Kontaktörler ve röleler arasındaki temel fark, akım kapasiteleri ve uygulama kapsamlarıdır: kontaktörler, motorlar ve HVAC sistemleri gibi yüksek akımlı yükler (tipik olarak 9 amperin üzerinde) için tasarlanmış ağır hizmet tipi elektromanyetik anahtarlardır, röleler ise düşük akımlı kontrol devreleri (tipik olarak 10 amperin altında) ve sinyal anahtarlaması için hassas anahtarlardır. Doğru cihazı seçmek, elektrik güvenliğini, mevzuat uyumluluğunu sağlar ve ekipman arızasını önler.
Bu ayrımı anlamak, endüstri mühendisleri, elektrik yüklenicileri ve tesis yöneticileri için kritik öneme sahiptir. Yanlış seçim, kaynaklı kontaklara, gereksiz arızalara ve NEC Madde 430 kapsamında potansiyel mevzuat ihlallerine yol açar. Bu kılavuz, her bir cihazın ne zaman kullanılacağını, nasıl doğru boyutlandırılacağını ve uyumlu elektrik sistemlerine nasıl entegre edileceğini açıklamaktadır.
Kontaktör ve Röle Nedir?
Kontaktör Tanımı
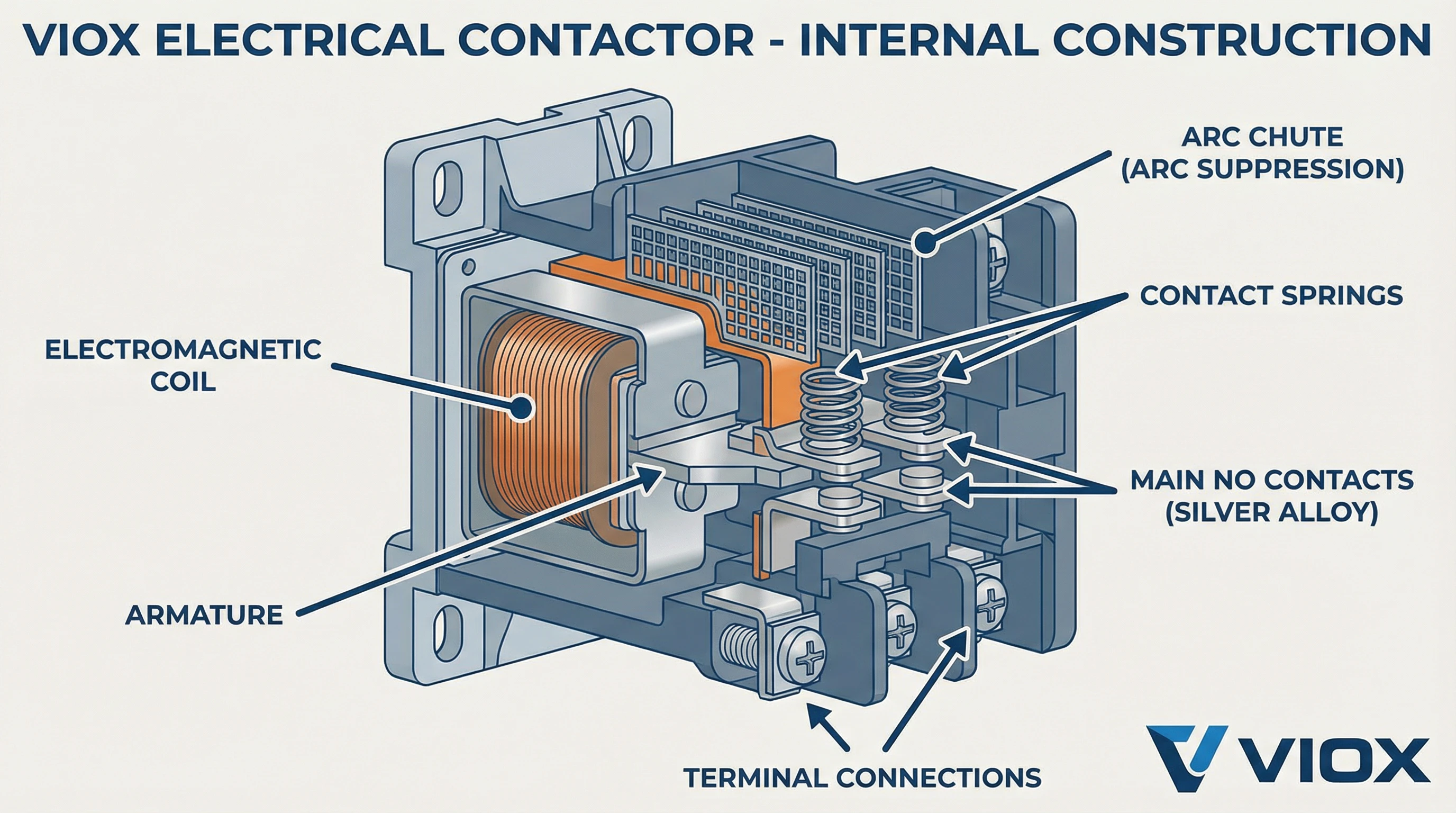
A kontaktör yüksek güçlü yük devrelerini bağlayan ve kesen, elektrikle kontrol edilen bir anahtardır—en yaygın olarak üç fazlı motorlar, büyük fanlar, HVAC kompresörleri ve endüstriyel ısıtma elemanları. Kontaktörler, dahili ark bastırma mekanizmaları ile yük altında sık anahtarlama için tasarlanmıştır.
Temel özellikler:
- Gümüş alaşımlı veya tungsten kontaklı ağır hizmet tipi yapı
- Kontrol gücü kaybında açık devre olan normalde açık (NO) ana kontaklar
- Yüksek enerjili devrelerin güvenli bir şekilde kesilmesi için dahili ark olukları
- 9 amperden 1000 amperin üzerine kadar akım değerleri
- IEC 60947-4-1 ve UL 508 standartlarına göre tasarlanmıştır
 and auxiliary contacts for industrial motor control applications.png)
