O seu painel elétrico está cheio. Precisa de adicionar outro circuito para um novo quarto, tomada de cozinha ou oficina - mas não há onde o colocar. Antes de chamar um eletricista para orçamentar uma atualização de painel de €1.200 a €3.000, considere os disjuntores tandem. Estes engenhosos dispositivos de poupança de espaço permitem-lhe encaixar dois circuitos independentes de 120 volts num único slot de disjuntor, duplicando efetivamente a capacidade do seu painel sem o custo ou interrupção de uma substituição completa.
Mas aqui está o problema: nem todos os painéis podem usá-los. Instalar um disjuntor tandem no tipo de painel errado cria sérios riscos de incêndio, violações de código e inspeções reprovadas. A diferença entre uma atualização segura e um atalho perigoso muitas vezes resume-se a entender um detalhe crítico: Classificações CTL e compatibilidade do painel.
Este guia explica o que são os disjuntores tandem, como funcionam, quando são seguros de usar e quando as alternativas fazem mais sentido. Quer seja um proprietário a realizar uma renovação ou um eletricista a especificar disjuntores para um trabalho de modernização, aprenderá as normas técnicas que determinam a compatibilidade - e os passos práticos para garantir que a sua instalação permanece em conformidade com o código e segura.
1: COMPREENDER OS DISJUNTORES TANDEM - OS FUNDAMENTOS
O que é um Disjuntor Tandem?
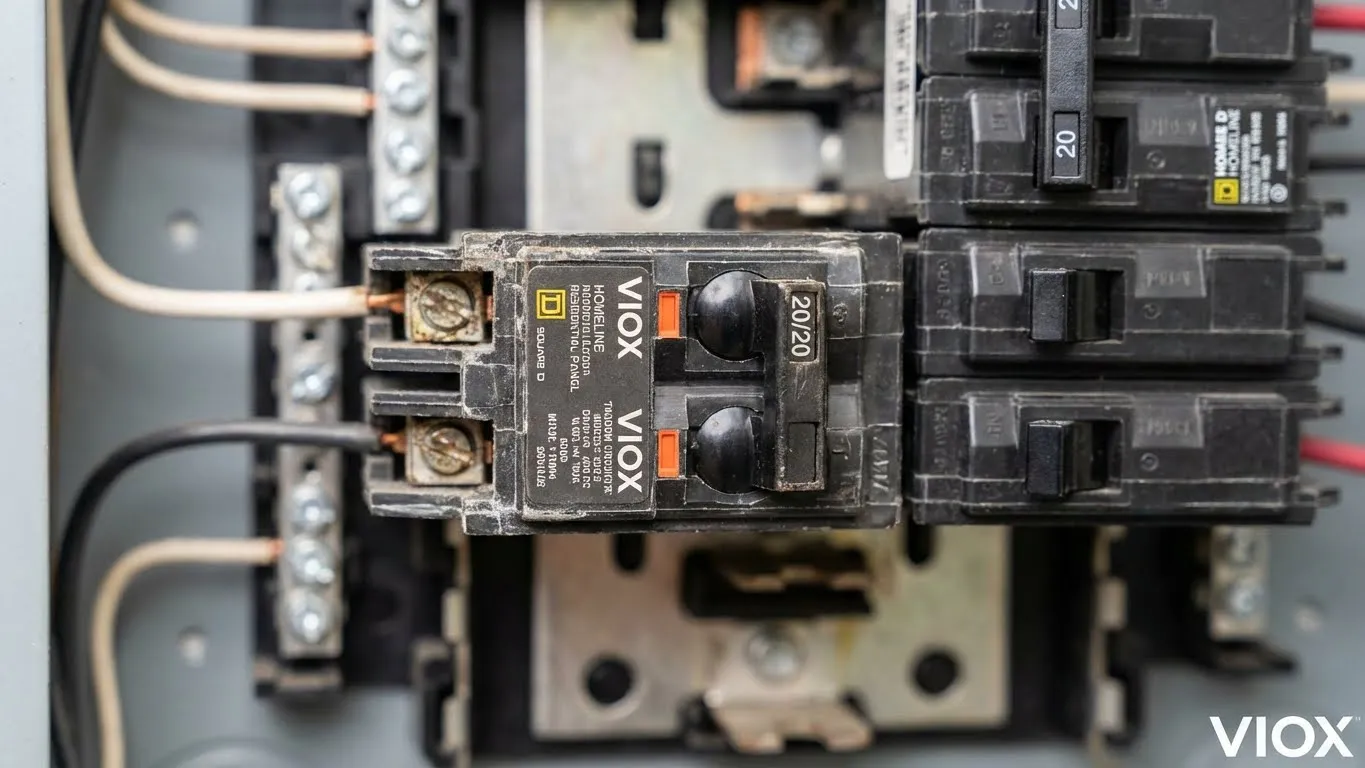
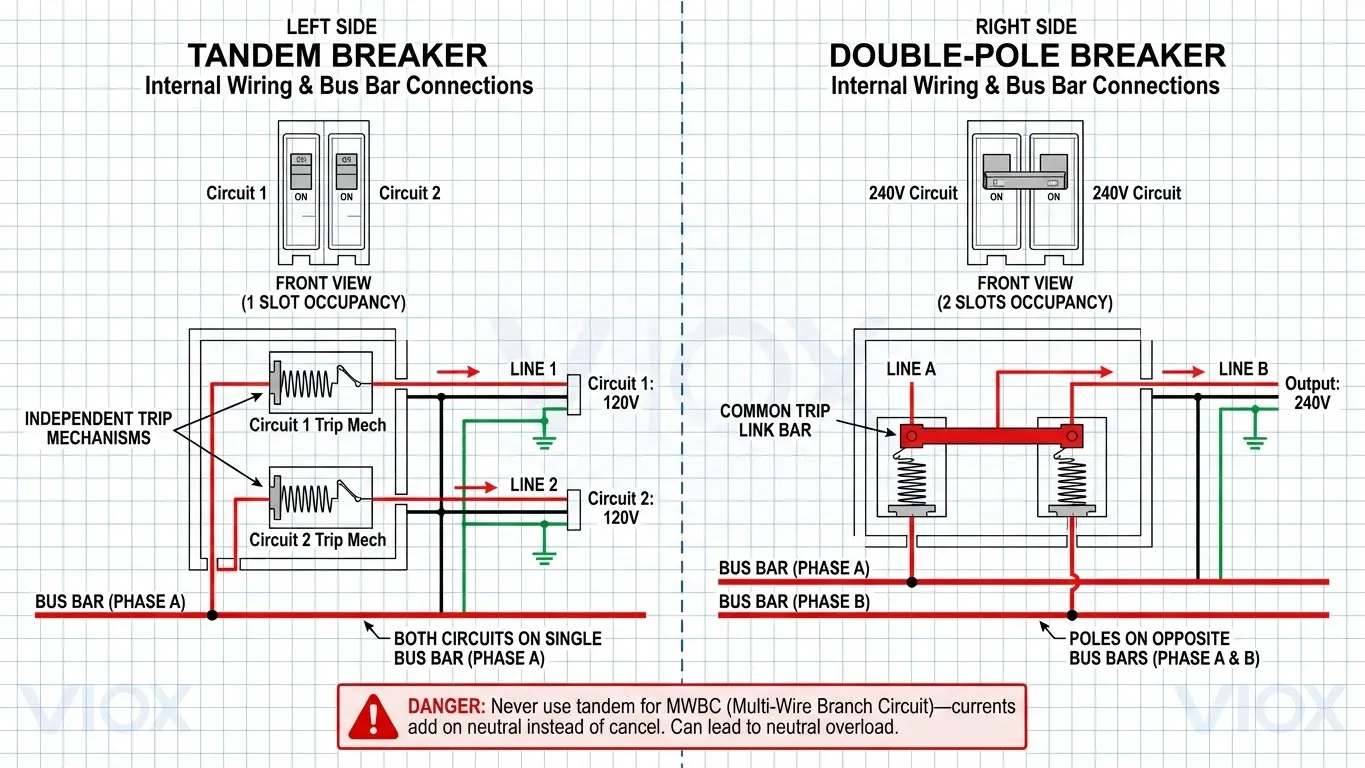
Um disjuntor tandem é um dispositivo elétrico especializado que aloja dois disjuntores independentes dentro de uma única caixa de disjuntor de largura padrão. Também conhecidas como disjuntores duplex, duplos, piggyback ou “double-stuff”, estas unidades ocupam apenas um slot no seu painel elétrico, proporcionando proteção completa para dois circuitos separados de 120 volts.
Ao contrário dos disjuntores monopolares padrão que protegem um circuito, ou dos disjuntores bipolares que fornecem 240 volts através de dois polos, os disjuntores tandem conectam-se apenas a um polo da barra de barramento do seu painel elétrico. Esta conexão monofásica é crucial - ambos os circuitos recebem 120 volts independentemente da mesma fase elétrica, e cada um mantém o seu próprio mecanismo de disparo. Se um circuito sofrer uma sobrecarga ou curto-circuito, apenas esse disjuntor específico dispara, enquanto o outro continua a funcionar normalmente.
