Introduction to Electrical Insulation
Electrical insulation is fundamental to the safety and functionality of all electrical systems. It prevents the flow of current between conductors and protects against electrical shorts, ensuring electricity travels only along intended pathways. This guide focuses on four critical insulation options widely used across industries: standoff insulators, epoxy powder coating, heat shrink tubing, and insulating films. Each offers unique advantages for specific applications, from circuit board protection to high-voltage isolation in power systems.
Understanding these insulation options helps engineers, technicians, and DIY enthusiasts select the optimal solution for their particular electrical requirements, ensuring both safety and performance.
Standoff Insulators (Isolators)
What Are Standoff Insulators?
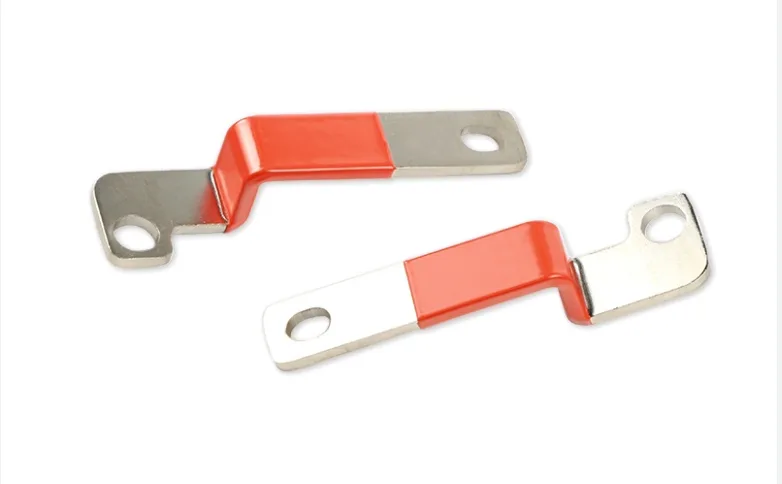
Standoff insulators, also known as isolators, are rigid components designed to physically separate and electrically isolate conductive parts in an electrical system. They maintain a fixed distance between electrical components and their mounting surfaces, preventing unwanted electrical connections while providing structural support.
VIOX Standoff Insulators (Busbar Insulators)
Types of Standoff Insulators
Ceramic Standoffs
- Material Properties: Typically made from porcelain or steatite
- Electrical Properties: Excellent dielectric strength (10-40 kV/mm)
- Temperature Resistance: Can withstand temperatures up to 1000°C
- Applications: High-voltage equipment, high-temperature environments, outdoor electrical installations
Plastic Standoffs
- Material Options: Nylon, PBT, PEEK, polypropylene
- Electrical Properties: Good dielectric strength (15-25 kV/mm)
- Temperature Range: Varies by material (generally -40°C to 150°C)
- Applications: PCB mounting, low to medium voltage applications, indoor equipment
Glass Standoffs
- Electrical Properties: Superior dielectric strength (20-40 kV/mm)
- Temperature Resistance: Excellent thermal stability
- Applications: Specialized high-frequency applications, laboratory equipment
Common Applications
- Circuit Board Mounting: Elevating PCBs from chassis or enclosures
- Terminal Block Isolation: Separating high-voltage terminal blocks from mounting surfaces
- Component Spacing: Maintaining proper clearance between electrical components
- Busbar Support: Isolating high-current busbars in power distribution systems
- Transformer Isolation: Supporting and isolating transformer windings
Advantages and Limitations
Advantages
- Provide both mechanical support and electrical isolation
- Available in standardized sizes for easy integration
- Highly reliable with minimal degradation over time
- Offer precise spacing control
- Many options are resistant to environmental factors
Limitations
- Limited flexibility once installed
- Can create mounting challenges in compact designs
- Premium materials (like PEEK or ceramic) can be costly
- Potential breakage points in high-vibration environments
Epoxy Powder Coat
What Is Epoxy Powder Coating?
Epoxy powder coating is a dry insulation method where fine particles of epoxy resin are electrostatically applied to a conductive surface and then cured under heat to form a continuous insulating layer. This process creates a durable, uniform coating that provides excellent electrical insulation while protecting against environmental factors.
