Основные выводы
- Стандартное расстояние: Провод 12/2 на 20-амперном автомате может безопасно работать на расстоянии 15-18 метров при полной нагрузке, поддерживая рекомендованное NEC падение напряжения 3%
- Максимальное безопасное расстояние: До 28 метров возможно при падении напряжения 3% при 240 В, но только 15-17 метров при 120 В
- Нагрузка имеет значение: Фактическое используемое расстояние сильно зависит от подключенной нагрузки — меньший ампераж позволяет более длинные провода
- Критически важно для безопасности: За пределами рекомендованных расстояний увеличивается импеданс контура замыкания, что потенциально может помешать срабатыванию автоматических выключателей во время коротких замыканий
- Правило обновления: Для проводов, превышающих 18 метров при 20 амперах, перейдите на 10 AWG; для 30+ метров рассмотрите провод 8 AWG
Понимание двух ограничений: допустимая токовая нагрузка против падения напряжения
Когда электрики и инженеры обсуждают, как далеко можно проложить провод 12/2 на 20-амперном автомате, они на самом деле рассматривают два совершенно разных ограничения:
Тепловой предел (допустимая токовая нагрузка)
Согласно таблице 310.16 NEC, медный провод 12 AWG рассчитан на 20 ампер при 60°C и 25 ампер при 90°C (для изоляции THHN/THWN-2). Этот рейтинг гарантирует, что провод не перегреется и не расплавит свою изоляцию — независимо от длины.

Предел производительности (падение напряжения)
Падение напряжения — это тихий убийца электрической производительности. Когда ток течет по проводу, сопротивление вызывает снижение напряжения. NEC рекомендует ограничить падение напряжения до:
- Максимум 3% для ответвлений (NEC 210.19(A)(1) FPN № 4)
- Максимум 5% в совокупности для питающих и ответвлений
- Максимум 2% для чувствительного электронного оборудования (NEC 647.4(D))
