サージ保護装置(SPD)について
定義とコア機能

A サージ保護装置(SPD) サージ電流を迂回または制限することで過渡電圧を制限する保護装置であり、規定に従ってこれらの機能を繰り返すことができます。SPDは以前は過渡電圧サージサプレッサ(TVSS)または二次サージアレスタ(SSA)と呼ばれていましたが、2009年にANSI/UL 1449第3版が採択されたことで、用語がSPDに標準化されました。
SPDの基本原理は、保護対象負荷の電源回路に並列接続することです。並列接続されたSPDは高いインピーダンスを持ちます。システムに過渡過電圧が発生すると、SPDのインピーダンスが低下し、サージ電流がSPDを通過して高感度機器をバイパスします。
SPD分類システム
米国電気工事規程 (NEC) および ANSI/UL 1449 によれば、SPD は設置場所と用途に基づいて主に 3 つのタイプに分類されます。
タイプ1 SPD: サービス入口保護
タイプ1:恒久的に接続され、サービス変圧器の二次側とサービス遮断過電流装置(サービス機器)の線路側との間に設置することを目的としています。主な目的は、雷や商用コンデンサバンクの開閉によって引き起こされる外部サージから電気システムの絶縁レベルを保護することです。
主な仕様
– 電流波形:10/350 µsインパルス電流
– 電流処理能力: 50,000~200,000アンペア
– 設置:サービスエントランス設備
– 直撃雷に対する一次保護
タイプ2 SPD: 配電盤保護
タイプ2:恒久的に接続され、サービス遮断装置(サービス機器)の負荷側(ブランドパネルの設置場所を含む)に設置することを目的としています。主な目的は、敏感な電子機器およびマイクロプロセッサベースの負荷を、残留雷エネルギー、モーター発生サージ、その他の内部発生サージから保護することです。
主な仕様
– 電流波形:8/20 µs電流波形
– 電流処理能力: 20,000~100,000アンペア
– 設置:配電盤および負荷センター
– 建物の電気システムの主な保護
タイプ3のSPDポイント・オブ・ユース保護
タイプ 3: 電気サービス パネルから利用ポイントまでの最小導体長さが 10 メートル (30 フィート) のところに設置される利用ポイント SPD。
主な仕様
– 電流波形:1.2/50 μsの電圧と8/20 μsの電流の組み合わせ
– 電流処理能力: 5,000~20,000アンペア
– 設置場所: 保護された機器の近く
– 局所的な保護の最終層
その他の電気サージ保護方法
無停電電源装置(UPS)システム
UPSシステムは、単純なサージ保護にとどまらない包括的な電源保護を提供します。これらのデバイスは入力電圧を継続的に監視し、停電や深刻な障害発生時にはバッテリー電源に切り替えることで電力品質の問題に対応します。
UPS 保護特性:
– 応答時間: 電力伝達に2~10ミリ秒
– 保護範囲: 個人装備レベル
– 電流処理: ユニット容量に応じて変動
– 追加機能: バッテリーバックアップ、電力調整、電圧調整
– コストの範囲: $100~5,000以上(容量により異なる)
UPS のサージ保護に関する制限:
– SPDに比べて応答時間が遅い
– サージ電流処理能力が限られている
– バッテリーのメンテナンスと交換が必要
– 高エネルギー雷サージに耐えられるよう設計されていません
電源タップのサージプロテクターとベーシックな電源タップ
基本的な電源タップ
電源タップとは、複数の電気機器に1つのコンセントから電力を供給できるコンセントの集合体です。見た目はサージプロテクターに似ていますが、基本的な電源タップはサージ保護機能を備えていません。
特徴
– 機能: 電力分配のみ
– 保護: 過負荷専用のブレーカー
– 応答時間: サージ保護機能なし
– コスト: $10-30
– 用途: サージ保護が不要な非クリティカルデバイス
消費者向けサージプロテクター電源タップ
サージプロテクターと電源タップの主な違いは、サージプロテクターにはMOV(金属酸化物バリア)が内蔵されていることです。MOVは、接続された機器から有害な電気サージを遮断します。
特徴
– 電流処理能力: 通常1,000~4,000ジュール
– 応答時間: 25ナノ秒 (MOVベース)
– 保護範囲: ストリップに直接接続されたデバイスのみ
– クランプ電圧:330~600ボルト
– 寿命: サージが発生するたびに劣化します
