When it comes to protecting electrical cabinets and control panels from fire hazards, DIN rail aerosol fire extinguishers represent a fundamental shift from traditional fire suppression approaches. These compact, rail-mounted devices integrate directly into electrical infrastructure, offering automatic fire protection exactly where electrical fires most often ignite—inside enclosed equipment cabinets.
Unlike bulky wall-mounted extinguishers or complex gaseous suppression systems, DIN rail aerosol fire extinguishers snap onto standard 35 mm mounting rails alongside circuit breakers, relays, and other electrical components. This positioning allows them to detect and suppress fires at the source, often before flames spread beyond the enclosure. For facility managers, electrical engineers, and OEM manufacturers, understanding what makes these devices different is essential to specifying the right fire protection for mission-critical electrical equipment.
What Are DIN Rail Aerosol Fire Extinguishers?
The DIN Rail Foundation
DIN rail refers to a standardized metal mounting rail defined by IEC 60715, commonly used in electrical panels to secure circuit breakers and components. The most widely used profile is the “top-hat” TH 35 rail (35 mm wide). Equipment designed for DIN rail mounting features spring-loaded clips that snap securely onto the rail, allowing quick installation and repositioning without drilling.
How Aerosol Fire Suppression Works
Condensed aerosol fire extinguishing technology uses a solid chemical compound stored within a compact generator. When activated, this compound undergoes a controlled reaction that produces ultra-fine aerosol particles (typically less than 10 microns) suspended in nitrogen gas. These particles flood the protected enclosure and interrupt the combustion chain reaction at a molecular level—specifically disrupting the free radicals that sustain flames.
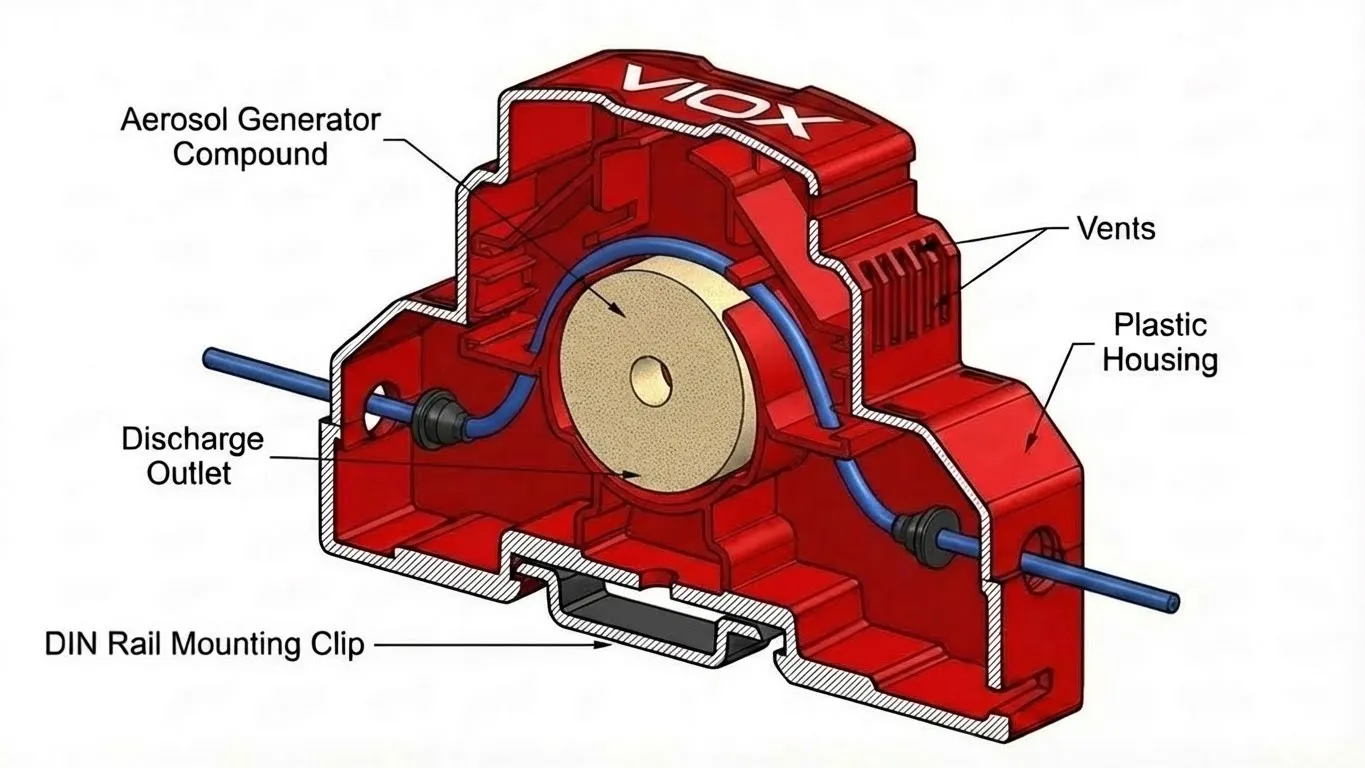
This extinguishing mechanism differs fundamentally from traditional methods:
- Water and foam cool the fire and remove oxygen
- CO₂ and inert gases displace oxygen to smother flames
- Dry chemical powders coat and separate fuel from oxygen
- Condensed aerosols break the chemical chain reaction itself
Because aerosol suppression targets the fire chemistry rather than relying on oxygen displacement, it requires significantly less agent by weight to achieve effective suppression in enclosed spaces.
