
Introduction: Understanding Your Control Options
When selecting electrical control components, push buttons and toggle switches represent two fundamentally different approaches to circuit activation. While both serve the purpose of controlling electrical circuits, their operational mechanisms, reliability characteristics, and ideal applications differ significantly. This comprehensive guide explores the key differences, electrical specifications, safety considerations, and real-world applications to help you make the right choice for your industrial or commercial project.
Whether you’re designing a control panel, upgrading industrial machinery, or selecting components for HVAC systems, understanding when to use push buttons versus toggle switches is essential for operational safety, code compliance, and system longevity.
Fundamental Differences: Quick Reference
| Feature | Push Button Switches | Toggle Switches |
|---|---|---|
| Activation Method | Pressing a button cap | Flipping a lever/handle |
| Default State | Momentary (returns) or Latching (maintains) | Maintained (stays in position) |
| Visual Feedback | Limited unless illuminated | Clear lever orientation |
| Compact Design | Highly compact, space-efficient | Larger footprint |
| Tactile Response | Short travel, responsive click | Robust mechanical snap |
| Durability | May wear with very frequent use | Excellent for harsh environments |
| Multiple States | Typically ON/OFF | Can handle ON/OFF/ON configurations |
| Accidental Activation | Risk with palm strikes | Lower risk, requires deliberate action |
