For electrical engineers and installers, the rapid expansion of Electric Vehicle (EV) infrastructure presents a specific protection challenge: DC fault currents. Unlike standard household loads, the rectification circuits within EV On-Board Chargers (OBC) can generate smooth DC leakage currents in the event of a fault.
If not properly isolated, these DC currents can blind upstream Type A Residual Current Devices (RCDs), rendering the entire electrical installation unsafe.
This engineering guide analyzes the three compliant protection strategies defined by IEC 60364-7-722 နှင့် IEC 61851-1: using a Type B RCD, a Type F RCD (with specific conditions), or the newer “Type EV” (RDC-DD) approach. We will examine the technical distinctions between IEC 62423 နှင့် IEC 62955 to determine the optimal selection for safety, compliance, and cost-efficiency.
The “Blinding” Effect: Why Type A is Insufficient
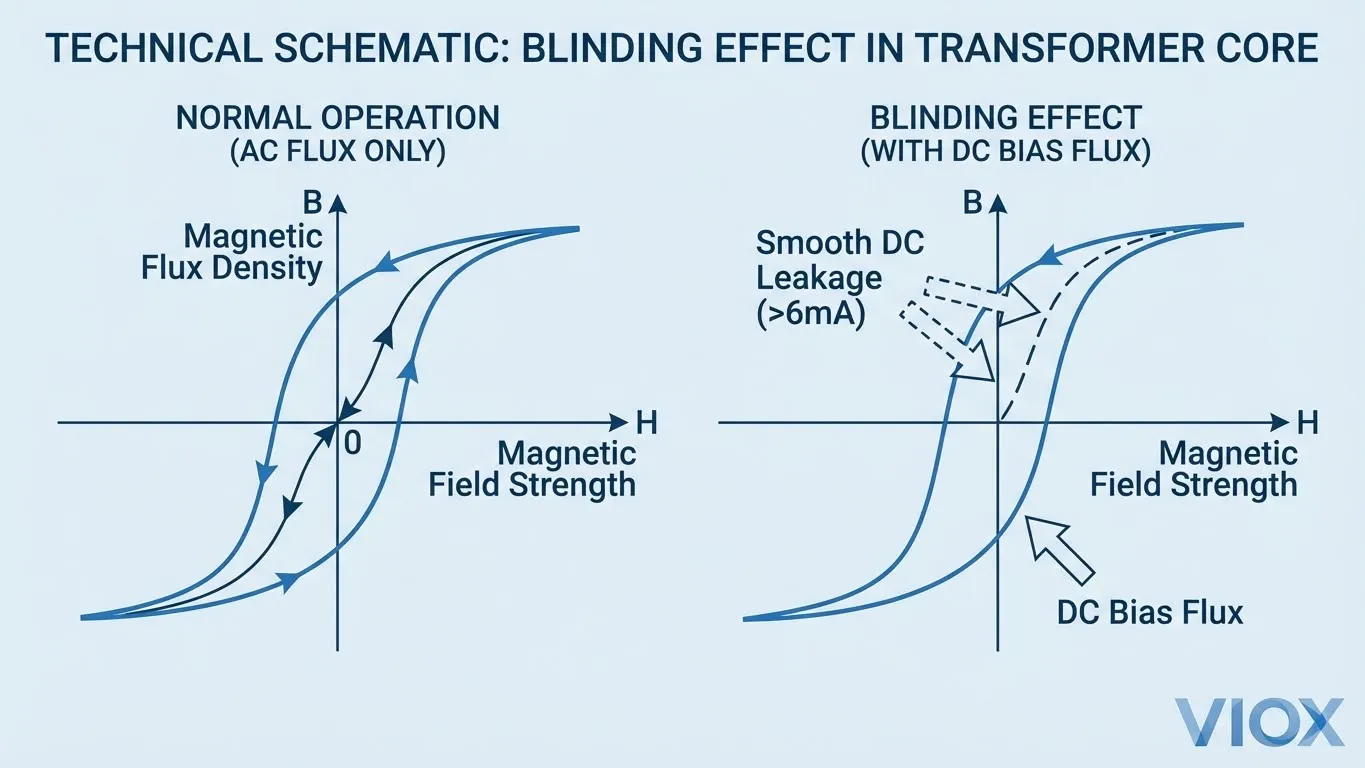
The fundamental issue in EV protection is the magnetic saturation of the sensing core in standard RCDs. A standard Type A RCD (commonly used in residential and commercial circuits) uses a toroidal transformer optimized for 50/60Hz AC and pulsating DC.