Röle Tanımı
A röle ayrı devreleri kontrol eden kontakları çalıştırmak için küçük bir kontrol sinyali kullanan elektromanyetik bir anahtarlama cihazıdır. Röleler, hassasiyet ve kompakt boyutun gerekli olduğu kontrol mantığı, otomasyon arayüzleri ve sinyal anahtarlamasında mükemmeldir.
Temel özellikler:
- DIN rayı veya PCB montajı için optimize edilmiş kompakt yapı
- Çoklu kontak konfigürasyonları: SPDT, DPDT, NO, NC, değiştirme
- Tipik olarak 0,1 ila 10 amper arasında akım değerleri
- Hızlı anahtarlama hızı (1-20 milisaniye)
- IEC 61810 ve UL 508 standartlarına göre tasarlanmıştır

Temel Farklılıklar: Kontaktörler ve Röleler
Kapsamlı Karşılaştırma Tablosu
| Özellik | Kontaktörler | Röleler |
|---|---|---|
| Güncel Değerlendirme | 9-1000+ amper | 0,1-10 amper |
| Birincil Uygulama | Güç devresi anahtarlaması | Kontrol devresi anahtarlaması |
| İletişim Yapılandırması | NO ana kontaklar + yardımcı | NO, NC, SPDT, DPDT seçenekleri |
| Ark Bastırma | Dahili ark olukları | Minimum veya hiç yok |
| Fiziksel Boyut | Büyük (3-12 inç) | Kompakt (0,5-3 inç) |
| Gerilim Değerlendirmesi | 120V-1000V AC | 5V-480V AC/DC |
| Anahtarlama Hızı | Orta (50-100ms) | Hızlı (1-20ms) |
| Maliyet Aralığı | $50-500+ | $5-100 |
| Tipik Standartlar | IEC 60947-4-1, UL 508 | IEC 61810, UL 508 |
| Mekanik Ömür | 1-10 milyon operasyon | 10-100 milyon operasyon |
Yük Kapasitesi ve Gerilim
Birincil ayrım, akım taşıma kapasitesinde yatmaktadır. Kontaktörler, motor çalıştırmanın tipik özelliği olan yüksek ani akımları kaldırır—genellikle çalışma akımının 6-8 katı. Röleler bu koşullara dayanamaz ve güç devrelerine yanlış uygulanırsa kaynaklanır veya erken arızalanır.
