Selecting the correct 50 amp wire size is a critical decision in electrical system design, directly impacting safety, code compliance, and equipment performance. For B2B contractors, facility managers, and industrial electricians, understanding the nuances of the National Electrical Code (NEC) regarding conductor sizing is essential to preventing overheating, voltage drop, and potential fire hazards.
At VIOX Electric, we manufacture high-performance electrical equipment designed to meet rigorous industrial standards. This guide details the technical requirements for sizing conductors for 50-amp circuits, ensuring your installations are safe, compliant, and built to last.
The Standard: What Size Wire Do I Need for a 50 Amp Breaker?
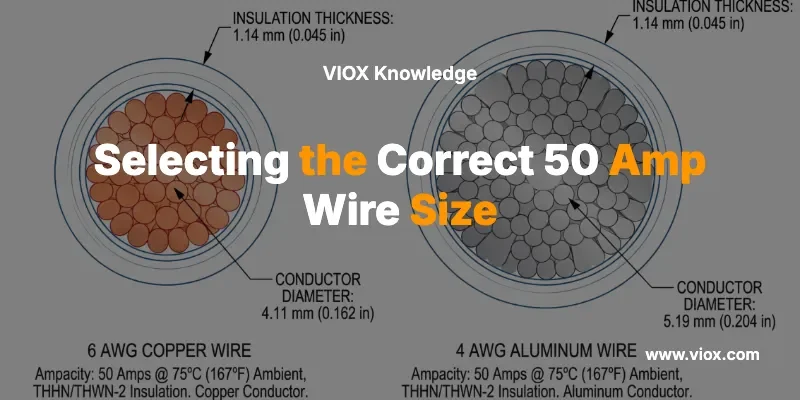
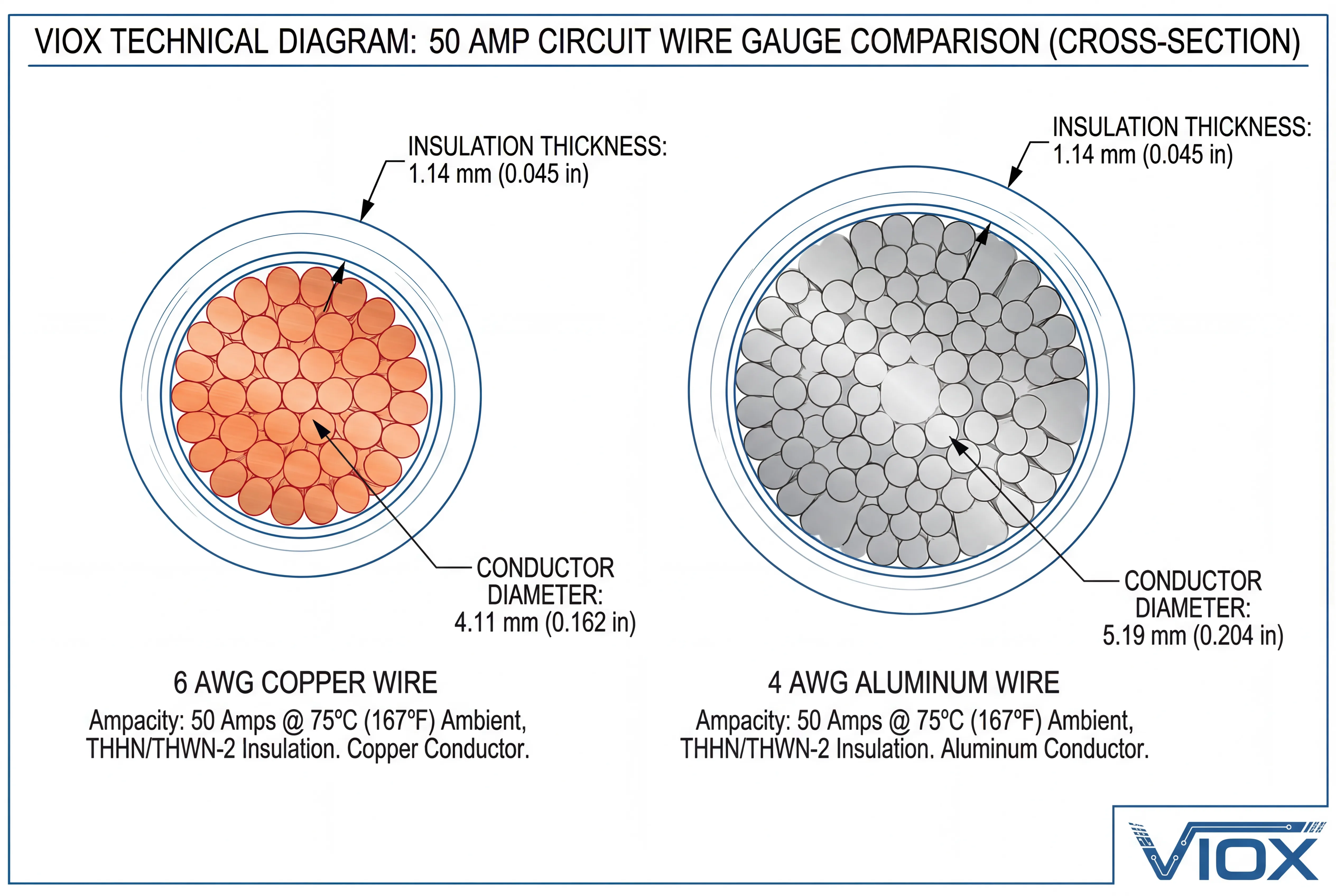
For most standard installations, the correct wire size for a 50 amp breaker is 6 AWG copper wire or 4 AWG aluminum wire.
While specific variables such as distance, temperature, and conduit fill can alter this requirement, these gauges represent the industry standard for safe operation under typical conditions.
Quick Reference: 50 Amp Wire Size
| Conductor Material | Minimum Wire Size (AWG) | NEC Temperature Rating |