ဘယ်တော့လဲ smooth DC current (DC current with less than 10% ripple) flows through this toroid, it creates a constant magnetic flux. If this DC leakage exceeds 6mA, it can shift the operating point of the magnetic core into saturation. Once saturated, the core cannot detect the alternating magnetic field generated by a life-threatening AC earth fault. The RCD becomes “blind” and will not trip, leaving users unprotected against electric shock.
Therefore, international standards mandate that any EV charging point must be protected by a device that disconnects the supply in case of DC fault current ≥ 6mA.

Defining the Contenders: Type B vs. Type F vs. Type EV
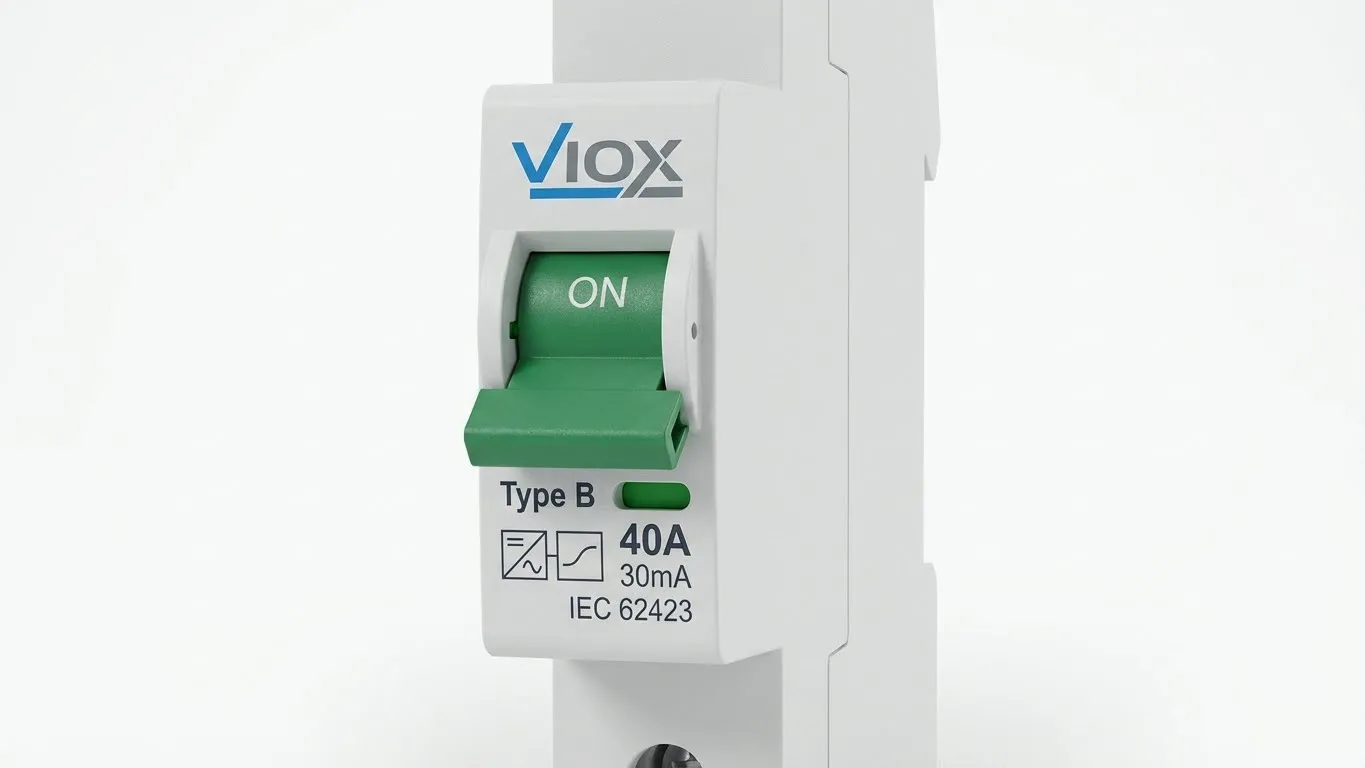
1. Type B RCD (IEC 62423)
ဟိ Type B RCD is the most robust solution. It contains two detection systems: a standard fluxgate for AC/pulsating DC and a separate high-frequency electronic detection circuit for smooth DC.
