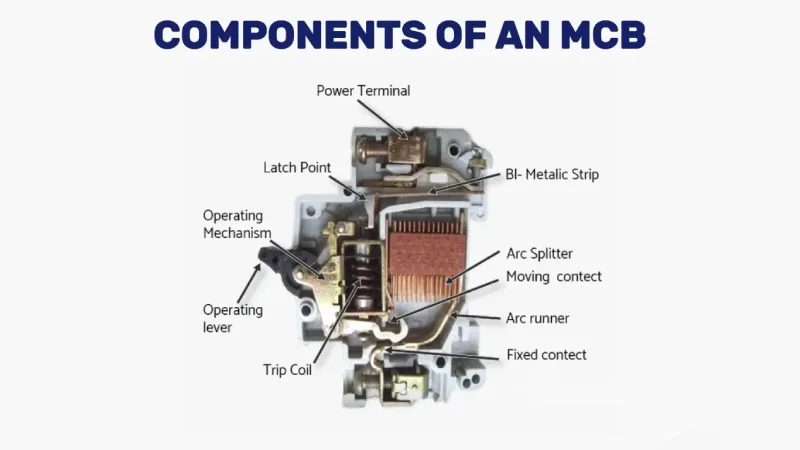
Un interruttore automatico magnetotermico (MCB) è un dispositivo di sicurezza elettrico ad azionamento automatico progettato per proteggere i circuiti elettrici da danni causati da corrente eccessiva derivante da sovraccarichi o cortocircuiti. A differenza dei fusibili tradizionali che devono essere sostituiti dopo l'attivazione, gli MCB possono essere ripristinati e riutilizzati, il che li rende la scelta preferita per le moderne installazioni elettriche residenziali, commerciali e industriali.
Comprendere gli MCB è fondamentale per la sicurezza elettrica, la conformità alle normative e per prendere decisioni informate sulla protezione del proprio sistema elettrico. Questa guida completa copre tutto ciò che è necessario sapere sugli MCB, dal funzionamento di base ai criteri di selezione professionali.
Cosa rende un MCB diverso dagli altri dispositivi di protezione del circuito?
MCB vs. Fusibile vs. RCD: Differenze chiave
| Funzione | MCB | Fusibile | RCD/GFCI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tipo Di Protezione | Sovracorrente (sovraccarico + cortocircuito) | Solo sovracorrente | Dispersione verso terra/guasto a terra |
| Metodo di ripristino | Reset manuale dell'interruttore | Sostituire il filo/cartuccia del fusibile | Pulsante di ripristino manuale |
| Il Tempo Di Risposta | Istantaneo per cortocircuiti | Varia in base al tipo di fusibile | 25-40 millisecondi |
| Riutilizzabilità | Reset illimitati | Solo per uso singolo | Reset illimitati |
| Installazione | A scatto nel pannello | A vite o a cartuccia | Cablato in serie |
| Costo | Iniziale più alto, a lungo termine più basso | Iniziale più basso, sostituzione più alta | Costo iniziale più alto |
| Precisione | Caratteristiche di intervento precise | Meno preciso | Altamente sensibile |
Perché gli MCB sono superiori per le applicazioni moderne
Funzionalità di sicurezza avanzate:
- Caratteristiche di intervento precise prevengono interventi intempestivi
- Indicazione visiva dello stato di intervento
- Tecnologia di estinzione dell'arco per un'interruzione sicura
- Funzionamento indipendente dalla temperatura
Vantaggi economici:
- Nessun costo di sostituzione dopo l'attivazione
- Tempi di inattività ridotti grazie alla rapidità reset
- Minori requisiti di manutenzione
- Durata prolungata (tipicamente 20+ anni)
Esperto Suggerimento: Sebbene gli MCB costino inizialmente di più rispetto ai fusibili, in genere si ripagano entro 2-3 attivazioni grazie all'eliminazione dei costi di sostituzione e alla riduzione dei tempi di inattività.
Come funzionano gli interruttori automatici magnetotermici?