Putting It Together: The DIN Rail Aerosol Concept
A DIN rail aerosol fire extinguisher combines these two elements into a single, self-contained module that mounts directly inside electrical cabinets. Typical units measure between 50-100 mm in width and 60-80 mm in height, fitting in crowded panels alongside existing switchgear.
What Makes DIN Rail Aerosol Fire Extinguishers Different?
1. Installation Location and Integration
Traditional Fire Extinguishers: Mounted on walls outside equipment, requiring human intervention to open cabinets, aim, and discharge. They protect rooms but not the interior of sealed enclosures.
Gaseous Suppression Systems: Require separate agent cylinders (often stored in dedicated rooms), piping networks, nozzles, and complex installation. Systems are designed for total room flooding rather than point protection.
DIN Rail Aerosol Extinguishers: Install directly inside the hazard zone on standard mounting rails. No external piping, cylinder rooms, or structural modifications required. The suppression agent generator sits mere centimeters from potential ignition sources like busbars, terminals, and SPDs.
2. Activation Methods
DIN rail aerosol units offer three activation approaches, often combined in a single system:
Thermal Activation: A fusible link or thermal cord (typically rated at 175°C ±5°C) automatically triggers the unit when temperature exceeds the threshold. This provides autonomous protection even when detection systems are offline or in unmanned facilities.
Electrical Activation: Integration with fire detection panels, smoke detectors, or thermal sensors allows coordinated system-wide response. This method enables remote monitoring, alarm notification, and integration with building management systems.
Manual Activation: Pull stations or manual actuators (per UL 2775 amendments) allow personnel to trigger suppression in emergency situations.
This multi-method flexibility is uncommon in traditional extinguishers (manual only) and often limited in gaseous systems (typically electrical only).
3. Space Efficiency and Footprint