| Typical Applications | Emergency stops, momentary actions | Maintained control, lighting, selectors |
| Response Speed | Instantaneous | Instantaneous |
Operating Principles and Electrical Configurations
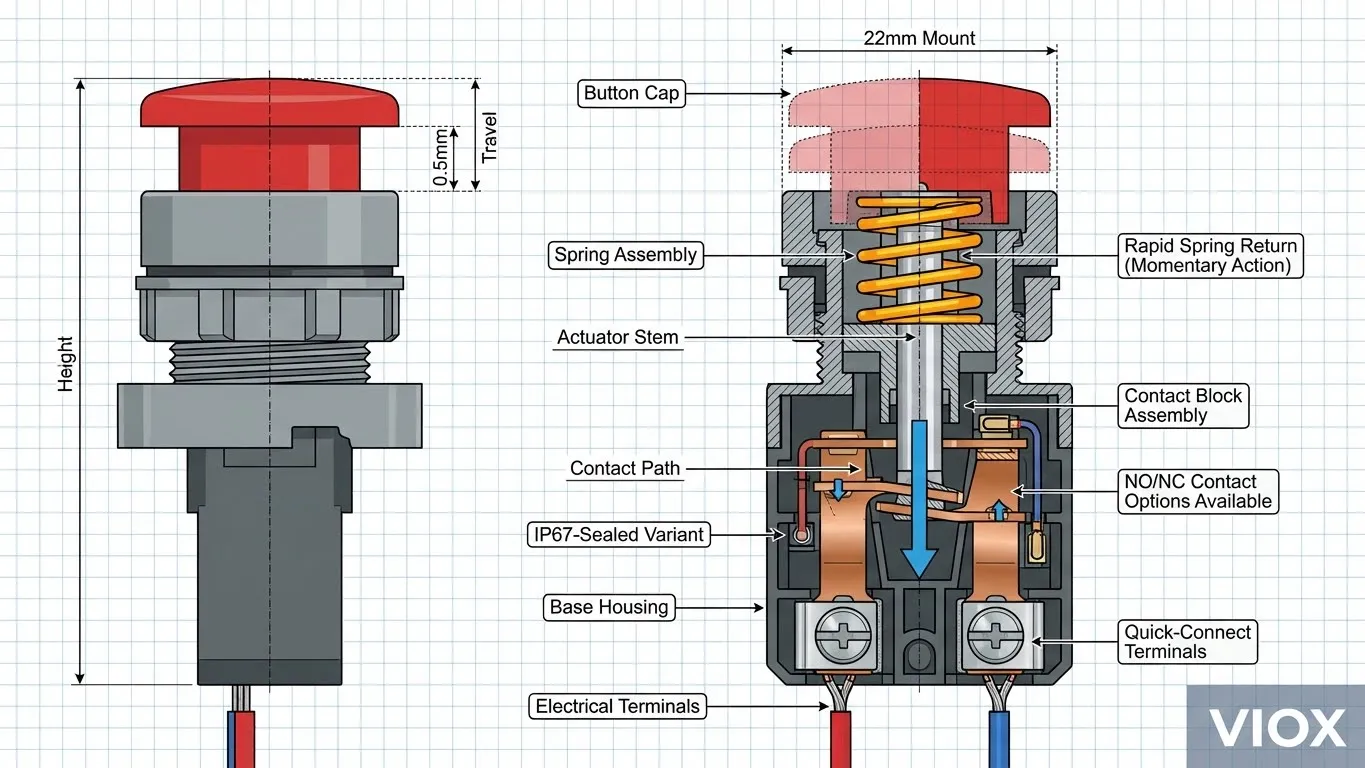
Push Button Switch Operation
Push buttons operate through two distinct modes:
Momentary Mode (Most Common)
- Circuit is active only while the button is pressed
- Ideal for emergency stop buttons, doorbells, and momentary control signals
- Returns to its original position when released
- Typical response time: <10 milliseconds
Latching Mode (Rare)
- First press activates and maintains the circuit
- Second press deactivates the circuit
- Useful for power buttons and maintained ON/OFF control
- Popular in vintage equipment and specific industrial applications
Toggle Switch Operation
Toggle switches maintain their position until manually changed:
- The lever mechanically locks in the selected position
- User receives both visual and tactile confirmation of state
- Ideal for applications requiring sustained operation without continuous pressure
- Superior for low-light environments where visual status is crucial
Electrical Configuration: SPST, SPDT, and DPDT
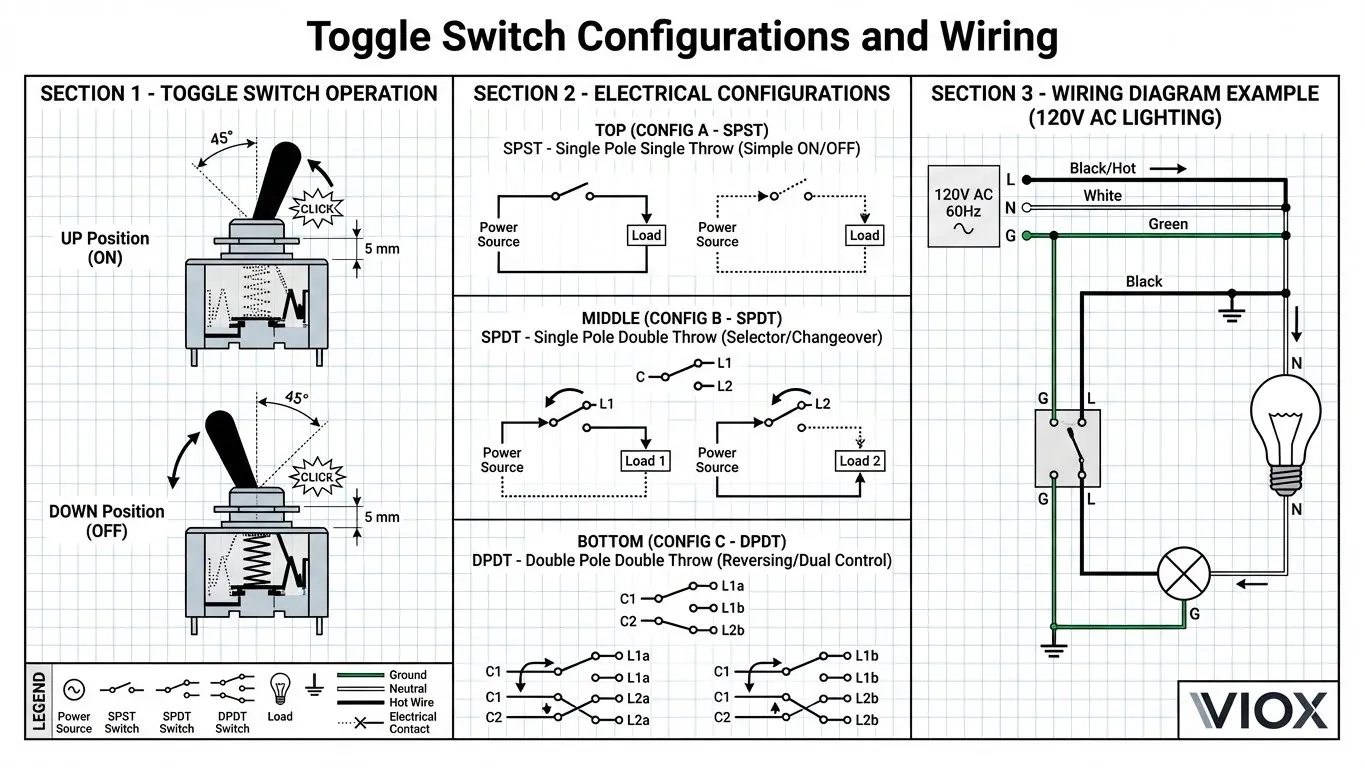
Both switch types are available in multiple electrical configurations:
| Configuration | Description | Common Use |
|---|---|---|
| SPST (Single Pole Single Throw) | One circuit, two positions (ON/OFF) | Simple lighting control |
| SPDT (Single Pole Double Throw) | Routes one input to two different outputs | Selector switches, changeover applications |