金属酸化物バリスタ(MOV)
金属酸化物バリスタは、電圧依存抵抗器であり、ほとんどの民生用サージプロテクターの中核技術を成しています。MOVは、酸化亜鉛粒子のセラミックマトリックスで構成され、粒界がダイオード接合を形成します。
MOV操作:
– 通常の状態: 最小の電流で高い抵抗
– サージ条件: 雪崩破壊により低抵抗経路が形成される
– 応答時間: 25ナノ秒
– 電流処理: サイズに応じて1,000~20,000アンペア
MOV の制限:
– 繰り返しサージに晒されると劣化が進行する
– 複数のサージに対処した後、最終的には交換が必要になります
– 基本的な実装では保護状態が示されない
過渡電圧抑制(TVS)ダイオード
TVS ダイオードは、敏感な電子機器の超高速サージ保護用に設計された特殊なアバランシェ ダイオードです。
TVSダイオードの特性:
– 応答時間: 1ピコ秒(最速)
– 電流処理: 10,000~30,000アンペアのピークパルス
– 電圧精度: 非常に正確なクランプレベル
– 寿命: 老化の影響がなく、長期安定性に優れています
– の応用: 電子機器におけるPCBレベルの保護
MOV に対する利点:
– 経年劣化なし
– ESD保護のための非常に高速な応答
– 正確な電圧クランプ特性
– デバイスの寿命全体にわたって信頼性の高い動作
ガス放電管(GDT)
ガス放電管は、不活性ガス放電の原理を利用した電圧制御スイッチとして機能し、通信機器でよく使用されます。
GDT 特性:
– 応答時間: <1マイクロ秒
– 電流処理: 10,000~40,000アンペア
– 通常状態: 非常に高いインピーダンス、最小限の静電容量
– アクティブ状態: 低インピーダンス伝導経路
– アプリケーション: 通信、高電圧保護
回路遮断器と安全保護
従来のサーキットブレーカー
回路ブレーカーは過電流保護を提供しますが、サージ保護用に設計されていません。
回路ブレーカーの仕様:
– 機能: 過電流および短絡保護
– 応答時間: 16~100ミリ秒
– サージ保護: なし(電圧スパイクには遅すぎる)
– 電流処理: 連続運転時の定格アンペア数
– の応用: 一般的な電気回路保護
GFCIとAFCI保護
– GFCI: 漏電保護(5 mA感度、25~30 ms応答)
– AFCI: 火災予防のためのアーク故障保護
– 機能: 安全保護であり、サージ保護ではありません
– 要件: NECにより特定の場所で義務付けられている
雷保護システム
避雷器
避雷器は、送電システムと配電システムを直撃雷撃やスイッチング過渡現象から保護します。
避雷器の特性:
– 電流処理: 100,000アンペア以上
– 電圧レベル: 送電システム電圧(>1000V)
– 応答時間: マイクロ秒
– の応用: 公共送配電システム
– コスト: 伝送クラスデバイスの場合、$1,000~10,000以上
避雷針(エアターミナル)
– 機能: 優先的な落雷経路を提供する
– 保護: 建物の構造保護
– 統合: 接地システムと連動
– 電流処理: 最大雷電流(最大200,000アンペア)
電力品質および調整装置
電圧レギュレータと安定器
パワーコンディショナーは、過渡サージ保護ではなく、安定した電力品質に重点を置いています。
電圧調整特性:
– 機能: 一定の電圧レベルを維持 (±1-5%)
– 応答時間: 電圧補正(ミリ秒)
– 保護タイプ: 電圧低下および過電圧保護
– の応用: 電力品質が悪い地域
– コスト: $100~1,000以上(容量により異なります)
絶縁トランス
– 機能: 電気的絶縁とサージ低減
– 保護: コモンモードサージ減衰(-60dB以上)
– 電圧ハンドリング: 30kVインパルス入力、10kV出力(標準)
– の応用: 医療機器、精密機器
電力線フィルタとEMI保護
– 機能: 電磁干渉と電気ノイズをフィルタリング
– 操作: 伝導EMI/RFIの連続フィルタリング
– コンポーネント: インダクタ、コンデンサ、フェライトコア
– 範囲: サージ保護を補完するものであって、置き換えるものではない
SPDとその他の電気サージ保護方法の比較
| 方法 | 機能 | 応答 | 所在地 | 現在 | 電圧 | 寿命 | コスト | アプリケーション |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPDタイプ1 | 雷サージ | 25ナノ秒 | サービスエントリー | 50~200 kA | 700~1500V | 高い耐久性 | 高 | サービスパネル |