Principio di funzionamento
Gli MCB operano su due meccanismi di protezione principali:
- Protezione termica (sovraccarico)
- La striscia bimetallica si riscalda durante una sovracorrente prolungata
- La striscia si piega e rilascia il meccanismo di intervento
- Fornisce caratteristiche di tempo inverse (corrente più alta = intervento più rapido)
- Protezione magnetica (cortocircuito)
- La bobina elettromagnetica crea un campo magnetico durante un'elevata corrente di guasto
- La forza magnetica rilascia istantaneamente il meccanismo di intervento
- Fornisce protezione istantanea per i cortocircuiti
Caratteristiche di intervento spiegate
| Livello attuale | Tempo di viaggio | Metodo di protezione |
|---|---|---|
| 100-113% della corrente nominale | Nessun intervento (tolleranza) | Nessuno |
| 113-145% della corrente nominale | 1+ ore | Termica |
| 145-300% della corrente nominale | 1-60 minuti | Termica |
| 300%+ della corrente nominale | Istantaneo | Magnetico |
Avviso Di Sicurezza: Non tentare mai di modificare o bypassare le caratteristiche di intervento dell'MCB. Ciò può causare rischi di incendio, danni alle apparecchiature e violazioni delle normative.
Tipi di MCB e loro applicazioni
Tipi di MCB in base alle caratteristiche di intervento
MCB di tipo B (3-5 volte la corrente nominale)
- Ideale per: Circuiti residenziali, illuminazione, prese generali
- Autonomia del viaggio: 3-5 × In (corrente nominale)
- Applicazioni: Case, uffici, attività commerciali leggere
- Conformità al codice: Incontra NEC Requisiti dell'articolo 240
MCB di tipo C (5-10 volte la corrente nominale)
- Ideale per: Circuiti motore, trasformatori, illuminazione fluorescente
- Autonomia del viaggio: 5-10 × In
- Applicazioni: Apparecchiature HVAC, macchinari industriali
- Caratteristica speciale: Gestisce le correnti di avviamento del motore
MCB di tipo D (10-20 volte la corrente nominale)
- Ideale per: Attrezzature industriali pesanti, saldatrici
- Autonomia del viaggio: 10-20 × In
- Applicazioni: Grandi motori, trasformatori, processi industriali
- Requisito: In genere richiede una valutazione ingegneristica
Valori nominali e capacità di corrente degli MCB
| Corrente nominale (A) | Applicazioni Tipiche | Dimensione del filo (AWG) | Tipo di pannello |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6-10A | Circuiti di illuminazione | 14-12 | Residenziale |
| 15-20A | Prese generali, piccoli elettrodomestici | 12-10 | Residenziale/Commerciale |
| 25-30A | Grandi elettrodomestici, HVAC | 10-8 | Residenziale/Commerciale |
| 40-63A | Sottoquadri, grandi apparecchiature | 8-4 | Commerciale/industriale |
| 80-100A | Alimentatori principali, grandi carichi | 4-2/0 | Industriale |
Criteri di selezione MCB: Come scegliere l'MCB giusto
Processo di selezione passo dopo passo
Fase 1: determinare i requisiti di carico
- Calcola il carico totale del circuito (watt ÷ voltaggio = amperaggio)
- Aggiungi un margine di sicurezza del 25% per carichi continui
- Considerare le future esigenze di espansione
- Controlla la massima portata del cavo
Passaggio 2: Seleziona il tipo appropriato
- Tipo B: La maggior parte delle applicazioni residenziali e commerciali leggere
- Tipo C: Carichi motore e apparecchiature induttive
- Tipo D: Solo applicazioni industriali pesanti
Passaggio 3: verificare la conformità del codice
- Assicurarsi che la corrente nominale corrisponda alla portata del cavo (NEC Tabella 310.15(B)(16))
- Conferma AFCI/GFCI requisiti per luoghi specifici
- Controlla le modifiche e i requisiti locali
Passaggio 4: Considera le caratteristiche speciali
- Funzionalità di interruttore di circuito per guasto da arco (AFCI)
- Protezione con interruttore di circuito per guasto a terra (GFCI)
- Funzionalità smart/connesse per il monitoraggio
Criteri di selezione professionale
Considerazioni sulla sicurezza:
- Non sovradimensionare mai la corrente nominale dell'MCB oltre la capacità del cavo
- Considera la riduzione della potenza in base alla temperatura ambiente
- Valuta la corrente di guasto disponibile nel punto di installazione
- Assicurare un coordinamento adeguato con la protezione a monte
Indicatori di qualità:
- Elenco UL 489 per il Nord America
- IEC 60898 conformità agli standard internazionali
- Produttore reputazione e termini di garanzia
- Capacità di interruzione adeguata per l'installazione
Esperto Suggerimento: Consultare sempre i codici elettrici locali e prendere in considerazione l'assunzione di un elettricista autorizzato per la selezione dell'MCB in applicazioni commerciali o residenziali complesse.