Этот предел падения напряжения, а не допустимая токовая нагрузка, определяет практическое максимальное расстояние для провода 12/2.
Математика максимального расстояния провода
Формула расчета падения напряжения
Основная формула для расчета падения напряжения в двухпроводной цепи:
VD = (2 × R × I × L) / 1000
Где:
- VD = Падение напряжения (вольты)
- R = Сопротивление на 1000 футов (омы)
- I = Ток (ампер)
- L = Расстояние в одну сторону (футы)
- 2 = Учитывает как горячий, так и нейтральный проводники
Для медного провода 12 AWG: R = 1,93 Ом на 1000 футов (Глава 9 NEC, Таблица 8)
Формула максимального расстояния
Перестановка формулы для решения максимального расстояния:
Максимальное расстояние (футы) = (Максимальное VD × 1000) / (2 × R × I)
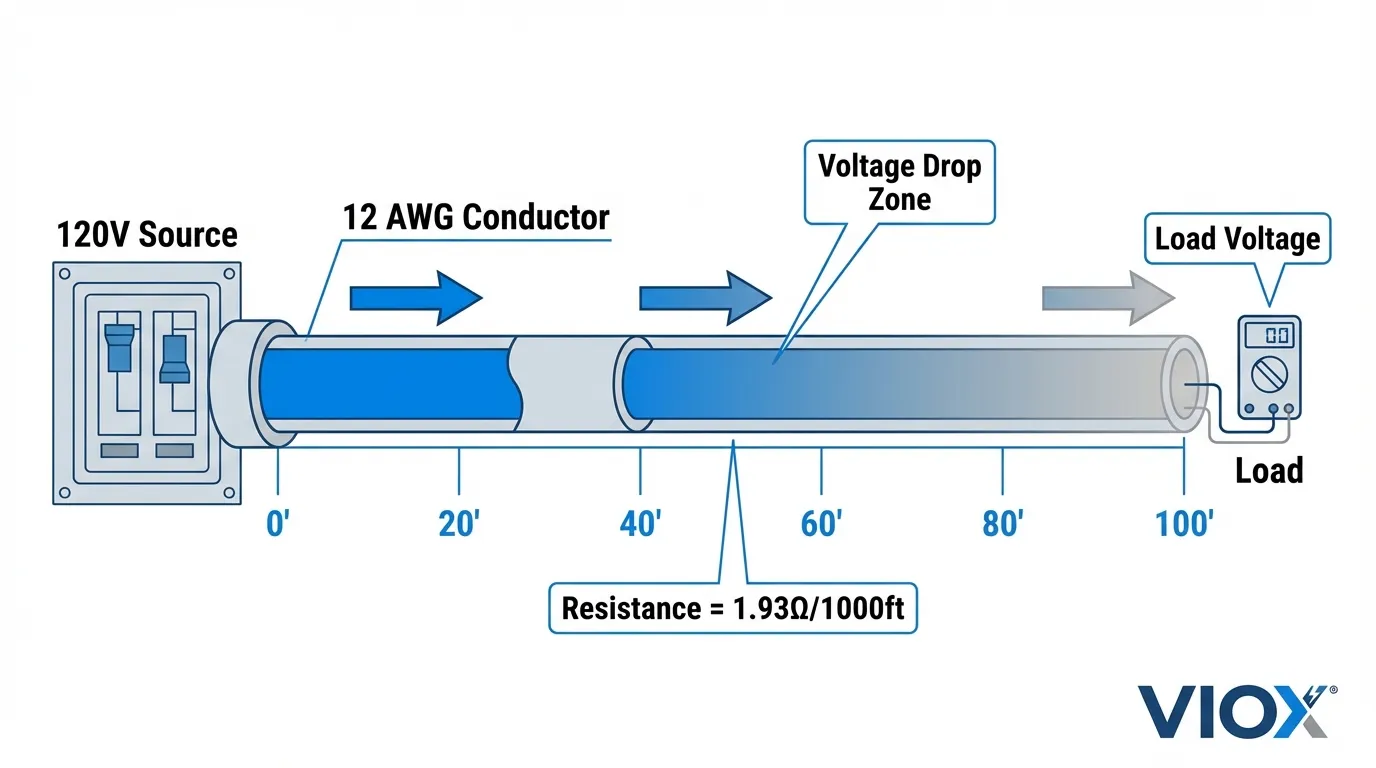
Таблица максимальных расстояний: провод 12/2 на 20-амперном автомате
| Напряжение системы | Ток нагрузки | Макс. расстояние (3% VD) | Макс. расстояние (5% VD) | Фактическое напряжение на нагрузке (3%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 120В | 20A (100%) | 16 метров | 26 метров | 116.4V |
| 120В | 16A (80%) | 20 метров | 32 метра | 116.4V |
| 120В | 12A (60%) | 26 метров | 43 метра | 116.4V |
| 120В | 8A (40%) | 39 метров | 213 футов | 116.4V |
| 240V | 20A (100%) | 28 метров | 155 футов | 232.8 В |
| 240V | 16A (80%) | 116 футов | 194 футов | 232.8 В |
Примечание: Расстояния являются измерениями в одну сторону от панели до нагрузки
Почему важно правило 80%
NEC требует, чтобы непрерывные нагрузки (работающие 3+ часа) рассчитывались при 125% от фактической нагрузки, что означает, что цепь на 20 ампер должна выдерживать только 16 ампер непрерывно (80% от номинальной мощности). Это обеспечивает запас прочности и увеличивает практическое максимальное расстояние.
