When specifying electrical distribution equipment for industrial facilities, power plants, or commercial buildings, you’ll encounter various low-voltage switchgear designations such as GGD, GCK, GCS, MNS, and XL-21. Understanding these classifications is critical for procurement managers, electrical engineers, and facility planners who need to select the right switchgear for their power distribution requirements.
Low-voltage switchgear operates at voltages typically below 1kV and serves as the backbone of electrical distribution systems. Each designation represents a specific design philosophy, structural configuration, and application scope. This guide provides a detailed analysis of these common low-voltage switchgear types to help you make informed purchasing decisions.

Classification of Low-Voltage Switchgear: Two Main Categories
Low-voltage switchgear can be fundamentally divided into two structural categories based on their component installation method:
Fixed-Type Switchgear
Fixed-type low-voltage switchgear features permanently installed components with fixed wiring. All electrical devices, including circuit breakers, contactors, and busbars, are mounted directly to the cabinet framework and cannot be easily removed for maintenance. This traditional design offers simplicity and cost-effectiveness but requires complete shutdown for service work.
Representative Models: XL-21, GGD
Withdrawable-Type (Drawer-Type) Switchgear
Withdrawable or drawer-type low-voltage switchgear utilizes a modular design where individual circuit units are housed in removable drawers. These drawers can be physically withdrawn from the cabinet while maintaining hot-swappable connections to the vertical busbars, enabling maintenance and replacement without system-wide shutdown.
Representative Models: GCK, GCS, MNS
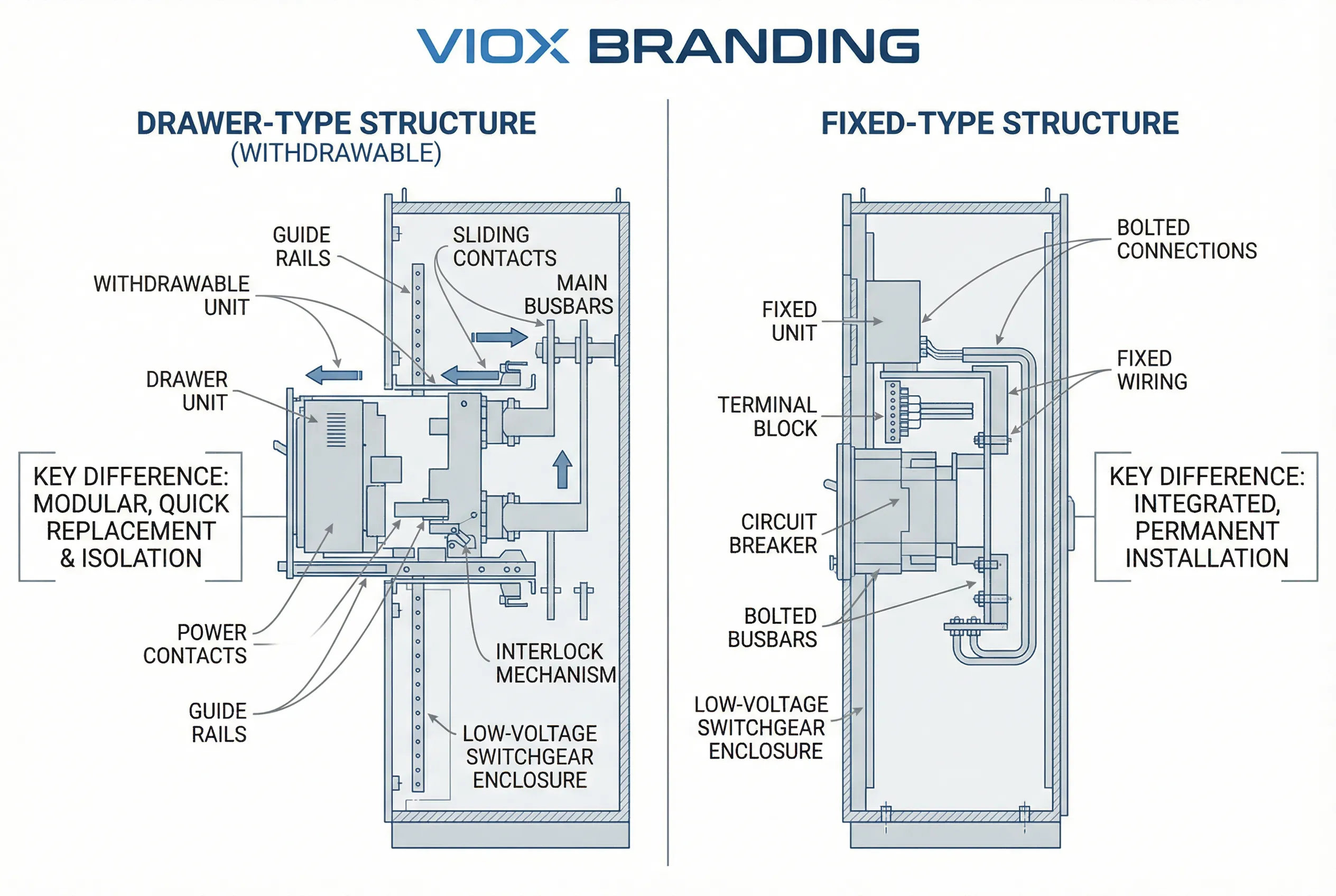
Comparison Table: Fixed vs. Withdrawable Low-Voltage Switchgear
| Feature | Fixed-Type (XL-21, GGD) | Withdrawable-Type (GCK, GCS, MNS) |
|---|---|---|
| Installation Method | Permanent mounting | Plug-in drawer modules |
| Maintenance | Requires power shutdown | Hot-swappable capability |
| Circuit Density | Lower (fewer circuits per cabinet) | Higher (more circuits per cabinet) |