Como Funcionam os Disjuntores Tandem: Arquitetura Interna
A magia de um disjuntor tandem reside no seu design interno compacto. Cada unidade contém dois mecanismos de comutação distintos alojados lado a lado numa única estrutura. Eis o que os faz funcionar:
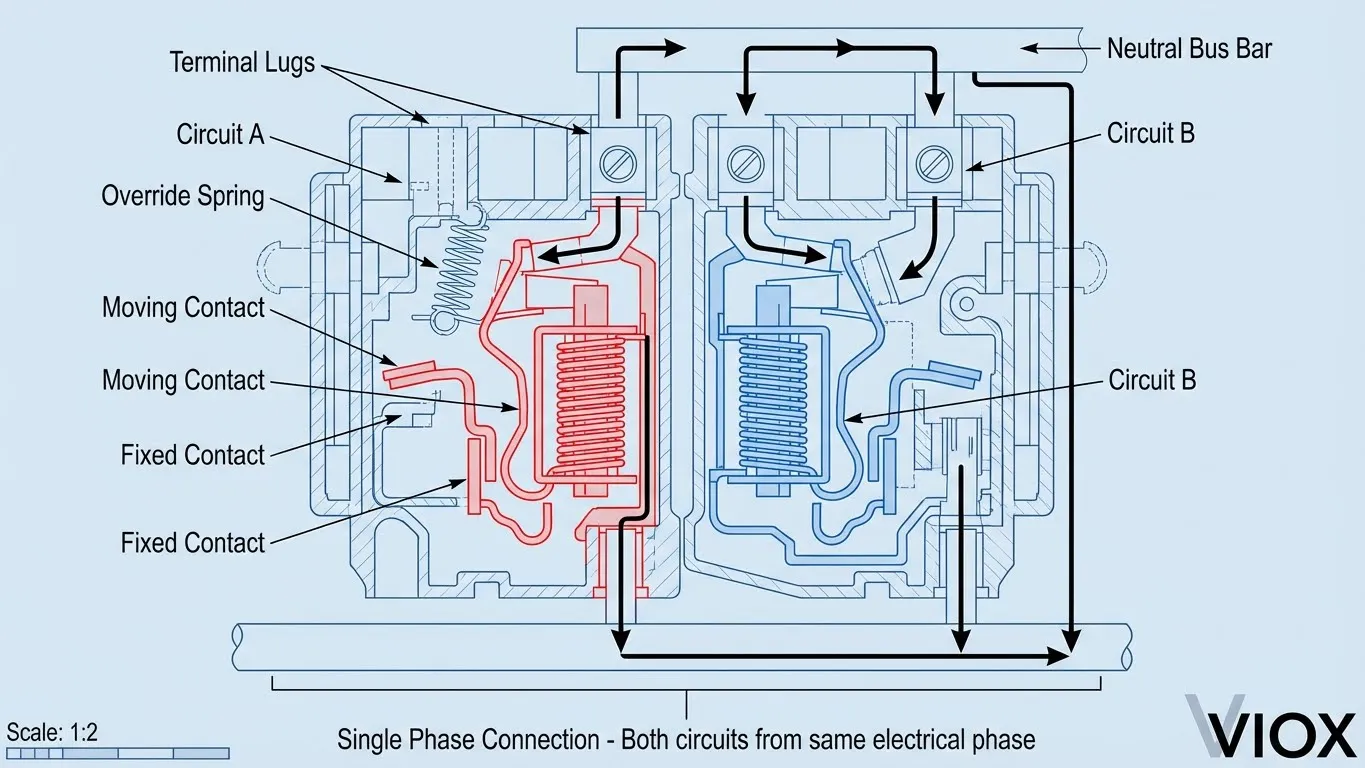
Interruptores Duplos e Mecanismos de Disparo Independentes: Cada lado tem o seu próprio interruptor de alavanca e mecanismo de deteção de sobrecorrente separado. Estes mecanismos funcionam independentemente, o que significa que uma falha num circuito não afeta o outro. É por isso que pode ter um disjuntor na posição “disparado” enquanto o outro permanece totalmente operacional.
Conexão de Barra de Barramento Única: Ambos os circuitos conectam-se a um polo do sistema de barra de barramento de corrente alternada do seu painel. Esta conexão monofásica é a razão pela qual os disjuntores tandem não podem fornecer energia de 240 volts - os circuitos de 240V requerem conexão a duas fases opostas do sistema elétrico, que apenas os disjuntores bipolares podem fornecer.
Gestão de Fios Neutros: O fio neutro de cada circuito conecta-se à barra de barramento neutro independentemente, tal como os disjuntores padrão. Isto é fundamental para a segurança e distingue os disjuntores tandem das configurações de circuito de derivação multi-fio (MWBC), que partilham um único neutro - uma configuração incompatível com os disjuntores tandem.
Classificações de Amperagem e Configurações
Os disjuntores tandem estão disponíveis em combinações de amperagem limitadas, refletindo o seu papel como soluções de poupança de espaço e de serviço leve:
- 15/15 amp: Comum para circuitos de iluminação e tomadas de uso geral padrão
- 20/20 amp: Popular para tomadas de cozinha, circuitos de casa de banho e áreas de lavandaria
- 15/20 amp: Configurações mistas onde um circuito precisa de maior capacidade do que o outro
Os tandems de maior amperagem (30 ou 50 ampères) não são fabricados porque as cargas pesadas requerem disjuntores de tamanho normal dedicados ou configurações bipolares para operação de 240 volts.
