សេចក្តីផ្តើម
In modern electrical systems, protecting equipment from overvoltage events is critical for operational continuity and safety. While the terms “surge arrester” and “lightning arrester” are often used interchangeably, these devices serve distinct purposes in comprehensive protection strategies. Understanding the differences between surge arresters and lightning arresters is essential for engineers, facility managers, and procurement professionals tasked with designing effective electrical protection systems.
Lightning strikes remain one of nature’s most destructive forces, capable of delivering instantaneous surges exceeding 100,000 amperes. However, electrical systems face numerous other threats including switching transients, power fluctuations, and induced overvoltages. This article clarifies the technical distinctions between lightning arresters and surge arresters, examines their respective applications, and provides guidance for selecting appropriate protection devices for your facility.
What is a Lightning Arrester?
Definition and Primary Purpose
A lightning arrester is a protective device specifically engineered to safeguard electrical infrastructure from direct or nearby lightning strikes. Its primary mission is to intercept massive electrical surges caused by lightning and provide a low-resistance path to safely divert this enormous current to ground, preventing catastrophic damage to structures, transmission lines, and connected equipment.
Lightning arresters are typically installed at service entrances, on rooftops, along overhead power lines, and at substations where exposure to direct lightning strikes is highest. These devices are designed to handle extremely high discharge currents—often exceeding 10,000 amperes (10 kA)—with very steep wavefronts characteristic of lightning events.
គោលការណ៍ការងារ
The lightning arrester operates based on voltage-dependent impedance characteristics. Under normal operating conditions, the arrester maintains high impedance and does not affect circuit operation. When a lightning-induced voltage surge exceeds the arrester’s threshold voltage, the device rapidly transitions to a low-impedance state, creating a preferred conductive path to ground.
This discharge process diverts the lightning current away from sensitive equipment, limiting the voltage to safe levels. Once the surge passes, the arrester automatically returns to its high-impedance state, restoring normal system operation without interruption. Modern lightning arresters utilize metal oxide varistor (MOV) technology, primarily zinc oxide (ZnO), which provides excellent non-linear voltage-current characteristics and self-restoration capabilities.

What is a Surge Arrester?
Definition and Primary Purpose
A surge arrester, also known as a surge protective device (SPD) or transient voltage surge suppressor (TVSS), is designed to protect electrical and electronic equipment from transient overvoltages caused by internal system disturbances. These disturbances include switching operations, capacitor bank switching, motor startups, load variations, and indirect lightning-induced surges.
Unlike lightning arresters that handle direct high-energy lightning strikes, surge arresters address smaller, more frequent voltage spikes that occur within the electrical distribution system. They are installed closer to sensitive equipment—inside electrical panels, at branch circuits, and near critical loads requiring protection from operational transients.
គោលការណ៍ការងារ
Surge arresters function by continuously monitoring the voltage in the electrical system. Under normal conditions, the device remains in a high-impedance state with minimal effect on circuit operation. When a transient overvoltage is detected—whether from switching events or induced surges—the surge arrester rapidly decreases its impedance, clamping the voltage to a safe level and diverting excess current to ground.
The clamping voltage (also called voltage protection level or Up) is a critical specification that determines the maximum voltage appearing across protected equipment terminals during a surge event. High-quality surge arresters provide fast response times (typically nanoseconds to microseconds) and precise voltage limiting to protect sensitive electronic components from damage or degradation.