Реальные сценарии расстояний
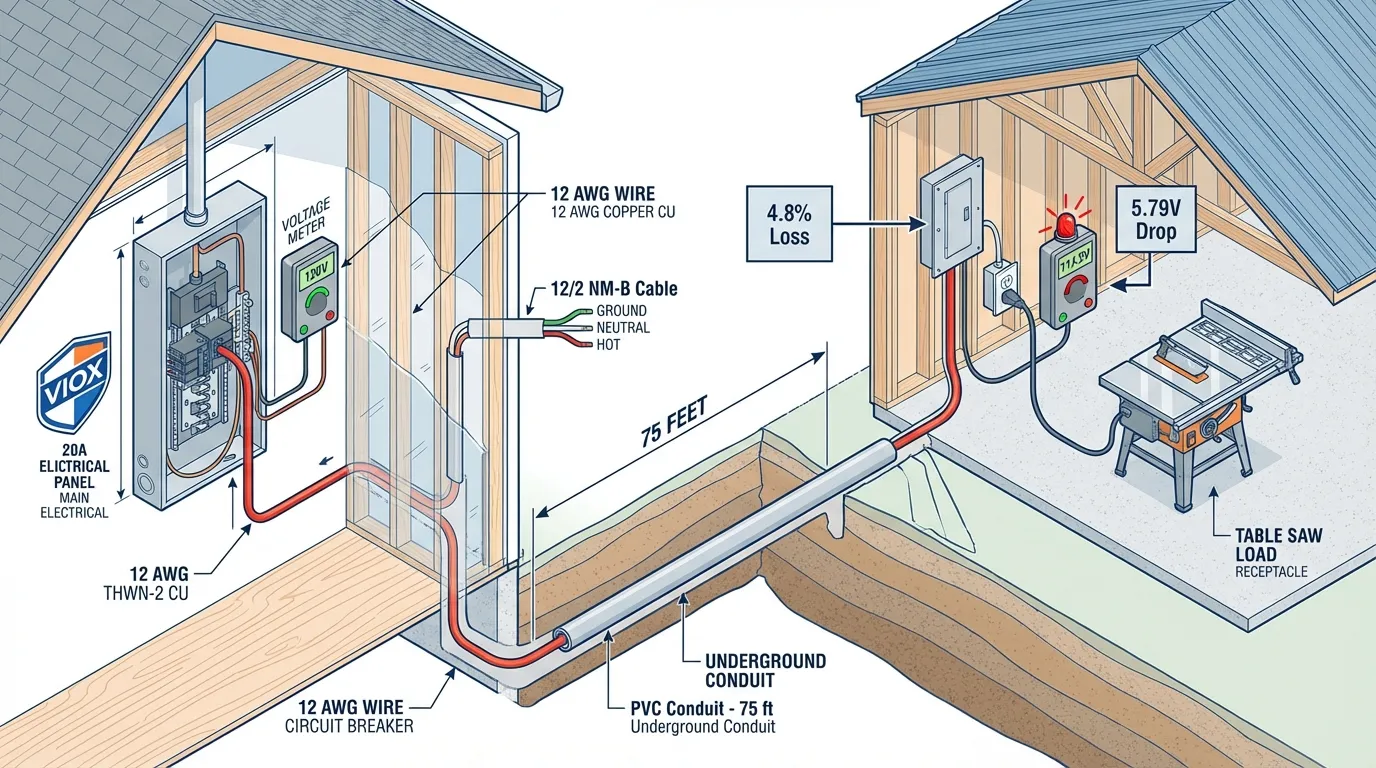
Сценарий 1: Уличная мастерская (полная нагрузка 20 А)
Настройка: Прокладка провода 12/2 от главной панели к уличной мастерской с электроинструментами (циркулярная пила, воздушный компрессор), потребляющими 18-20 ампер.
Расстояние: 75 футов
Расчет:
- VD = (2 × 1,93 × 20 × 75) / 1000 = 5,79 вольт
- Процент падения напряжения = 5,79 В / 120 В = 4.8%
Результат: ❌ Превышает рекомендацию 3% (но в пределах максимального значения 5%)
Рекомендация: Обновите до провод 10 AWG чтобы уменьшить падение напряжения до 2,9% (3,6 В)
Сценарий 2: Ландшафтное освещение (низкий ток)
Настройка: Светодиодное ландшафтное освещение потребляет всего 3 ампера, на расстоянии 150 футов от панели.