| DPDT (Double Pole Double Throw) | Controls two separate circuits simultaneously | Motor reversing, dual-circuit switching |
Electrical Ratings and Specifications
Voltage and Current Ratings
Push Button Switches:
- Standard rating: 12V–24V DC for control circuits (low-power signaling)
- Industrial grade: Up to 600V AC/DC in specialized applications
- Current capacity: 1A–10A typical, up to 20A for industrial variants
- Power consumption: Minimal (signaling device only)
Toggle Switches:
- Industrial standard: 120V–480V AC or DC
- Current capacity: 10A–30A typical, up to 60A+ in heavy-duty applications
- Direct power switching (not signaling only)
- Suitable for higher inrush currents from motors and resistive loads
Load Type Compatibility
Push buttons are designed for low-current signaling — they send control signals to relays, PLC inputs, or motor starters rather than directly interrupting main power.
Toggle switches are designed for direct power switching — they can directly control lighting circuits, heating elements, and motor circuits while maintaining the electrical load continuously.
Environmental Sealing and Safety Ratings
IP Rating Comparison
| Rating | Protection Level | Push Button | Toggle Switch |
|---|---|---|---|
| IP65 | Dust and water jet resistant | ✓ Available | ✓ Available |
| IP67 | Submersible up to 1 meter | ✓ Available (sealed variants) | ✓ Available |
| IP69K | High-pressure/temperature washdown | ✓ Industrial grade | ✓ Industrial grade |
