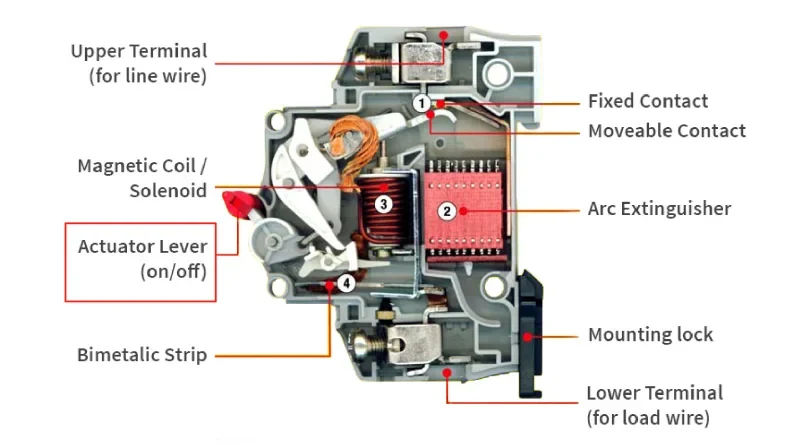
Co to jest MCB i dlaczego pozycja przełącznika ma znaczenie
A Wyłącznik instalacyjny (MCB) to automatyczny wyłącznik elektryczny zaprojektowany w celu ochrony obwodów elektrycznych przed przeciążeniami i zwarciami. Pozycja przełącznika bezpośrednio kontroluje, czy energia elektryczna przepływa przez obwody, co sprawia, że właściwe zrozumienie jest niezbędne dla bezpieczeństwa i funkcjonalności.
⚠️ OSTRZEŻENIE DOTYCZĄCE BEZPIECZEŃSTWA: Zawsze wyłącz główne zasilanie przed rozpoczęciem pracy z MCB. Prace elektryczne powinny być wykonywane przez wykwalifikowanych elektryków, gdy wymagają tego lokalne przepisy.
Pozycje przełącznika MCB: Kompletny przewodnik wizualny
| Pozycja | Status | Kierunek dźwigni | Bieżący przepływ | Wskaźnik wizualny |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NA | Obwód aktywny | GÓRA ⬆️ | Przepływ prądu | Dźwignia skierowana do góry |
| WYŁ. | Obwód nieaktywny | DÓŁ ⬇️ | Brak prądu | Dźwignia skierowana w dół |
| WYŁĄCZONY (TRIPPED) | Wykryto usterkę | ŚRODEK ↔️ | Brak prądu | Dźwignia w pozycji środkowej |
Kluczowe różnice między pozycjami MCB
Pozycja WŁĄCZONA (GÓRA):
- Dźwignia skierowana do góry w kierunku oznaczenia “1” lub “ON”
- Obwód jest zasilany i prąd płynie normalnie
- Wszystkie podłączone urządzenia otrzymują energię elektryczną
- Może być widoczny zielony lub niebieski wskaźnik (w zależności od marki)
Pozycja WYŁĄCZONA (DÓŁ):
- Dźwignia skierowana w dół w kierunku oznaczenia “0” lub “OFF”
- Obwód jest odłączony od zasilania i nie ma przepływu prądu
- Podłączone urządzenia nie otrzymują energii elektrycznej
- Może być widoczny czerwony wskaźnik (w zależności od marki)
Pozycja WYŁĄCZONY (TRIPPED) (ŚRODEK):
- Dźwignia znajduje się między pozycjami ON i OFF
- Wskazuje automatyczne odłączenie z powodu usterki
- Należy go zresetować przed normalną pracą
- Często towarzyszy mu widoczny wskaźnik
Jak prawidłowo obsługiwać przełącznik MCB
Włączanie MCB (zasilanie obwodu):
- Sprawdź bezpieczeństwo: Upewnij się, że obszar jest suchy i nie dotykasz metalowych części
- Sprawdź pozycję: Upewnij się, że dźwignia znajduje się w pozycji DOLNEJ (OFF)
- Mocne pchnięcie w górę: Naciśnij mocno dźwignię do góry, aż zatrzaśnie się na swoim miejscu
- Sprawdź połączenie: Dźwignia powinna być całkowicie w pozycji GÓRNEJ bez oporu
- Operacja testowa: Sprawdź, czy podłączone urządzenia otrzymują zasilanie
Wyłączanie MCB (odłączanie obwodu od zasilania):
- Zidentyfikuj właściwy wyłącznik: Upewnij się, że przełączasz zamierzony obwód
- Mocne pchnięcie w dół: Naciśnij mocno dźwignię w dół, aż zatrzaśnie się
- Potwierdź pozycję: Dźwignia powinna być całkowicie w pozycji DOLNEJ (OFF)
- Sprawdź odłączenie: Sprawdź, czy podłączone urządzenia nie mają zasilania
Resetowanie Wyłącznika Nadprądowego (MCB):
- Zidentyfikuj przyczynę awarii: Określ, co spowodowało wyłączenie (przeciążenie/zwarcie)