Application Process
- Surface Preparation: Cleaning and often phosphating or sandblasting
- Powder Application: Electrostatic charging of powder particles causes them to adhere to the grounded substrate
- Curing: Heating at 160-200°C to melt and cross-link the epoxy
- Cooling: Controlled cooling to ensure optimal hardness and adhesion
Electrical Properties
- Dielectric Strength: Typically 15-20 kV/mm
- Volume Resistivity: >10^12 ohm-cm
- Tracking Resistance: Excellent resistance to electrical tracking
- Thickness Range: Usually applied at 25-100 microns depending on requirements
Applications
- Transformer Components: Insulating laminations and cores
- Motor Windings: Additional insulation layer on magnet wire
- Busbars: Insulating exposed conductive surfaces
- Electronic Enclosures: Providing both insulation and corrosion protection
- Switchgear Components: Insulating metal parts in medium voltage equipment
Advantages and Limitations
Advantages
- Environmentally friendly (no solvents or VOCs)
- Excellent adhesion to metal surfaces
- Uniform coating thickness even on complex geometries
- Superior chemical and impact resistance
- Long service life with minimal degradation
Limitations
- Requires specialized application equipment
- Not easily field-applied (typically factory process)
- Limited repairability once applied
- Temperature limitations (typically up to 150°C continuous operation)
- Not suitable for applications requiring flexibility
Heat Shrink Tube
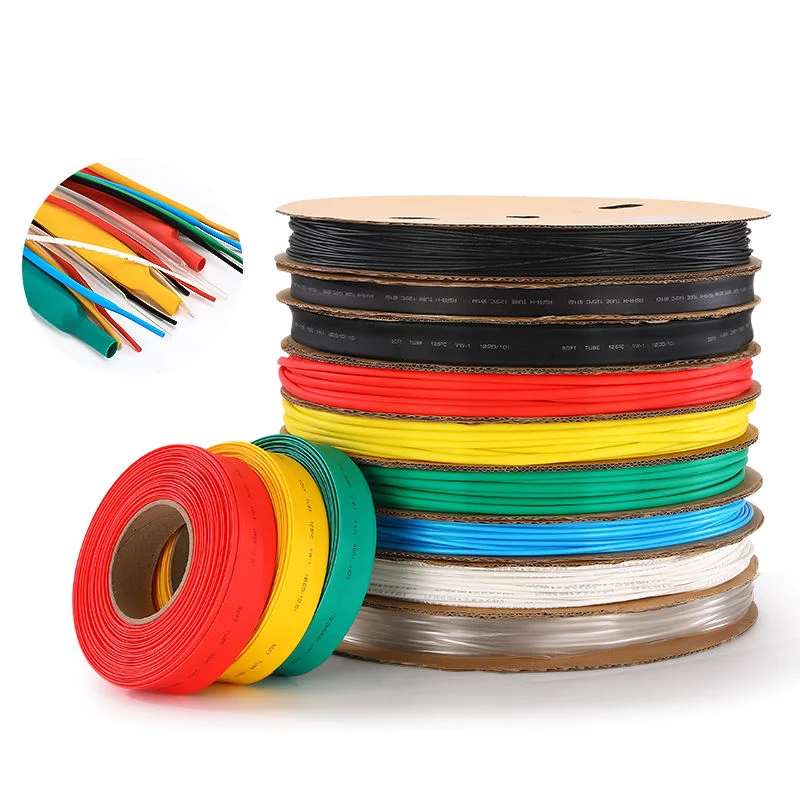
What Is Heat Shrink Tubing?
Heat shrink tubing is a flexible, pre-expanded polymer sleeve that contracts when heat is applied, creating a tight-fitting insulative covering around wires, connections, and components. Available in various materials, diameters, and shrink ratios, it provides a versatile solution for insulation, strain relief, and environmental protection.