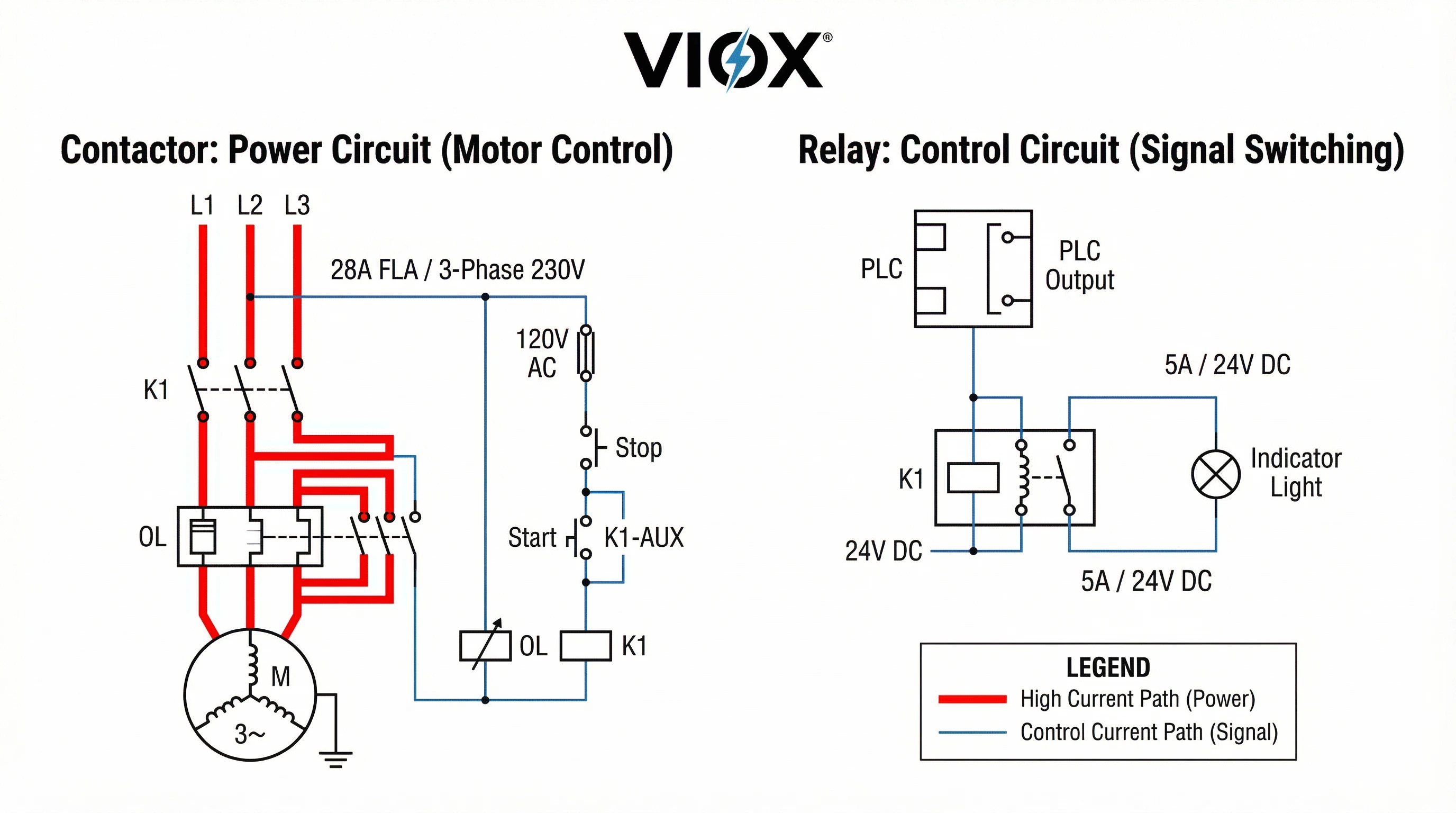
Kontaktörler, 1000V'a kadar üç fazlı AC güç sistemleri için üretilmiştir. Röleler, tek fazlı veya düşük voltajlı DC/AC kontrol devrelerine hizmet eder. Motor uygulamaları, ana güç yolu için her zaman kontaktör gerektirir, röle değil.