Linee guida per l'installazione e la manutenzione dell'MCB
Requisiti per l'installazione
Lista di controllo pre-installazione:
- [ ] Verificare che l'alimentazione sia spenta e bloccata
- [ ] Confermare la compatibilità dell'MCB con il produttore del pannello
- [ ] Controllare le distanze adeguate secondo NEC 110.26
- [ ] Assicurare una corretta messa a terra e collegamento equipotenziale
- [ ] Verificare che i collegamenti dei cavi siano saldi e sicuri
Fasi di installazione:
- Disattivare l'alimentazione principale al pannello di servizio
- Rimuovere il coperchio del pannello seguendo le procedure di sicurezza
- Inserire l'MCB nello slot appropriato (design a scatto)
- Collegare il cavo del circuito al terminale MCB (solo cavo caldo)
- Verificare il collegamento sicuro con un delicato test di trazione
- Etichettare il circuito in modo chiaro e permanente
- Operazione di prova prima di eccitare il circuito
Manutenzione e test
Ispezione visiva mensile:
- Controllare se ci sono segni di surriscaldamento (scolorimento, odore di bruciato)
- Verificare che tutte le etichette siano leggibili e accurate
- Cercare collegamenti allentati o corrosione
- Assicurarsi che l'accesso al pannello sia libero e non ostruito
Procedura di test annuale:
- Spegnere il circuito sull'MCB
- Testare il funzionamento premendo il pulsante di test (se presente)
- Far scattare e ripristinare manualmente l'MCB
- Verificare il corretto funzionamento e l'innesto positivo
- Verificare la funzione del circuito dopo il ripristino
Avviso Di Sicurezza: Se un MCB scatta ripetutamente, non continuare a ripristinarlo. Ciò indica un grave problema elettrico che richiede l'immediata attenzione di un professionista.
Risoluzione dei problemi comuni dell'MCB
L'MCB continua a scattare
Possibili cause e soluzioni:
| Problema | Causa Probabile | Soluzione |
|---|---|---|
| Viaggio immediato su reset | Cortocircuito | Chiama immediatamente un elettricista |
| Scatta dopo pochi minuti | Condizione di sovraccarico | Ridurre il carico del circuito |
| Casuale di intervento | Collegamenti allentati | Stringere tutti i collegamenti |
| Scatta durante l'avviamento del motore | Tipo di MCB errato | Passa a un MCB di tipo C |
L'MCB non si ripristina
Passaggi per la risoluzione dei problemi:
- Assicurarsi che l'MCB sia completamente OFF prima di tentare il ripristino
- Verificare la presenza di danni visibili all'alloggiamento dell'MCB
- Verificare che non ci siano fili allentati nel pannello
- Testare con un MCB funzionante, se disponibile
- Sostituire l'MCB se si sospetta un guasto meccanico
Soluzioni per lo scatto intempestivo
Soluzioni comuni:
- Illuminazione fluorescente: Utilizzare un MCB di tipo C invece di un tipo B
- Circuiti motore: Verificare il metodo di avviamento corretto e il tipo di MCB
- Carichi elettronici: Considerare MCB specializzati per carichi non lineari
- Molteplici piccoli carichi: Controllare il calcolo dell'amperaggio totale del circuito
Sicurezza e conformità al codice
Requisiti del Codice elettrico nazionale (NEC)
Articoli chiave del NEC per gli MCB:
- Articolo 240: Requisiti di protezione da sovracorrente
- Articolo 210: Requisiti del circuito derivato
- Articolo 408: Requisiti per quadri e pannelli di distribuzione
- Articolo 110: Requisiti generali per le installazioni elettriche
Punti critici di conformità:
- La corrente nominale dell'MCB non deve superare la capacità di corrente del cavo
- Protezione AFCI richiesta nella maggior parte delle aree residenziali
- Protezione GFCI richiesta in luoghi umidi/bagnati
- Etichettatura e identificazione corrette obbligatorie
Migliori pratiche di sicurezza
Cose da fare:
- Utilizzare sempre le procedure di lockout/tagout
- Testare gli MCB annualmente o dopo qualsiasi lavoro elettrico
- Mantenere i pannelli elettrici puliti e accessibili
- Utilizzare solo accessori approvati dal produttore
- Mantenere distanze adeguate attorno ai pannelli
Cose da non fare:
- Non utilizzare mai gli MCB come interruttori per il funzionamento di routine
- Non ignorare le condizioni di scatto ripetute
- Non modificare o manomettere mai i meccanismi degli MCB
- Non utilizzare il tipo di MCB errato per l'applicazione
- Non installare mai MCB oltre la loro capacità di interruzione
Raccomandazione professionale: Per qualsiasi lavoro elettrico che vada oltre la semplice sostituzione dell'MCB, consultare un elettricista autorizzato per garantire la conformità al codice e la sicurezza.