- Capabilities: Detects sinusoidal AC, pulsating DC, and smooth DC residual currents. Also detects currents at frequencies up to 1000Hz (critical for detecting switching frequency leakage from inverters).
- Tripping Threshold: ပုံမှန်အားဖြင့် 30mA AC နှင့် 60mA DC. (Note: While the standard allows up to 2x IΔn for DC, VIOX Type B breakers often trip earlier for enhanced safety).
- လျှောက်လွှာ Required for three-phase chargers where DC leakage can be smooth, and for installations requiring maximum uptime and selectivity.
2. Type F RCD (IEC 62423)
ဟိ Type F RCD is an enhanced Type A. It offers better immunity to nuisance tripping from surge currents and can detect residual currents with mixed frequencies (up to 1kHz).
- Limitation: Crucially, Type F does not detect smooth DC.
- EV Application: 您 မ use a Type F RCD alone for EV charging. It must be paired with an RDC-DD (Residual Direct Current Detecting Device) that handles the 6mA DC detection.
3. Type EV / RDC-DD (IEC 62955)
Often marketed as “Type EV,” this is technically a Residual Direct Current Detecting Device (RDC-DD). It is specifically designed to prevent Type A upstream RCDs from being blinded.
- အလုပ္အမ်ိဳးအစား: It monitors the circuit for smooth DC leakage.
- Threshold: ဒါဟာ must trip at 6mA DC.
- စံနှုန်းများ- Governed by IEC 62955.
- Variants:
- RDC-MD (Monitoring Device): Detects leakage and signals the EV charger’s contactor to open. If the contactor contacts weld, protection fails.
- RDC-PD (Protective Device): Includes its own disconnection mechanism (similar to a circuit breaker).
For a deeper understanding of how these devices fit into broader commercial systems, refer to our guide on Commercial EV Charging Protection.
Technical Comparison Matrix
The following table summarizes the detection capabilities and standard compliance for each device type.
| အင်္ဂါ | Type A RCD | Type F RCD | Type B RCD | RDC-DD (Type EV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| စံ | IEC 61008 / 61009 | IEC 62423 | IEC 62423 | IEC 62955 |
| AC Residual Current | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | (Dependent on integrated Type A) |
| Pulsating DC | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | (Dependent on integrated Type A) |
| Mixed Frequencies (1kHz) | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
| ချောမွေ့သော DC ထောက်လှမ်းခြင်း | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ (Yes) | ✅ (Yes) |
| DC Trip Threshold | မရှိ | မရှိ | ≤ 60mA* | 6mA |
| မျက်စိကွယ်ခြင်းကို ကာကွယ်ပေးပါသလား။ | အမွတ္ | အမွတ္ | ဟုတ်ကဲ့ (ခုခံနိုင်စွမ်းရှိသည်) | ဟုတ်ကဲ့ (ဖြတ်တောက်ခြင်းဖြင့်) |
| ကုန်ကျစရိတ် | အနိမ့် | လတ် | မြင့် | အလယ်အလတ် (ပေါင်းစပ်ထားသည်) |
*IEC 62423 သည် DC ဖြတ်တောက်မှုသည် AC ကျန်ရှိသော လျှပ်စီးကြောင်း (IΔn) ၏ အဆ ၂ ဆအထိ ခွင့်ပြုထားသည်။ 30mA စက်ပစ္စည်းအတွက် 60mA DC ဖြစ်သည်။ သို့သော် စက်ပစ္စည်းကိုယ်တိုင်က မျက်စိကွယ်ခြင်းမရှိဘဲ ဤ DC အဆင့်ကို ခံနိုင်ရည်ရှိအောင် ဒီဇိုင်းထုတ်ထားသည်။.
IEC 62955 နှင့် IEC 62423- မည်သည့်စံနှုန်းကို အသုံးပြုသင့်သနည်း။
IEC 62423 နှင့် ကိုက်ညီသော စက်ပစ္စည်း (Type B) နှင့် IEC 62955 စက်ပစ္စည်း (RDC-DD) အကြား ရွေးချယ်မှုသည် အားသွင်းစက်ပစ္စည်းနှင့် တပ်ဆင်သည့် ပတ်ဝန်းကျင်ပေါ်တွင် မူတည်ပါသည်။.