| Space Efficiency | Occupies more floor space | Compact, space-saving design |
| Initial Cost | Lower capital investment | Higher initial cost |
| Operational Flexibility | Limited | High flexibility and scalability |
| Safety During Maintenance | Requires de-energization | Enhanced safety with isolation |
| Typical Applications | Simple distribution, lighting | Motor control centers, complex distribution |
XL-21 Power Distribution Cabinet: Wall-Mounted Fixed Type
Model Designation Explained
The XL-21 designation breaks down as follows:
- X = Box-type enclosure
- L = Power distribution
- 21 = Design series number
Technical Specifications
The XL-21 is a wall-mounted, fixed-installation low-voltage distribution cabinet designed for AC systems with voltages up to 500V in three-phase four-wire or five-wire configurations. It’s commonly used as terminal distribution switchgear in buildings and industrial facilities.
Key Features:
- Rated voltage: 380V AC
- Rated frequency: 50Hz/60Hz
- Protection class: IP30-IP54 (depending on configuration)
- Compact wall-mounted design
- Front-access maintenance
- Integrated knife switch for main power isolation
Applications
XL-21 switchgear is ideal for:
- Floor-level power distribution in multi-story buildings
- Workshop lighting and power distribution
- Small-scale industrial facilities
- Final distribution point in electrical systems
Advantages and Limitations
Advantages:
- Cost-effective solution for simple distribution needs
- Easy installation and operation
- Minimal maintenance requirements
- Suitable for locations with limited floor space
Limitations:
- Fixed components require shutdown for maintenance
- Lower circuit capacity per cabinet
- Not suitable for complex automation systems
- Limited expandability
GGD Low-Voltage Distribution Cabinet: Fixed Power Distribution
Model Designation Explained
GGD stands for:
- G = Low-voltage distribution cabinet (Guī – 柜)
- G = Fixed installation and wiring (Gù dìng – 固定)
- D = Power cabinet (Dòng lì – 动力)
Technical Specifications
GGD low-voltage switchgear is widely used for main power distribution in substations and industrial facilities. This fixed-type switchgear handles AC systems with frequencies of 50-60Hz and voltages up to 500V.