Consider a standard electrical cabinet measuring 800 mm (H) × 600 mm (W) × 300 mm (D):
- A traditional 2 kg CO₂ extinguisher mounted outside the cabinet occupies wall space and provides zero protection when the cabinet door is closed
- A gaseous FM-200 or Novec system for this volume would require external cylinders, piping, and multiple nozzles
- A DIN rail aerosol unit occupies approximately 80 mm of rail space (roughly the width of two circuit breakers) and protects the entire interior volume
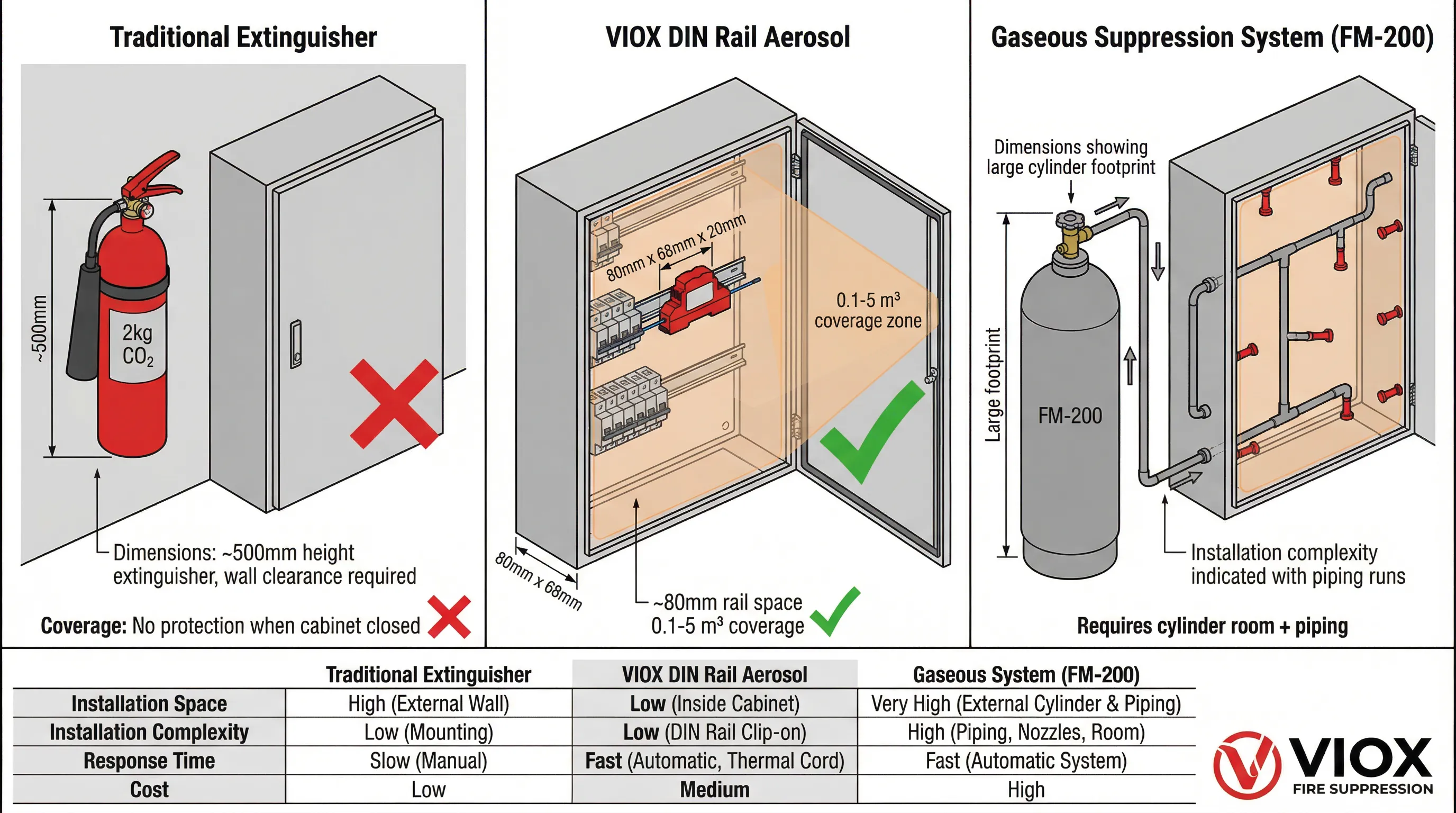
For panel builders and OEMs, this space efficiency translates to more compact designs.
4. Suppression Agent Characteristics
Residue and Cleanup: Condensed aerosol discharge consists of ultra-fine particles that settle after suppression. While more residue is left compared to gaseous agents, the particles are non-corrosive and electrically non-conductive when properly formulated. Cleanup involves vacuuming or wiping, not equipment replacement.
Environmental Impact: Modern aerosol formulations have zero Ozone Depletion Potential (ODP) and minimal Global Warming Potential (GWP). They don’t require EPA SNAP approval like many halocarbon agents and are suitable for environmentally sensitive installations.
Electrical Non-Conductivity: Properly engineered aerosol compounds are tested for dielectric strength, making them safe for use on energized electrical equipment without risk of short circuits during discharge.
5. System Complexity and Maintenance
DIN rail aerosol systems dramatically simplify both initial installation and ongoing maintenance:
Installation: Snap the unit onto the DIN rail, connect optional electrical actuator wires (if using detection integration), and verify proper positioning. No pressure vessels, piping welds, or hydrostat testing required.
Maintenance: Visual inspection of unit integrity, verification of activation mechanisms, and checking that discharge paths remain unobstructed. Units have defined service lives (typically 5-10 years) after which they’re replaced as complete modules. No pressure gauge monitoring or cylinder recharging cycles.