Guida Di Riferimento Rapido
Tabella di selezione rapida MCB
| Applicazione | Tipo di MCB | Valore nominale tipico | Requisiti speciali |
|---|---|---|---|
| Circuiti di illuminazione | Tipo B | 15-20A | AFCI in camere da letto/zone giorno |
| Prese generali | Tipo B | 15-20A | GFCI in luoghi umidi |
| Elettrodomestici da cucina | Tipo B | 20A | GFCI per prese da banco |
| Apparecchiature HVAC | Tipo C | Per apparecchiatura | Dimensionato secondo le specifiche del produttore |
| Motori (generale) | Tipo C | 125% corrente a pieno carico del motore (FLA) | Considerare il metodo di avviamento del motore |
| Saldatura/industriale | Tipo D | Secondo il calcolo del carico | Richiesta valutazione ingegneristica |
Informazioni di contatto di emergenza
Quando chiamare un elettricista:
- L'MCB scatta immediatamente dopo il ripristino
- Odore di bruciato o danni visibili
- Più MCB che scattano contemporaneamente
- Installazione di nuovi circuiti
- Aggiornamenti o modifiche del pannello
Domande Frequenti
Qual è la differenza tra un interruttore automatico e un MCB?
Un MCB è un tipo specifico di interruttore automatico progettato per correnti nominali inferiori (tipicamente fino a 100 A) in applicazioni residenziali e commerciali leggere. Tutti gli MCB sono interruttori automatici, ma non tutti gli interruttori automatici sono MCB.
Quanto durano in genere gli MCB?
Gli MCB di qualità durano in genere 20-30 anni con una corretta manutenzione. Tuttavia, devono essere testati annualmente e sostituiti se mostrano segni di usura, non superano i test o sono stati sottoposti a molteplici condizioni di guasto.
Posso sostituire un fusibile con un MCB?
Sì, ma richiede la modifica o la sostituzione del pannello. Gli MCB e i fusibili hanno sistemi di montaggio diversi, quindi di solito è necessario un nuovo pannello progettato per gli MCB. Questo lavoro deve essere eseguito da un elettricista qualificato.
Perché il mio MCB scatta quando accendo determinati apparecchi?
Questo di solito indica un circuito sovraccarico o un apparecchio con un'elevata corrente di spunto (come i motori). La soluzione potrebbe essere l'aggiornamento a un MCB di tipo C, l'utilizzo di un circuito dedicato o la manutenzione dell'apparecchio.
È sicuro ripristinare un MCB scattato?
Sì, se rimane ripristinato e non scatta di nuovo immediatamente. Tuttavia, se un MCB scatta ripetutamente, non continuare a ripristinarlo: questo indica un problema serio che richiede l'attenzione di un professionista.
Qual è la differenza tra i tipi B, C e D di MCB?
La differenza sta nelle loro caratteristiche di intervento magnetico: il tipo B interviene a 3-5 volte la corrente nominale, il tipo C a 5-10 volte e il tipo D a 10-20 volte. Questo determina la quantità di sovracorrente temporanea che possono gestire prima di intervenire.
Gli MCB proteggono dalle scosse elettriche?
No, gli MCB standard proteggono solo dalle sovracorrenti. Per la protezione contro le scosse elettriche, è necessaria la protezione GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter) o RCD (Residual Current Device), che può essere combinata con gli MCB in alcuni prodotti.
Come faccio a sapere di quale dimensione di MCB ho bisogno?
La dimensione dell'MCB deve corrispondere alla portata del cavo del circuito e ai requisiti di carico. Per un circuito da 15 A con cavo 14 AWG, utilizzare un MCB da 15 A. Non utilizzare mai un MCB più grande di quanto il cavo possa gestire in sicurezza.
Consulenza di esperti disponibile: Per progetti elettrici complessi, aggiornamenti del pannello o problemi di sicurezza, consultare sempre un elettricista qualificato che possa garantire un'installazione corretta, la conformità alle normative e la sicurezza ottimale per la propria applicazione specifica.
Correlati
Che cosa è acceso e spento in MCB
Guida completa ai simboli degli interruttori automatici
Come sapere se l'interruttore automatico è difettoso
7 segnali critici che indicano che l'interruttore automatico dell'aria sta cedendo