Ark Enerjisi Yönetimi
Yüksek akımlı yükleri anahtarlarken, açılan kontaklar arasında elektrik arkları oluşur. Kontaktörler, arkları güvenli bir şekilde bölen, soğutan ve söndüren metal bariyerler olan ark oluklarını içerir. Bu özellik rölelerde bulunmaz, bu da onları yüksek enerjili kesme için uygunsuz hale getirir.
Röleler, endüktif kontrol yüklerini anahtarlarken harici bastırma (geri dönüş diyotları, RC bastırıcılar) gerektirir. Bastırma olmadan, kontak ömrü hızla azalır.
Kontak Konfigürasyonu ve Yardımcı Fonksiyonlar
Kontaktörler tipik olarak durum göstergesi ve kilitleme için NO ana kontaklara ve yardımcı kontaklara sahiptir. Bu konfigürasyon, arızaya karşı güvenli davranış sağlar—kontrol gücü kaybı devreyi açar.
Röleler, kontrol mantığı için gerekli olan esnek kontak formları (NO, NC, değiştirme) sunar. Tek bir röle, aynı anda birden fazla devreyi yapabilir ve kesebilir, bu da karmaşık otomasyon dizilerini mümkün kılar.
Uygulamalar ve Kullanım Örnekleri
Kontaktörler Ne Zaman Kullanılır?
Üç Fazlı Motor Kontrolü
Motor çalıştırma, klasik kontaktör uygulamasıdır. NEC Madde 430, aşırı yük cihazları ve branşman devresi kısa devre koruması dahil olmak üzere uygun motor devresi koruması gerektirir. Kontaktörler, motor starterlerinde kontrollü anahtarlama elemanı olarak hizmet eder.
- Pompalar ve kompresörler: 5-200 HP endüstriyel motorlar
- Konveyör sistemleri: sık başlatma/durdurma görev döngüleri
- Takım tezgahları: koordineli çoklu motor kontrolü
- Fanlar ve üfleyiciler: HVAC ve endüstriyel havalandırma
Kontaktör boyutlandırması NEC 430.83'ü takip eder: cihaz, NEC Tablo 430.251(B) başına kilitli rotor akımını kaldırabilmelidir. 10 HP, 230V üç fazlı bir motor (FLA 28A) için, uygun ani akım kapasitesine sahip en az 35A sürekli değerine sahip bir kontaktör seçin.
HVAC Güç Devreleri
Ticari ve endüstriyel HVAC sistemleri, kompresörleri, kondenserleri ve elektrikli ısıtma elemanlarını anahtarlamak için kontaktörler kullanır. Bu yükler yüksek ani akımlar çeker ve IEC 60947-4-1'e göre AC-3 görev derecesine sahip cihazlar gerektirir.
