Правильное чтение MCB паспортной таблички имеет важное значение для электробезопасности, правильной установки и соответствия нормам. На паспортной табличке содержится важная информация о номинальном токе, отключающей способности, номинальном напряжении и классах безопасности, которые определяют, подходит ли выключатель для вашего конкретного применения.
Понимание того, как интерпретировать каждый символ, число и маркировку на паспортной табличке миниатюрного автоматического выключателя, может предотвратить поражение электрическим током, обеспечить соответствие нормам и помочь вам выбрать правильное защитное устройство для вашей электрической системы.
Что такое паспортная табличка MCB и почему это важно?
Паспортная табличка миниатюрного автоматического выключателя - это стандартизированная этикетка, на которой отображаются основные технические характеристики, показатели безопасности и информация о соответствии требованиям международных электротехнических стандартов (IEC 60898, UL 489 и местных электротехнических норм).
⚠️ Предупреждение о безопасности: Никогда не устанавливайте и не используйте MCB, не понимая спецификаций его паспортной таблички. Неправильная установка может привести к пожару, повреждению оборудования или поражению электрическим током.
Паспортная табличка выполняет три важные функции:
- Обеспечение безопасности посредством надлежащей проверки номинальных характеристик
- Соответствие Кодексу путем соответствия требованиям электротехнических стандартов
- Защита системы путем обеспечения правильного выбора выключателя
Ключевые компоненты паспортной таблички: Полная разбивка
Ниже приведена таблица, в которой показаны основные элементы, которые можно найти на каждой паспортной табличке MCB:
| Компонент | Назначение | Пример | Важные примечания |
|---|---|---|---|
| Текущий рейтинг | Максимальный постоянный ток | 16A, 20A, 32A | Не должен превышать потребность цепи |
| Номинальное напряжение | Максимальное рабочее напряжение | 230V, 400V | Должно соответствовать или превышать напряжение системы |
| Разрывная способность | Максимальный ток короткого замыкания, который он может прервать | 6kA, 10kA | Должен превышать уровни тока короткого замыкания системы |
| Тип кривой | Характеристика срабатывания | B, C, D | Определяет чувствительность к перегрузкам |
| Стандартная маркировка | Сертификация соответствия | IEC 60898, UL 489 | Требуется для соответствия нормам |
| Информация о производителе | Идентификация бренда и модели | VIOX | Необходима для замены |
Пошаговое руководство: Как читать паспортные таблички MCB
Шаг 1: Найдите и изучите паспортную табличку
Паспортная табличка обычно располагается на передней или боковой стороне корпуса MCB. Обеспечьте надлежащее освещение и используйте фонарик, если необходимо, чтобы четко прочитать мелкий текст.
Шаг 2: Определите номинальный ток
Ищите: Число, за которым следует “A” (амперы)
Examples: 6A, 10A, 16A, 20A, 25A, 32A, 40A, 50A, 63A
Что это значит: Максимальный непрерывный ток, который выключатель может проводить без срабатывания
💡 Совет эксперта: Номинальный ток должен составлять не менее 125% от непрерывного тока нагрузки в соответствии с требованиями NEC.
Шаг 3: Проверьте номинальное напряжение
Ищите: Числа, за которыми следует “V” или “VAC”
Общие номинальные значения: 120V, 230V, 400V, 480V
Важное примечание: Номинальное напряжение должно соответствовать или превышать рабочее напряжение вашей системы
Шаг 4: Проверьте отключающую способность
Ищите: Числа, за которыми следует “kA” (килоамперы)
Общие значения: 3kA, 6kA, 10kA, 15kA, 25kA
Что это значит: Максимальный ток короткого замыкания, который выключатель может безопасно прервать
Шаг 5: Определите тип кривой отключения
Ищите: Буквы B, C или D
- Тип B: 3-5-кратный номинальный ток (цепи освещения)
- Тип C: 5-10-кратный номинальный ток (общее назначение, двигатели)
- Тип D: 10-20-кратный номинальный ток (нагрузки с высоким пусковым током)
Шаг 6: Проверьте соответствие стандартам
Ищите: Маркировка IEC 60898, UL 489, CSA или местного стандарта
Почему это важно: Гарантирует, что выключатель соответствует требованиям электротехнических норм
Расширенная информация на паспортной табличке
Номинальные характеристики вспомогательных контактов
Многие автоматические выключатели (MCB) включают спецификации вспомогательных контактов для удаленного мониторинга или управления.