Key Differences Between Lightning Arrester and Surge Arrester
Comprehensive Comparison
While both devices protect against overvoltage, their design, application, and protective capabilities differ significantly:
| ទិដ្ឋភាព | Lightning Arrester | Surge Arrester |
|---|---|---|
| គោលបំណងចម្បង | Protection against direct lightning strikes and associated high-energy surges | Protection against switching transients and operational overvoltages |
| វិសាលភាពការពារ | External electrical infrastructure, service entrance, overhead lines | Internal equipment, branch circuits, sensitive electronics |
| ការគ្រប់គ្រងថាមពល | Extremely high (handles currents up to 100+ kA) | Moderate to low (typically 5-40 kA depending on type) |
| ជួរវ៉ុល | High voltage systems (3 kV to 1000 kV); Low voltage (0.28-0.5 kV) | Primarily low voltage (≤1.2 kV, commonly 220-380V) |
| ទីតាំងដំឡើង | Service entrance, substations, transmission towers, rooftops | Distribution panels, branch circuits, near protected equipment |
| ឆ្លើយតបពេលវេលា | Fast (microseconds) | Very fast (nanoseconds to microseconds) |
| Current Waveform | 10/350 μs (lightning impulse) | 8/20 μs (switching surge) |
| ស្តង់ដារ | IEEE C62.11, IEC 60099-4 | IEC 61643-11, UL 1449, IEEE C62.62 |
| រាងកាយទំហំ | Larger due to external insulation requirements | Compact, suitable for panel mounting |
| Application Context | First line of defense against lightning | Secondary/tertiary protection layer |
Functional Distinction
Lightning arresters are specialized for handling the massive, instantaneous energy discharge from direct lightning strikes. They must withstand peak currents with extremely steep rise times (microseconds) and safely dissipate energy that can exceed 10 megajoules. Their construction prioritizes high discharge capacity and robust external insulation.
ឧបករណ៍ចាប់រន្ទះ focus on suppressing smaller, more frequent transient overvoltages that occur during normal system operation. They provide fine-tuned voltage clamping to protect sensitive electronic circuits, instrumentation, and control systems from degradation caused by repetitive surge exposure.
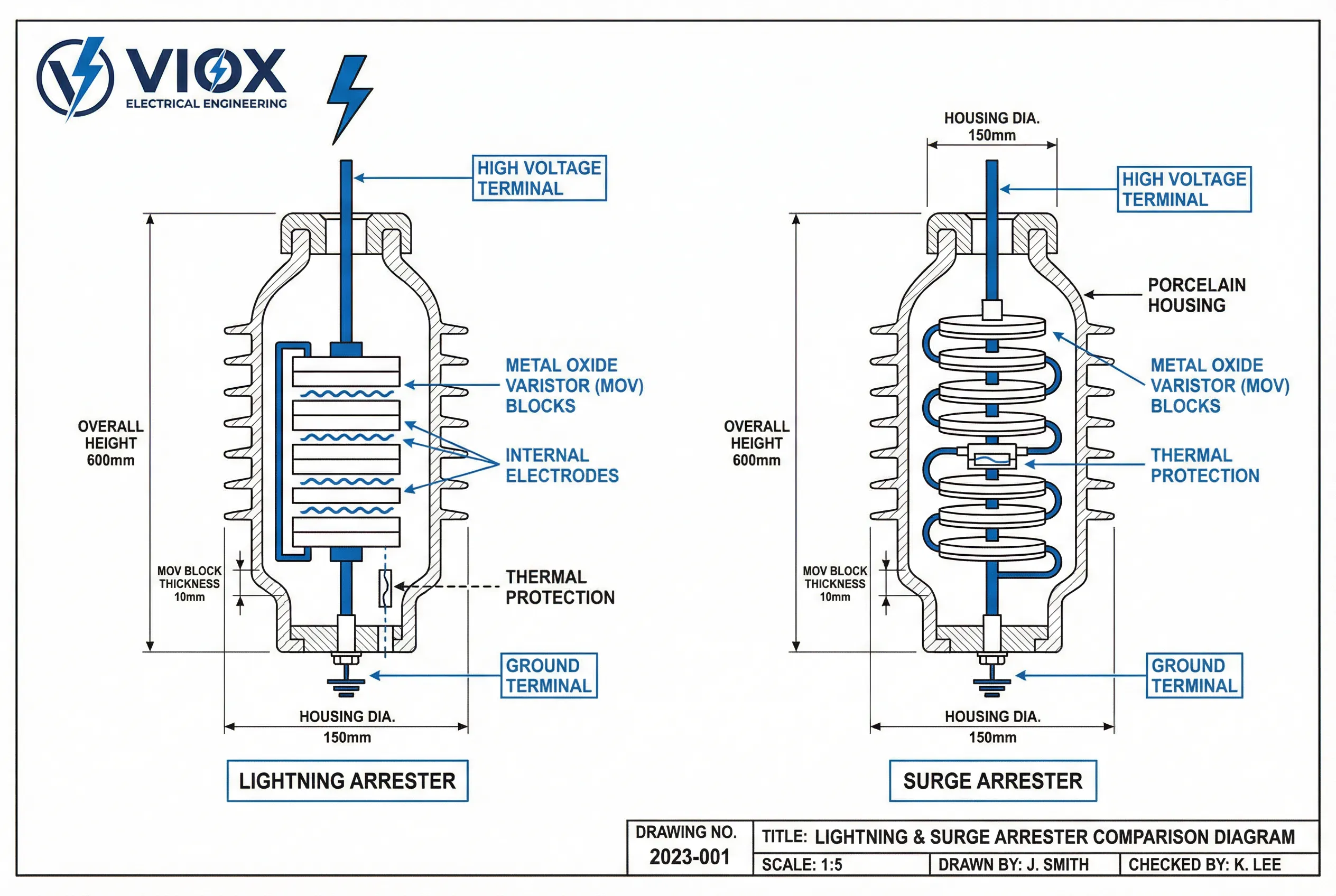
Types of Lightning Arresters
1. Rod Gap Lightning Arrester