|---|---|---|
| Copper | 6 AWG | 75°C (Standard Terminations) |
| Aluminum | 4 AWG | 75°C (Standard Terminations) |
Using wire smaller than these recommendations (such as 8 AWG copper) is often a point of confusion. While 8 AWG copper is rated for 50 amps at 75°C in the NEC tables, it leaves zero margin for error. Most professional engineers and electricians specify 6 AWG copper to account for voltage drop, continuous loading, and thermal dissipation, ensuring a robust safety margin for VIOX equipment and other critical machinery.
NEC Requirements and Ampacity Explained
To accurately determine the 50 amp wire size, professionals must refer to NEC Table 310.16 (formerly Table 310.15(B)(16)). This table dictates the allowable ampacity of insulated conductors based on material and temperature ratings.
Understanding Temperature Columns (60°C vs. 75°C vs. 90°C)
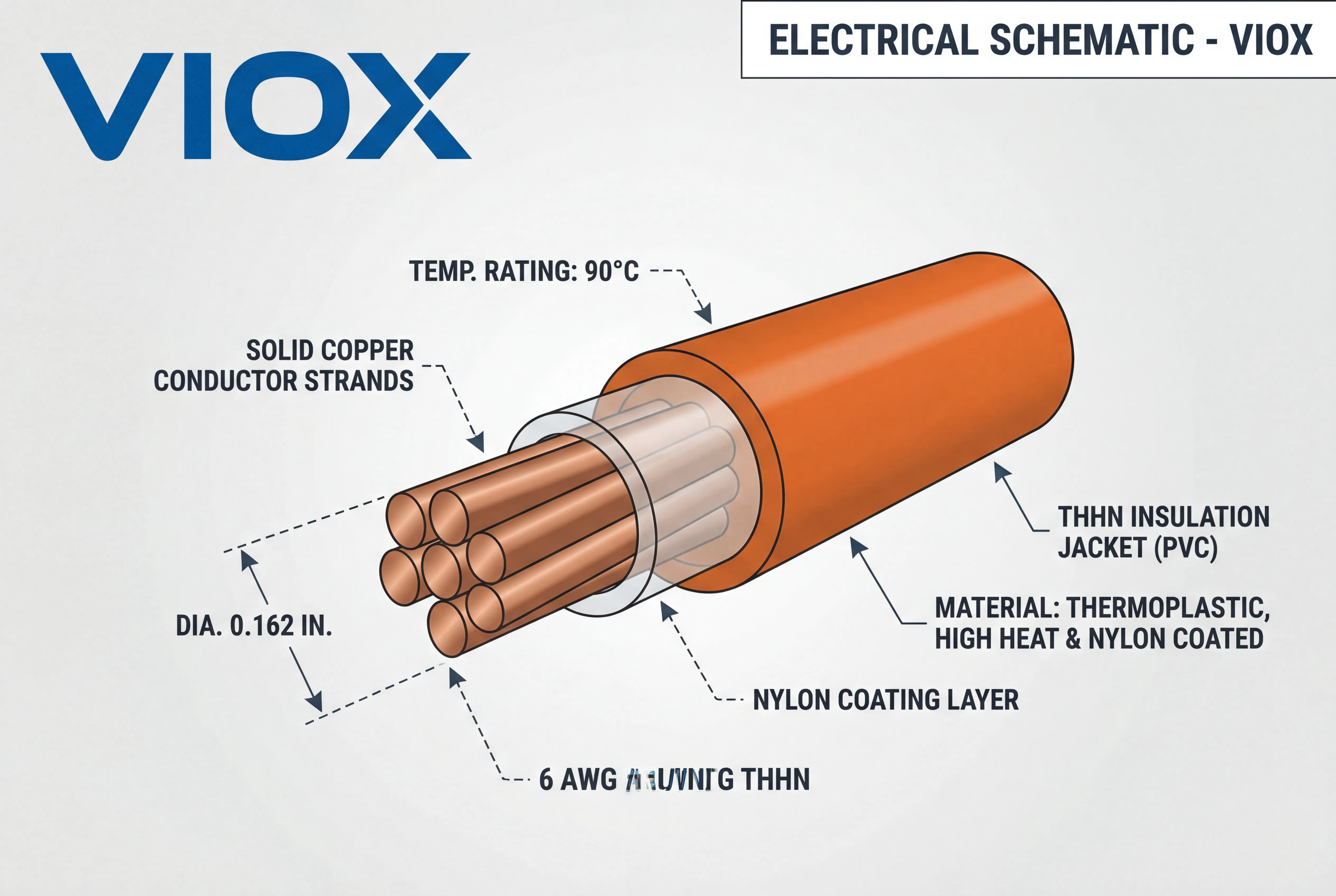
Wire insulation types (like THHN/THWN-2) are often rated for 90°C. However, the weakest link rule applies:
- Terminations: Most circuit breakers, including industrial VIOX breakers, and equipment terminals are rated for 75°C.
- Result: Even if you use 90°C wire, you must use the ampacity listed in the 75°C column to match the termination rating.
Detailed Ampacity Comparison Table
The following table breaks down the ampacity ratings for common wire gauges relevant to 50-amp circuits.
| Wire Size (AWG) | Copper (75°C Rating) | Aluminum (75°C Rating) | Suitability for 50A Breaker |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8 AWG | 50 Amps | 40 Amps | Copper: Minimum allowed (often undersized). Al: Unsafe. |
| 6 AWG | 65 Amps | 50 Amps | Copper: Ideal/Standard. Al: Minimum allowed. |
| 4 AWG | 85 Amps | 65 Amps | Copper: Oversized (Good for long runs). Al: Ideal/Standard. |
Note: Data derived from NEC Table 310.16. Always verify local codes.
Critical Factors Affecting Wire Selection
Simply picking a wire gauge based on the breaker size is not enough. Several environmental and installation factors can derate the capacity of your conductors, requiring you to upsize to maintain the 50 amp wire size requirements.
1. Voltage Drop (Distance)
For long wire runs, electrical resistance causes voltage to drop. The NEC recommends keeping voltage drop below 3% for branch circuits to ensure equipment operates efficiently. If your run is longer than 100 feet, you typically need to increase the wire size.
