Vented electrical enclosures are specialized housings designed to protect electrical components while allowing for adequate airflow, crucial for managing heat and humidity in various industrial and commercial applications. These enclosures feature ventilation mechanisms such as passive vents, louvers, or forced air systems to maintain optimal operating temperatures and prevent condensation, ensuring the longevity and reliability of the enclosed electrical equipment.
VIOX Vented Electrical Enclosure
Ventilation Mechanisms
Vented electrical enclosures employ various ventilation mechanisms to maintain optimal internal conditions. These mechanisms range from passive systems to more complex active solutions, each designed to address specific cooling and moisture control needs. Here are the primary ventilation mechanisms used in electrical enclosures:
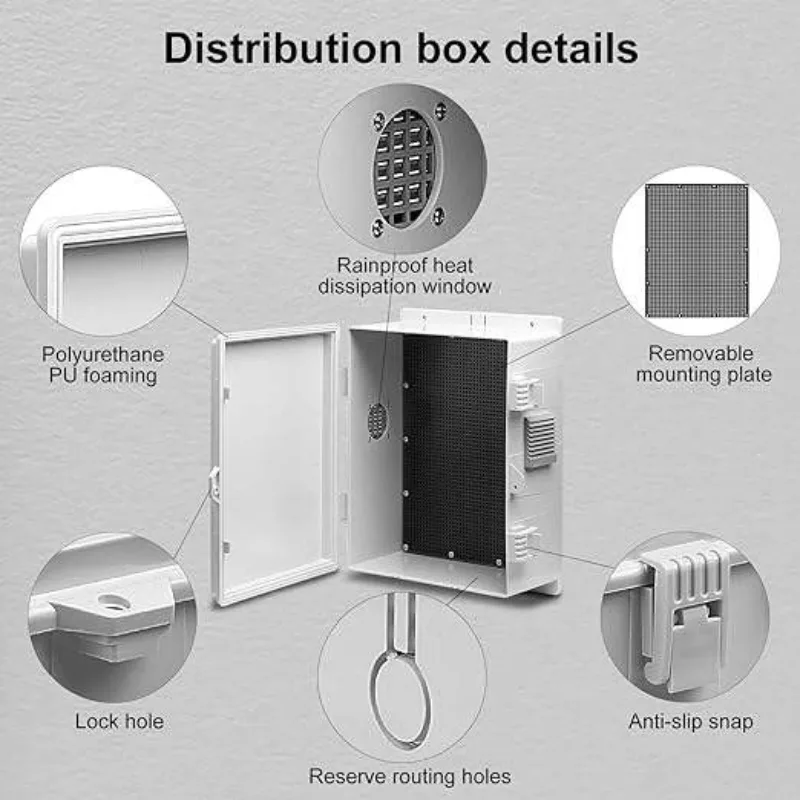
- Passive Vents: Simple openings or louvered panels that allow natural air circulation through convection. Typically positioned at the bottom and top of the enclosure to create a chimney effect.
- Filtered Vents: Incorporate air filters to prevent dust and debris from entering the enclosure while allowing airflow. These are crucial for maintaining clean internal environments.
- Pressure Equalization Vents: Specialized vents that allow for pressure balancing between the enclosure’s interior and exterior, protecting against moisture ingress and maintaining seal integrity.
- Forced Air Systems: Active cooling solutions that use fans or blowers to circulate air through the enclosure, providing more efficient heat dissipation for high-heat applications.
- Louvered Doors: Doors with built-in ventilation slots or pressed louvre vents, often strategically placed to optimize air circulation.
- Weatherproof Vents: Designed for outdoor applications, these vents allow airflow while protecting against water ingress, suitable for NEMA-rated enclosures.
Each of these mechanisms can be tailored to specific environmental conditions and equipment requirements, ensuring optimal performance and longevity of the enclosed electrical components.
Benefits of Vented Enclosures
Vented enclosures offer several key advantages for electrical systems. They effectively control temperature by facilitating airflow, which helps maintain optimal operating conditions for electronic components, thus extending their lifespan and reliability. These enclosures also play a crucial role in preventing condensation by reducing humidity levels inside, which protects against corrosion and short circuits. Additionally, the vents allow for pressure equalization, accommodating changes due to temperature fluctuations or altitude variations, which is essential for maintaining the integrity of seals and gaskets used in the enclosure. This pressure equalization feature is particularly important in protecting against dust, water, oils, and solvents across various industries.
Industry Applications
Vented electrical enclosures find widespread use across various industries due to their ability to protect electrical components while managing heat and humidity. Here’s an overview of key industry applications:
- Manufacturing: Used to house control systems, switchgear, and transformers, providing ventilation for heat-generating equipment in factory settings.
- Telecommunications: Ideal for outdoor installations of network equipment, with weatherproof vented enclosures helping to expel heat in high-temperature environments.
- Energy: Employed in power distribution systems, protecting electrical components while allowing for pressure equalization and heat dissipation.
- Industrial Automation: Houses sensitive control equipment, maintaining optimal operating temperatures for PLCs, drives, and other automation components.
- Outdoor Utilities: Weatherproof vented enclosures protect equipment from environmental factors while allowing necessary airflow for cooling.
- Data Centers: Used to house servers and networking equipment, with ventilation systems crucial for maintaining component temperatures within design limits.
- Marine Applications: Specialized vented enclosures protect against saltwater corrosion while allowing for pressure equalization in changing environments.
These applications demonstrate the versatility of vented electrical enclosures in addressing diverse industry needs for equipment protection and thermal management.
Design Considerations
When selecting or designing a vented electrical enclosure, several key factors must be considered to ensure optimal performance and protection. The amount of heat generated by the enclosed components is crucial, as larger or high-performance devices may require more robust ventilation solutions. Environmental conditions, including temperature, humidity, and dust levels, should be carefully evaluated to determine the necessary level of protection and type of ventilation required. It’s also essential to ensure compliance with relevant safety standards such as NEMA or IEC, depending on the specific application. Additionally, the choice of materials, such as stainless steel, galvanized steel, or aluminum, should be based on durability requirements and resistance to environmental factors.