The simplest design featuring a rod electrode with a predetermined gap distance. When voltage exceeds the breakdown threshold, an arc forms across the gap, conducting surge current to ground. These arresters are limited in application and primarily used in low-voltage systems due to their inability to interrupt follow-on current effectively.
2. Horn Gap Lightning Arrester
An improvement over rod gap design, featuring two horn-shaped electrodes separated by an air gap. When lightning strikes, the arc forms at the narrowest point and then rises due to electromagnetic forces and thermal convection. The increasing gap distance helps extinguish the arc naturally. Horn gap arresters are suitable for medium-voltage applications (typically up to 33 kV).
3. Multi-Gap (Expulsion Type) Lightning Arrester
This design incorporates multiple series gaps with fiber tubes or chambers. During operation, the arc generates gas pressure that helps extinguish the arc and interrupt follow-on current. Multi-gap arresters provide better protection than simple gap types but have been largely superseded by modern designs.
4. Valve-Type Lightning Arrester
A significant advancement incorporating non-linear resistors (typically silicon carbide) in series with spark gaps. The non-linear resistance provides low resistance during surge conditions and high resistance during normal operation, effectively limiting follow-on current. Valve-type arresters offer superior protection characteristics and were widely used in medium and high-voltage applications.
5. Metal Oxide (MOV) Lightning Arrester
The most advanced and widely used technology today, metal oxide arresters utilize zinc oxide (ZnO) varistor elements without series gaps. The highly non-linear voltage-current characteristic of zinc oxide provides:
- Excellent surge absorption capability
- No follow-on current issues
- Superior voltage limiting performance
- អាយុកាលសេវាកម្មយូរជាមួយនឹងការរិចរិលតិចតួចបំផុត។
- ការរចនាបង្រួម
- Self-restoration after surge events
MOV arresters are available for all voltage levels from low voltage (under 1 kV) to ultra-high voltage (over 800 kV) and have become the industry standard for modern electrical systems.