Key Consideration: Push buttons with sealed membranes are easier to completely seal than toggle switches with lever mechanisms, making them preferable for washdown environments.
Emergency Stop Standards
For emergency stop applications, large red mushroom-head push buttons are the global standard because they:
- Can be activated by palm strike in panic situations
- Meet ISO 13850 emergency stop requirements
- Provide intuitive, universal recognition
- Toggle switches cannot safely replace emergency stops due to activation difficulty
Application-Specific Selection Guide
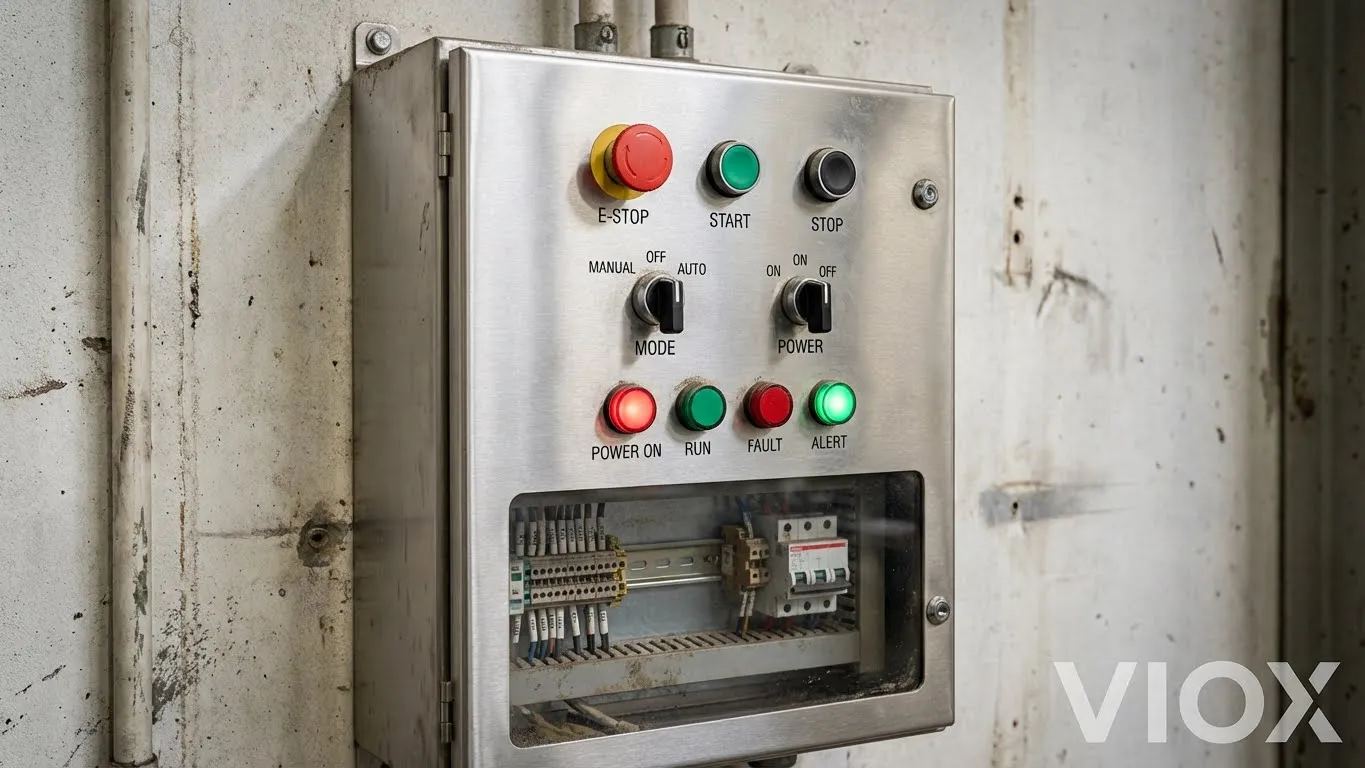

Industrial Control Panels
Choose Push Buttons When:
- Designing dense control stations with many functions
- Emergency stops or momentary actions are required
- Operators need intuitive, quick responses
- Space is limited within the panel
Example: A woodworking machinery control panel with START, STOP, and EMERGENCY STOP buttons for operator safety and ergonomic control.
Lighting and HVAC Systems
Choose Toggle Switches When:
- Users need clear visual indication of ON/OFF status
- Circuits require continuous operation without repeated activation
- Switches are in low-light areas where lever position is visible
- Long service life with minimal maintenance is required
Example: Residential and commercial lighting circuits, ceiling fan speed controls, thermostat mode selection (Heat/Off/Cool).
Selector and Mode-Selection Applications
Hybrid Approach: Combination switch devices that integrate both push button and toggle functionalities for complex control scenarios.