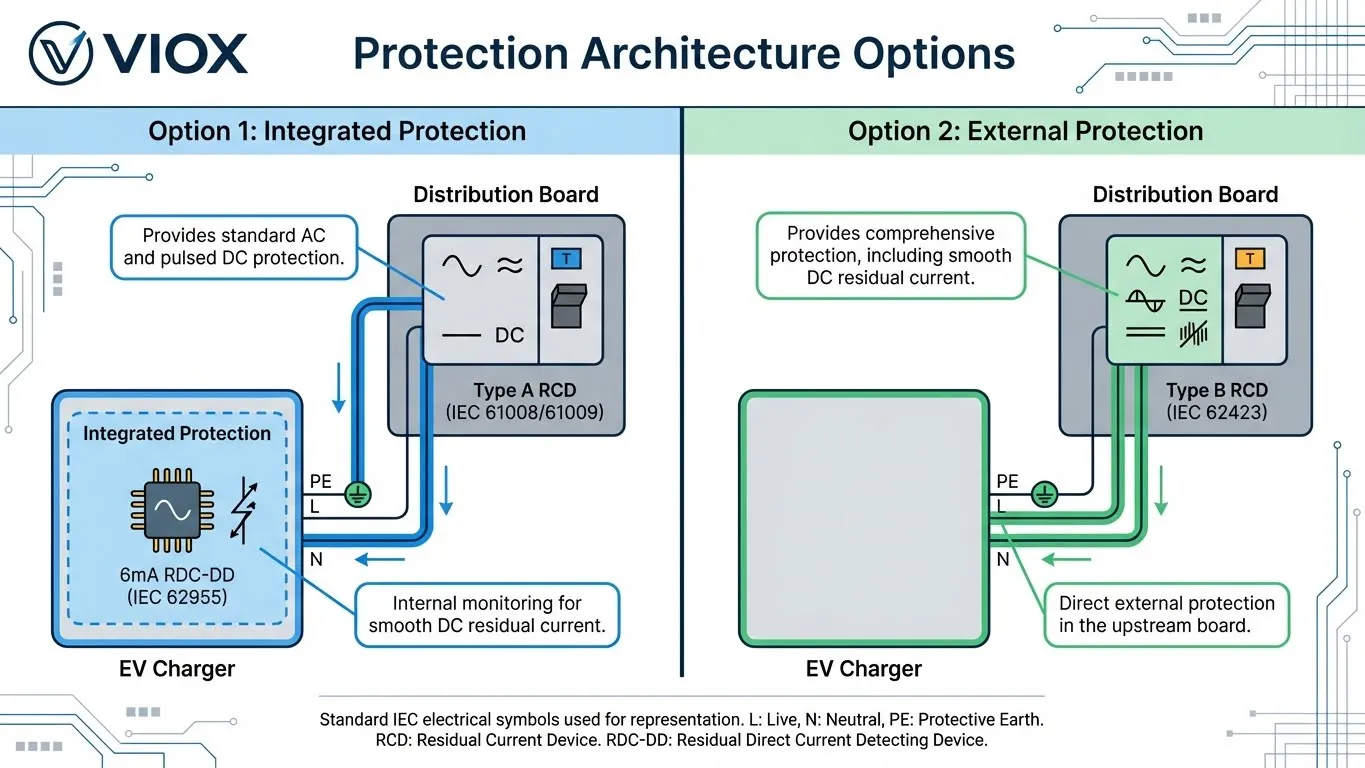
အခြေအနေ ၁- “ပေါင်းစပ်ထားသော” နည်းလမ်း (IEC 62955)
ခေတ်မီ AC wallbox အများအပြား (7kW – 22kW အားသွင်းစက်များ) တွင် 6mA DC ရှာဖွေခြင်းကို ထည့်သွင်းထားသည်။ ၎င်းသည် RDC-DD IEC 62955 နှင့် ကိုက်ညီသည်။.
- လိုအပ်ချက်- သင်သည် Type A RCD AC ချို့ယွင်းချက်များကို ကိုင်တွယ်ရန်အတွက် ဖြန့်ဖြူးရေးဘုတ်တွင် upstream ကို တပ်ဆင်ရပါမည်။.