Types of Surge Arresters (ឧបករណ៍ការពាររលក)
According to IEC 61643-11 and related standards, surge arresters are classified based on their protection level and typical installation location:
SPD ប្រភេទ 1 (ថ្នាក់ I)
លក្ខណៈ៖
- បានធ្វើតេស្តជាមួយទម្រង់រលកកម្លាំង 10/350 μs
- សមត្ថភាពស្រូបយកថាមពលខ្ពស់បំផុត
- រចនាឡើងដើម្បីទប់ទល់នឹងចរន្តរន្ទះផ្ទាល់
- ចរន្តកម្លាំងធម្មតា (Iimp): 25 kA ទៅ 100 kA
- ចរន្តបញ្ចេញអតិបរមា: 50 kA ទៅ 100 kA
កម្មវិធី៖
- បន្ទះចែកចាយមេនៅច្រកចូលសេវាកម្ម
- អគារដែលមានប្រព័ន្ធការពាររន្ទះខាងក្រៅ (LPS)
- ទីតាំងដែលមានហានិភ័យរន្ទះខ្ពស់
- ស្រទាប់ការពារបឋម (ការផ្លាស់ប្តូរ LPZ 0 ទៅ LPZ 1)
SPD ប្រភេទ 2 (ថ្នាក់ II)
លក្ខណៈ៖
- បានធ្វើតេស្តជាមួយទម្រង់រលកកម្លាំង 8/20 μs
- ការស្រូបយកថាមពលកម្រិតមធ្យម
- ការពារប្រឆាំងនឹងរន្ទះដោយប្រយោល និងការកើនឡើងនៃកុងតាក់
- ចរន្តបញ្ចេញបន្ទាប់បន្សំធម្មតា (In): 5 kA ទៅ 40 kA
- ប្រភេទ SPD ដែលត្រូវបានដាក់ពង្រាយជាទូទៅបំផុត
កម្មវិធី៖
- បន្ទះរងចែកចាយ
- ឧស្សាហកគ្រប់គ្រងបន្ទះ
- ការដំឡើងអគ្គិសនីពាណិជ្ជកម្ម
- ស្រទាប់ការពារបន្ទាប់បន្សំ (ការផ្លាស់ប្តូរ LPZ 1 ទៅ LPZ 2)
SPD ប្រភេទ 3 (ថ្នាក់ III)
លក្ខណៈ៖
- បានធ្វើតេស្តជាមួយរលករួមបញ្ចូលគ្នា (វ៉ុល 1.2/50 μs, ចរន្ត 8/20 μs)
- សមត្ថភាពថាមពលទាបបំផុត
- ការកែសម្រួលការការពារឧបករណ៍ដែលងាយរងគ្រោះ
- ចរន្តបញ្ចេញធម្មតា: 1.5 kA ទៅ 10 kA
- កម្រិតការពារវ៉ុលទាបបំផុត
កម្មវិធី៖
- រន្ធដោតនៅជិតឧបករណ៍ដែលងាយរងគ្រោះ
- សៀគ្វីសាខាចុងក្រោយ
- ឧបករណ៍ IT, ឧបករណ៍វាស់ស្ទង់ និងប្រព័ន្ធគ្រប់គ្រង
- ស្រទាប់ការពារទីបី (ការផ្លាស់ប្តូរ LPZ 2 ទៅ LPZ 3)
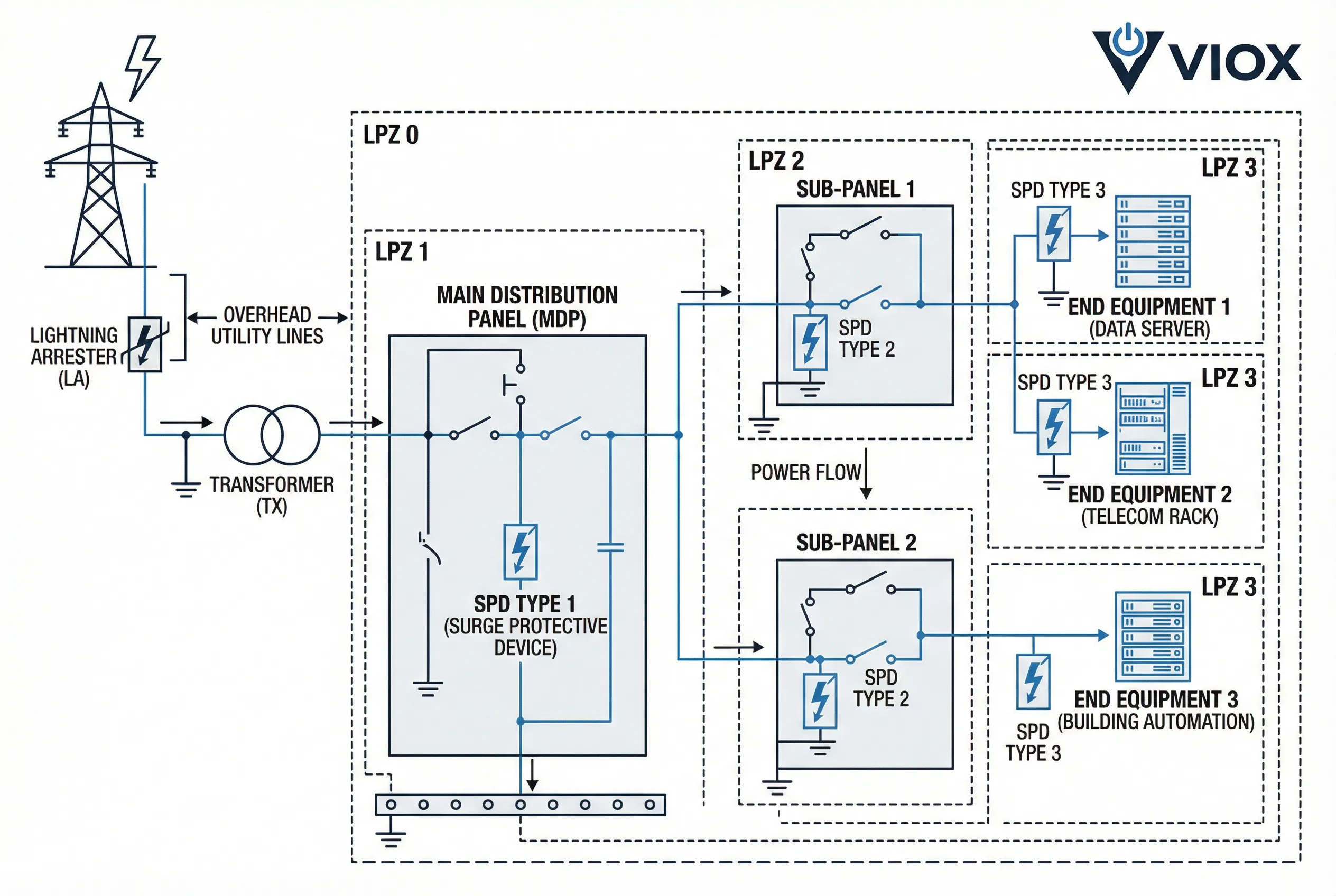
ការការពារ SPD ដែលបានសម្របសម្រួល
