アーマードケーブルグランドは、危険な環境で使用されるワイヤブレードケーブル用に設計された特殊な終端装置であり、様々な産業用途において確実な接続と安全性を維持しながら、環境シール、ストレインリリーフ、二次アース接続などの重要な機能を提供します。
定義と目的
アーマードケーブル用に特別に設計されたケーブルグランドは、危険区域での重要な終端デバイスとして機能し、ATEX認証により安全性が強化されています。これらの特殊なコンポーネントは、防爆 Ex d および安全性向上 Ex e を維持し、カメラやジャンクションボックスなどの機器とアーマードケーブルの接続を確実にします。主な機能は以下の通りです:
- ケーブルのアウターシースとインナーシースにIP66の環境シールを施す
- 湿気やほこりの侵入を防ぐ
- アーマー・ワイヤー・ターミネーションによる機械的導通
- 二次アース接続として機能
- アーマードケーブルにストレインリリーフを提供
これらの役割を果たすことで、アーマードケーブルグランドは、厳しい産業環境における電気設備の完全性と安全性を維持する上で重要な役割を果たします。
構造と素材
通常、ステンレス鋼や真鍮のような耐久性のある材料で作られたアーマードケーブルグランドは、本質的な保護を提供しながら、過酷な環境に耐えるように設計されています。これらの堅牢なコンポーネントは、特にアーマードワイヤとアウターシースの追加バルクを考慮して、より大きな直径を持つケーブルに対応するように設計されています。これらのグランドの構造は、4芯16mm、3芯10mm、3芯6mmのアーマードケーブルなど、異なる芯数とサイズを含む様々なケーブル構成に効果的に対応できることを保証し、幅広い産業用途に対応します。
主要コンポーネントの説明
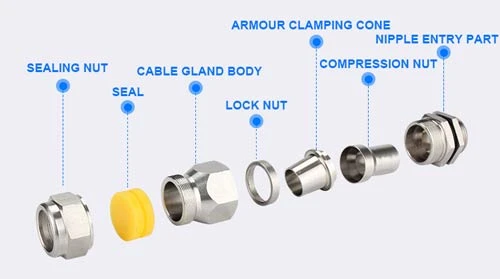
アーマードケーブルグランドは、安全で信頼性の高いケーブル終端を提供するために、いくつかの重要なコンポーネントで構成されています:
- シーリングナット:水密性を確保
- ケーブルグランド本体:すべてのコンポーネントを保持するメインハウジング
- ロックナット:グランドを機器に固定する
- アーマークランプコーン:ケーブルのアーマーをつかみ、終端する。
- 圧縮ナット:圧力をかけてシールを作る
- ニップルエントリー部:ケーブルを機器に導く
これらの部品は、様々なケーブルサイズやタイプに対応できるよう設計されており、様々な産業用途に柔軟に対応します。各部品の精密な設計は、危険区域での防爆および環境密閉を維持するグランドの能力に貢献しています。
アーマードケーブルグランドサイズ表
アーマードケーブルグランドのサイズ決定は、適切なフィットと機能性を確保するために非常に重要です。サイズの選択は、ケーブルの直径、コア数、アーマーの厚さなどの要因に依存します。アーマードケーブルグランドの典型的なサイズチャートは以下の通りです:
- 1.5mm²~400mm²のケーブルサイズ
- 1~48コアのコア構成
- グランドサイズは通常20S、20、25、32、40、50、63、75と表記される
例えば、4芯4.0mm²のアーマード・ケーブルには通常20mmのグランドが必要ですが、4芯240mm²のケーブルには63mmのグランドが必要です。. 屋外で使用する場合、屋内用とは異なるグランドサイズが必要になる場合があることに注意することが重要で、接頭辞 "CW "は屋外用グランドに、"BW "は屋内用に使用されることが多い。.
グランドのサイズを選択する際には、アーマーを含むケーブル全体の直径とグランド内径の両方を考慮することが重要です。. ケーブルとグランドの製造業者によって若干の違いがあるため、正確なグランドの選定を行うためには、必ず製造業者別の表を参照し、実際のケーブルの寸法を測定すること。
様々な環境でのアプリケーション
多用途で堅牢なこの特殊グランドは、様々な産業分野で幅広く使用されています。一般的に、電力ネットワーク、ケーブルダクト、電気通信の伝送ボックスに使用されます。その耐久性により、地下システムを含む屋内外の設置に適しています。危険区域では、これらのグランドは、装甲ケーブルがカメラやジャンクションボックスなどの機器と接続する際、安全な接続を維持します。さまざまなケーブル構成やサイズに対応する能力と保護機能により、安全性と信頼性が最も重要視される環境で不可欠な製品となっています。
装甲ケーブルグランドの設置ガイドライン
装甲ケーブルグランドを適切に設置することは、安全性と最適な性能を確保するために極めて重要です。以下の重要なガイドラインに従ってください:
- ご使用のケーブルと環境に適したグランドサイズとタイプをお選びください。
- ケーブルのアウター・シースとアーマーを剥き、内部導体を露出させる。
- 正しい順序でグランドにケーブルを通す。
- アーマーを腺のコーンまたはスピゴットの周りに均等に広げる。
- エンクロージャーの入口から始め、次に中央のナット、最後に背面のナットと、順次部品を締め付ける。
- 過度の締め付けを避けるため、メーカー指定のトルク設定を使用すること
- 適切な密閉性を確認し、電気安全を確保するために適切なテストを実施する。
設置の完全性を長期間維持するためには、定期的な点検とメンテナンスが不可欠です。グランドの種類やブランドによって詳細が異なる場合があるため、必ずメーカー指定の説明書を参照してください。