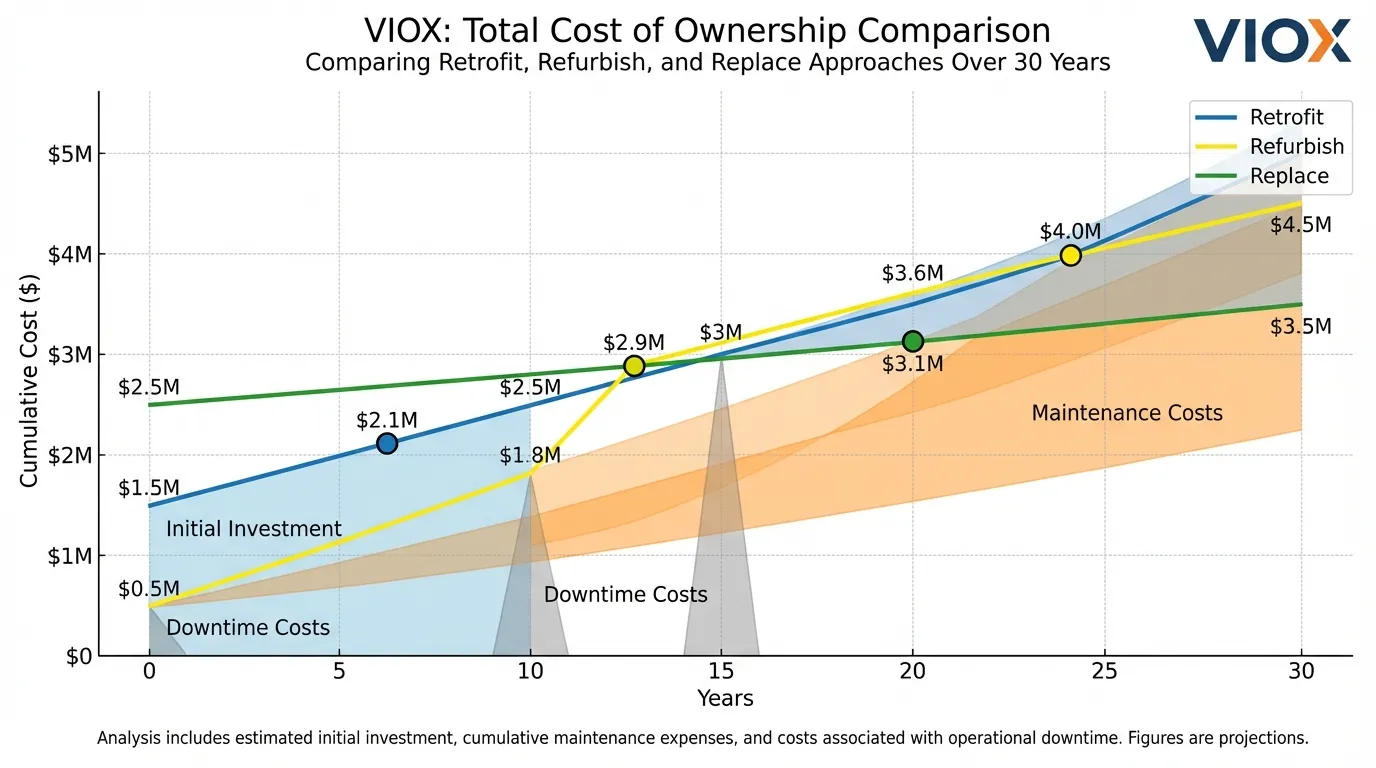
Lifecycle Cost Analysis
Evaluate total cost of ownership over expected service life:
Retrofit ROI Calculation:
- Initial investment: $690,000
- Annual maintenance savings: $35,000
- Energy savings: $18,000/year
- Service life: 20 years
- Total savings: $1,060,000
- Net ROI: 54% over 20 years
Replacement ROI Calculation:
- Initial investment: $3,870,000
- Annual maintenance savings: $55,000
- Energy savings: $42,000/year
- Service life: 30 years
- Total savings: $2,910,000
- Net ROI: -25% over 30 years (negative due to high downtime costs)
This analysis demonstrates that while replacement offers superior long-term performance, the combination of high upfront costs and extensive downtime often makes retrofit the financially optimal choice for facilities with critical operations.
Phased Implementation Strategy
For large facilities with multiple switchgear lineups, phased implementation spreads costs over multiple budget cycles while minimizing operational risk:
Year 1: Retrofit most critical or deteriorated equipment
Year 2: Refurbish secondary systems in good condition
Year 3-5: Complete remaining retrofits or plan replacements for end-of-life equipment
This approach maintains continuous improvement while avoiding the financial and operational shock of simultaneous replacement.