| SPDタイプ2 | 分布 | 25ナノ秒 | 分布 | 20~100 kA | 600~1200V | 高い耐久性 | 中 | 分岐回路 |
| SPDタイプ3 | 使用場所 | 25ナノ秒 | 機器の近く | 5~20kA | 330~600V | 中程度の耐久性 | 低 | 敏感な電気 |
| UPSシステム | 電源バックアップ | 2~10ミリ秒 | 装備レベル | 変数 | ±3-5% | バッテリー依存 | 高 | クリティカル装備 |
| サーキットブレーカー | 過電流 | 16~100ミリ秒 | 分布 | 変数 | なし | 非常に高い | 低 | 一般回路 |
| MOV | 電圧クランプ | 25ナノ秒 | デバイスレベル | 1~20kA | 変数 | 劣化する | 非常に低い | コンポーネント保護 |
| TVSダイオード | 高速過渡 | 1ps | PCBレベル | 10~30kA | 非常に正確 | 老化なし | 低 | エレクトロニクス |
| ガス放電 | 高電圧 | <1 µs | 装備レベル | 10~40kA | 高電圧 | 非常に高い | 中 | 通信 |
| 雷撃停止 | 雷保護 | マイクロ秒 | トランスミッション | 100kA以上 | kVレベル | 非常に高い | 高 | 電力システム |
| 電源状態 | 電力品質 | 連続 | 装備レベル | 負荷依存 | ±5-10% | 高 | 高 | 敏感な装備 |
| 隔離トランス | 電気絶縁 | 連続 | 装備レベル | 負荷依存 | 良好な隔離 | 非常に高い | 高 | 医療機器 |
包括的な比較:SPDとその他の保護方法
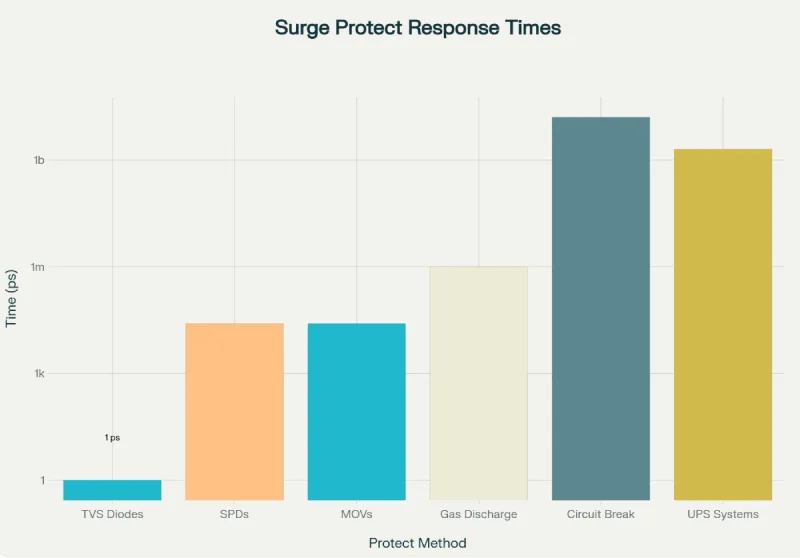
応答時間分析
超高速保護(ピコ秒):
– TVSダイオード: 1ピコ秒 – ESDおよび高速過渡現象に最適
高速保護(ナノ秒):
– SPD(全タイプ):25ナノ秒 – 電圧サージに最適
– MOV: 25ナノ秒 – 中程度のサージに適しています
中程度の速度(マイクロ秒):
– ガス放電管: <1マイクロ秒 – 高エネルギーイベントに最適
遅い応答(ミリ秒):
– UPSシステム: 2~10ミリ秒 – 電力転送には十分
– GFCI/AFCI: 25~30ミリ秒 – 安全性重視のアプリケーション
– 回路ブレーカー: 16~100ミリ秒 – 過電流保護のみ
電流処理能力の比較
最高エネルギー(100kA以上):
– 避雷器:伝送レベルの保護
– SPDタイプ1:50~200 kAサービス入口保護
高エネルギー(20~100 kA):
– SPDタイプ2:20~100 kA配電保護
– ガス放電管:10~40 kA通信保護
中程度のエネルギー(5~30 kA)
– SPDタイプ3:5~20 kA使用点保護
– TVSダイオード:10~30 kAの高精度電子機器保護
制限エネルギー(1~20 kA)
– 民生用サージプロテクター:1~4 kAデバイス保護
– MOV: 1~20 kAのコンポーネント保護
サージ保護なし:
– 基本電源タップ: 回路ブレーカーの定格のみ
– 回路ブレーカー:過電流保護、サージ処理なし
設置場所とシステム統合
階層型SPDインストール
SPD は体系的な設置アプローチに従って調整された保護を提供します。
1. タイプ1 SPD: サービス入口 – 第一防衛線
2. タイプ2 SPD: 配電盤 - メインビルディング保護
3. タイプ3 SPD: 使用時点 – 最終機器の保護
その他の方法のインストール
– UPSシステム: 機器レベル、負荷接続が必要
– 消費者向けサージプロテクター: デバイスレベル、ポータブル
– 回路保護: 配電盤、安全性重視
– コンポーネント保護: PCBレベルまたは機器内
– 電力品質機器: 機器レベル、特定のアプリケーション
標準および規制遵守
SPD標準フレームワーク
– ANSI/UL 1449: 北米の主要SPD規格
– IEC 61643シリーズ: 国際SPD規格
– NEC第285条: SPDの設置要件
– 必須要件NEC 2020+では、住居ユニットにSPDが義務付けられています
その他の方法基準
– UPSシステム: UL 1778、IEC 62040シリーズ