Типичные обозначения:
– Номинальный ток контактов: 6A/250VAC
– Количество контактов: 1NO (нормально открытый) или 1NC (нормально закрытый)
Экологические классификации
Обратите внимание на следующие дополнительные обозначения:
| Обозначение | Значение | Приложение |
|---|---|---|
| IP20 | Стандартная защита для помещений | Только для сухих мест |
| от -25°C до +70°C | Диапазон рабочих температур | Экологическая пригодность |
| Номинальная высота | Максимальная высота установки | Применения на большой высоте |
Общие конфигурации паспортной таблички MCB
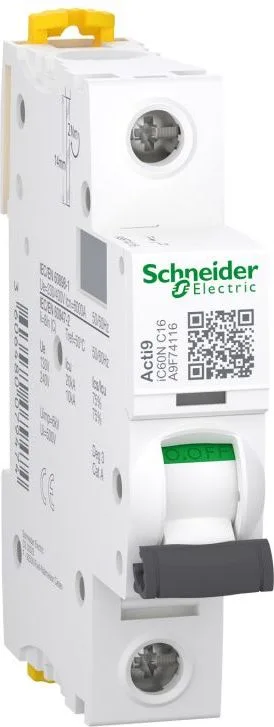
Пример паспортной таблички однополюсного MCB
SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC
Перевод:
– Производитель: Schneider Electric
– Модель: iC60N с характеристикой C, номинальный ток 16A
– Напряжение: 230V фаза-нейтраль, 400V фаза-фаза
– Отключающая способность: 6kA
– Стандарт: Соответствует IEC 60898-1
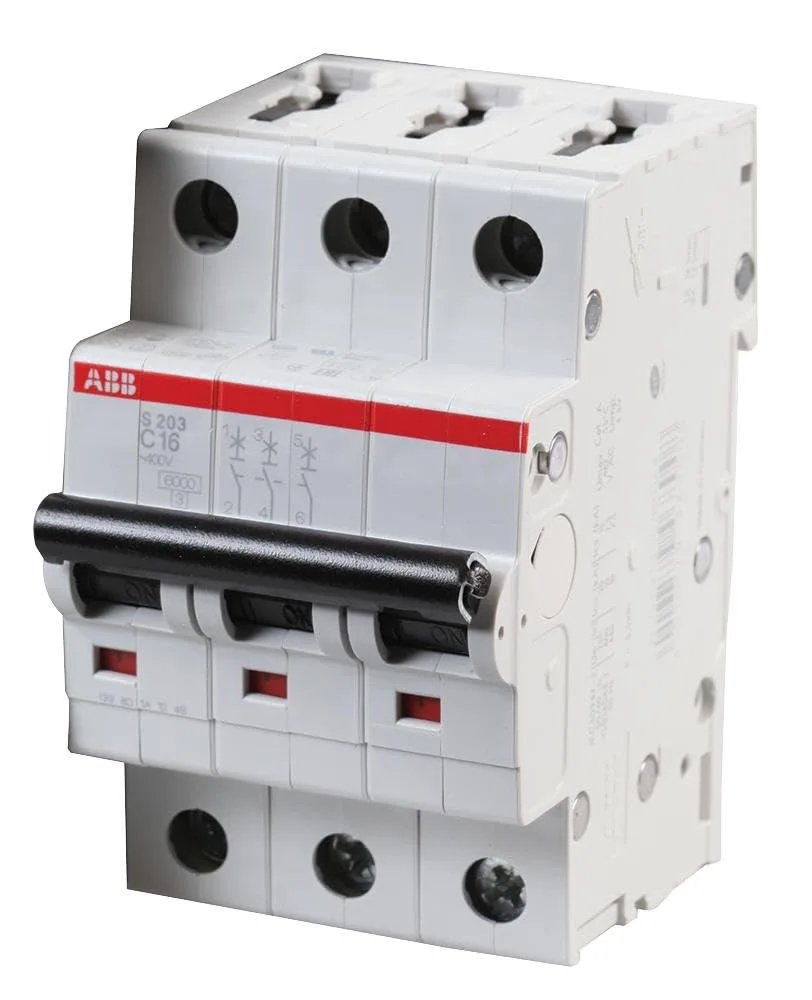
Пример паспортной таблички трехполюсного MCB
ABB S203
Перевод:
– Производитель: ABB
– Модель: серия S203
– Характеристика: C-кривая, 16A, 400V трехфазный
– Отключающая способность: 6kA
– Конфигурация: 3-полюсный
Выбор MCB на основе информации на паспортной табличке
Руководство по выбору номинального тока
Шаг 1: Рассчитайте ток нагрузки
– Измерьте или рассчитайте фактический потребляемый ток
– Добавьте запас прочности 25% в соответствии с электротехническими нормами
Шаг 2: Выберите подходящий MCB номинал
– Выберите следующий стандартный номинал, превышающий ваши расчетные требования
– Общие номиналы: 6A, 10A, 16A, 20A, 25A, 32A, 40A, 50A, 63A
Требования к отключающей способности
Ниже приведена таблица, показывающая минимальные требования к отключающей способности:
| Тип приложения | Минимальный номинал Icn | Типичные системы |
|---|---|---|
| Жилой | 3-6kA | Однофазные дома |
| Коммерческая | 6-10kA | Малый бизнес, офисы |
| Рабочая обувь | 10-25kA | Производство, крупные объекты |
| Подключенные к сети | 15-50kA | Подключения к сети, подстанции |
Вопросы безопасности и соответствия нормам
Критические требования безопасности
⚠️ Внимание: Всегда проверяйте эти критерии безопасности перед установкой:
- Совместимость с текущими рейтингами с требованиями к защите цепи
- Адекватность номинального напряжения для уровней напряжения системы
- Достаточность отключающей способности для доступного тока короткого замыкания
- Экологическая пригодность для места установки
- Соблюдение стандартов в соответствии с местными электротехническими нормами
Требования к профессиональной установке
Когда следует обратиться к профессионалу:
– Коммерческие или промышленные установки
– Системы с номинальным током выше 50A
– Высокие требования к отключающей способности (>10kA)
– Необходима проверка соответствия нормам
Устранение неполадок при чтении паспортной таблички
Проблема: Текст на паспортной табличке выцвел или не читается
Решение:
– Используйте яркий светодиодный фонарик или увеличительное стекло
– Очистите поверхность паспортной таблички сухой тканью
– Сверьтесь с документацией производителя
– Замените MCB, если паспортная табличка полностью неразборчива
Проблема: Указано несколько номинальных напряжений
Объяснение: Многие MCB рассчитаны на несколько конфигураций напряжения
Пример: 230/400V означает 230V фаза-нейтраль ИЛИ 400V фаза-фаза
Действие: Выберите номинал, соответствующий конфигурации вашей системы
Проблема: Противоречивые стандартные маркировки
Причина: Некоторые MCB имеют несколько сертификаций (IEC, UL, CSA)
Решение: Убедитесь, что автоматический выключатель соответствует требованиям вашего местного электротехнического кодекса
Рекомендация: В случае сомнений проконсультируйтесь с местным инспектором электросети
