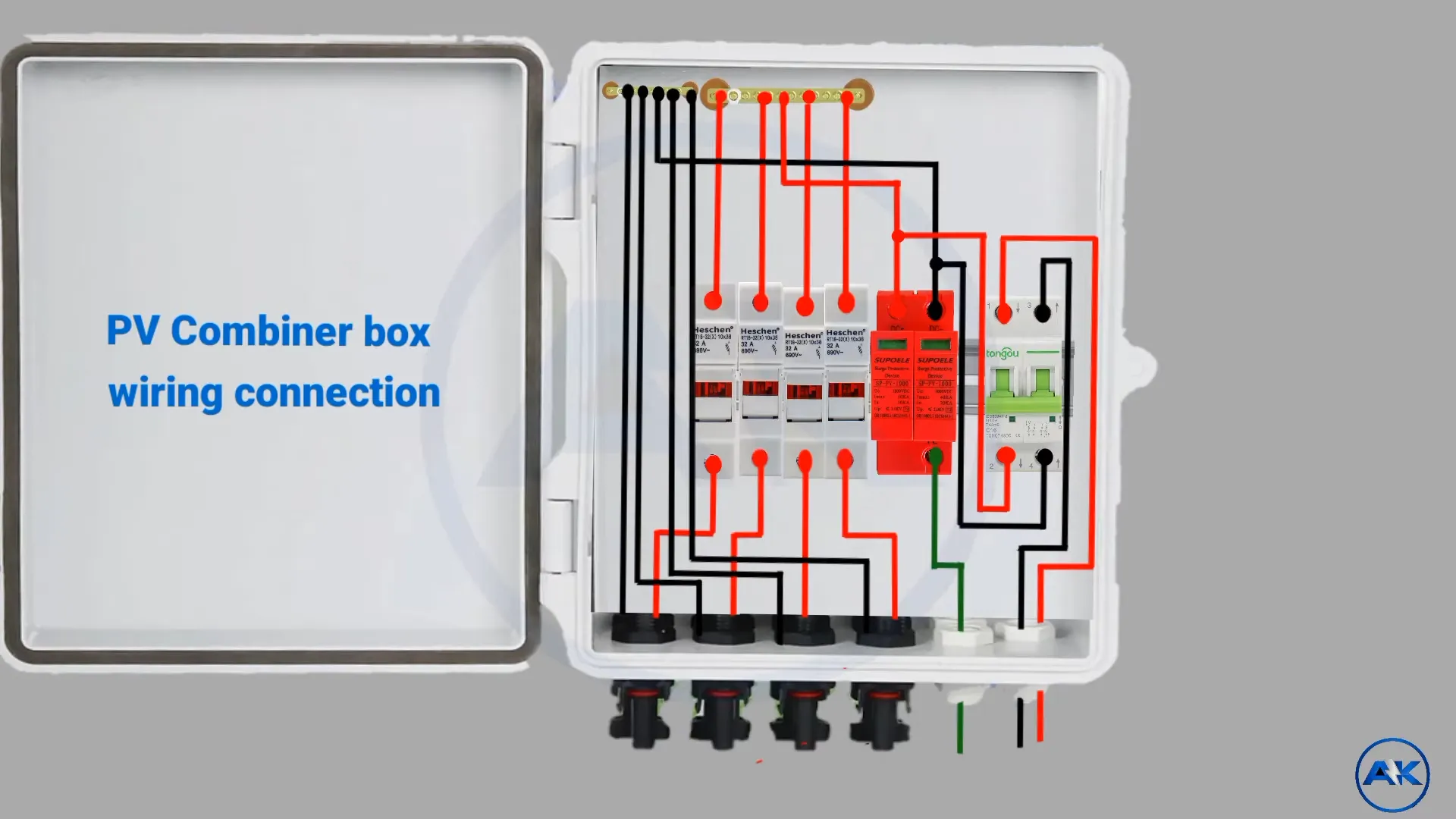
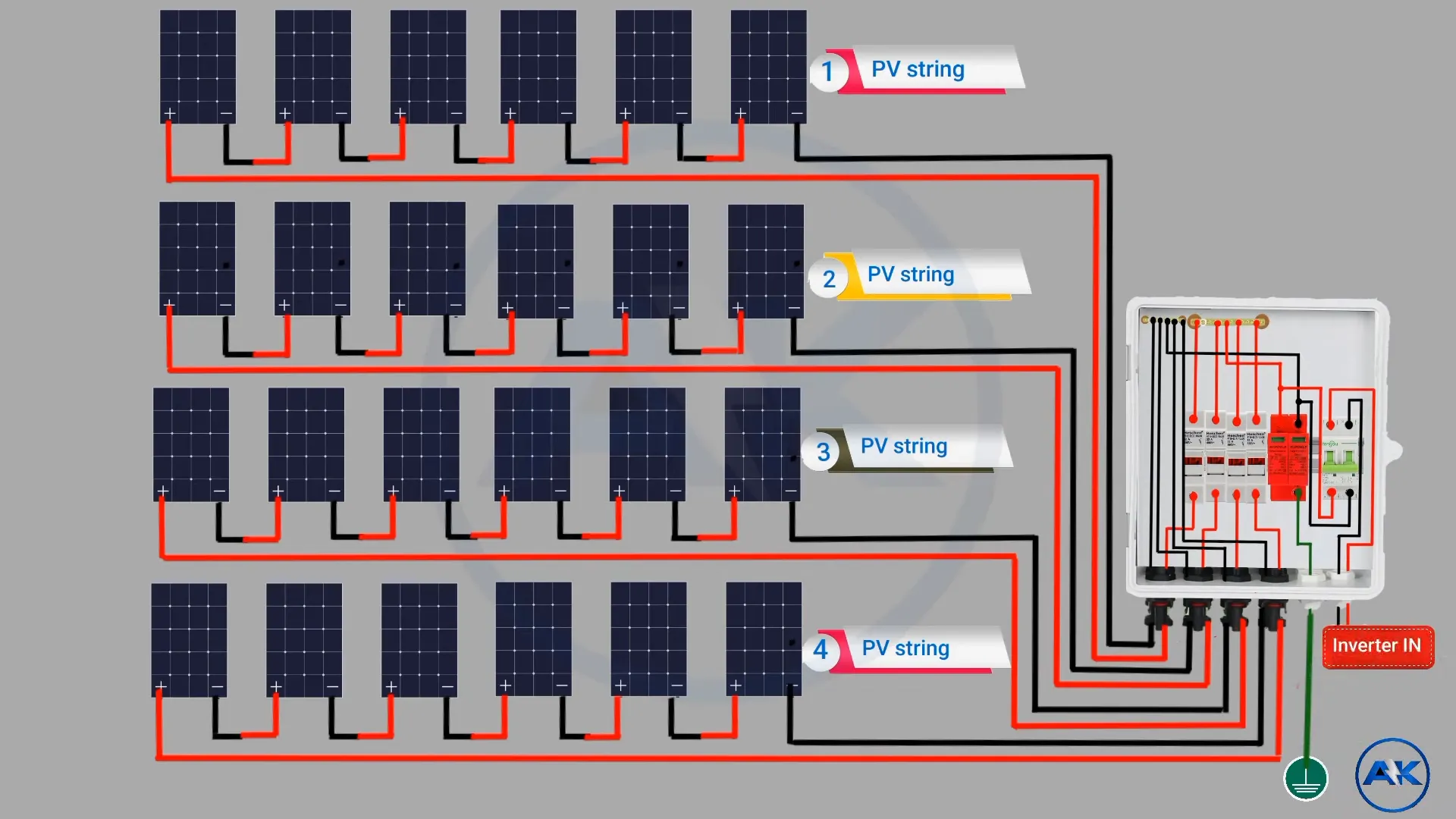
A solar combiner box is a crucial component in photovoltaic systems, consolidating multiple solar panel strings into a single output for improved efficiency and safety. Proper installation and wiring of these boxes are essential for optimal performance and longevity of solar power systems.
Solar Combiner Box Components
A typical solar combiner box consists of several key components that work together to ensure safe and efficient operation. These include:
- An enclosure to protect internal parts from environmental factors.
- Fuse holders or circuit breakers for overcurrent protection.
- Busbars or terminal blocks for connecting positive and negative cables.
- A ground busbar for proper system grounding.
- Cable entry ports to maintain waterproof sealing.
- Surge protective devices (SPDs) to safeguard against voltage spikes.
The enclosure houses these components, providing a central point for consolidating multiple strings of photovoltaic panels into a single output, which enhances overall system efficiency and safety.
Wiring Diagram and Procedures
When installing a solar combiner box, following a proper wiring diagram and procedures is crucial for system efficiency and safety. A typical wiring diagram for a PV DC solar combiner box includes multiple string inputs and fewer output connections to the inverter.
For a 4-string input, 2-string output configuration:
- Connect the positive (+) wires from each of the four solar panel strings to individual fuses or circuit breakers within the combiner box.
- Join the negative (-) wires from all four strings to a common negative busbar.