Predictive Maintenance Integration
Modern retrofit solutions enable predictive maintenance capabilities that reduce long-term costs:
- Smart circuit breakers with embedded sensors
- Continuous monitoring of temperature, vibration, and electrical parameters
- Cloud-based analytics for trend analysis and failure prediction
- Automated alerts for maintenance requirements
- Integration with computerized maintenance management systems (CMMS)
These capabilities shift maintenance from reactive (responding to failures) to predictive (preventing failures), reducing downtime by 30-50% and maintenance costs by 25-40%.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How long does switchgear typically last before requiring retrofit or replacement?
A: Medium-voltage switchgear typically has a design life of 25-40 years, while low-voltage equipment ranges from 20-30 years. However, actual service life depends heavily on operating environment, maintenance quality, and load conditions. Equipment operating in harsh environments (high temperature, humidity, or contamination) may require intervention at 15-20 years, while well-maintained systems in controlled environments can exceed 40 years. The key decision point is when maintenance costs and failure risks exceed the cost of retrofit or replacement.
Q: Can I retrofit switchgear from any manufacturer, or am I limited to the original brand?
A: Modern retrofit solutions are available for most major switchgear manufacturers including ABB, Siemens, Schneider Electric, Eaton, GE, and many legacy brands. Specialized retrofit providers offer cross-manufacturer solutions that allow installation of current-generation circuit breakers into older switchgear from different manufacturers. However, each retrofit must be engineered specifically for the existing equipment and certified by a Nationally Recognized Testing Laboratory (NRTL) such as UL or Intertek to maintain safety compliance and warranty coverage.
Q: What are the warning signs that my switchgear needs immediate attention?
A: Critical warning signs include frequent nuisance tripping, visible overheating or discoloration, unusual sounds (buzzing, arcing), burning odors, declining insulation resistance test results, increasing maintenance frequency, difficulty sourcing replacement parts, and equipment age exceeding 25-30 years. Any of these symptoms warrant immediate professional evaluation. Additionally, if your facility has experienced changes in electrical load, power quality issues, or near-miss safety incidents, comprehensive switchgear assessment should be prioritized.
Q: How do I ensure my retrofit maintains UL certification and insurance compliance?
A: Proper retrofit certification requires working with manufacturers or service providers who hold NRTL certification and follow IEEE C37.59-2018 standards for retrofit applications. The retrofit must be designed, tested, and documented by qualified engineers, with all modifications performed under NRTL supervision. Upon completion, updated labeling and documentation must be provided showing continued compliance with applicable UL and ANSI standards. Notify your insurance carrier before beginning retrofit work to ensure coverage continuity and obtain any required pre-approvals.
Q: What is the typical payback period for a switchgear retrofit project?
A: Payback periods typically range from 3-7 years depending on equipment condition, energy savings, and avoided downtime costs. Facilities with high energy costs or critical operations requiring maximum uptime often see payback in 3-4 years through combined energy savings (20-30% reduction), maintenance cost reduction (40-50% decrease), and avoided downtime from equipment failures. The payback calculation should include both direct savings (energy, maintenance) and avoided costs (downtime, emergency repairs, safety incidents). For facilities facing imminent equipment failure, the payback is often immediate as retrofit prevents catastrophic failure and extended outages.
VIOX Electric: Your Switchgear Modernization Partner
At VIOX Electric, we understand that switchgear decisions involve complex technical, financial, and operational considerations. Our comprehensive approach helps facility managers navigate the retrofit, refurbish, or replace decision with confidence.
Our Switchgear Solutions:
- Custom-engineered retrofit solutions for all major manufacturers
- Direct replacement circuit breakers with minimal downtime
- Comprehensive refurbishment services with factory-level testing
- Complete switchgear systems for new installations and replacements
- Arc flash mitigation and safety upgrades
- Digital monitoring and predictive maintenance integration
Why Choose VIOX Electric:
- 20+ years of switchgear engineering and manufacturing expertise
- NRTL-certified retrofit solutions maintaining UL compliance
- Comprehensive lifecycle support from assessment to commissioning
- Competitive pricing with transparent cost breakdowns
- Rapid response for critical applications
- Global supply chain ensuring component availability
Whether you’re evaluating a single circuit breaker replacement or planning facility-wide switchgear modernization, VIOX Electric provides the technical expertise, quality products, and responsive service to ensure project success.
Related Resources:
- Switchgear Current Ratings: INA, INC, and RDF Guide – Understanding switchgear ratings for proper selection
- Low Voltage Switchgear Types: GGD, GCK, GCS, MNS, XL21 Guide – Comprehensive guide to LV switchgear configurations
- Circuit Breaker Ratings: ICU, ICS, ICW, ICM – Essential ratings for retrofit compatibility
- How to Build an Electrical Maintenance Program – Preventive maintenance strategies to extend equipment life
- Switchboard vs. Switchgear: Understanding the Differences – Clarifying terminology for better decision-making
Contact our technical team today for a complimentary switchgear assessment and customized modernization recommendations tailored to your facility’s specific requirements.