Key Parameters:
- Rated voltage: 380V/400V
- Maximum current capacity: 4000A
- Short-circuit capacity: High breaking capacity with proper circuit breakers
- Cabinet height: 2200mm (standard)
- Protection grade: IP30
- Complies with IEC439 and GB7251 standards
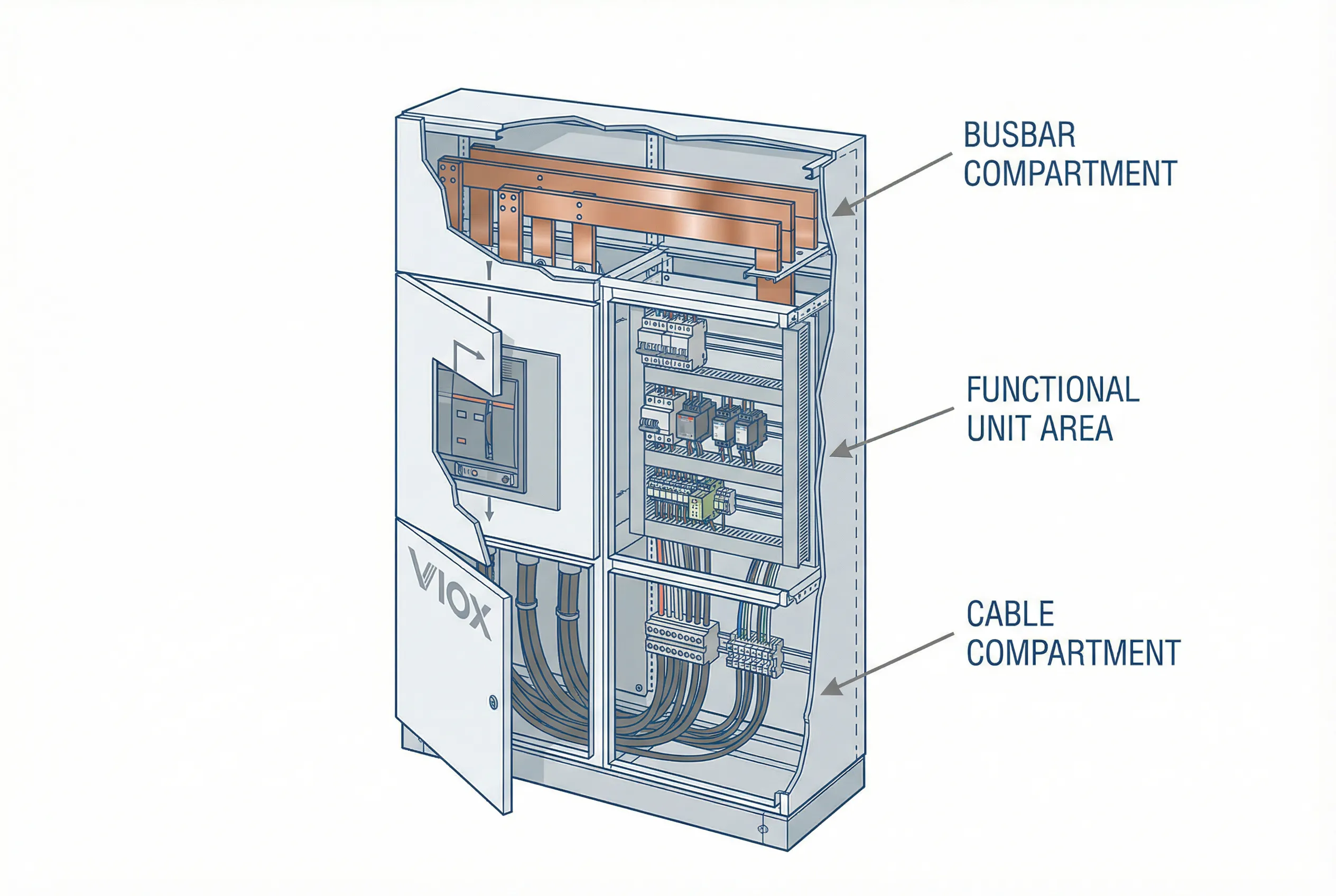
Structural Design
The GGD switchgear frame is constructed using welded cold-rolled steel plates and angle steel, providing a robust and rigid structure. The cabinet is divided into functional compartments with a fixed busbar system located at the top or rear of the enclosure.