2: CTL vs. NÃO CTL - O AVANÇO DA COMPATIBILIDADE
Compreender a diferença entre os disjuntores CTL e Não CTL é essencial para uma instalação segura do disjuntor tandem. Esta distinção separa as instalações em conformidade com o código dos atalhos perigosos.
O Que Significa CTL: Padrão de Limitação Total de Circuitos
CTL (Limitação Total de Circuitos) é uma norma de segurança UL estabelecida por volta de 1965 para fazer cumprir o limite de 42 circuitos do Código Elétrico Nacional para painéis residenciais de “iluminação e eletrodomésticos”. A norma foi concebida para evitar a sobrecarga do painel, restringindo o número total de circuitos que podiam ser instalados, independentemente da contagem de slots físicos.
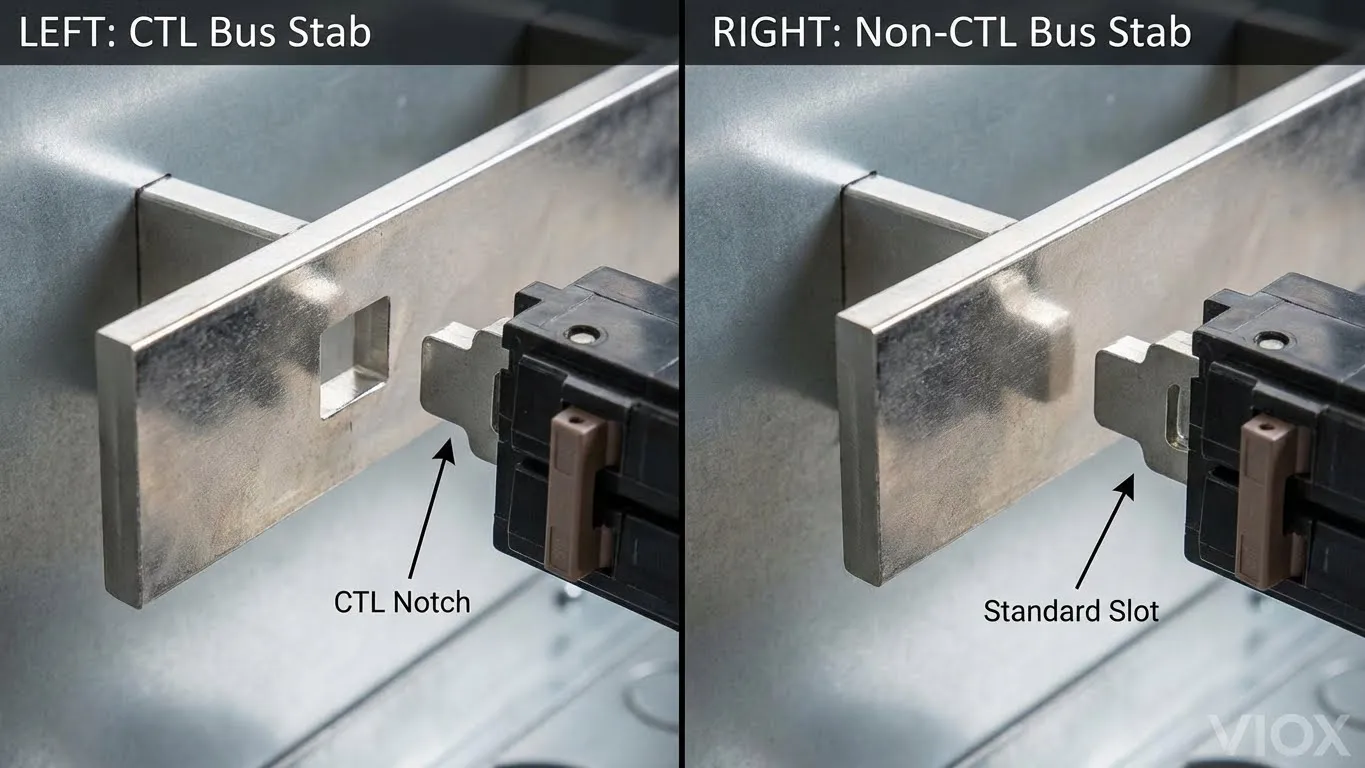
Características de Rejeição CTL: Os disjuntores e painéis modernos com classificação CTL incluem mecanismos físicos de “rejeição” que permitem que os disjuntores se encaixem apenas em slots designados. Estas características de rejeição assumem várias formas, dependendo do fabricante:
- Punções de barramento entalhadas: Um entalhe quadrado cortado no pino de metal onde os disjuntores se conectam
- Trilhos de montagem modificados: Profundidades de gancho diferentes que aceitam apenas tipos de disjuntores compatíveis
- Design do clipe do disjuntor: Os disjuntores tandem têm clipes moldados para se encaixarem apenas em slots entalhados
Estas características impedem fisicamente a instalação em locais não autorizados, tornando literalmente impossível forçar um disjuntor tandem CTL num slot padrão.