- Çatı üniteleri: 30-90A değerinde kompresör kontaktörleri
- Soğutma sistemi: sıralı başlatma için birden fazla kontaktör
- Elektrikli ısıtıcılar: yüksek kararlı durum akımına sahip dirençli yükler
Yüksek Kapasiteli Aydınlatma
Endüstriyel tesisler, otoparklar ve spor mekanları, merkezi aydınlatma kontrolü için kontaktörler kullanır. Bireysel devreler 20A'nın altında olsa da, birden fazla devrenin eşzamanlı olarak anahtarlanması kontaktör sağlamlığı gerektirir.
Röleler Ne Zaman Kullanılır?
Kontrol Devresi Anahtarlaması
Röleler, endüstriyel kontrol mantığının omurgasını oluşturur. Elektrik yalıtımı ve mantık fonksiyonları sağlayarak PLC'ler, sensörler ve kontrollü cihazlar arasında arayüz oluştururlar.
- Güvenlik kilitlemeleri: acil durdurma devreleri, koruma izleme
- Sıra kontrolü: adım adım süreç otomasyonu
- Alarm sistemleri: arıza bildirimi ve olay kaydı
- PLC G/Ç genişletme: ayrık giriş/çıkış modülleri
Kontrol devreleri tipik olarak 24V DC veya 120V AC'de çalışır. Röle bobinleri kontrol voltajıyla eşleşirken kontaklar yük devresini değiştirir—kontrol ve güç alanları arasında elektriksel yalıtım sağlar.
Sinyal ve Veri Anahtarlama
Röleler, enstrümantasyon, telekomünikasyon ve test ekipmanlarında düşük akımlı sinyalleri işler. Hızlı anahtarlama ve temiz kontak kapamaları, onları hassas zamanlama ve yönlendirme uygulamaları için ideal kılar.
- Ses/video yönlendirme: stüdyo anahtarlama matrisleri
- Test ekipmanı: otomatik ölçüm sistemleri