6. Cost Considerations
For small to medium enclosures (0.1 to 5 m³), DIN rail aerosol units offer significant cost advantages:
- Lower initial investment: No separate cylinders, piping, or installation labor for complex networks
- Reduced design time: Standard rail mounting eliminates custom bracket fabrication
- Scalability: Additional cabinets receive independent protection without interconnected systems
- Replacement economics: Failed or discharged units swap out in minutes
These factors make DIN rail aerosol particularly attractive for distributed electrical infrastructure.
Technical Comparison: Fire Suppression Methods
| Feature | DIN Rail Aerosol | Traditional Extinguisher | Gaseous System (FM-200/Novec) | CO₂ System |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Installation Location | Inside cabinet on DIN rail | Wall-mounted outside equipment | Separate cylinder room + piping | Cylinder room + piping |
| Activation | Automatic (thermal/electrical) + manual | Manual only | Electrical (detection-based) | Electrical |
| Response Time | Instant (thermal) or <10s (electrical) | Depends on human response | 10-30 seconds after detection | 10-30 seconds |
| Enclosure Volume | 0.05 – 5 m³ typical | N/A (room protection) | 10 – 500 m³ typical | 10 – 1000 m³ |
| Space Requirement | 50-100 mm rail space | Wall clearance + access | Cylinder room + piping runs | Large cylinder space |
| Residue After Discharge | Fine particles (cleanable) | Varies by type (powder/foam) | None (clean agent) | None (gas) |
| Electrical Safety | Non-conductive | Depends on agent type | Non-conductive | Non-conductive |
| Environmental Impact | Zero ODP, low GWP | Varies | Low GWP | Zero ODP, moderate GWP |
| Maintenance Frequency | 6-12 months visual check | Annual inspection + recharge | Quarterly inspection + annual test | Quarterly + weighing |
| Replacement After Use | Replace entire module | Refill/recharge | Cylinder refill | Cylinder refill |
| Typical Unit Cost | $100 – $500 | $50 – $300 | $3,000 – $20,000+ (system) | $2,000 – $15,000+ |
| Installation Complexity | Low (snap-on) | Low (bracket mount) | High (piping/commissioning) | High |
| Best Application | Individual electrical cabinets | General facility safety | Large equipment rooms | Industrial spaces |
| Unmanned Operation | Yes (automatic thermal) | No | Yes (with detection) | Yes (with detection) |
Applications and Use Cases
DIN rail aerosol fire extinguishers excel in protecting enclosed electrical equipment where traditional suppression methods are impractical or impossible. Here are the primary applications:
Electrical Distribution and Control
Electrical Cabinets and Switchgear: Main distribution boards, sub-distribution panels, and motor control centers housing busbars, circuit breakers, and contactors—all potential ignition sources from overload or short circuits.
PLC and Instrumentation Panels: Programmable logic controllers, SCADA systems, and industrial automation equipment where downtime from fire damage can halt entire production lines.
Critical Infrastructure
Data Centers: DIN rail units protect individual server racks, network switches, and power distribution units, providing equipment-level protection within larger facilities.
Telecommunications Equipment: Cell tower cabinets and remote communication sites where unmanned operation is standard and fire response times are measured in hours.
Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS): Inverter cabinets and battery management enclosures where thermal runaway demands immediate suppression.
Transportation and OEM Integration
Railway Signal Cabinets: Trackside equipment where service interruption affects safety and schedules.
Marine and Offshore: Electrical panels on vessels and platforms where harsh environments demand sealed enclosures.
Technical Specifications and Standards
When specifying DIN rail aerosol fire extinguishers, engineers should verify compliance with applicable standards and understand key technical parameters:
Regulatory Standards
| Standard | Region | Coverage |
|---|---|---|
| NFPA 2010 | United States | Fixed aerosol fire-extinguishing system design, installation, testing, and maintenance |
| UL 2775 | North America | Component standard for condensed aerosol extinguishing system units (total flooding) |
| EN 15276-2:2019 | European Union | Fixed firefighting systems – Condensed aerosol systems – Design, installation, and maintenance |
| ISO 15779:2011 | International | Condensed aerosol fire extinguishing systems – Requirements and test methods |
| IEC 60715 | International | DIN rail mounting dimensions and mechanical requirements |
Key Technical Parameters
Protected Volume: Rated enclosure size (m³). Common DIN rail units range from 0.05 m³ to 5 m³ coverage.