Disjuntores Não CTL: Padrão Legado Apenas para Substituição
Disjuntores Não CTL não têm características de rejeição e são rotulados como “Apenas para uso de substituição”. Estes disjuntores mais antigos foram concebidos para painéis fabricados antes de 1965 que não têm restrições de segurança CTL. Usar um disjuntor Não CTL num painel CTL moderno é:
- Uma violação de código (NEC 110.3(B))
- Uma inspeção reprovada
- Um potencial risco de incêndio (ignora os limites de segurança projetados)
Alguns eletricistas instalam disjuntores Não CTL quebrando o clipe de rejeição de um disjuntor CTL - uma prática chamada de usar um disjuntor “trapaceiro”. Isto é perigoso porque anula os controlos de engenharia do fabricante projetados para evitar a sobrecarga.
Atualização NEC 2008: O Limite de 42 Circuitos Removido
O Código Elétrico Nacional removeu o limite de 42 circuitos em 2008, permitindo que os fabricantes projetassem painéis com 60, 84 ou até mais circuitos. No entanto, isto não elimina os requisitos CTL. Os painéis modernos ainda devem ser instalados de acordo com a listagem específica do fabricante (NEC 110.3(B)), e a compatibilidade é determinada pelo design de cada modelo de painel, não por uma regra universal.
3: IDENTIFICAR A COMPATIBILIDADE DO PAINEL
Antes de comprar um disjuntor tandem, deve verificar se o seu painel elétrico foi projetado para o aceitar. Eis como verificar:
Verificação 1: O Número do Modelo do Painel
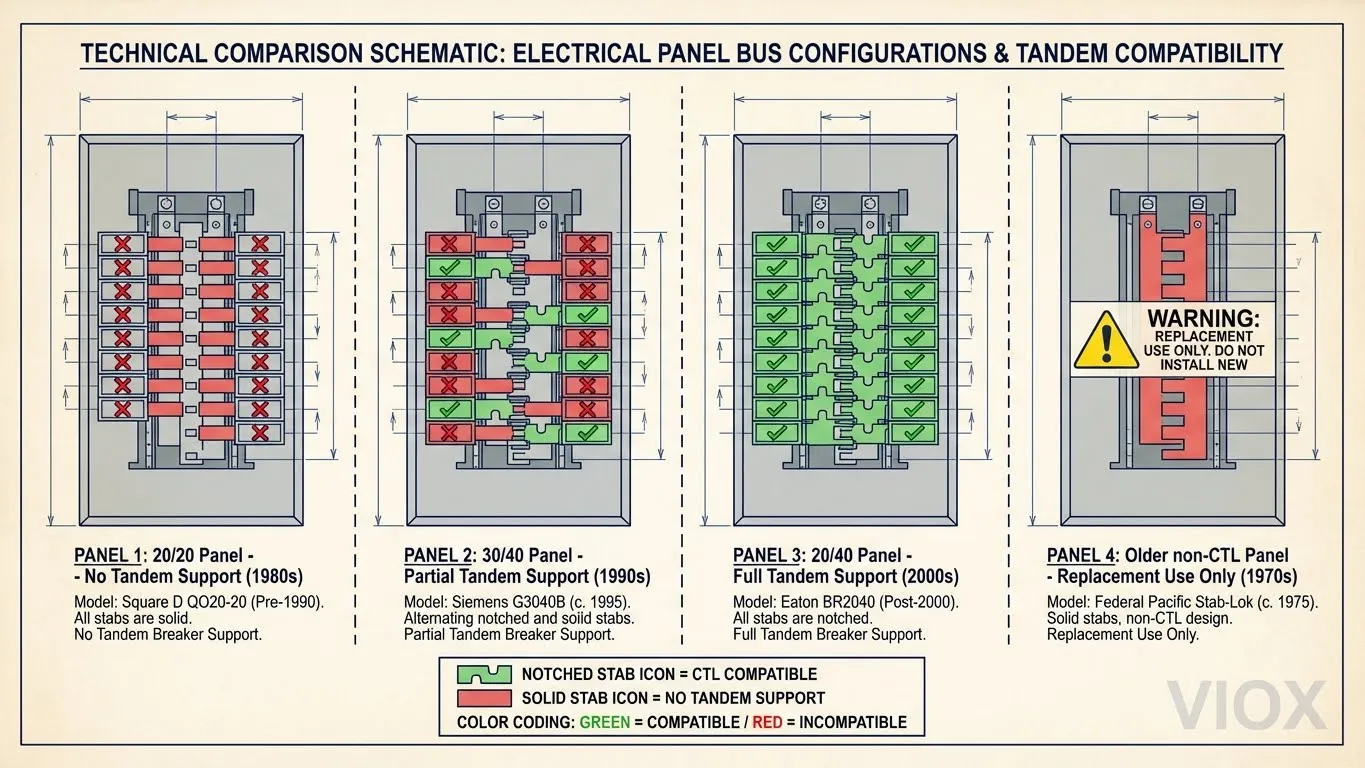
Os fabricantes usam uma convenção de nomenclatura de “espaços/circuitos” que revela instantaneamente a compatibilidade tandem:
| Número do modelo | Significado | Suporte para Disjuntor Tandem? |
|---|---|---|
| 20/20 | 20 slots, 20 circuitos permitidos | ❌ Sem tandems |
| 30/40 | 30 slots, 40 circuitos permitidos | ✅ Sim, 10 slots suportam tandems |
| 20/40 | 20 slots, 40 circuitos permitidos | ✅ Todos os slots suportam tandems |
| 40/50 | 40 slots, 50 circuitos permitidos | ✅ Sim, 10 slots suportam tandems |
Se o número do seu painel for 20/20, 20/30 ou 30/30 (onde os slots são iguais ao número máximo de circuitos), o seu painel não suporta disjuntores tandem. O “segundo número mais alto” indica que existem slots com capacidade tandem.