Heat Shrink Materials
Polyolefin
- Electrical Properties: Good dielectric strength (15-20 kV/mm)
- Temperature Range: Typically -55°C to 135°C
- Features: Most common type, available in many colors, halogen-free options
- Applications: General-purpose wire insulation, bundling, identification
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride)
- Electrical Properties: Moderate dielectric strength (10-15 kV/mm)
- Temperature Range: -20°C to 105°C
- Features: Flexible, flame-retardant, cost-effective
- Applications: Low-voltage applications, general industrial use
PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene)
- Electrical Properties: Excellent dielectric properties (20-40 kV/mm)
- Temperature Range: -55°C to 260°C
- Features: Extreme temperature resistance, chemical inertness
- Applications: Aerospace, military, high-temperature environments
Viton® (Fluoroelastomer)
- Electrical Properties: Good dielectric strength
- Temperature Range: -40°C to 225°C
- Features: Exceptional chemical and fuel resistance
- Applications: Automotive, chemical processing, oil and gas
Specialized Heat Shrink Products
Adhesive-Lined Tubing
- Contains inner adhesive layer that melts during shrinking
- Creates moisture-tight seal
- Ideal for outdoor and harsh environment applications
Dual-Wall Tubing
- Outer layer provides mechanical protection
- Inner layer melts to fill gaps and irregularities
- Excellent environmental sealing properties
Heavy-Wall Tubing
- Thicker walls for enhanced mechanical protection
- Higher voltage ratings
- Often used for cable repair and reinforcement
Applications
- Wire Splices: Insulating and protecting electrical connections
- Terminal Insulation: Covering exposed conductive terminals
- Cable Entry Points: Sealing and strain relief where cables enter enclosures
- Component Protection: Insulating electronic components
- Wire Harness Organization: Bundling and protecting wire groups
- Corrosion Protection: Sealing connections from moisture and contaminants
Advantages and Limitations
Advantages
- Adaptable to irregular shapes
- Creates custom-fit insulation
- Available in various sizes, colors, and materials
- Can be installed with simple heating tools
- Provides strain relief and abrasion protection
Limitations
- Requires access to ends of wires for installation
- Cannot be easily removed without destruction
- May require specialized tools for large-scale installation
- Some types emit fumes during installation
- Limited tensile strength compared to mechanical protectors
Insulating Films
What Are Insulating Films?
Insulating films are thin, flexible sheet materials designed to provide electrical isolation with minimal thickness. Available in various polymers and composites, these films offer excellent dielectric properties while taking up minimal space, making them ideal for applications where dimensional constraints are critical.
Types of Insulating Films
Polyimide Films (Kapton®)
- Electrical Properties: Outstanding dielectric strength (3-7 kV/mil)
- Temperature Range: -269°C to 400°C
- Features: Exceptional temperature stability, radiation resistant, low outgassing
- Applications: Flexible circuit boards, aerospace, motor and generator windings
PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) Films
- Electrical Properties: Good dielectric strength (5-8 kV/mil)
- Temperature Range: -70°C to 150°C
- Features: Cost-effective, good mechanical strength, moisture resistance
- Applications: Capacitors, transformer insulation, general electrical barriers
PTFE Films
- Electrical Properties: Excellent dielectric constant (2.1) and dissipation factor
- Temperature Range: -200°C to 260°C
- Features: Low friction, chemical inertness, excellent electrical properties
- Applications: High-frequency circuit boards, wire wrapping, high-temperature applications
Composite Films
- Construction: Multiple layers of different materials laminated together
- Examples: Nomex®-Mylar®-Nomex® (NMN), mica-glass composites
- Applications: High-voltage insulation, oil-filled transformers, specialized requirements
Application Methods
- Die-Cut Shapes: Custom-cut pieces for specific component insulation
- Layer Insulation: Separating conductive layers in transformers and capacitors
- Slot Liners: Insulating motor and generator slots
- Wrapping: Spiral wrapping around conductors or component groups
- Adhesive-Backed: Applied directly to surfaces requiring insulation
Advantages and Limitations
Advantages
- Minimal space requirements
- Excellent conformability to irregular surfaces
- Can be precisely cut to custom shapes
- Many types offer high temperature resistance
- Uniform thickness and controlled properties
Limitations
- Limited mechanical protection compared to rigid insulators
- May require adhesives or mechanical fastening
- Some types are susceptible to tearing or puncture
- Specialized films can be costly
- Installation may be labor-intensive for complex geometries
Selecting the Right Insulation Option
Application-Based Selection Guide