- Rozwiąż problem: Odłącz wadliwe urządzenia lub rozwiąż problemy z okablowaniem
- Sekwencja resetowania: Najpierw wciśnij dźwignię całkowicie W DÓŁ, a następnie wciśnij W GÓRĘ do pozycji ON
- Monitoruj działanie: Obserwuj, czy nie nastąpi natychmiastowe ponowne wyłączenie, wskazujące na trwające usterki
💡 PORADA EKSPERTA: Jeśli wyłącznik MCB wyłącza się wielokrotnie po resecie, przestań próbować go resetować i natychmiast skontaktuj się z wykwalifikowanym elektrykiem.
Typowe Zastosowania i Przypadki Użycia MCB
Zastosowania mieszkaniowe:
- Obwody oświetleniowe: Kontrola zasilania systemów oświetlenia pomieszczeń
- Gniazdka elektryczne: Zarządzanie energią elektryczną do gniazdek ściennych i kontaktów
- Obwody urządzenia: Dedykowane obwody dla głównych urządzeń
- Systemy HVAC: Ochrona urządzeń grzewczych i chłodzących
Zastosowania komercyjne:
- Sprzęt biurowy: Ochrona obwodów komputerowych i technologicznych
- Urządzenia przemysłowe: Sterowanie obwodami silników i urządzeń
- Systemy awaryjne: Izolacja i ochrona systemów krytycznych
- Izolacja konserwacyjna: Bezpieczne odłączenie obszaru roboczego
Wymagania Bezpieczeństwa i Najlepsze Praktyki MCB
🔒 Krytyczne Zasady Bezpieczeństwa:
| Wymaganie Bezpieczeństwa | Dlaczego to Ma Znaczenie | Profesjonalna rekomendacja |
|---|---|---|
| Tylko suche ręce | Zapobiega porażeniu prądem | W miarę możliwości używaj izolowanych narzędzi |
| Wyłącz główne zasilanie | Eliminuje pracę pod napięciem | Wymagane do modyfikacji panelu |
| Weryfikacja wizualna | Potwierdza pozycję przełącznika | Sprawdź dwa razy przed założeniem statusu |
| Profesjonalna pomoc | Złożone problemy wymagają wiedzy specjalistycznej | Zadzwoń do elektryka w przypadku powtarzających się wyłączeń |
Kwestie Zgodności z Przepisami:
- Artykuł 240 NEC: Wymagania i zastosowania wyłączników automatycznych
- Lokalne przepisy elektryczne: Przepisy specyficzne dla danej gminy
- Standardy instalacji: Wymagania dotyczące prawidłowego montażu i dostępności
- Wymagania dotyczące inspekcji: Profesjonalna weryfikacja zgodności z zasadami bezpieczeństwa
Rozwiązywanie Problemów z Pozycją MCB
Problem: MCB Nie Pozostaje w Pozycji ON
Możliwe przyczyny:
- Stan przeciążenia obwodu
- Zwarcie w podłączonym okablowaniu
- Wadliwy mechanizm MCB
- Nieprawidłowa instalacja
Rozwiązania:
- Zmniejsz podłączone obciążenie i spróbuj zresetować
- Sprawdź, czy nie ma uszkodzonych przewodów lub urządzeń
- Wymień MCB, jeśli mechanizm jest wadliwy
- Zleć profesjonaliście weryfikację instalacji
Problem: MCB Nie Wyłącza Się
Możliwe przyczyny:
- Mechaniczne zablokowanie mechanizmu przełącznika
- Korozja lub zanieczyszczenia w stykach
- Zużyty lub uszkodzony zespół przełącznika
Rozwiązania:
- Zastosuj mocny, równomierny nacisk
- Sprawdź, czy nie ma fizycznych przeszkód
- Wymień MCB, jeśli mechanizm zawiedzie
- Skontaktuj się z elektrykiem w sprawie problemów z panelem