Советы по выбору экспертов
💡 Профессиональные рекомендации:
- Всегда выбирайте более высокую отключающую способность когда сомневаетесь – это обеспечивает дополнительный запас прочности
- Сопоставьте типы кривых с характеристиками нагрузки – Используйте тип C для общих применений
- Учитывайте будущий рост нагрузки при выборе номинальных токов
- Проверьте совместимость с существующим производителем электрической панели
- Задокументируйте всю информацию с заводской таблички для ведения журналов технического обслуживания
Краткий справочник: Контрольный список заводской таблички MCB
Проверка перед установкой:
- [ ] Номинальный ток ≥ 125% от тока нагрузки
- [ ] Номинальное напряжение ≥ напряжения системы
- [ ] Отключающая способность ≥ доступного тока короткого замыкания
- [ ] Соответствующий тип кривой для нагрузки
- [ ] Соответствие стандартам проверено
- [ ] Подходящий экологический рейтинг
- [ ] Совместимость с производителем подтверждена
Вопросы и ответы
Что произойдет, если я использую MCB с недостаточным номинальным током?
Использование MCB с заниженным номиналом приведет к ложным срабатываниям, снижению надежности системы и потенциально создаст угрозу безопасности из-за повторных тепловых циклов.
Могу ли я использовать MCB с более высокой отключающей способностью, чем требуется?
Да, использование более высокой отключающей способности обеспечивает дополнительный запас прочности и всегда допустимо. Однако это может увеличить первоначальную стоимость.
Что означает символ тильды (~) на заводских табличках MCB?
Тильда (~) указывает на номинал переменного тока (AC), отличая его от применений постоянного тока (DC), в которых используются другие символы.
Как проверить, соответствует ли MCB моему местному электротехническому кодексу?
Проверьте наличие соответствующих стандартных маркировок (UL 489 для США, IEC 60898 для международных стандартов) и проконсультируйтесь с местным инспектором электросети или органом, обладающим юрисдикцией.
Что делать, если на заводской табличке указано несколько номинальных токов?
Несколько номиналов обычно указывают на различные конфигурации (однополюсный против многополюсного). Используйте номинал, соответствующий вашей конкретной конфигурации установки.
Могу ли я заменить MCB другой маркой, если номиналы совпадают?
Хотя номиналы могут совпадать, убедитесь в механической совместимости с вашей электрической панелью и убедитесь, что оба MCB соответствуют одним и тем же стандартам для соответствия кодексу.
Что означают “Icn” и “Icu” на заводских табличках MCB?
– Icn: Сервисная отключающая способность (нормальный режим работы)
– Icu: Предельная отключающая способность (максимальная отключающая способность)
Используйте Icn для стандартных применений и Icu для сценариев с экстремальными токами короткого замыкания.
Как часто следует проверять заводские таблички MCB?
Проверяйте заводские таблички во время планового технического обслуживания электрооборудования (ежегодно для коммерческих объектов, каждые 3-5 лет для жилых) или всякий раз, когда возникают вопросы о пригодности выключателя.
—
Профессиональная рекомендация: Если у вас есть сомнения относительно интерпретации заводской таблички MCB или пригодности применения, проконсультируйтесь с квалифицированным электриком или инженером-электриком. Правильный выбор выключателя имеет решающее значение для электробезопасности и соответствия кодексу.
Следующие шаги: Используйте эту информацию с заводской таблички, чтобы проверить текущие установки MCB и убедиться, что они соответствуют требованиям безопасности и электротехническим нормам. Держите это руководство под рукой для будущих проектов по техническому обслуживанию и модернизации электрооборудования.