Discharge Time: Typically 2-5 seconds for fast fire suppression.
Activation Temperature: For thermal models, typically 175°C ±5°C.
Operating Temperature Range: Industrial units typically -50°C to +90°C.
Fire Class Rating: Usually Class A, B, C, and E.
Service Life: Typically 5-10 years from manufacture, replacement required even if never discharged.
Mounting Compatibility: Verify TH 35-7.5 or TH 35-15 rail compatibility per IEC 60715.
VIOX DIN Rail Aerosol Fire Extinguisher
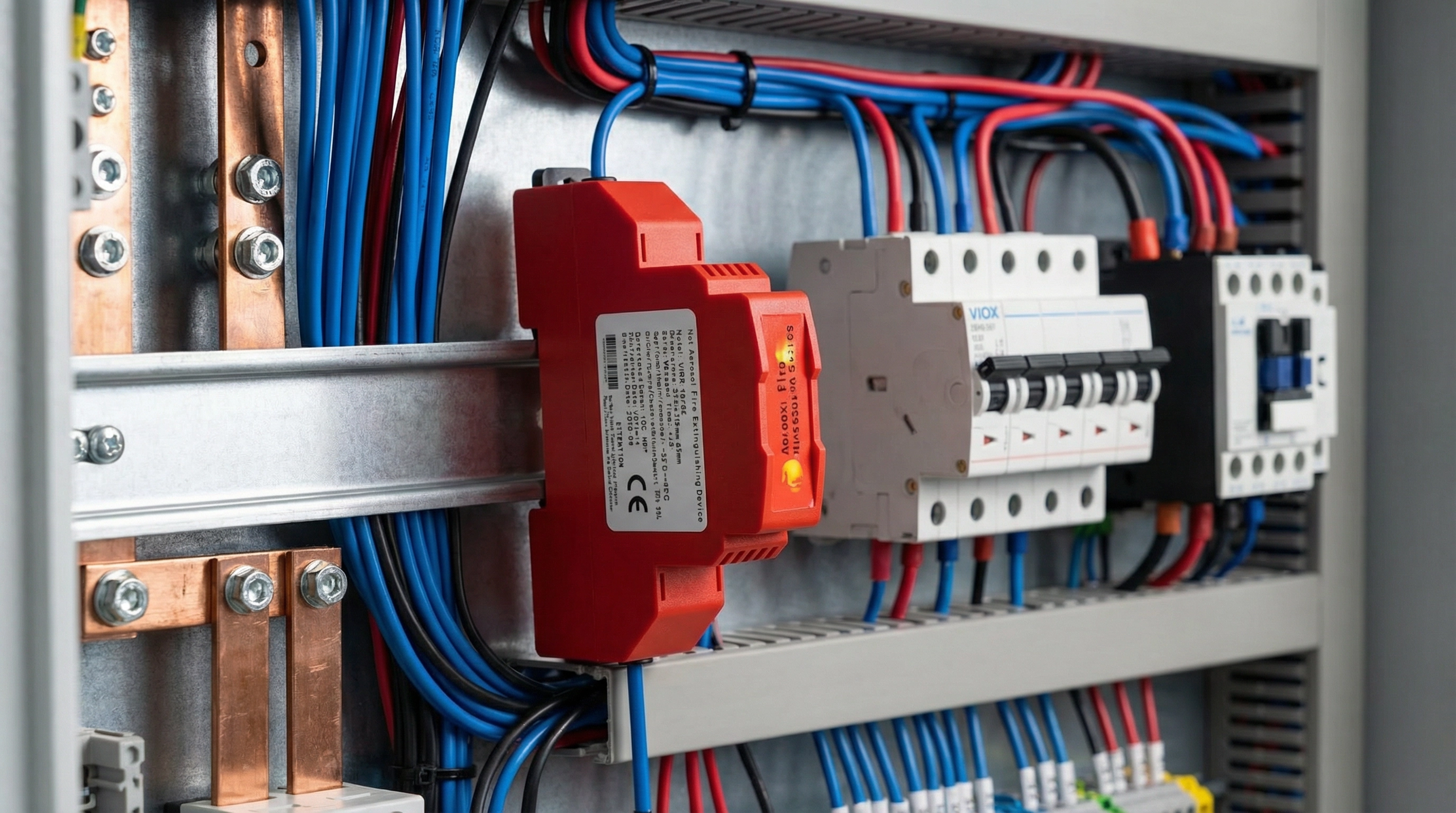
VIOX Electric manufactures the QRR0-01G-S DIN Rail Aerosol Fire Extinguisher, designed specifically for electrical cabinet protection. This compact unit embodies the differentiating features discussed throughout this article:
Product Highlights:
- Standard DIN Rail Mounting: Snap-fits onto TH 35 rails per IEC 60715, compatible with all standard electrical enclosures
- Automatic Thermal Activation: Integrated thermal cord triggers at 175°C ±5°C for autonomous fire response
- Wide Operating Range: Functions reliably from -50°C to +90°C, suitable for harsh industrial and outdoor installations
- Compact Footprint: Approximately 80 mm × 68 mm × 20 mm, occupying minimal rail space
- CE Certified: Meets European safety and performance standards for electrical equipment
- Multi-Class Protection: Effective against Class A, B, C, and E fires
- Fast Discharge: 3-4 second suppression cycle minimizes fire propagation
- Long Service Life: Factory-sealed unit with multi-year operational lifespan
The VIOX QRR0-01G-S is engineered for integration by panel builders, OEM equipment manufacturers, and facility maintenance teams seeking reliable, code-compliant fire protection for electrical infrastructure. Its potassium/strontium nitrate-based aerosol compound provides electrically non-conductive suppression without damaging sensitive electronics.
For technical specifications, installation guidelines, and procurement information, visit the VIOX Aerosol Fire Extinguisher product page.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can DIN rail aerosol fire extinguishers damage sensitive electronics?
Modern condensed aerosol formulations are electrically non-conductive and non-corrosive when properly certified to UL 2775 or ISO 15779 standards. These devices undergo dielectric strength testing to verify safe discharge on energized equipment without causing shorts. The ultra-fine particles settle after discharge and can be removed through vacuuming and wiping.
How do I calculate how many units I need for my electrical cabinet?