Расчет:
- VD = (2 × 1,93 × 3 × 150) / 1000 = 1,74 вольт
- Процент падения напряжения = 1,74 В / 120 В = 1.45%
Результат: ✅ В пределах лимита 3%
Ключевое понимание: Ток нагрузки важнее, чем номинал провода. Несмотря на то, что провод 12/2 рассчитан на 20 ампер, нагрузки с низким током могут проходить гораздо большие расстояния.
Сценарий 3: Установка зарядного устройства для электромобилей
Настройка: Зарядное устройство для электромобилей уровня 2 (16 А непрерывно) на расстоянии 85 футов от панели.
Расчет:
- VD = (2 × 1,93 × 16 × 85) / 1000 = 5,25 вольт
- Процент падения напряжения = 5,25 В / 120 В = 4.4%
Результат: ❌ Превышает рекомендацию 3%
Профессиональное решение: Использование провод 10 AWG или запустить на 240V (что вдвое уменьшает процент падения напряжения) цитата
Скрытая опасность: полное сопротивление цепи замыкания
Помимо падения напряжения, существует критически важный вопрос безопасности который большинство домашних мастеров упускают из виду: полное сопротивление цепи замыкания.
Что такое полное сопротивление цепи замыкания?
Когда происходит короткое замыкание, автоматический выключатель должен обнаружить огромный скачок тока (обычно в 5-10 раз превышающий номинальный ток), чтобы мгновенно запустить механизм магнитного расцепления. Для выключателя на 20 ампер это означает 100-200 ампер тока короткого замыкания.
Проблема: По мере увеличения длины провода увеличивается общее сопротивление цепи, что снижает ток короткого замыкания.
Почему это опасно
Сценарий: Вы прокладываете 500 футов провода 12/2 к удаленному зданию.
- Общее сопротивление цепи = (2 × 1,93 × 500) / 1000 = 1,93 Ом
- Ток короткого замыкания = 120 В / 1,93 Ом = 62 ампера
Критическая проблема: 62 ампер может быть недостаточно для срабатывания магнитного расцепителя. Выключатель может полагаться на свой более медленный механизм теплового расцепления, который может занять 30-60 секунд для активации.
Последствие: В течение этих 30-60 секунд провод становится гигантским нагревательным элементом, потенциально воспламеняя окружающие материалы до срабатывания автоматического выключателя.

Профессиональное решение
Для протяженных линий всегда проверяйте, что ожидаемый ток короткого замыкания превышает порог мгновенного срабатывания автоматического выключателя. Это часто требует:
- Увеличение сечения проводников сверх требований по падению напряжения
- Установка дополнительных щитов ближе к нагрузкам
- Использование более высокого напряжения (240 В вместо 120 В)
Сравнительная таблица увеличения сечения провода
| Расстояние | 120 В @ 20 A | 120 В @ 16 A | 240 В @ 20 A | Рекомендуемый размер провода |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0-50 футов | 2.61% VD | 2.11% VD | 1.31% VD | 12 AWG ✅ |
| 51-75 футов | 3.91% VD | 3.11% VD | 1.91% VD | 10 AWG ⚠️ |
| 76-100 футов | 5.21% VD | 4.11% VD | 2.61% VD | 10 AWG ⚠️ |
| 101-150 футов | 7.71% VD | 6.21% VD | 3.91% VD | 8 AWG ⚠️ |
| 151-200 футов | 10.31% VD | 8.31% VD | 5.21% VD | 6 AWG ⚠️ |
Легенда: ✅ Приемлемо | ⚠️ Требуется обновление
Практические рекомендации по установке
Когда провод 12/2 приемлем
- ✅ Цепи ответвления жилых помещений до 50 футов
- ✅ Небольшие нагрузки (освещение, розетки) до 10 ампер
- ✅ Короткие участки от дополнительных щитов до ближайших розеток
- ✅ Цепи 240 В где падение напряжения уменьшается вдвое
Когда следует увеличить сечение провода 12/2
- ⚠️ Расстояния, превышающие 60 футов при полной нагрузке 20 А
- ⚠️ Нагрузки двигателя (воздушные компрессоры, электроинструменты), требующие высокого пускового тока
- ⚠️ Зарядные устройства для электромобилей работающие непрерывно при 16 А+
- ⚠️ Чувствительная электроника требующие стабильного напряжения
- ⚠️ Наружные постройки 100+ футов от главного щита
Контрольный список соответствия требованиям NEC
При планировании установки провода 12/2 убедитесь в соответствии следующим требованиям NEC:
| Раздел кода | Требование | Проверка соответствия |