– サーキットブレーカー: UL 489、IEC 60947シリーズ
– 消費者向けサージプロテクター: UL 1449 (タイプ3分類)
– コンポーネント保護: さまざまなコンポーネント固有の標準
経済的および実用的考慮
費用便益分析
SPD投資のメリット:
– システム全体の保護とデバイスごとのコスト
– 最小限のメンテナンスで長い動作寿命
– 単一の設置で規制遵守
– 建物の配線と内蔵機器の保護
総所有コスト:
– タイプ2 SPD: $200-800プラス設置で家全体を保護
– 複数の消費者向けサージプロテクター: $20-100個(複数台必要)
– UPSシステム: $100-5,000+プラスバッテリー交換費用
– サージダメージ: 平均的な産業施設は年間1兆4千億3900万ドルの損失を被っている
メンテナンス要件
メンテナンスの手間がかからない:
– SPD:状態監視、定期検査
– TVSダイオード:メンテナンス不要
– サーキットブレーカー:定期的なテスト
メンテナンス費用が高い:
– UPSシステム:3~5年ごとのバッテリー交換
– MOV:劣化後の交換
– パワーコンディショナー:フィルターの交換、校正
アプリケーション固有の推奨事項
住宅用アプリケーション
主な保護: メインパネルのタイプ 2 SPD (NEC 2020 年以降必須)
二次保護: 敏感な電子機器用のタイプ3 SPD
バックアップ電源: 重要な機器(コンピューター、医療機器)用のUPS
商業用および工業用アプリケーション
主な保護: サービス入口のタイプ 1 またはタイプ 2 SPD
配布保護: サブパネルのタイプ2 SPD
機器の保護: 重要なシステム向けのタイプ3 SPDとUPS
特殊保護: 敏感なプロセス向けのパワーコンディショナー
電気通信とデータセンター
AC保護: 協調型SPD設置(タイプ1、2、3)
DC保護: 通信回線用特殊SPD
高速データ: 信号ライン保護用のTVSダイオード
重要なシステム: 中断のない動作を実現するバッテリーバックアップ付きUPS
主な違いの概要
SPDと一般消費者向けサージプロテクター
– エネルギー処理: SPDは20~200 kAを扱うのに対し、民生用ユニットは1~4 kAを扱う
– 保護範囲: システム全体と個々のデバイスの保護
– インストール: 恒久的なパネルマウントとポータブルプラグイン
– 標準: プロフェッショナル向け電気規格と消費者向け製品規格
– 寿命だ: 大きなサージ後の交換ではなく、長寿命を実現する設計
SPDとUPSシステム
– 主な機能: サージ保護と電源バックアップ
– 応答時間: 25ナノ秒対2~10ミリ秒
– エネルギー処理: 高いサージ電流と制限されたサージ保護
– メンテナンス 最小限のバッテリー交換が必要
– 料金: 一度限りの設置と継続的なバッテリーコスト
SPDと電力品質機器
– 保護タイプ: 過渡サージ保護と定常電力品質
– 応答速度: ナノ秒とミリ秒
– アプリケーション サージイベントと継続的な電力調整
– インストール: 並列接続と直列接続
結論
サージ保護装置は、電気サージ保護に対する専門的かつ非常に効果的なアプローチであり、体系的な適用、規制への適合性、そして包括的な保護機能において、他の保護方法とは根本的に異なります。UPSシステム、回路遮断器、MOV、TVSダイオード、パワーコンディショナーといった他の保護方法もそれぞれ電気保護において重要な役割を果たしますが、SPDは以下の点で独自の利点を提供します。
– 標準化された分類システム (タイプ1、2、3)協調的な保護
– 迅速な対応時間 (25ナノ秒)効果的なサージクランプ
– 高電流処理能力 (20,000~200,000アンペア)深刻なサージ事象に対応
– 包括的な規制枠組み 特定のNEC要件を満たす
– 体系的なインストール階層 建物全体の保護のため
主な違いは、SPDが電気システム全体に対する基本的なサージ保護を提供するのに対し、他の方法は通常、個々の機器を保護したり、異なる電気問題に対処したりする点です。現代の電気設備は、適切に調整されたSPDと、特定のアプリケーション要件に基づいた適切な補助保護方法を組み合わせた階層型保護アプローチから最大の恩恵を受けています。
これらの違いを理解することで、電気専門家は、住宅、商業、産業アプリケーション全体にわたって保護投資を最適化しながら、パフォーマンス目標と規制要件の両方を満たす包括的な保護戦略を設計できます。