Voltage Drop Sizing Chart (240V Circuit @ 40A Load)
| Wire Length (Feet) | Recommended Copper Wire Size | Voltage Drop % |
|---|---|---|
| 0 – 100 ft | 6 AWG | < 1.5% |
| 100 – 150 ft | 4 AWG | < 1.8% |
| 150 – 250 ft | 3 AWG | < 2.5% |
| 250+ ft | 2 AWG or larger | Consult Calculator |
2. Ambient Temperature
High ambient temperatures reduce a wire’s ability to dissipate heat. If you are installing VIOX distribution equipment in a hot industrial facility, boiler room, or attic where temperatures exceed 86°F (30°C), you must apply NEC correction factors. This often necessitates upsizing from 6 AWG to 4 AWG copper.
3. Continuous Loads (The 80% Rule)
The NEC defines a continuous load as one that runs for 3 hours or more (e.g., EV chargers, industrial lighting, data center cooling).
- Rule: Circuit breakers and conductors should be sized at 125% of the continuous load.
- Calculation: For a 50A breaker, the maximum continuous load is 40 Amps (50A × 0.80).
- Implication: If your actual continuous load is 50 Amps, you do not use a 50A breaker. You require a 62.5A capacity (50A × 1.25), meaning you would install a standard 70 Amp breaker and size wire accordingly (likely 4 AWG copper).
Common Applications for 50 Amp Circuits
Different equipment imposes different demands on electrical infrastructure. Here is how wire sizing applies to common industrial and commercial use cases.
Electric Vehicle (EV) Chargers
Level 2 EV chargers are classified as continuous loads.
- Requirement: A 40A charger requires a 50A breaker.
- Wire Size: Must use 6 AWG Copper. Using 8 AWG is dangerous due to the sustained heat generation over hours of charging. Hardwiring is preferred over receptacles for durability.
Industrial Machinery & Welders
Heavy-duty motors and welders often have high inrush currents. While standard 50 amp wire sizing (6 AWG Cu) applies, always check the machine’s nameplate for Minimum Circuit Ampacity (MCA). Some welders allow for smaller wires due to low duty cycles, but B2B best practices suggest sticking to the standard size for versatility.
Commercial Ranges and Ovens
Commercial kitchens require robust power delivery. For a 50-amp range circuit:
- Wire: 6 AWG Copper or 4 AWG Aluminum.
- Connection: Often utilizes a NEMA 14-50R receptacle. Ensure the neutral conductor is sized correctly if the appliance utilizes 120V components (timers, lights).
Installation Best Practices for VIOX Equipment