Verificação 2: Inspecione os Entalhes da Barra de Barramento
Abra a porta do seu painel (com segurança) e observe as abas de metal onde os disjuntores se conectam.
- Abas de barramento entalhadas (entalhe quadrado cortado no centro): Projetado para disjuntores tandem CTL ✅
- Abas retangulares sólidas: Apenas slots padrão, sem suporte tandem ❌
Diferentes marcas usam diferentes designs de rejeição, mas uma inspeção visual geralmente confirma a compatibilidade rapidamente.
Verifique #3: Revise o Diagrama do Painel
A etiqueta dentro da porta do seu painel inclui um diagrama de fiação. Os slots que aceitam disjuntores tandem são frequentemente marcados com uma linha divisória ou região destacada. Este diagrama é definitivo—se não estiver claro, fotografe-o e consulte a documentação do fabricante do painel online.
Compatibilidade Específica do Fabricante
Marcas comuns de painéis residenciais e seu suporte tandem:
- Square D QO/Homeline: Amplamente compatível com tandems CTL
- Eaton BR/CH: Suporta tandems CTL; painéis BR modernos frequentemente suportam configurações totalmente tandem
- Siemens QW/Q-Line: Compatível com tandems CTL; também oferece Non-CTL (“NC” suffix) para painéis mais antigos
- GE THQL: Modelo mais antigo com slots tandem limitados; verifique o diagrama
Sempre verifique com a placa de identificação e o diagrama do seu painel específico, não apenas a marca.
4: DISJUNTORES TANDEM VS. ALTERNATIVAS—TABELA DE COMPARAÇÃO
Quando você precisa de circuitos adicionais, os disjuntores tandem são uma das várias opções. Veja como eles se comparam:
Matriz de Comparação de Opções
| Recurso | Disjuntor Tandem | Disjuntor Bipolar | Subpainel | Atualização do Painel |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slots do Painel Usados | 1 slot | 2 slots | N/A (unidade separada) | N/A (substitui o existente) |
| Circuitos Adicionados | 2 × 120V | 1 × 240V | 8–24+ circuitos | 20–40+ circuitos |
| Tensão Capacidade | Dois circuitos de 120V | Um circuito de 240V | Flexível | Flexível |
| Custo de instalação | $150–$400 | $100–$300 | $500–$1,500 | $1,200–$3,000 |
| Cronograma | 1–2 horas | 1–2 horas | 1–2 dias | 1–3 dias |
| Flexibilidade Futura | Limitada (dependente do espaço) | Limitada (uso de alta amperagem apenas) | Boa (expansível) | Excelente (maior capacidade) |
| Compatibilidade com o Código | Apenas painéis compatíveis | Todos os painéis modernos | Todos os códigos | Todos os códigos |
| AFCI/GFCI Disponível? | Raramente | Sim | Sim (com disjuntores adequados) | Sim |
| Melhor para | Adicionando luzes/tomadas quando o painel está cheio | Cargas de alta amperagem (secadora, AC) | Expansão parcial da capacidade | Flexibilidade a longo prazo |
| Pior Desvantagem | Só funciona em painéis compatíveis | Ocupa 2 espaços | Requer caixa de subpainel e conduíte | Caro e invasivo |
Fatores Chave de Decisão
Use um Disjuntor Tandem quando:
- Seu painel está completamente cheio, sem espaços padrão restantes
- Você precisa de 1–2 circuitos adicionais de 120V para luzes ou tomadas padrão
- Seu painel é compatível com CTL e possui espaços tandem designados disponíveis
- O orçamento é uma preocupação primária
- A solução é temporária até que uma atualização maior se torne viável
Use um Disjuntor Bipolar quando:
- Você precisa alimentar um eletrodoméstico de 240V (secadora, aquecedor de água, ar condicionado)
- Seu painel tem dois espaços vazios adjacentes
- A carga requer 30–60 amperes de capacidade
Use um Subpainel quando:
- Você precisa de mais de 4 circuitos adicionais
- Você deseja centralizar cargas em uma área específica (garagem, oficina, exterior)
- A expansão futura é provável
Atualize o Painel Principal quando:
- Sua capacidade de serviço elétrico é insuficiente
- Você está adicionando novas cargas importantes (carregador de EV, bomba de calor)
- Você deseja flexibilidade à prova de futuro por mais de 10 anos
5: AVISOS DE SEGURANÇA CRÍTICOS—MWBC E SOBRECARGA DO NEUTRO
A aplicação incorreta mais perigosa de disjuntores tandem envolve circuitos de derivação multi-fio (MWBC)—uma configuração encontrada em muitas casas mais antigas. Entender este risco é essencial para sua segurança.