- Bina otomasyonu: termostat arayüzleri, aydınlatma kontrolleri
- Otomotiv sistemleri: yakıt pompaları, marş motorları, aksesuar kontrolü
Pilot Görev Uygulamaları
Röleler genellikle kontaktör bobinlerini kontrol ederek bir kontrol hiyerarşisi oluşturur. Bir PLC tarafından çalıştırılan küçük bir 24V DC röle, bir kontaktör bobinine 120V AC gücü anahtarlar, bu da üç fazlı motoru anahtarlar. Bu kademeli kontrol, yalıtım sağlar, kontrol kablolama maliyetlerini azaltır ve uzaktan çalıştırmayı mümkün kılar.
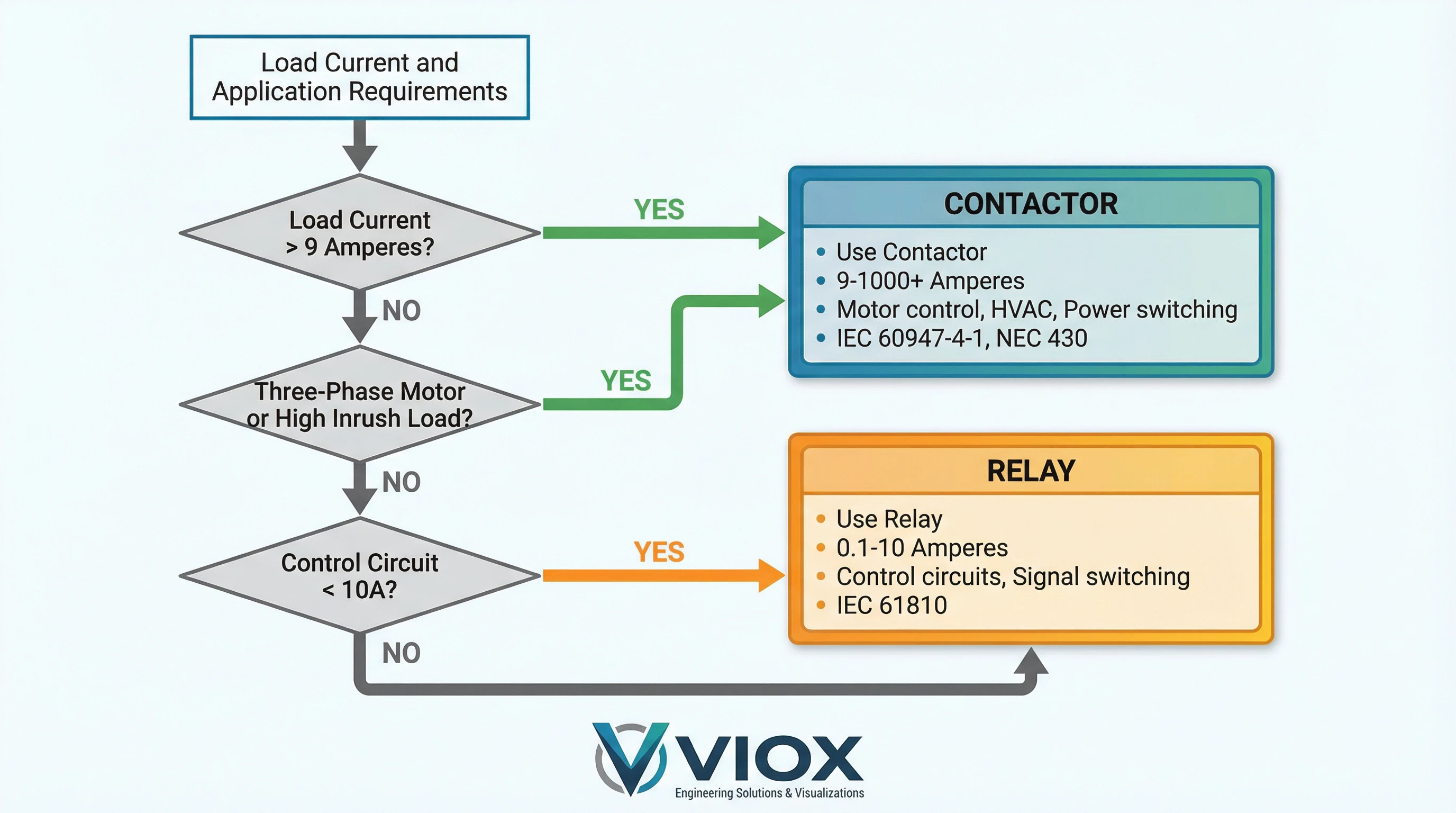
Seçim Kriterleri: Nasıl Seçilir
Adım 1: Yük Akımını Hesaplayın
Yükünüzün sürekli durum akımını ve ani akımını belirleyin. Motorlar için, isim plakası FLA'sını (tam yük amper) kullanın ve kilitli rotor akımını NEC Tablo 430.251(B)'den hesaplayın.
Isıtıcılar gibi dirençli yükler için, ani akım sürekli duruma eşittir. Kapasitif yükler (güç kaynakları, LED sürücüleri) için, üreticiden ani akım özelliklerini ölçün veya talep edin.
Genel kural: Sürekli durum akımı 9-10 amperi aşarsa veya ani akım önemliyse, bir kontaktör kullanın.
Adım 2: Voltaj ve Fazı Eşleştirin
Sistem voltajını ve faz konfigürasyonunu doğrulayın. Üç fazlı motor devreleri üç kutuplu kontaktörler gerektirir. Tek fazlı yükler, akıma bağlı olarak kontaktörler veya ağır hizmet tipi röleler kullanabilir.
DC devreleri için, DC arklarının AC arklarından daha zor söndürüldüğünü unutmayın. Uygun voltaj değerlerine sahip DC çalışması için özel olarak derecelendirilmiş cihazlar kullanın.