PCB and Electronics Applications
- Best Options: Standoff insulators for mounting, insulating films for layer separation
- Key Considerations: Space constraints, temperature exposure, voltage requirements
- Typical Combinations: Nylon standoffs with polyimide film barriers
Power Distribution Equipment
- Best Options: Epoxy powder coating for busbars, standoff insulators for support
- Key Considerations: System voltage, environmental exposure, maintenance requirements
- Typical Combinations: Ceramic standoffs with epoxy-coated connection points
Wire and Cable Connections
- Best Options: Heat shrink tubing, possibly with adhesive lining
- Key Considerations: Installation environment, voltage rating, mechanical stresses
- Recommended Products: Dual-wall heat shrink for outdoor connections
Motor and Transformer Manufacturing
- Best Options: Insulating films for layer separation, epoxy coating for structural components
- Key Considerations: Temperature class, service life requirements, vibration exposure
- Typical Combinations: Nomex films with epoxy-coated laminations
Comparison Matrix
| Property | Standoff Insulators | Epoxy Powder Coat | Heat Shrink Tube | Insulating Films |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Form Factor | Rigid, fixed | Permanent coating | Flexible tube | Thin, flexible sheet |
| Installation | Mechanical | Factory process | Heat application | Manual placement |
| Voltage Range | Low to very high | Low to medium | Low to medium | Low to very high |
| Temperature Limit | -55°C to 1000°C | -40°C to 150°C | -55°C to 260°C | -269°C to 400°C |
| Space Efficiency | Low | Medium | Medium | Very high |
| Field Repairability | Good | Poor | Excellent | Good |
| Cost Range | Low to high | Medium to high | Low to medium | Low to very high |
Testing and Maintenance
Insulation Testing Methods
For All Insulation Types
- Visual Inspection: Regular examination for cracks, discoloration, or physical damage
- Insulation Resistance Testing: Measuring resistance with appropriate test voltage
- Hipot Testing: Applying voltage higher than rating to verify no breakdown
Type-Specific Tests
- Standoff Insulators: Load testing for mechanical integrity
- Epoxy Coating: Adhesion testing, thickness measurement
- Heat Shrink: Seal verification, water immersion tests
- Insulating Films: Dielectric testing, tear resistance verification
Signs of Insulation Failure
- Physical Indicators: Cracks, discoloration, melting, deformation
- Electrical Indicators: Leakage current, intermittent faults, partial discharge
- Environmental Indicators: Moisture ingress, contamination buildup
Preventive Maintenance
- Environment Control: Minimize exposure to extreme temperatures, humidity, and contaminants
- Regular Inspection Schedules: Implement systematic visual examinations
- Cleaning Procedures: Appropriate cleaning based on insulation type
- Documentation: Maintain records of insulation performance and test results
FAQs About Electrical Insulation Options
Q: How do I choose between standoff insulators and adhesive-mounted insulating films?
A: Consider space constraints, voltage requirements, and mechanical stress. Standoffs provide better mechanical support but take up more space, while films offer superior space efficiency but less mechanical protection. For high vibration environments, standoffs are generally more reliable.
Q: Can epoxy powder coating be applied in the field, or is it factory-only?
A: Epoxy powder coating typically requires specialized equipment and controlled conditions found in factory settings. For field applications, alternatives like liquid electrical tape, RTV silicone coatings, or heat shrink products are more practical options.
Q: What heat shrink ratio do I need for my application?
A: The shrink ratio (expressed as 2:1, 3:1, etc.) indicates how much the tubing will shrink from its expanded state. For covering connectors or irregular shapes, higher ratios (3:1 or 4:1) are recommended. For simple wire insulation, 2:1 is usually sufficient. Ensure the expanded diameter fits over your component and the recovered diameter will be tight enough.
Q: How thick should insulating film be for a specific voltage application?
A: Film thickness requirements vary by material and voltage. As a general guideline, each kV of potential difference typically requires 7-10 mils of film thickness, depending on the film’s dielectric strength. Always consult manufacturer specifications and apply appropriate safety factors for your specific application and environmental conditions.
Q: Can different insulation types be combined effectively?
A: Yes, combining insulation types often provides optimal protection. Common combinations include standoff insulators with insulating films for layered protection, epoxy coating with heat shrink at terminations, and films wrapped around components with standoffs for mounting. When combining types, ensure compatibility with operating temperatures and expansion/contraction characteristics.