- From the fuses/breakers, route two positive output wires to the inverter’s MPPT1 (Maximum Power Point Tracking) input, effectively paralleling two strings at the inverter.
- Connect the third and fourth strings to MPPT2 on the inverter.
- Run a single negative output wire from the negative busbar to the inverter’s negative terminal.
When implementing this wiring scheme:
- Ensure all cables entering the combiner box are properly sealed to maintain its environmental rating.
- Use cable glands or conduit fittings appropriate for the wire size and box specifications.
- Label all wires clearly within the box for easy identification during maintenance or troubleshooting.
- Verify that the total current from paralleled strings does not exceed the inverter’s input capacity.
- It’s essential to keep the connecting wires as short and straight as possible to minimize power losses. The cross-sectional area of these wires should be no less than 16 square millimeters to handle the combined current effectively.
Before closing the combiner box, double-check all connections against the wiring diagram and internal markings to ensure accuracy. This final verification step is crucial for preventing potential issues and ensuring the system operates as intended.
Remember that while this wiring diagram serves as a general guide, always consult the specific manufacturer’s instructions and local electrical codes for your particular solar combiner box model and installation requirements.
Step-by-Step Installation Guide
To ensure a safe and efficient installation of a solar combiner box, follow these step-by-step guidelines:
- Mounting the combiner box:
- Choose a location that is easily accessible and protected from direct sunlight and rain.
- Securely attach the box to a sturdy surface using appropriate mounting hardware.
- Preparing the wiring:
- Turn off all circuit breakers and disconnect switches before beginning work.
- Strip approximately 12mm of insulation from the ends of all wires to be connected.
- Use wire with a cross-sectional area of at least 16 square millimeters for optimal performance.
- Connecting input strings:
- Route the positive and negative wires from each solar panel string through the designated cable entry ports.
- Connect positive wires to the appropriate fuse holders or circuit breakers.
- Attach negative wires to the negative busbar or terminal block.
- Installing protective devices:
- If using fuses, ensure they are of the correct rating for your system.
- For configurations with circuit breakers, verify they are properly sized and securely installed.
- Install surge protective devices (SPDs) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Wiring the output:
- Connect the main output cables to the positive and negative busbars.
- Ensure the output cables are properly sized to handle the combined current from all input strings.
- Grounding:
- Connect all equipment grounding conductors to the ground busbar within the combiner box.
- Verify that the main grounding electrode conductor is properly attached.
- Labeling and documentation:
- Clearly label all wire connections and components within the box.
- Create a detailed wiring diagram for future reference and maintenance.
- Final checks and testing:
- Verify all connections against the wiring diagram and internal markings.
- Conduct insulation resistance tests if required by local codes or system specifications.
- Close the combiner box securely, ensuring all seals are intact to maintain its environmental rating.
By following these steps and adhering to local electrical codes and manufacturer guidelines, you can ensure a proper and safe installation of your solar combiner box.
Common Wiring Configurations
Solar combiner boxes can accommodate various wiring configurations to suit different system requirements and panel arrangements. Here are some common wiring configurations used in solar installations:
- Series-Parallel Configuration:
- Multiple strings of panels are wired in series to increase voltage.
- These series strings are then connected in parallel within the combiner box.
- This configuration balances voltage and current requirements for the inverter.
- Typically used in larger systems to optimize power output.
- Single MPPT Configuration:
- All strings are combined into a single output.
- Suitable for systems with uniform panel orientation and minimal shading.
- Simplifies wiring but may reduce overall system efficiency in some cases.
- Multi-MPPT Configuration:
- Strings are grouped and connected to separate MPPT inputs on the inverter.
- Allows for optimization of different panel orientations or shading conditions.
- Fused String Configuration:
- Each string has its own fuse for overcurrent protection.
- Allows for easy isolation and maintenance of individual strings.
- Enhances safety by preventing reverse current flow.
- Ungrounded System Configuration:
- Both positive and negative conductors are isolated from ground.
- Requires special attention to insulation and monitoring.
- Often used in certain types of thin-film solar installations.
- Bipolar Configuration:
- Positive and negative strings are wired separately.
- Creates a center-tapped system with positive and negative voltages.
- Can reduce overall system voltage while maintaining power output.
When implementing these configurations, it’s crucial to consider factors such as:
- Maximum system voltage and current ratings.
- Inverter specifications and MPPT capabilities.
- Local electrical codes and regulations.
- Environmental conditions and panel characteristics.
Proper selection and implementation of wiring configurations can significantly impact system performance, safety, and maintainability. Always consult with a qualified solar professional to determine the best configuration for your specific installation.
If you need further changes or additional details, feel free to ask!