Problem: Niejasna Pozycja Przełącznika
Możliwe przyczyny:
- Zużyte oznaczenia pozycji
- Pozycja przełącznika pośredniego
- Uszkodzone wskaźniki pozycji
Rozwiązania:
- Porównaj z sąsiednimi MCB w celu odniesienia
- Użyj bezkontaktowego testera napięcia, aby zweryfikować stan
- Wymień wyłącznik MCB z nieczytelnymi oznaczeniami
- Zleć elektrykowi weryfikację stanu obwodu
Jak wybrać odpowiedni wyłącznik MCB do swoich potrzeb
Kryteria wyboru:
Aktualna ocena:
- Dopasuj amperaż wyłącznika MCB do wymagań obwodu
- Typowe wartości znamionowe: 6A, 10A, 16A, 20A, 25A, 32A
- Nigdy nie przekraczaj obciążalności przewodów
Zdolność łamania:
- Minimum 6kA dla zastosowań domowych
- 10kA lub więcej dla instalacji komercyjnych
- Dopasuj do poziomów prądu zwarciowego instalacji elektrycznej
Charakterystyka wyzwalania:
- Typ B: Obciążenia rezystancyjne (oświetlenie, ogrzewanie)
- Typ C: Obciążenia mieszane (silniki, transformatory)
- Typ D: Aplikacje z wysokim prądem rozruchowym
Liczba biegunów:
- Jednobiegunowy: Obwody 120V/230V
- Dwubiegunowy: Obwody 240V/400V
- Trójbiegunowy: Aplikacje trójfazowe
Profesjonalne wytyczne dotyczące instalacji i konserwacji
Kiedy należy udać się do Profesjonalisty:
- Nowa instalacja MCB: Wymaga pozwoleń elektrycznych i kontroli
- Modyfikacje panelu: Dodawanie obwodów lub modernizacja instalacji
- Powtarzające się wyłączenia: Wskazują na podstawowe problemy elektryczne
- Zgodność z kodeksem: Spełnienie lokalnych wymagań elektrycznych
⚠️ OSTRZEŻENIE DOTYCZĄCE BEZPIECZEŃSTWA
: Instalacja MCB i prace przy panelu elektrycznym muszą być zgodne z lokalnymi przepisami elektrycznymi i mogą wymagać profesjonalnej instalacji przez licencjonowanych elektryków.
Harmonogram konserwacji:
- Miesięczny: Kontrola wzrokowa pozycji przełączników i wskaźników
- Kwartalny: Testowanie działania poprzez wyłączenie i włączenie
- Rocznie:Profesjonalna inspekcja instalacji elektrycznej
- As needed: Resetowanie po wyłączeniach i badanie przyczyn
Krótki przewodnik referencyjny
Pomoc w zapamiętywaniu pozycji MCB:
- GÓRA = WŁĄCZONY (Prąd płynie w GÓRĘ przez obwód)
- DÓŁ = WYŁĄCZONY (Prąd płynie w DÓŁ do uziemienia/neutralnego)
- ŚRODEK = WYŁĄCZONY (TRIPPED) (Automatyczne odłączenie bezpieczeństwa)
Procedury awaryjne:
- Awaria elektryczna: Natychmiast wyłącz główny wyłącznik
- Iskrzenie lub zapach spalenizny: Odłącz zasilanie i wezwij elektryka
- Powtarzające się wyłączenia: Przestań resetować i poszukaj profesjonalnej pomocy
- Nieczytelne pozycje: Użyj testera napięcia, aby zweryfikować stan obwodu
Pytania i odpowiedzi
W którą stronę jest WŁĄCZONY wyłącznik MCB?
Pozycja WŁĄCZONA dla wyłącznika MCB jest wtedy, gdy uchwyt wskazuje GÓRA w kierunku górnej części panelu elektrycznego. Ta pozycja umożliwia przepływ prądu przez obwód i zasilanie podłączonych urządzeń.
Jak można stwierdzić, czy wyłącznik MCB jest WŁĄCZONY czy WYŁĄCZONY?