Adım 3: Görev Döngüsünü ve Anahtarlama Frekansını Değerlendirin
- AC-3: Normal motor görevi (başlatma, çalıştırma, durdurma)
- AC-4: Ağır motor görevi (fişleme, jogging, inching)
Rölelerin mekanik ve elektriksel ömür özellikleri vardır. 5A'da 10 milyon işlem için derecelendirilmiş bir röle, maksimum derecelendirilmiş akımında yalnızca 100.000 işleme ulaşabilir.
Adım 4: Kontrol Arayüzünü Göz Önünde Bulundurun
Kontrol sisteminizle eşleşen bobin voltajını seçin. Yaygın seçenekler: 24V DC (PLC kontrolü), 120V AC (pilot görevi), 24V AC (HVAC kontrolü).
Durum geri bildirimi, kilitleme veya aşağı akış kontrolü için yardımcı kontaklara ihtiyaç olup olmadığını belirleyin. Kontaktörler tipik olarak ek yardımcı kontak blokları içerir veya destekler.
Hızlı Seçim Rehberi
| Yük Akımı | Uygulama Türü | Cihaz Seçimi | Anahtar Standart |
|---|---|---|---|
| < 5A | Kontrol devreleri | Genel amaçlı röle | IEC 61810 |
| 5-9A | Hafif güç anahtarlama | Güç rölesi veya küçük kontaktör | UL 508 |
| 9-30A | Tek/üç fazlı motorlar | Kontaktör (AC-3 dereceli) | NEC 430, IEC 60947-4-1 |
| 30-100A | Endüstriyel motorlar, HVAC | Standart kontaktör | NEC 430.83 |
| > 100A | Ağır sanayi | Ağır hizmet tipi kontaktör | IEC 60947-4-1 |
Kurulum ve Güvenlik Gereksinimleri
Motor Devresi Koruması (NEC Madde 430)
Aşırı Yük Koruması
- motor FLA'sının 125%'si servis faktörü ≥1.15 veya 40°C sıcaklık artışı olan motorlar için
- motor FLA'sının 115%'si diğer tüm motorlar için
Aşırı yük röleleri genellikle motor yol verici tertibatlarında kontaktörlerle entegre edilmiştir. 1.15 servis faktörüne sahip 28A FLA motor için, aşırı yük açmasını maksimum 35A'e (28A × 1.25) ayarlayın.
Branşman Devresi Koruması
- Ters zamanlı kesici: 28A × 2.5 = maksimum 70A
- Anında açma kesici: 28A × 8 = maksimum 224A
- Zaman gecikmeli sigorta: 28A × 1.75 = maksimum 49A
İletken Boyutlandırma
NEC 430.22, iletkenlerin minimum motor FLA'sının 125%'si boyutunda olmasını gerektirir. 28A motor için: 28A × 1.25 = minimum 35A akım taşıma kapasitesi. Kurulum koşullarına göre NEC Tabloları 310.16 veya 310.17'den iletkenler seçin.
Kontrol Devresi Kurulumu
- Uygun tel boyutlandırması: Kontrol devresi akımını ve sıcaklık değerini eşleştirin
- Endüktif yük bastırma: DC bobinler için flyback diyotlar, AC yükler için RC snubber'lar
- Açık dokümantasyon: Şematiklere göre kontak formlarını (NO/NC) ve terminal numaralarını etiketleyin
- Aşırı akım koruması: Sınıf 1 kontrol devreleri için NEC 725'e göre sigorta veya kesici
Sorun Giderme Hızlı Kılavuzu
- Yük altındayken multimetre ile bobin voltajını doğrulayın
- Kontrol devresi sürekliliğini ve koruyucu cihazları kontrol edin
- Mekanik engelleri veya aşınmış bağlantıları inceleyin
- Bobin direncini test edin (tipik olarak derecelendirmeye bağlı olarak 10-1000 ohm)
- Yük akımını ölçün; kontaktör değerinin içinde olduğunu doğrulayın
- Aşırı akım veya kısa devre koşullarını kontrol edin
- Ark oluğu durumunu ve kontak hizalamasını inceleyin
- Uygun AC-3/AC-4 kategorisine sahip daha yüksek dereceli cihaza yükseltin
- Yük akımını kontak değerine göre değerlendirin
- Endüktif yükler için bastırma ekleyin (diyotlar, snubber'lar)
- Kirlenmiş ortamlar için sızdırmaz röle ile değiştirin
- Anahtarlama frekansının nominal elektriksel ömrü aşmadığını doğrulayın
Sıkça Sorulan Sorular
Kontaktörleri yüksek güçlü uygulamalar için daha güvenli yapan nedir?