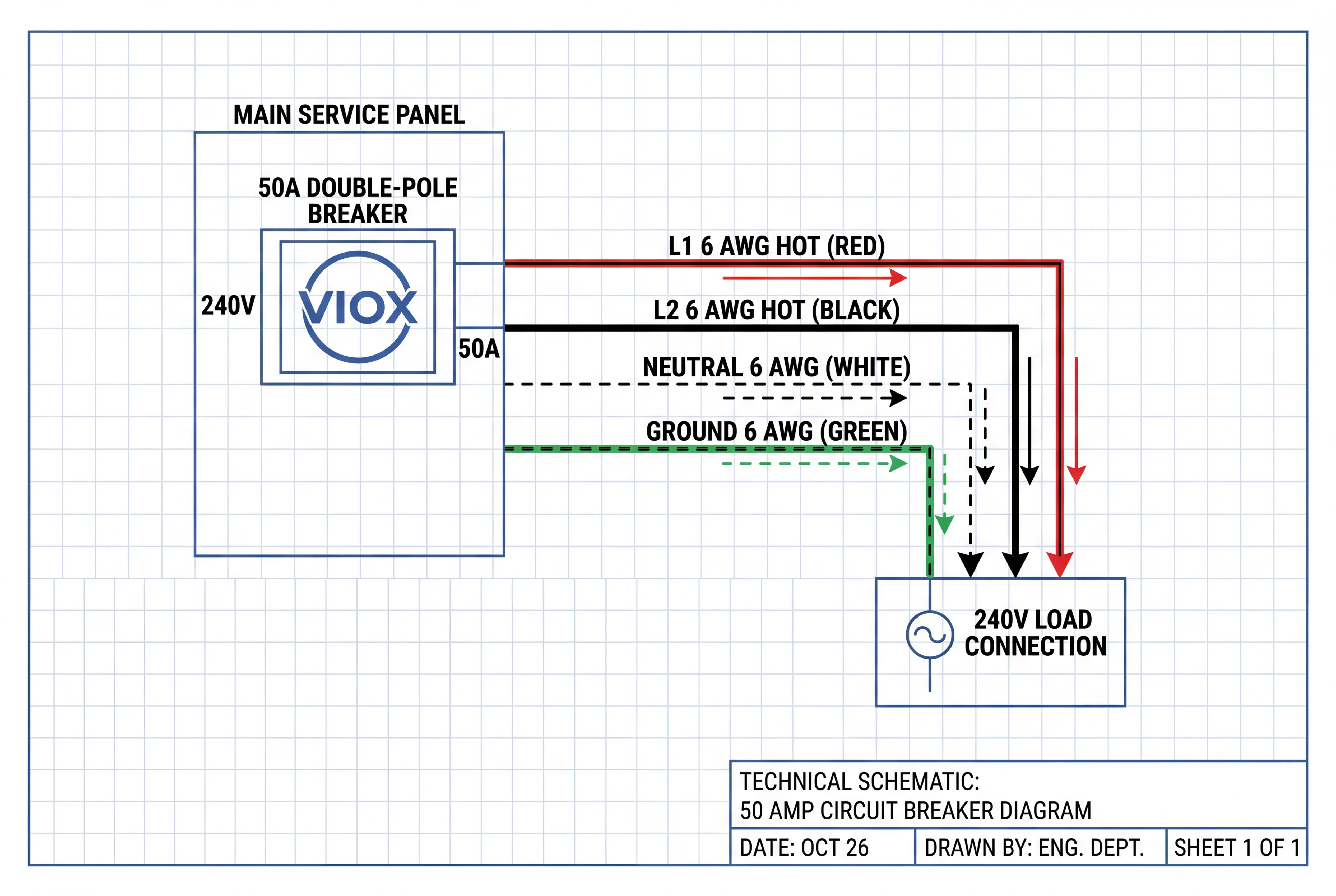
When installing VIOX breakers and panels, adhering to strict installation protocols ensures longevity and safety.
- Conduit Fill: When running multiple 50-amp circuits in a single conduit, you must derate ampacity. For example, 4-6 current-carrying conductors in a pipe require an 80% adjustment factor.
- Torque Terminations: Loose connections are a leading cause of electrical failure. Always torque the lugs on the 50 amp breaker to the manufacturer’s specifications (typically measured in inch-pounds) to prevent arcing and overheating.
- Grounding: For a 50-amp circuit, use a minimum 10 AWG copper equipment grounding conductor (per NEC Table 250.122).
- Wire Type: Use stranded wire (THHN/THWN-2) for conduit runs as 6 AWG solid wire is extremely difficult to pull.
FAQ: 50 Amp Wire Sizing
Q: Can I use 8 gauge wire for a 50 amp breaker?
A: Technically, 8 AWG copper (rated 50A at 75°C) meets the bare minimum NEC requirement for non-continuous loads. However, it is not recommended for most applications due to lack of safety margin. 6 AWG copper is the professional standard.
Q: Does a 50 amp breaker require a neutral wire?
A: It depends on the load. A purely 240V load (like a water heater or welder) requires two hot wires and a ground (3 wires total). A 120/240V load (like a dryer, range, or RV outlet) requires two hots, a neutral, and a ground (4 wires total).
Q: What is the maximum wattage for a 50 amp circuit?
A: At 240 Volts, a 50 amp circuit provides 12,000 Watts of power (Volts × Amps). For continuous loads (limited to 40A), the maximum safe wattage is 9,600 Watts.
Q: Can I use aluminum wire for a 50 amp EV charger?
A: While 4 AWG aluminum is rated for 50 amps, many EV charger manufacturers and NEMA 14-50 receptacles specify copper wire only. Aluminum expands and contracts more than copper, which can loosen connections in high-load charging cycles. Always check the charger’s terminal rating.
Q: What size ground wire do I need for a 50 amp circuit?
A: According to NEC Table 250.122, a 10 AWG copper or 8 AWG aluminum equipment grounding conductor is required for a 50 amp overcurrent device.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only. Electrical work entails significant risk. Always consult the National Electrical Code (NEC) and hire a licensed professional electrician for installation. VIOX Electric assumes no liability for work performed based on this guide.