- အကောင်းအဆိုး: panel တွင် အစိတ်အပိုင်းကုန်ကျစရိတ် သက်သာသည်။.
- ငး္အ: အားသွင်းစက်၏ အတွင်းပိုင်းရှာဖွေတွေ့ရှိမှု ပျက်ကွက်ပါက Type A RCD upstream သည် မျက်စိကွယ်နိုင်ခြေရှိသည်။ ပြုပြင်ထိန်းသိမ်းမှုတွင် DIN-rail အစိတ်အပိုင်းအစား အားသွင်းစက် PCB တစ်ခုလုံးကို အစားထိုးခြင်း ပါဝင်သည်။.
အခြေအနေ ၂- “ပြင်ပကာကွယ်မှု” နည်းလမ်း (IEC 62423)
DIN-rail တပ်ဆင်ထားသော Type B RCD (သို့မဟုတ် B RCBO ဟုရိုက်ပါ။) ကို ဖြန့်ဖြူးရေးဘုတ်တွင် အသုံးပြုခြင်း။.
- လိုအပ်ချက်- အားသွင်းစက်အတွင်း၌ RDC-DD ထပ်ဆောင်းရန် မလိုအပ်ပါ။ Type B RCD သည် AC၊ pulsating DC နှင့် smooth DC ချို့ယွင်းချက်များကို ကိုင်တွယ်သည်။.
- အကောင်းအဆိုး: ဗဟိုပြုပြုပြင်ထိန်းသိမ်းမှု၊ ပိုမိုမြင့်မားသော ယုံကြည်စိတ်ချရမှု၊ ပြင်ပ DC နှောင့်ယှက်မှုမှ ကင်းလွတ်ခြင်း၊ ချို့ယွင်းချက်အမျိုးအစားကို ရှင်းလင်းစွာဖော်ပြခြင်း (အဆင့်မြင့်မော်ဒယ်များတွင်)။.
- ငး္အ: ကနဦး အစိတ်အပိုင်းကုန်ကျစရိတ် မြင့်မားသည်။.
ရွေးချယ်မှု ဆုံးဖြတ်ခြင်း မူဘောင်
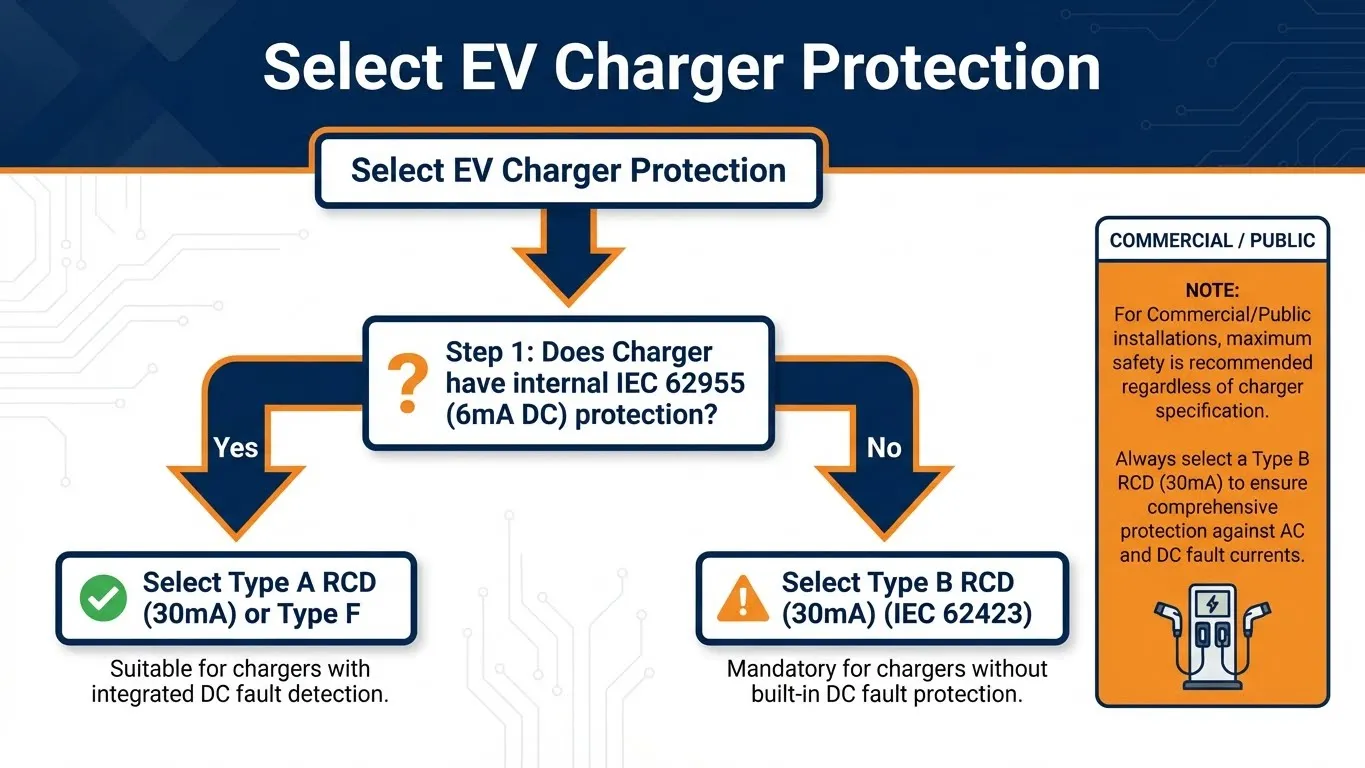
ပရောဂျက်တစ်ခုအတွက် ကာကွယ်ရေးကို သတ်မှတ်သည့်အခါ IEC 60364-7-722 နှင့် ကိုက်ညီကြောင်း သေချာစေရန် ဤယုတ္တိဗေဒကို လိုက်နာပါ-
- အားသွင်းစက် ဒေတာစာရွက်ကို စစ်ဆေးပါ- EVSE (လျှပ်စစ်ယာဉ် ထောက်ပံ့ရေးပစ္စည်း) သည် IEC 62955 နှင့် ကိုက်ညီသော RDC-DD ကို ထည့်သွင်းထားကြောင်း ကြေညာပါသလား။