Można rozpoznać pozycję MCB po kierunku uchwytu: GÓRA oznacza WŁĄCZONY z przepływem prądu, DÓŁ oznacza WYŁĄCZONY bez zasilania. Wiele wyłączników MCB ma również oznaczenia “1” (WŁĄCZONY) i “0” (WYŁĄCZONY) oraz kolorowe wskaźniki.
Co to znaczy, gdy wyłącznik MCB jest w pozycji środkowej?
Kiedy uchwyt MCB jest w pozycji środkowej, został automatycznie wyłączony WYŁĄCZONY (TRIPPED) z powodu przeciążenia lub zwarcia. Obwód nie ma zasilania i należy zresetować wyłącznik, przesuwając go całkowicie w DÓŁ, a następnie w GÓRĘ, aby przywrócić działanie.
Czy samodzielne resetowanie wyłączonego wyłącznika MCB jest bezpieczne?
Tak, resetowanie wyłączonego wyłącznika MCB jest generalnie bezpieczne jeśli przestrzegasz właściwych procedur: upewnij się, że obszar jest suchy, zidentyfikuj i usuń przyczynę wyłączenia, przesuń uchwyt całkowicie w DÓŁ, a następnie w GÓRĘ i monitoruj, czy nie nastąpi natychmiastowe ponowne wyłączenie. Jednakże, wezwij elektryka, jeśli MCB wielokrotnie się wyłącza.
Dlaczego mój MCB nie pozostaje w pozycji ON?
Jeśli MCB nie pozostaje w pozycji ON, prawdopodobnie występuje trwający stan awarii taki jak przeciążenie obwodu, zwarcie lub uszkodzone okablowanie. Najpierw zmniejsz obciążenie elektryczne i spróbuj zresetować. Jeśli problem będzie się powtarzał, odłącz podejrzane wadliwe urządzenia i skontaktuj się z elektrykiem.
Czy pozycja MCB może wpływać na bezpieczeństwo elektryczne?
Absolutnie. Nieprawidłowe pozycje MCB mogą pozostawić obwody pod napięciem, gdy spodziewasz się, że są WYŁĄCZONE, stwarzając poważne zagrożenie porażeniem prądem. Zawsze sprawdzaj wizualnie pozycję MCB i używaj bezdotykowego testera napięcia gdy bezpieczeństwo jest krytyczne.
Jak często należy testować działanie wyłącznika MCB?
Testuj działanie MCB kwartalnie przełączając z ON na OFF i z powrotem na ON, zapewniając płynne działanie i prawidłowe ustawienie. Nigdy nie testuj pod obciążeniem – najpierw wyłącz podłączone urządzenia. Zaplanuj coroczny profesjonalny przegląd dla pełnego bezpieczeństwa instalacji elektrycznej.
Jaka jest różnica między pozycjami MCB OFF i wyzwoloną?
Pozycja OFF (DÓŁ) to zamierzone sterowanie użytkownika z dźwignią całkowicie w dół. Pozycja WYTRĄCONY (ŚRODEK) to automatyczne odłączenie bezpieczeństwa z dźwignią między GÓRĄ a DOŁEM. Wyzwolone MCB wymagają ręcznego resetu poprzez naciśnięcie w DÓŁ, a następnie w GÓRĘ, aby przywrócić działanie.
💡 Rekomendacja eksperta: Zrozumienie pozycji MCB ma fundamentalne znaczenie dla bezpieczeństwa elektrycznego. W razie wątpliwości co do stanu obwodu, zawsze używaj bezdotykowego testera napięcia i konsultuj się z wykwalifikowanymi elektrykami w przypadku złożonych problemów elektrycznych. Prawidłowe działanie MCB chroni zarówno instalację elektryczną, jak i bezpieczeństwo osobiste.
Pamiętać: Prace elektryczne wykraczające poza podstawową obsługę MCB powinny być wykonywane przez licencjonowanych elektryków zgodnie z lokalnymi przepisami elektrycznymi i wymogami bezpieczeństwa.
Powiązane
Jak sprawdzić, czy wyłącznik automatyczny jest uszkodzony
Wyłączniki nadprądowe kontra wyłączniki nadprądowe: kompletny przewodnik porównawczy
Co to jest wyłącznik obwodu prądu stałego
Jak wybrać odpowiedni wyłącznik miniaturowy: Kompletny przewodnik techniczny