Applications
GGD switchgear serves as core distribution equipment in:
- Power receiving and distribution in substations
- Section switching and feeder cabinets
- Capacitor bank installations
- Main distribution boards for industrial plants
- Mining operations and heavy industry
Advantages and Limitations
Advantages:
- Proven reliability and robust construction
- High breaking capacity suitable for industrial loads
- Good dynamic and thermal stability
- Wide range of electrical configurations
- Lower initial investment compared to withdrawable types
Limitations:
- Requires complete shutdown for maintenance
- Fewer circuits per cabinet compared to drawer types
- Occupies more floor space
- Cannot interface with automation systems easily
- Units cannot be arbitrarily combined
GCK Withdrawable Low-Voltage Switchgear: Early Drawer Design
Model Designation Explained
GCK represents:
- G = Cabinet structure (Guì – 柜)
- C = Withdrawable/Drawable type (Chōu chū shì – 抽出式)
- K = Control center (Kòng zhì – 控制)
Technical Specifications
GCK is one of the earlier Chinese-designed drawer-type low-voltage switchgear, combining Power Distribution Center (PC) and Motor Control Center (MCC) functions.
Key Parameters:
- Rated voltage: 380V/660V
- Maximum current capacity: 4000A
- Rated frequency: 50/60Hz
- Minimum drawer unit: 1 module (200mm height)
- Cabinet depth: 600mm (single-sided operation)
- Complies with IEC439 and GB7251 standards
Structural Characteristics
The GCK switchgear uses C-profile steel for the main framework, assembled through standardized modular design. A notable feature is that the horizontal busbar is traditionally positioned at the top of the cabinet, and the vertical busbar lacks flame-retardant plastic functional boards found in more modern designs.
Key Design Elements:
- Drawer units in multiples of 1 module (200mm)
- Maximum 8 full-height drawers per cabinet
- Cable outlet: Rear or right-side cable compartment
- Simpler drawer propulsion mechanism compared to GCS/MNS
- Three-compartment design: busbar, functional units, and cable areas
Applications
GCK switchgear is deployed in:
- Power distribution centers (PC)
- Motor control centers (MCC)
- Power plants and substations
- Factory power distribution systems
- Reactive power compensation installations
Advantages and Limitations
Advantages:
- Modular drawer design enables hot-swap maintenance
- Space-efficient compared to fixed switchgear
- Suitable for motor control applications
- Lower cost than GCS/MNS alternatives
- Proven track record in Chinese market
Limitations:
- Horizontal busbar at top reduces safety
- No flame-retardant separation for vertical busbar
- Simpler mechanism may lack smooth operation
- Lower module flexibility (1 module minimum vs. 1/2 or 1/4)
- Older design compared to GCS/MNS
GCS Low-Voltage Withdrawable Switchgear: Modern Chinese Standard
Model Designation Explained
GCS stands for:
- G = Enclosed switchgear cabinet (Guì – 柜)
- C = Withdrawable type (Chōu chū shì – 抽出式)
- S = Senyuan electrical system (designed by Senyuan Company)
Technical Specifications
GCS represents a new generation of drawer-type switchgear designed in the mid-1990s, incorporating design improvements inspired by ABB’s MNS system while maintaining Chinese manufacturing standards.