យុទ្ធសាស្រ្តការពារទំនើបអនុវត្តការដំឡើង SPD ដែលបានដាក់បញ្ចូល ឬសម្របសម្រួលនៅទូទាំងតំបន់ការពារច្រើន (តំបន់ការពាររន្ទះ – LPZ)។ SPDs ប្រភេទ 1 នៅច្រកចូលសេវាកម្មដោះស្រាយការកើនឡើងថាមពលខ្ពស់, SPDs ប្រភេទ 2 នៅបន្ទះចែកចាយផ្តល់នូវការការពារកម្រិតមធ្យម, និង SPDs ប្រភេទ 3 នៅទីតាំងប្រើប្រាស់ចុងក្រោយផ្តល់នូវការការពារចុងក្រោយសម្រាប់ឧបករណ៍សំខាន់ៗ។.
ការប្រៀបធៀបលក្ខណៈបច្ចេកទេស
| ប៉ារ៉ាម៉ែត្រ | Lightning Arrester | ឧបករណ៍ចាប់រលក (SPD) |
|---|---|---|
| វ៉ុលដែលបានវាយតម្លៃ | 3 kV ទៅ 1000 kV (HV); 0.28-0.5 kV (LV) | ≤1.2 kV; ជាធម្មតា 230-690V AC |
| វ៉ុលប្រតិបត្តិការបន្តអតិបរមា (MCOV) | អាស្រ័យលើប្រព័ន្ធ, ជាធម្មតា 0.8-0.84 pu | 1.05-1.15 × វ៉ុលបន្ទាប់បន្សំ |
| សមត្ថភាពចរន្តបញ្ចេញ | 10 kA ទៅ 100+ kA (10/350 μs) | ប្រភេទ 1: 25-100 kA; ប្រភេទ 2: 5-40 kA; ប្រភេទ 3: 1.5-10 kA (8/20 μs) |
| Voltage Protection Level (Up) | សម្របសម្រួលជាមួយឧបករណ៍ BIL | ≤2.5 × វ៉ុលប្រព័ន្ធ |
| ឆ្លើយតបពេលវេលា | <100 nanoseconds (ប្រភេទ MOV) | <25 nanoseconds (ប្រភេទ 3); <100 nanoseconds (ប្រភេទ 1/2) |
| ការស្រូបយកថាមពល | ខ្ពស់ណាស់ (>10 MJ) | ប្រភេទ 1: ខ្ពស់ (250-500 kJ); ប្រភេទ 2: មធ្យម (50-150 kJ); ប្រភេទ 3: ទាប |
| ការរំខានចរន្តតាម | ពន្លត់ដោយខ្លួនឯង (ប្រភេទ MOV) | ពន្លត់ដោយខ្លួនឯង |
| ជួរសីតុណ្ហភាពប្រតិបត្តិការ | -40°C ទៅ +60°C | -40°C ដល់ +85°C |
| ជីវិតសេវាកម្ម | 20-30 ឆ្នាំ | 10-25 ឆ្នាំ (អាស្រ័យលើការប៉ះពាល់នឹងការកើនឡើង) |
| គ្រឿងបន្លាស់សំខាន់ៗ | ZnO varistors, លំនៅដ្ឋានសេរ៉ាមិច | MOV, GDT (បំពង់បញ្ចេញឧស្ម័ន), TVS diodes, តម្រង |
កម្មវិធី និងទីតាំងដំឡើង
កម្មវិធីចាប់រន្ទះ
ការបញ្ជូន និងចែកចាយថាមពល៖
- ខ្សែបញ្ជូនលើអាកាស (គ្រប់កម្រិតវ៉ុល)