|---|---|---|
| NEC 210.19(A)(1) | Падение напряжения в ответвленной цепи ≤ 3% рекомендуется | Рассчитайте VD при максимальной нагрузке |
| NEC 240.4(D) | Провод 12 AWG, защищенный устройством защиты от сверхтока макс. 20A | Используйте автоматический выключатель на 20A (не 25A или 30A) |
| NEC 310.16 | Допустимая токовая нагрузка проводника соответствует нагрузке | 12 AWG = 20A при 60°C, 25A при 90°C |
| NEC 110.14(C) | Температурные характеристики клемм | Большинство устройств рассчитаны на 60°C или 75°C |
| NEC 334.80 | Поддержка кабеля NM каждые 4,5 фута | Надежно закрепите Romex |
Анализ затрат и выгод: Когда следует увеличивать сечение провода
Сравнение стоимости материалов (на 100 футов)
| Размер провода | Приблизительная стоимость | Падение напряжения при 20A/100 футов | Долгосрочные потери энергии |
|---|---|---|---|
| 12 AWG | $45-65 | 5.2% | $15-25/год* |
| 10 AWG | $75-95 | 3.3% | $10-15/год* |
| 8 AWG | $125-165 | 2.1% | $6-10/год* |
*На основе непрерывной нагрузки 16A при $0.12/кВтч
Расчет ROI (окупаемости инвестиций): Для участка длиной 100 футов, проводящего 16A непрерывно:
- Модернизация с 12 AWG до 10 AWG стоит $30 больше
- Годовая экономия энергии: $10-15
- Срок окупаемости: 2-3 года
- Улучшение срока службы оборудования: Двигатели и электроника служат дольше при стабильном напряжении
Профессиональная рекомендация: Для любой стационарной установки, превышающей 75 футов, увеличьте сечение провода на один калибр. Предельные затраты минимальны по сравнению с долгосрочной производительностью и преимуществами безопасности.
Особые соображения для различных применений
Цепи HVAC и тепловых насосов
Электрическое оборудование для отопления и охлаждения особенно чувствительно к падению напряжения:
- Компрессорные двигатели потребляют высокий пусковой ток (LRA = ток заклинившего ротора)
- Пониженное напряжение приводит к перегреву двигателей и преждевременному выходу из строя
- Рекомендация: Ограничьте падение напряжения до Максимум 2% для цепей HVAC
Станции зарядки электромобилей
Зарядные устройства для электромобилей уровня 2 создают уникальные проблемы:
- Непрерывная нагрузка: Работает при 80% номинала автоматического выключателя в течение нескольких часов
- Расстояние: Часто расположены в гаражах или на подъездных путях далеко от панели
- Решение: Использование Цепи 240 В чтобы вдвое уменьшить процент падения напряжения, или установить выделенную подпанель
Солнечные фотоэлектрические и аккумуляторные системы
Цепи постоянного тока имеют другие соображения:
- Отсутствие реактивного сопротивления: Имеет значение только сопротивление
- Более высокие напряжения: Системы 48 В более устойчивы к падению напряжения
- Рекомендация: Следуйте требованиям NEC 690.8 для цепей источника PV
Устранение проблем с падением напряжения
Симптомы чрезмерного падения напряжения
- 🔴 Приглушение света при запуске приборов
- 🔴 Двигатели перегреваются или не запускаются
- 🔴 Электроника перезагружается или неисправна
- 🔴 Ложное срабатывание GFCI на длинных участках
- 🔴 Недостаточная производительность приборов (медленный нагрев, слабое охлаждение)
Этапы диагностики
- Измерьте напряжение на панели: Должно быть 118-122 В (номинальное 120 В)
- Измерьте напряжение на нагрузке под нагрузкой: Должно быть в пределах ±3% от напряжения панели
- Рассчитайте фактическое падение напряжения: Напряжение панели – Напряжение нагрузки
- Сравните с рекомендациями NEC: ±3% = 3.6V для цепей 120V
Варианты устранения
Вариант 1: Увеличьте сечение проводников (наиболее постоянное решение)
Вариант 2: Установите подпанель ближе к нагрузкам
Вариант 3: Перераспределить нагрузки для укорочения цепей
Вариант 4: Преобразуйте в 240V (для совместимого оборудования)
Решения VIOX для проводки на большие расстояния
При увеличении сечения провода для преодоления падения напряжения вы столкнетесь с распространенной проблемой: провода большего сечения не подходят к стандартным клеммам устройств.