Kontaktörler, yüksek akımlı devreleri keserken oluşan elektrik arklarını bölen, soğutan ve söndüren ark olukları içerir. Bu yerleşik ark bastırma özelliği, sağlam kontak malzemeleri ve mekanik yapısıyla birleştiğinde, standart röleleri tahrip edecek motorların ve diğer yüksek enerjili yüklerin güvenli bir şekilde tekrarlı olarak anahtarlanmasını sağlar.
Bir röle, motor kontrolü için bir kontaktörün yerini alabilir mi?
Motor ana devre anahtarlaması için bir röle kullanmak tehlikelidir ve NEC Madde 430'u ihlal eder. Motor kalkış akımları (çalışma akımının 6-8 katı) röle kontaklarını kaynak yaparak yangın tehlikesi oluşturur. Röleler, motor devreleri için gerekli olan ark bastırma, kontak kütlesi ve akım kapasitesine sahip değildir. Motor uygulamaları için NEC 430.83'e göre derecelendirilmiş kontaktörler kullanın.
Üç fazlı bir motor için kontaktör boyutlandırması nasıl yapılır?
Motor etiketindeki FLA değerini ve NEC tablolarını kullanın. IEC 60947-4-1'e göre uygun AC-3 görev sınıfına sahip, motor FLA'sının en az 1.25 katı değerde bir kontaktör seçin. Kontaktörün NEC Tablo 430.251(B)'ye göre kilitli rotor akımını kaldırabildiğini doğrulayın. 50 HP, 460V motor (65A FLA) için, minimum 81A sürekli akım değerine sahip bir kontaktör seçin (65A × 1.25).
Yardımcı kontakları ne zaman kullanmalıyım?
- PLC durum izleme (kontaktör kapalı/açık göstergesi)
- Güvenlik kilitlemeleri (birden fazla kontaktörün aynı anda kapanmasını önleyin)
- Sıralı kontrol (kontaktör A, kontaktör B enerjilenmeden önce kapanmalıdır)
- Alarm devreleri (operatörleri beklenmedik kontaktör durumları hakkında bilgilendirin)
Sonuç
Yüksek akımlı güç anahtarlaması için kontaktörleri seçin özellikle dokuz amperin üzerinde, özellikle üç fazlı motorlar, HVAC kompresörleri ve ark bastırma ile sık anahtarlama gerektiren endüstriyel yükler. Kontrol devreleri için röleleri seçin hassasiyet, hız, esnek kontak formları ve kompakt boyutun öncelikli olduğu 10 amperin altında.
Doğru seçim, elektriksel güvenliği, NEC Madde 430'a göre kod uyumluluğunu ve güvenilir sistem çalışmasını sağlar. Cihaz değerlerini her zaman yük karakteristikleri, görev döngüsü ve koruyucu cihazlarla koordine edin. Şüpheniz varsa, NEC tablolarına, ekipman veri sayfalarına başvurun ve kritik uygulamalar için profesyonel mühendislik incelemesini düşünün.
VIOX Electric, endüstriyel sınıf kontaktörler ve röleler üretmektedir B2B uygulamaları için. Mühendislik ekibimiz, motor kontrol, HVAC ve otomasyon sistemleri için uygulama desteği sağlamaktadır. Proje gereksinimlerinize göre uyarlanmış cihaz seçimi yardımı ve teknik özellikler için bizimle iletişime geçin.