- ស្ថានីយអគ្គិសនី (HV, MV, LV)
- ឧបករណ៍បំលែងចែកចាយ
- ឧបករណ៍បំលែងដែលបានម៉ោនលើបន្ទះ
- បង្គោលកើនឡើងដែលបានម៉ោនលើបង្គោល
គ្រឿងបរិក្ខារឧស្សាហកម្ម៖
- រោងចក្រផលិតនៅតំបន់ដែលងាយនឹងរន្ទះ
- ទីតាំងគីមី និងគីមីឥន្ធនៈ
- ប្រតិបត្តិការរុករករ៉ែ
- រោងចក្រប្រព្រឹត្តកម្មទឹក
- ស្មុគស្មាញឧស្សាហកម្មធុនធ្ងន់
ហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ:
- ប៉មទូរគមនាគមន៍
- ប្រព័ន្ធចរន្តអគ្គិសនីផ្លូវដែក
- គ្រឿងបរិក្ខារអាកាសយានដ្ឋាន
- ប្រព័ន្ធប្រមូលផ្តុំថាមពលពន្លឺព្រះអាទិត្យ និងខ្យល់
ការប្រើប្រាស់ឧបករណ៍ទប់លំនឹង (SPD)
អគារពាណិជ្ជកម្ម៖
- អគារការិយាល័យ
- ផ្សារទំនើប
- សណ្ឋាគារ និងបដិសណ្ឋារកិច្ច
- មណ្ឌលថែទាំសុខភាព
- Educational institutions
ប្រព័ន្ធគ្រប់គ្រងឧស្សាហកម្ម៖
- ឧបករណ៍បញ្ជាតក្កវិជ្ជាដែលអាចសរសេរកម្មវិធីបាន (PLCs)
- ប្រព័ន្ធគ្រប់គ្រងចែកចាយ (DCS)
- ឧបករណ៍បញ្ជាប្រេកង់អថេរ (VFDs)
- មជ្ឈមណ្ឌលគ្រប់គ្រងម៉ូទ័រ
- ប្រព័ន្ធ SCADA
បច្ចេកវិទ្យាព័ត៌មាន និងទូរគមនាគមន៍៖
- មជ្ឈមណ្ឌលទិន្នន័យ
- បន្ទប់ម៉ាស៊ីនមេ
- ឧបករណ៍បណ្តាញ
- ប្រព័ន្ធទំនាក់ទំនង
- ការកសាងប្រព័ន្ធស្វ័យប្រវត្តិកម្ម
ថាមពលកកើតឡើងវិញ៖
- ប្រព័ន្ធថាមពលពន្លឺព្រះអាទិត្យ (PV)
- ប្រព័ន្ធទួរប៊ីនខ្យល់
- ប្រព័ន្ធផ្ទុកថាមពល
- មីក្រូហ្គ្រីដ
Standards and Compliance
ស្តង់ដារអន្តរជាតិ
ស្តង់ដារ IEC៖
- IEC 61643-11៖ តម្រូវការ SPD វ៉ុលទាប និងវិធីសាស្ត្រធ្វើតេស្ត (ស្តង់ដារចម្បងសម្រាប់ឧបករណ៍ទប់លំនឹង)
- IEC 60099-4៖ ឧបករណ៍ទប់លំនឹងអុកស៊ីដលោហៈដោយគ្មានចន្លោះសម្រាប់ប្រព័ន្ធ AC (ឧបករណ៍ទប់រន្ទះ)
- IEC 62305៖ ការការពារប្រឆាំងនឹងរន្ទះ (ការរចនាប្រព័ន្ធការពារទាំងមូល)
ស្តង់ដារ IEEE៖
- IEEE C62.11៖ ឧបករណ៍ទប់លំនឹងអុកស៊ីដលោហៈសម្រាប់សៀគ្វីថាមពល AC (ឧបករណ៍ទប់រន្ទះ)