Key Parameters:
- Rated voltage: 400V/690V
- Maximum current capacity: 4000A
- Rated frequency: 50/60Hz
- Minimum drawer unit: 1/2 module (100mm height)
- Maximum drawers: Up to 22 units per cabinet (with half-modules)
- Cabinet depth: 800mm (single-sided operation)
- Protection rating: IP30-IP40
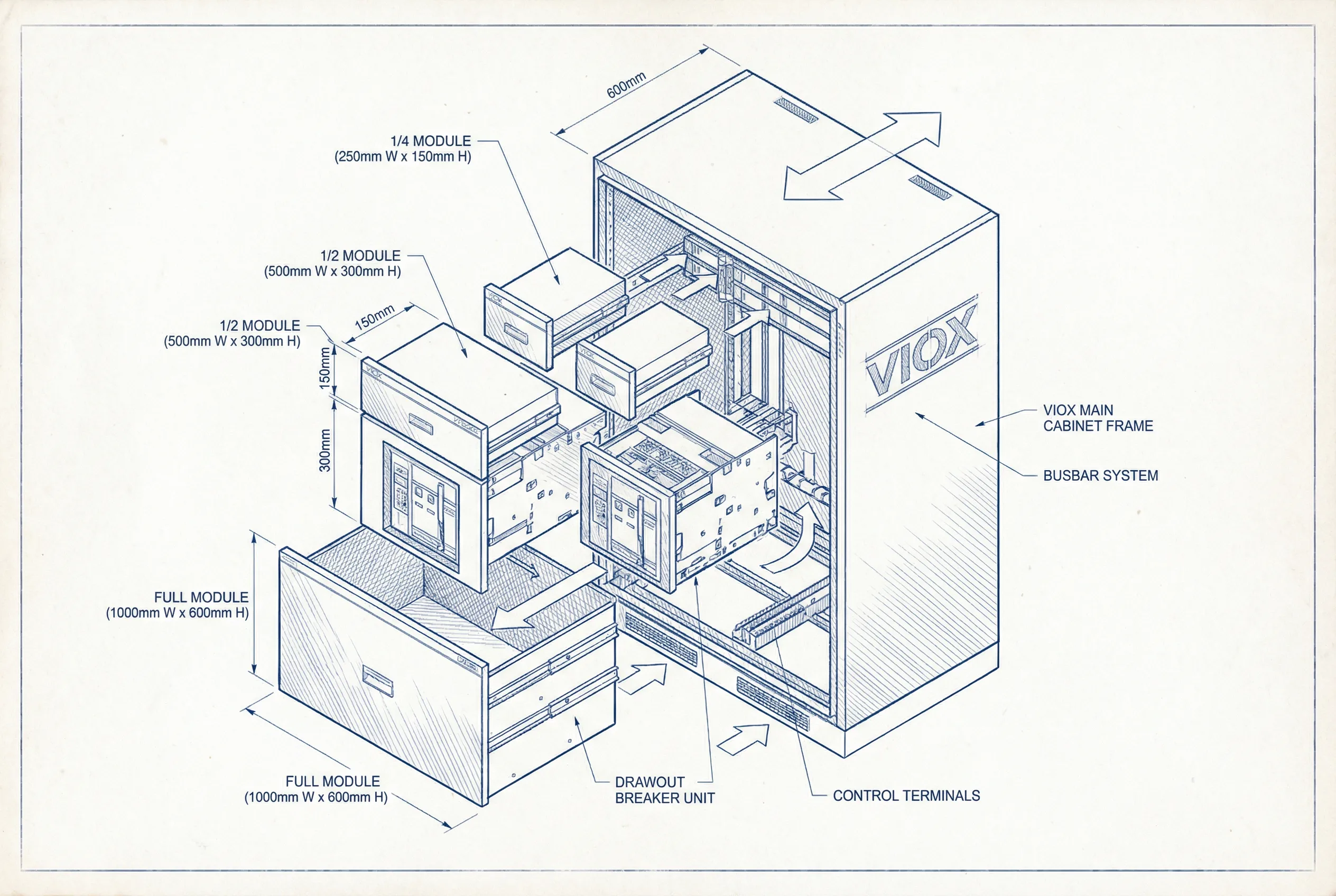
Structural Design
The GCS switchgear features significant improvements over earlier GCK designs:
Advanced Features:
- Horizontal busbar positioned at rear of cabinet
- Vertical busbar enclosed in flame-retardant plastic functional plates
- Improved drawer push-pull mechanism for smoother operation
- Five-compartment isolation: horizontal busbar, vertical busbar, functional units, cable room, and neutral/ground busbar
- C-profile steel framework with galvanized surface treatment
Applications
GCS switchgear excels in:
- Large-scale power distribution projects
- Power plants and substations
- Petrochemical facilities
- Heavy industrial motor control
- High-rise building distribution systems
- Applications requiring computer communication interfaces
Advantages and Limitations
Advantages:
- High technical performance competitive with imported products
- Enhanced safety with compartmentalized design
- Flexible electrical schemes and convenient combination
- Higher module density (1/2 module capability)
- Better dynamic and thermal stability
- Suitable for automation and monitoring systems
Limitations:
- Single-sided operation only (800mm depth)
- Higher cost than GCK
- 20mm module system vs. ABB’s 25mm
- Not suitable for double-sided maintenance applications
MNS Low-Voltage Withdrawable Switchgear: International ABB Standard
Model Designation Explained
MNS is an ABB product designation that has become widely adopted:
- Originally based on ABB’s modular switchgear technology
- The letters don’t follow Chinese naming conventions
- Represents a complete system design philosophy
Technical Specifications
MNS represents the highest specification among common low-voltage switchgear, manufactured under ABB technology transfer or license.