Применение продукции VIOX
1. Клеммные блоки и распределительные шины
При переходе от питающего провода 8 AWG или 10 AWG к ответвлениям 12 AWG клеммные блоки VIOX обеспечивают:
- Надежные соединения для проводов разного сечения
- Соответствие нормам переходы провод-провод
- Простота поиска неисправностей с доступными точками подключения
2. Сверхмощные распределительные коробки
Для наружных трасс на большие расстояния атмосферостойкие распределительные коробки VIOX предлагают:
- Степень защиты IP65/IP67 для жестких условий эксплуатации
- Большая емкость для проводов для проводников увеличенного сечения
- Снятие напряжения для переходов подземных кабелепроводов
3. Решения для подпанелей
Установка подпанели сокращает расстояния цепей ответвления:
- Главная панель → Подпанель: Используйте 6 AWG или больше
- Подпанель → Нагрузки: Стандартный 12 AWG для коротких трасс
- Результат: Оптимальное падение напряжения во всех цепях
Вопросы и ответы
Могу ли я использовать кабель 12/2 длиной 100 футов с автоматическим выключателем на 20 ампер?
Да, но с ограничениями. При полной нагрузке 20A падение напряжения составит примерно 5.2%, превышая рекомендацию NEC в ±3%. Это приемлемо для:
- Нагрузок нечастого использования
- Цепей, потребляющих менее 12 ампер
- Цепей 240V (процент падения напряжения уменьшается вдвое)
Для непрерывных нагрузок 20A, перейдите на провод 10 AWG.
Влияет ли длина провода на срабатывание автоматического выключателя?
Да, значительно. Более длинные трассы проводов увеличивают сопротивление цепи, что снижает ток короткого замыкания. В крайних случаях (более 200 футов) ток короткого замыкания может быть слишком низким, чтобы вызвать мгновенное магнитное отключение автоматического выключателя, создавая опасность пожара. Всегда проверяйте, чтобы предполагаемый ток короткого замыкания превышал 5-кратный номинал автоматического выключателя.
В чем разница между проводом 12/2 и 12/3 для расстояния?
Пропускная способность провода по расстоянию одинакова. Цифры относятся к количеству проводников (2 или 3 изолированных проводника), а не к сечению провода. В обоих используются проводники 12 AWG с одинаковым сопротивлением. Используйте 12/3, когда вам нужно:
- Цепи трехпозиционного переключателя
- Многопроводные цепи ответвления
- Отдельные токоведущие проводники для 240V + нейтраль
Могу ли я использовать алюминиевый провод вместо медного, чтобы сэкономить деньги на длинных участках проводки?