- IEEE C62.41៖ លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានរំញ័រ
- IEEE C62.62៖ លក្ខណៈបច្ចេកទេសតេស្តសម្រាប់ SPDs
- IEEE C62.72៖ មគ្គុទ្ទេសក៍កម្មវិធីសម្រាប់ SPDs
ស្តង់ដារក្នុងតំបន់៖
- UL 1449 (ការបោះពុម្ពលើកទី 4)៖ ស្តង់ដារអាមេរិកសម្រាប់ SPDs
- EN 61643-11៖ ការអនុម័តស្តង់ដារ IEC របស់អឺរ៉ុប
- CSA C22.2 លេខ 269៖ ស្តង់ដារ SPD របស់កាណាដា
គោលការណ៍ណែនាំស្តីពីការអនុលោមតាម
នៅពេលបញ្ជាក់ឧបករណ៍ទប់រន្ទះ ឬឧបករណ៍ទប់លំនឹង ត្រូវប្រាកដថាអនុលោមតាម៖
- តម្រូវការកម្រិតវ៉ុល សមស្របសម្រាប់ប្រព័ន្ធរបស់អ្នក
- សមត្ថភាពចរន្តបញ្ចេញ ត្រូវគ្នានឹងបរិស្ថានរំញ័រដែលរំពឹងទុក
- កម្រិតការពារវ៉ុល ត្រូវគ្នាជាមួយនឹងភាពធន់ទ្រាំអ៊ីសូឡង់ឧបករណ៍
- កម្រិតសីតុណ្ហភាព សមស្របសម្រាប់បរិស្ថានដំឡើង
- សញ្ញាសម្គាល់វិញ្ញាបនបត្រ ពីមន្ទីរពិសោធន៍ធ្វើតេស្តដែលទទួលស្គាល់ (UL, CE, TÜV, CB)
- ស្តង់ដារដំឡើង យោងតាមមាត្រា 285 នៃ NEC (សហរដ្ឋអាមេរិក) ឬក្រមអគ្គិសនីក្នុងស្រុក
សំណួរដែលសួរញឹកញាប់ (FAQ)
1. តើឧបករណ៍ទប់លំនឹងអាចជំនួសឧបករណ៍ទប់រន្ទះបានទេ?
No, surge arresters cannot replace lightning arresters for direct lightning strike protection. While a lightning arrester can provide some protection against smaller surges, surge arresters lack the high discharge current capacity (10/350 μs waveform) required to safely handle direct lightning strikes. Comprehensive protection requires both devices in a coordinated system: lightning arresters at the service entrance for primary protection and surge arresters at distribution and end-use locations for secondary protection.
2. តើខ្ញុំកំណត់ថាតើ SPD ប្រភេទណា (ប្រភេទ 1, 2 ឬ 3) ដែលត្រូវការដោយរបៀបណា?