Key Parameters:
- Rated voltage: 400V/690V
- Maximum current capacity: 6300A (higher than GCS/GCK)
- Rated frequency: 50/60Hz
- Minimum drawer unit: 1/4 module (62.5mm height based on 25mm modulus)
- Maximum drawers: Up to 36 units per cabinet (with 1/4 modules)
- Cabinet depth: 600mm (single-sided) or 1000mm (double-sided operation)
- Protection class: IP40-IP54
Structural Excellence
The MNS switchgear system offers the most advanced structural design:
Premium Features:
- 25mm module system (E=25mm) enabling 1/4 module divisions
- Double-sided operation capability with 1000mm depth
- Superior compartmentalization with galvanized C-profile framework
- Advanced flame-retardant plastic functional boards
- Horizontal busbar at rear with complete isolation
- Premium drawer mechanism with smooth, precise operation
- Self-tapping locking screws or high-grade hexagon bolts
Applications
MNS switchgear is preferred for:
- Mission-critical power distribution in data centers
- Airports and transportation hubs
- Petrochemical and refining facilities
- Metallurgical and steel plants
- High-specification commercial buildings
- Applications requiring maximum reliability and flexibility
Advantages and Limitations
Advantages:
- Highest module flexibility (1/4 module capability)
- Double-sided operation option
- Superior build quality and materials
- Maximum circuit density per cabinet
- Best-in-class safety features
- Internationally recognized design standards
- Excellent for small current applications with many circuits
Limitations:
- Highest initial cost among all types
- Requires careful specification and planning
- More complex installation requirements
- May be overspecified for simple applications
Technical Comparison Table: GCK vs. GCS vs. MNS
| Feature | GCK | GCS | MNS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Design Origin | Early Chinese design | Senyuan (1990s) | ABB technology |
| Module System | 1 module (200mm) | 1/2 module (100mm) | 1/4 module (62.5mm) |
| Max Drawers | 8 full units | 22 half-module units | 36 quarter-module units |
| Busbar Position | Horizontal at top | Horizontal at rear | Horizontal at rear |
| Busbar Protection | No flame-retardant board | Flame-retardant boards | Premium flame-retardant boards |
| Cabinet Depth | 600mm | 800mm | 600mm or 1000mm |
| Operation Sides | Single-sided | Single-sided | Single or double-sided |
| Drawer Mechanism | Simple | Improved | Premium precision |
| Current Capacity | Up to 4000A | Up to 4000A | Up to 6300A |
| Typical Cost | Lower | Medium | Higher |
| Best Applications | Standard motor control | General industrial distribution | High-specification projects |
Specification Advantages and Disadvantages Summary
| Switchgear Type | Primary Advantages | Primary Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| XL-21 | Low cost, simple installation, wall-mounted | Requires shutdown for maintenance, limited circuits |
| GGD | Robust construction, high capacity, proven reliability | Occupies more space, fixed installation, no hot-swap |
| GCK | Withdrawable design, cost-effective, adequate for most applications | Top busbar position, older design, simpler mechanism |
| GCS | Good balance of cost and performance, rear busbar, flame-retardant protection | Single-sided only, smaller module than MNS |
| MNS | Maximum flexibility, double-sided option, highest specifications | Highest cost, may be overspecified for simple needs |
How to Select the Right Low-Voltage Switchgear for Your Project
When specifying low-voltage switchgear for your facility, consider these key factors:
1. Application Requirements
- Simple distribution needs: XL-21 or GGD may suffice
- Motor control centers: GCK, GCS, or MNS
- Mission-critical facilities: MNS preferred
2. Maintenance Philosophy
- Planned outage acceptable: Fixed types (XL-21, GGD)
- Minimize downtime: Withdrawable types (GCK, GCS, MNS)
3. Circuit Density Needs
- Few circuits: XL-21 or GGD
- Moderate density: GCK or GCS
- Maximum density: MNS with 1/4 modules
4. Budget Considerations
- Cost-sensitive projects: XL-21 or GGD
- Balanced approach: GCK or GCS
- Premium applications: MNS
5. Future Expansion
- Fixed capacity: GGD or XL-21
- Modular expansion: GCK, GCS, or MNS
6. International Standards Compliance
- Domestic standards: GGD, GCK, GCS acceptable
- International projects: MNS preferred
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the main difference between fixed and withdrawable low-voltage switchgear?