- ဟုတ်ကဲ့- သင်သည် အမျိုးအစား A (သို့မဟုတ် Type F) RCD/RCBO ကို panel တွင် အသုံးပြုနိုင်သည်။.
- မဟုတ်ပါ- 您 根据 ကို အသုံးပြုပါ B အမျိုးအစား RCD ကို panel တွင် အသုံးပြုပါ။.
- Upstream Selectivity ကို စစ်ဆေးပါ-
- အားသွင်းစက်အတွက် Type B RCD ကို တပ်ဆင်ပါက fuse ကအနိုင်ရတယ် (သို့မဟုတ် သူတို့နှစ်ယောက်စလုံး ခရီးထွက်သွားတယ်)။ main RCD သည် Type A မဟုတ်ကြောင်း သေချာပါစေ။ Type B မှတဆင့် ဖြတ်သန်းသွားသော DC ချို့ယွင်းချက်သည် upstream Type A ကို မျက်စိကွယ်စေနိုင်သည်။ အကောင်းဆုံးအားဖြင့် EV ဆားကစ်ကို အခြားဆားကစ်များနှင့်အပြိုင် ချိတ်ဆက်သင့်သည်၊ ယေဘုယျ Type A ၏ downstream မဟုတ်ပါ RCCB, သို့မဟုတ် main switch သည် Type B (ရှားပါး/စျေးကြီး) သို့မဟုတ် non-RCD (TN-C-S/TN-S ခွင့်ပြုပါက) ဖြစ်သင့်သည်။.
- စီးပွားဖြစ် ပတ်ဝန်းကျင်များကို ထည့်သွင်းစဉ်းစားပါ-
- အားသွင်းစက်များစွာပါရှိသော စီးပွားဖြစ် ဆက်တင်များတွင် စုပြုံလာသော ယိုစိမ့်မှု (အားသွင်းစက်တစ်ခုလျှင် 6mA အောက်ပင်) သည် ပြဿနာဖြစ်နိုင်သည်။. အမျိုးအစား B အာရ်စီဒီများ သည် တာရှည်ခံမှုအတွက် ပိုမိုနှစ်သက်ပြီး အတွင်းပိုင်းအားသွင်းစက် အီလက်ထရွန်းနစ်ပစ္စည်းများ၏ ကွဲပြားသော အရည်အသွေးကို အားကိုးခြင်းကို ရှောင်ရှားရန်ဖြစ်သည်။.