Perigo do Circuito de Derivação Multi-Fio (MWBC)
Um MWBC é um método de fiação mais antigo onde dois fios quentes separados compartilham um único fio neutro. Aqui está o porquê de os disjuntores tandem serem incompatíveis:
Configuração Normal de MWBC (Errado com Tandem):
- O fio quente 1 se conecta à Fase A (digamos, 15 amperes de saída)
- O fio quente 2 se conecta à Fase B (digamos, 15 amperes de saída)
- As correntes estão 180° fora de fase, então elas se cancelam no neutro
- Corrente neutra máxima: ~0–1 amperes (seguro para um fio 14 AWG)
Se Você Usar Incorretamente um Tandem:
- Ambos os fios quentes se conectam à mesma fase (porque o tandem usa apenas 1 conexão de barra de distribuição)
- Ambas as correntes fluem na mesma direção no neutro
- A corrente se soma: 15 amperes + 15 amperes = 30 amperes no neutro
- Um fio neutro 14 AWG classificado para 15 amperes agora está transportando 30 amperes
- O fio superaquece silenciosamente—disjuntores neutros não existem, então o disjuntor nunca desarma
- Resultado: Incêndio elétrico sem qualquer aviso
A Solução: Use um Disjuntor Bipolar para MWBC
Se você tiver circuitos de neutro compartilhado (indicado por disjuntores em lados opostos do seu painel do mesmo número de circuito), sempre use um disjuntor bipolar para proteção. O mecanismo de disparo comum garante que ambos os quentes sejam desenergizados juntos, evitando a sobrecarga do neutro.
Incompatibilidade AFCI/GFCI
Os códigos elétricos modernos (NEC 2020/2023) exigem proteção AFCI ou GFCI para quase todos os circuitos residenciais. Disjuntores tandem não estão atualmente disponíveis com esses recursos de proteção—apenas disjuntores de tamanho normal oferecem opções AFCI/GFCI. Se sua área exige proteção AFCI/GFCI e seu painel não pode acomodar disjuntores padrão, você pode estar limitado a subpainéis ou atualizações de painel, não soluções tandem.
6: PROCESSO DE INSTALAÇÃO E CONFORMIDADE COM O CÓDIGO
A instalação profissional é não negociável para o trabalho do painel elétrico. No entanto, entender o processo ajuda você a verificar se o trabalho é feito com segurança e de acordo com o código.
Avaliação Pré-Instalação
Antes que qualquer trabalho comece:
- Verifique a Compatibilidade do Painel: Confirme se o modelo do painel suporta disjuntores tandem e se os espaços designados estão disponíveis
- Cálculo de Carga: Garanta que a entrada de serviço (tipicamente 100–200 amperes) possa lidar com segurança com os circuitos adicionais
- Requisitos de Permissão: Verifique os códigos de construção locais—a maioria das jurisdições exige licenças para modificações no painel
- Propósito do Circuito: Determine a carga, o calibre do fio e a classificação do disjuntor necessários (tipicamente 15–20 amperes, fio 14–12 AWG)
Etapas de Instalação (Apenas Profissional)
- Desligamento de energia: O disjuntor principal é desligado; a energia é verificada como morta usando um multímetro nas barras de distribuição
- Remoção do Disjuntor: Se estiver substituindo um disjuntor existente, ele é removido com segurança e a fiação desconectada
- Instalação Tandem: O novo disjuntor tandem é encaixado no espaço designado (exigindo o ajuste de rejeição CTL adequado)
- Conexão do Fio: A nova fiação do circuito é conectada aos terminais corretos—diferentes fabricantes têm diferentes posições de terminal
- Testes: A energia é restaurada e ambos os circuitos são testados para tensão e operação adequadas
- Inspeção: Inspetores locais verificam se a instalação atende aos códigos NEC e locais
Regras Críticas de Instalação
- Nunca pule a etapa de desligar o disjuntor principal—a eletricidade pode estar presente mesmo com o principal desligado
- Verifique o modelo exato do painel antes de encomendar disjuntores (disjuntores QO, BR e CH não são intercambiáveis)
- Use a bitola de fio adequada: Disjuntores de 15 ampères exigem 14 AWG no mínimo; 20 ampères exigem 12 AWG
- Testar a instalação com uma inspeção aprovada
7: MANUTENÇÃO E SOLUÇÃO DE PROBLEMAS
Uma vez instalados, os disjuntores tandem exigem manutenção mínima, mas a inspeção regular garante a segurança a longo prazo.