Да, но увеличьте на один калибр. Алюминий имеет более высокое сопротивление, чем медь:
- Используйте 10 AWG алюминий вместо 12 AWG медь
- Требуется антиоксидантный состав на соединениях
- Обязательно использовать Устройства, рассчитанные на алюминиевые проводники (AL-rated) (Маркировка CO/ALR)
- Экономия средств: на 30-40% дешевле для проводов большого сечения
Как рассчитать падение напряжения для нескольких розеток в одной цепи?
Используйте самую дальнюю розетку и максимальную одновременную нагрузку. Например:
- Цепь имеет 8 розеток на протяжении 120 футов
- Предположим 80% от номинала автоматического выключателя (16A для цепи 20A)
- Рассчитайте падение напряжения до последней розетки при 16A
- Это обеспечивает консервативный сценарий наихудшего случая
Влияет ли тип провода (THHN или Romex) на максимальное расстояние?
Нет. Падение напряжения зависит только от:
- Сечения провода (AWG)
- Материала проводника (медь или алюминий)
- Тока (амперы)
- Расстояния (футы)
Тип изоляции (THHN, THWN, NM-B) влияет на допустимую токовую нагрузку и способ установки, но не на сопротивление или падение напряжения.
Вывод: Инженерный подход к выбору сечения провода
На вопрос “Как далеко можно проложить провод 12/2 на автоматическом выключателе 20A?” нет однозначного ответа — это зависит от:
- Напряжение системы (120V или 240V)
- Фактического тока нагрузки (а не только от номинала автоматического выключателя)
- Допустимого падения напряжения (рекомендуется 3%, максимум 5%)
- Чувствительности применения (двигателям и электронике нужны более жесткие допуски)
- Меры безопасности (полного сопротивления контура замыкания для правильной работы автоматического выключателя)
Общие рекомендации:
- Менее 50 футов: 12 AWG подходит для цепей 20A
- 50-75 футов: Рассмотрите 10 AWG для приложений с полной нагрузкой
- 75-100 футов: Используйте 10 AWG для нагрузок 20A
- Более 100 футов: Используйте 8 AWG или установите подпанель
Лучшая профессиональная практика: Если сомневаетесь, увеличьте сечение на один размер. Незначительные затраты минимальны по сравнению с долгосрочными преимуществами:
- Снижение потерь энергии
- Увеличение срока службы оборудования
- Улучшенные запасы прочности
- Запас по мощности на будущее
Для сложных установок или коммерческих применений проконсультируйтесь с лицензированным электриком и рассмотрите возможность использования электрических компонентов VIOX , разработанных для надежного распределения электроэнергии на большие расстояния.
Внутренние ссылки
Для получения дополнительной технической информации см. следующие ресурсы VIOX:
- Руководство по выбору размера провода на 50 ампер. – Комплексный выбор сечения провода для цепей с высоким током
- Снижение номинальных характеристик электрооборудования: температура, высота над уровнем моря и факторы группировки – Как условия окружающей среды влияют на пропускную способность провода
- Руководство по снижению номинальных характеристик автоматических выключателей по высоте – Критические соображения для установок на большой высоте
- Типы размеров кабелей: Руководство по преобразованию мм² в AWG в BS – Международные стандарты размеров проводов
- Номинальные значения температуры окружающей среды и коэффициенты снижения номинальных характеристик для MCB. – Влияние температуры на защиту цепи
- Как рассчитать ток короткого замыкания для автоматического выключателя (MCB) – Понимание расчетов тока короткого замыкания
- Стандартные размеры автоматических выключателей – Полное руководство по номинальным характеристикам автоматических выключателей
- Руководство для домовладельцев по определению номинала автоматического выключателя и расчету нагрузки – Практическое руководство по электропроводке жилых помещений
О компании VIOX Electric: VIOX Electric — ведущий B2B производитель электрооборудования, специализирующийся на устройствах защиты цепей, клеммных колодках, распределительных коробках и решениях для распределения электроэнергии для жилых, коммерческих и промышленных объектов. Наша продукция соответствует или превосходит стандарты NEC, UL и IEC по безопасности и производительности.