ကုန်ကျစရိတ်နှင့် ဘေးကင်းလုံခြုံရေး ခွဲခြမ်းစိတ်ဖြာခြင်း
| အစိတ်အပိုင်း မဟာဗျူဟာ | စက်ပစ္စည်းကုန်ကျစရိတ် | တပ်ဆင်ခအလုပ်သမား | ယုံကြည်စိတ်ချရမှု | ပြုပြင်ထိန်းသိမ်းမှု |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type A RCD + 6mA RDC-DD (Built-in) | အနိမ့် | စံ | EVSE အရည်အသွေးပေါ်တွင် မူတည်သည်။ | ရှုပ်ထွေးသည် (အားသွင်းစက် ပြုပြင်ခြင်း) |
| Type B RCD (ပြင်ပ) | မြင့် | စံ | အလွန်မြင့်မားသည် (စက်မှုအဆင့်) | ရိုးရှင်းသည် (Breaker လဲလှယ်ခြင်း) |
| Type F RCD + RDC-DD | လတ် | စံ | လတ် | ရှုပ်ထွေးသည်။ |
တန်ဖိုးမြင့်ပစ္စည်းများနှင့် အရေးကြီးသော အခြေခံအဆောက်အအုံများအတွက် Type B RCD သည် အားသွင်းစက်၏ အတွင်းပိုင်း အီလက်ထရွန်းနစ်ပစ္စည်းများနှင့် လွတ်လပ်မှုကြောင့် အင်ဂျင်နီယာဆိုင်ရာ ဦးစားပေးအဖြစ် ဆက်လက်တည်ရှိနေပါသည်။ အစုလိုက်အိမ်ရာများအတွက် Type A + RDC-DD မော်ဒယ်သည် စီးပွားရေးစံနှုန်းဖြစ်သည်။.
အမြဲမေးလေ့ရှိသောမေးခွန်းများ
မေး- EV အားသွင်းရန်အတွက် Type AC RCD ကို သုံးနိုင်ပါသလား။
A- မရှိ Type AC RCDs များကို EV အားသွင်းရန်အတွက် တရားစီရင်ပိုင်ခွင့်အများစုတွင် (IEC 60364-7-722 အောက်တွင် အပါအဝင်) တားမြစ်ထားသည်၊ အကြောင်းမှာ ၎င်းတို့သည် EV ပြုပြင်ပြောင်းလဲရေး ဆားကစ်များတွင် အဖြစ်များသော pulsating DC ကို ရှာဖွေ၍မရသောကြောင့်ဖြစ်သည်။.
မေး- Type B RCD ရှိပါက မြေစိုက်ချောင်း လိုအပ်ပါသလား။
ဖြေ- RCD အမျိုးအစားသည် ယိုစိမ့်မှုကို ရှာဖွေခြင်းကို ညွှန်ပြသည်၊ မြေစိုက်ချိတ်ဆက်မှုများကို မဟုတ်ပါ။ သို့သော် PME (TN-C-S) ထောက်ပံ့မှုများအတွက် Type B သို့မဟုတ် Type A RCD ကို အသုံးပြုသည်ဖြစ်စေ open-PEN ရှာဖွေရေးကိရိယာ သို့မဟုတ် မြေစိုက်ချောင်း လိုအပ်နိုင်သေးသည်။.
မေး- RDC-MD နှင့် RDC-PD အကြား ကွာခြားချက်ကဘာလဲ။
ဖြေ- နှစ်ခုစလုံးကို IEC 62955 တွင် သတ်မှတ်ထားသည်။ တစ်ခု RDC-MD စောင့်ကြည့်သည်။ leakage and tells a contactor to open (cheaper, integrated). An RDC-PD has its own အကာအကွယ် (switching) mechanism, making it safer if the contactor welds shut.
Q: Can I use a Type B RCD downstream of a Type A RCD?
A: Generally, no. Ideally, RCDs should be coordinated. If a DC fault occurs, it flows through both. The downstream Type B will trip, but the DC current might have already blinded the upstream Type A, disabling it for other circuits. Best practice is to connect the EV circuit in parallel or ensure the upstream device is also Type B (or time-delayed Type S, if appropriate for the system earthing).
For more information on selecting the right circuit protection for your projects, explore our guides on Electrical Derating Factors နှင့် Circuit Breakers အမျိုးအစားများ.