A Power DB Box (Distribution box ) is a crucial electrical device that safely and efficiently distributes power from a single source to multiple circuits, incorporating essential components like circuit breakers, surge protectors, and residual current devices for enhanced safety and power management.
Essential DB Box Components
The heart of a power distribution box consists of several critical components working in tandem to ensure safe and efficient power distribution. These include:
- Switchgear and measuring instruments for controlling and monitoring electrical flow
- Circuit breakers and fuses to protect against overloads and short circuits
- Surge protection devices to safeguard against voltage spikes
- Bus bars and wiring for efficient power distribution
- Residual current devices (RCDs) to prevent electric shock hazards
These elements are housed within an enclosure that can accommodate various cable sizes and types, allowing for quick and flexible power distribution while maintaining safety standards.
DB Box Functions Explained
The primary functions of a distribution box revolve around safety protection and power management. As a critical safety feature, DB boxes rapidly cut off power during short circuits or overloads, preventing electrical accidents and protecting both equipment and personnel. They serve as a central hub for efficiently distributing electricity throughout a building or structure, allowing for flexible configuration and easy maintenance of multiple circuits from a single power source. This centralized control simplifies the process of power distribution while enhancing overall electrical system safety and efficiency.
Distribution Box Varieties
Distribution boxes come in various types, each designed for specific applications and environments. Here are some key types and their functions:
- Polycarbonate Distribution Boxes: Made from durable engineering thermoplastics, these boxes are lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and suitable for both indoor and outdoor use. They’re commonly used in residential and light commercial applications.
- Deep Drawn Boxes: Constructed from epoxy-coated steel, these metallic boxes offer robust protection and are ideal for industrial settings where durability is crucial.
- Sheet Molding Compound (SMC) Distribution Boxes: Made from thermoset plastics, SMC boxes provide excellent electrical insulation and are resistant to extreme temperatures, making them suitable for harsh environments.
- Explosion-Proof Boxes: Specifically designed for hazardous environments like chemical plants and refineries, these boxes can contain and mitigate explosions, ensuring safety in volatile industrial settings.
- Marine Distribution Boxes: Engineered to withstand corrosive marine environments, these boxes are made from materials resistant to saltwater exposure and are used on ships, offshore platforms, and other marine vessels.
Each type of distribution box serves specific functions, from dividing electrical power and protecting circuits to ensuring safety in specialized environments. The choice of box depends on the application, environment, and specific electrical requirements of the installation.
Key Benefits of DB Boxes
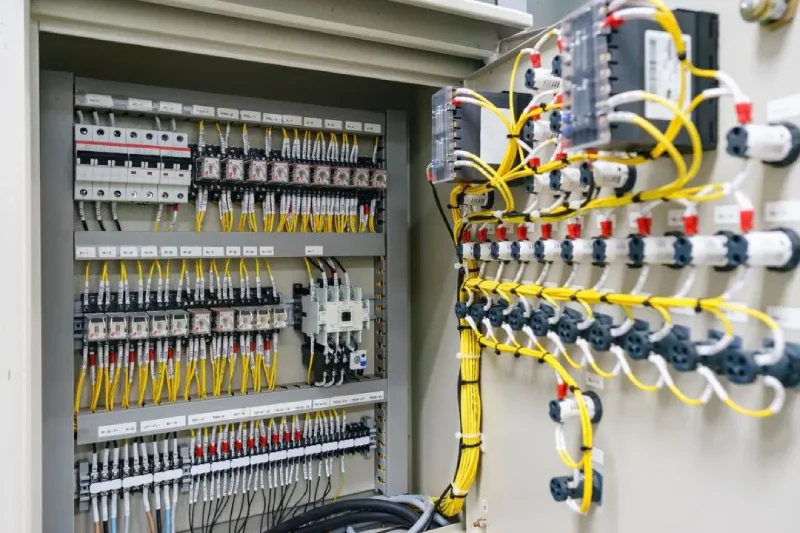
DB boxes offer several key advantages that make them indispensable in modern electrical systems. They provide centralized control of electrical distribution, simplifying management and troubleshooting processes. The integrated protection devices enhance overall safety, while the system’s design allows for efficient power management and flexible circuit expansion capabilities. These features not only streamline electrical operations but also contribute to cost-effectiveness by reducing the need for multiple power sources and simplifying maintenance procedures.
Boosting Electrical Dependability
Power distribution boxes significantly enhance electrical reliability through several key mechanisms:
- Load balancing: DB boxes allow for balanced power allocation across various circuits, preventing overload on individual circuits and ensuring equipment operates within safe limits.
- Consistent power supply: By efficiently distributing electricity, DB boxes minimize disruptions and downtime, which is crucial in commercial and industrial settings where even brief power interruptions can result in substantial financial losses.
- Circuit protection: Built-in safety features like circuit breakers and ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs) protect against electrical hazards such as overloads and short circuits, safeguarding both equipment and personnel.
- Streamlined power management: DB boxes provide a clear overview of the entire electrical system, simplifying circuit management and making it easier to isolate and control individual circuits during maintenance or emergencies.
These features collectively contribute to a more stable and dependable electrical system, reducing the risk of equipment damage and enhancing overall operational efficiency.
Installation Best Practices for DB Boxes
When installing a power distribution box, adherence to best practices ensures safety and optimal performance. The recommended installation height for a DB box is typically 1.5 meters (about 5 feet) from the ground, allowing easy access for operation and maintenance. It’s crucial to mount the box securely on a flat, firm surface, away from humid or corrosive environments.
Key installation considerations include:
- Proper leveling: Ensure the box is installed plumb, with vertical deviation not exceeding 3 millimeters.
- Accessibility: Maintain a clear space of 0.8-1.2 meters in front of the box for easy operation.
- Circuit protection: Install a leakage circuit breaker with current not exceeding 30mA, and separate circuits for lighting, air conditioning, and sockets.
- Labeling: Clearly mark each circuit’s name and number for easy identification.
- Wiring: Arrange electrical components neatly, ensuring firm connections and proper insulation.
By following these guidelines, installers can ensure the DB box functions safely and efficiently, providing reliable power distribution throughout the premises.
Explore More: https://viox.com/distribution-box-and-selection-guide/
Common Troubleshooting Tips for DB Boxes
When troubleshooting distribution box (DB box) issues, start by identifying the specific problem, such as frequent circuit breaker tripping or power fluctuations. For tripping breakers, check for overloaded circuits by reducing the number of devices connected or redistributing the load. Inspect for loose connections, which can cause arcing and overheating, by tightening all connections within the DB box. This should be done by a qualified electrician to ensure safety.
If you notice signs of overheating, such as a burning smell or discolored components, immediately shut off power and call a professional. For persistent issues, conduct a thorough visual inspection for signs of damage or wear, and use testing equipment like multimeters to diagnose electrical problems accurately. Always prioritize safety by turning off the main power supply before any inspection or maintenance work, and consider scheduling regular professional inspections to prevent potential hazards and ensure optimal performance of your DB box.