Fixed-type switchgear (XL-21, GGD) has permanently installed components that require power shutdown for maintenance. Withdrawable-type switchgear (GCK, GCS, MNS) uses removable drawer modules that can be hot-swapped, allowing maintenance without complete system shutdown. Withdrawable types offer greater flexibility and safety but come at higher initial cost.
Can I mix different switchgear types in the same electrical room?
Yes, but it’s generally recommended to separate different types. For example, you might use GGD for main incoming and distribution, and GCS or MNS for motor control centers. However, ensure proper coordination of protection devices and maintain clear documentation. Some manufacturers advise keeping PC (power distribution) and MCC (motor control) switchgear separate even within the same product family.
Which low-voltage switchgear type is best for motor control applications?
GCS and MNS are the preferred choices for motor control centers (MCC). GCS offers excellent value with good technical performance, while MNS provides the highest flexibility with 1/4 module divisions ideal for applications with many small motor circuits. GCK can also be used for cost-sensitive motor control projects. Avoid using fixed types (GGD, XL-21) for MCC applications.
How does the module size affect switchgear selection?
Module size determines circuit density and flexibility. GCK uses 1-module (200mm) units, GCS uses 1/2-module (100mm) units, and MNS uses 1/4-module (62.5mm) units. Smaller modules allow more circuits per cabinet. Choose GCK for larger loads and simpler layouts, GCS for balanced applications, and MNS when maximum circuit density is required for numerous small loads.
Are low-voltage switchgear systems compliant with international standards?
Most modern low-voltage switchgear complies with IEC 61439-1 (formerly IEC 439) and local standards such as GB7251 in China. GGD, GCK, and GCS primarily follow Chinese national standards with IEC compliance. MNS follows ABB’s international design standards and is widely accepted globally. Always verify specific certifications and standards compliance for your project requirements, especially for international installations.
What maintenance considerations should I plan for different switchgear types?
Fixed switchgear (GGD, XL-21) requires scheduled outages for maintenance and testing. Plan for annual or bi-annual shutdown periods. Withdrawable switchgear (GCK, GCS, MNS) enables drawer-by-drawer maintenance without full shutdown, but requires trained personnel familiar with proper isolation procedures. All types benefit from regular thermal imaging, connection torque checks, and cleaning. Budget for specialized testing equipment for withdrawable types and ensure spare drawer availability for critical circuits.
Conclusion
Understanding the designations GGD, GCK, GCS, MNS, and XL-21 is essential for making informed decisions about low-voltage switchgear procurement. Each type serves specific applications with distinct advantages:
- XL-21: Economical wall-mounted solution for simple distribution
- GGD: Robust fixed switchgear for main power distribution
- GCK: Cost-effective withdrawable design for standard applications
- GCS: Advanced Chinese withdrawable standard with excellent performance
- MNS: Premium ABB-based system for demanding applications
VIOX Electric manufactures comprehensive ranges of low-voltage switchgear meeting international standards. Our engineering team can assist with switchgear selection, customization, and integration to ensure your power distribution system meets performance, safety, and budgetary requirements.
For technical consultations and customized low-voltage switchgear solutions, contact VIOX Electric’s application engineering team to discuss your specific project requirements.