Pontos de Inspeção Regular
- Condição Física: Verifique se há descoloração, plástico queimado ou calor incomum — sinais de superaquecimento
- Operação do Interruptor: Teste ambos os interruptores mensalmente; eles devem se mover suavemente entre ON e OFF
- Comportamento do Circuito: Monitore para disparos incômodos frequentes, o que pode indicar sobrecarga ou um disjuntor defeituoso
Problemas Comuns e Soluções
| Questão | Causa provável | Solução |
|---|---|---|
| Frequentes tropeçar | Circuito sobrecarregado ou curto-circuito | Chame um eletricista; pode ser necessária redistribuição ou um disjuntor maior |
| Calor excessivo | Sobrecarga ou conexão ruim | Inspeção profissional; possível substituição do disjuntor |
| Operação difícil do interruptor | Corrosão interna ou desgaste | Substitua o disjuntor imediatamente |
| Um lado disparou, o outro OK | Operação normal (circuitos independentes) | Verifique o circuito disparado quanto a falhas; reinicie quando seguro |
PRINCIPAIS CONCLUSÕES
✓ Disjuntores tandem encaixam dois circuitos independentes de 120V em um único slot do painel, dobrando a capacidade disponível sem substituição total do painel
✓ A compatibilidade CTL é não negociável— use apenas disjuntores tandem em painéis especificamente projetados para eles; verifique o número do modelo e os entalhes da barra de barramento
✓ Nunca use disjuntores tandem para circuitos de derivação multifio (MWBC)— eles causam sobrecarga do neutro e risco de incêndio
✓ Comparação de custos: Tandems ($150–$400) vencem subpainéis ($500–$1,500) e atualizações de painel ($1,200–$3,000) quando o orçamento é apertado
✓ A proteção AFCI/GFCI não está disponível em configurações tandem — use disjuntores padrão se os códigos modernos exigirem esses recursos
✓ A instalação profissional é essencial— trabalhar com painéis elétricos energizados acarreta risco de eletrocussão e requisitos de conformidade com o código
FAQ
Q1: Os disjuntores tandem são seguros se instalados corretamente?
Sim, os disjuntores tandem são seguros quando instalados em painéis especificamente classificados para eles e conectados a cargas apropriadas. Eles são listados pela UL e estão em conformidade com os padrões NEC quando usados corretamente.
Q2: Posso usar um disjuntor tandem em qualquer painel?
Não. O seu painel deve ser compatível com CTL e ter slots designados para disjuntores tandem. Verifique o número do modelo (ex: 30/40 significa compatível com tandem) e inspecione os entalhes da barra de distribuição.
Q3: Qual é a diferença entre disjuntores tandem e bipolares?
Os disjuntores tandem fornecem dois circuitos de 120V em um slot. Disjuntores bipolares fornecem um circuito de 240V usando dois slots. Eles servem para propósitos completamente diferentes.
Q4: Por que não posso usar um tandem para um circuito de derivação multifio (MWBC)?
Os disjuntores tandem conectam-se a apenas uma fase elétrica, portanto, ambos os circuitos compartilham o mesmo caminho neutro. Isso faz com que as correntes se somem no neutro em vez de se cancelarem, causando superaquecimento e risco de incêndio. Use sempre um disjuntor bipolar para MWBC.
Q5: Como sei se meu painel aceita tandems?
Verifique três coisas: (1) Formato do número do modelo, como 30/40 (número mais alto no segundo valor = suporte tandem), (2) Terminais de barramento entalhados (não sólidos), (3) Diagrama do painel marcando os slots compatíveis com tandem.
Q6: Os disjuntores tandem podem fornecer energia de 240 volts?
Não. Os disjuntores tandem se conectam a apenas uma fase elétrica e só podem fornecer 120V por circuito. Para 240V, você precisa de um disjuntor bipolar.
Q7: O que acontece se eu forçar um tandem em um slot incompatível?
Isso cria um risco de incêndio porque o disjuntor não fará contato elétrico adequado. Também viola os códigos de construção e anula sua cobertura de seguro.
Q8: Preciso de uma licença para instalar um disjuntor tandem?
A maioria das jurisdições exige uma licença elétrica para qualquer modificação no painel. Verifique as regras do departamento de construção local. Eletricistas profissionais lidam com a logística da licença e decisões de centro de carga vs. quadro de distribuição para garantir total conformidade.