Calculate your cabinet’s internal volume: height × width × depth in meters. For example, 800 mm × 600 mm × 300 mm = 0.144 m³. Select a unit rated for at least this volume. Note: UL 2775 warns against simply adding multiple units beyond single-unit listing instructions. For larger cabinets, consult the manufacturer or a fire protection engineer for proper system design.
What happens if the unit activates accidentally?
Accidental discharge results in aerosol agent filling the enclosure. The non-toxic particles pose minimal health risk, though ventilation is advised. Ensure proper ventilation before re-energizing equipment, clean settled particles per manufacturer guidelines, and replace the discharged unit immediately. Thermal units activate at 175°C, well above normal operating conditions, but avoid installation near heat sources.
Are DIN rail aerosol extinguishers suitable for outdoor installations?
Yes, if they meet environmental specifications. Industrial units with -50°C to +90°C ranges handle temperature extremes. Verify IP (Ingress Protection) rating for moisture and dust protection. Coastal installations require attention to corrosion resistance, and the cabinet must maintain enclosure integrity per applicable standards.
How often do they need maintenance?
Typical maintenance includes owner inspections (monthly or quarterly) for physical damage, secure mounting, and service life verification, plus professional maintenance (semi-annually or annually) with functional testing and documentation review. Unlike pressurized extinguishers, no pressure checks or refilling needed—units are replaced as sealed modules.
Can I retrofit them into existing cabinets?
Absolutely. If your cabinet has TH 35 rails with 50-100 mm available space, simply snap the unit onto the rail and optionally connect electrical wiring. No structural modifications, piping, or external equipment required.
Conclusion
DIN rail aerosol fire extinguishers represent a specialized fire protection category that addresses the unique challenges of electrical cabinet safety. Their direct integration into equipment enclosures, automatic activation capabilities, compact footprint, and simplified installation make them fundamentally different from both traditional extinguishers and room-level suppression systems. For electrical engineers specifying protection for distributed infrastructure, facility managers protecting critical equipment, and OEM manufacturers building safety into products, understanding these differences is essential to deploying effective, code-compliant fire protection where it’s needed most—at the point of ignition.