Durability and Service Life
Push Button Durability Profile
- Typical Service Life: 500,000–2,000,000 cycles (depending on current rating and model)
- Wear Characteristics: Button membrane may develop hysteresis after extended use
- Maintenance: Replace when response becomes sluggish or contacts corrode
- Best For: Intermittent or occasional use environments
Toggle Switch Durability Profile
- Typical Service Life: 1,000,000–10,000,000+ cycles
- Wear Characteristics: Mechanical lever maintains consistent feel throughout life
- Maintenance: Minimal; typically outlasts connected equipment
- Best For: Frequent daily use in demanding industrial environments
- Environmental Resistance: Superior resistance to vibration, thermal cycling, and corrosive environments
Cost and Procurement Considerations
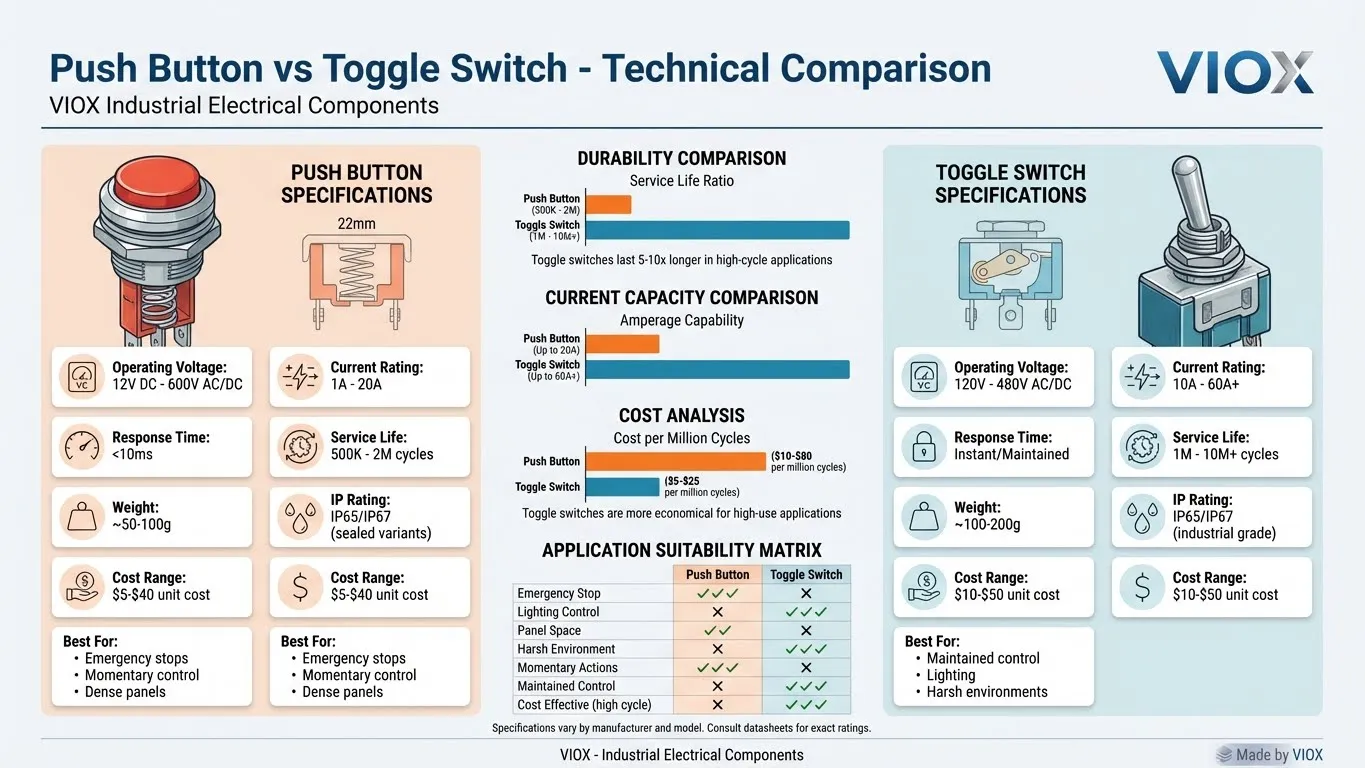
Price Comparison (Typical Industrial-Grade Units)
| Product Type | Unit Cost Range | Installation Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Push Button (22mm) | $5–$15 | $30–$50 |
| Industrial Emergency Stop Button | $20–$40 | $50–$100 |
| Standard Toggle Switch (industrial) | $10–$25 | $50–$80 |
| Heavy-Duty Toggle (sealed, high-amp) | $25–$50 | $75–$150 |
| Illuminated Push Button | $15–$35 | $50–$100 |
Total Cost of Ownership
While toggle switches may have slightly higher upfront costs, their extended service life (5–10x longer than push buttons in high-cycle applications) makes them more cost-effective for continuously-operated equipment.
Safety and Accident Prevention
Accidental Activation Risks
Push Buttons:
- Small profile makes accidental activation possible if struck by hand or object
- Mitigation: Use guarded or recessed variants for high-risk environments
- Emergency stops use large mushroom heads to prevent false activations
Toggle Switches:
- Lever design requires deliberate movement to change states
- Lower accidental activation rate in normal operation
- Safety covers (flip covers) available for critical applications
- Aerospace and marine industries prefer toggle switches for this reason
Sealing for Washdown Environments
For food processing, pharmaceutical manufacturing, or outdoor applications requiring regular washdown:
- Push buttons excel: Sealed membrane design provides complete waterproofing
- Toggle switches: Lever base requires additional protective covers for full washdown compatibility
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Can I replace a push button with a toggle switch in an existing installation?
Not always. If the original circuit was designed for momentary control signals, replacing it with a maintained toggle switch will change circuit behavior. Consult your equipment manual and a qualified electrician before making changes.
Q2: Why do some industrial control panels use both push buttons AND toggle switches?
This combination provides optimal functionality: push buttons for momentary actions (START/STOP) and toggle switches for maintained control (MODE/SPEED selection). This design balances safety, usability, and operational requirements.
Q3: What’s the maximum current a push button can safely switch?
Standard push buttons are rated for 1–10 amps. Industrial variants can handle up to 20 amps. However, for circuits exceeding 10 amps, relays are typically used to interface with the button, rather than direct switching.
Q4: Are illuminated push buttons significantly more expensive?
Illuminated buttons typically cost 50–100% more than standard variants ($15–$35 vs $5–$15), but provide valuable visual feedback for operator status indication, making them cost-justified in many applications.
Q5: Which switch type is better for outdoor/weatherproof applications?
Both are available in IP67-rated sealed variants. Push buttons are slightly easier to seal completely. Choose based on your application’s specific operational requirements (momentary vs maintained control), not sealing alone.
Q6: What’s the difference between a “selector” switch and a toggle switch?
Selector switches typically include a dial, rotary handle, or multi-position feature, whereas toggle switches flip between two main positions. Selectors are better for multi-mode applications (e.g., OFF/LOW/MEDIUM/HIGH).
Key Takeaways
- Choose Push Buttons for momentary actions: Emergency stops, START/STOP commands, momentary signal generation to control circuits, and dense control panel applications where space is limited.
- Choose Toggle Switches for maintained control: Lighting, continuous operation, clear visual status indication, and applications requiring long service life with minimal maintenance (aerospace, marine, harsh industrial environments).
- Understand electrical configurations: SPST, SPDT, and DPDT configurations are available for both types. Match the configuration to your specific circuit requirements—don’t assume single-throw operation.
- Electrical ratings matter: Push buttons are typically low-current signaling devices (1–10A), while industrial toggle switches directly switch higher currents (10–30A+). Using the wrong type can cause equipment failure or safety hazards.
- Environmental sealing varies: Both types can achieve IP65/IP67 protection, but sealed push button membranes may be easier to maintain than sealed toggle lever mechanisms in extreme washdown environments.
- Durability differences are significant: Toggle switches routinely outlast push buttons 5–10 times in high-cycle applications. For equipment operated daily or continuously, toggle switches offer better total cost of ownership.
- Safety standards are non-negotiable: Emergency stop applications must use approved red mushroom-head push buttons (ISO 13850). Never substitute toggle switches or non-compliant variants for safety-critical functions.
- Hybrid designs solve complex problems: Many modern control panels combine push buttons for momentary control with toggle switches for maintained operation, providing optimal ergonomics and safety.
Related Resources
- Understanding Circuit Breaker Safety: GFCI vs AFCI Protection
- 2-Wire vs 3-Wire Motor Control Safety Guide
- How to Choose Industrial Plugs and Sockets for Your Application
- Safety Contactors vs Standard Contactors: Force-Guided Contacts Guide
Professional Recommendation for B2B Procurement
When procuring push buttons and toggle switches for your facility or product design:
- Verify all electrical ratings match your specific voltage, current, and load requirements
- Request samples before large-scale procurement to validate tactile feel and durability in your application
- Specify IP rating requirements based on your operating environment (dust, moisture, washdown frequency)
- Include emergency stop certification (ISO 13850) for any safety-critical applications
- Consult with a qualified electrical engineer if uncertainty exists about circuit configuration requirements
For OEM applications, VIOX provides industrial-grade push buttons and toggle switches meeting IEC 60947 standards, with custom configurations available for high-volume orders. Contact our engineering team for specification consultation and lead time requirements.