ការជ្រើសរើស SPD អាស្រ័យលើគោលគំនិតតំបន់ការពាររន្ទះ (LPZ)៖
- ប្រភេទ 1 SPD៖ ដំឡើងនៅព្រំដែន LPZ 0-1 (ច្រកចូលសេវាកម្ម) នៅក្នុងអគារដែលមានប្រព័ន្ធការពាររន្ទះខាងក្រៅ ឬនៅក្នុងតំបន់ដែលមានហានិភ័យរន្ទះខ្ពស់
- ប្រភេទ 2 SPD៖ ដំឡើងនៅព្រំដែន LPZ 1-2 (បន្ទះចែកចាយ បន្ទះរង) សម្រាប់ការការពារអគារទូទៅ
- ប្រភេទ 3 SPD៖ ដំឡើងនៅព្រំដែន LPZ 2-3 (នៅជិតឧបករណ៍ដែលងាយរងគ្រោះ) នៅពេលដែលត្រូវការការការពារបន្ថែម
ភាគច្រើននៃគ្រឿងបរិក្ខារត្រូវការ SPDs ប្រភេទ 2 យ៉ាងហោចណាស់។ បន្ថែមប្រភេទ 1 ប្រសិនបើអ្នកមាន LPS ឬស្ថិតនៅក្នុងតំបន់ដែលមានហានិភ័យខ្ពស់។ រួមបញ្ចូលប្រភេទ 3 សម្រាប់ឧបករណ៍អេឡិចត្រូនិកសំខាន់ៗ។.
3. តើអ្វីជាភាពខុសគ្នារវាងបច្ចេកវិទ្យាការពាររំញ័រ MOV និង GDT?
Metal Oxide Varistor (MOV)៖
- រេស៊ីស្តង់អាស្រ័យវ៉ុលដោយប្រើស័ង្កសីអុកស៊ីដ
- ការស្រូបយកថាមពលបានល្អ
- វ៉ុលគៀបទាប
- បន្តិចម្តងៗចុះខ្សោយជាមួយនឹងការរំញ័រម្តងហើយម្តងទៀត
- ល្អបំផុតសម្រាប់ការទប់ស្កាត់ការរំញ័រថាមពលខ្ពស់
Gas Discharge Tube (GDT)៖
- បំពង់សេរ៉ាមិចដែលពោរពេញទៅដោយឧស្ម័នជាមួយអេឡិចត្រូត
- សមត្ថភាពចរន្តរំញ័រខ្ពស់ណាស់
- វ៉ុលគៀបខ្ពស់ជាង
- ពេលវេលាឆ្លើយតបយឺតជាង
- ល្អសម្រាប់ទូរគមនាគមន៍ និងខ្សែសញ្ញា
ជាទូទៅ SPD សម័យទំនើប ផ្សំបញ្ចូលបច្ចេកវិទ្យាទាំងពីរ៖ GDT សម្រាប់សមត្ថភាពចរន្តខ្លាំង និង MOV សម្រាប់ឆ្លើយតបលឿន និងការទប់វ៉ុល។.
4. តើឧបករណ៍ទប់រន្ទះ និងឧបករណ៍ទប់លំហូរភ្លើង គួរត្រូវបានធ្វើតេស្ត ឬផ្លាស់ប្តូរញឹកញាប់ប៉ុណ្ណា?
ឧបករណ៍ទប់រន្ទះ៖
- ត្រួតពិនិត្យដោយភ្នែក៖ ជារៀងរាល់ឆ្នាំ
- ធ្វើតេស្តអគ្គិសនី (ភាពធន់ទ្រាំអ៊ីសូឡង់, វ៉ុលប្រេកង់ថាមពល)៖ រៀងរាល់ 1-3 ឆ្នាំ
- ផ្លាស់ប្តូរ៖ 20-30 ឆ្នាំ ឬបន្ទាប់ពីមានហេតុការណ៍រន្ទះធ្ងន់ធ្ងរ
- ត្រួតពិនិត្យសូចនាករសភាព ប្រសិនបើបំពាក់
ឧបករណ៍ទប់លំហូរភ្លើង (SPDs)៖
- ត្រួតពិនិត្យដោយភ្នែក៖ រៀងរាល់ 6-12 ខែ
- ពិនិត្យមើលសូចនាករស្ថានភាព (ប្រសិនបើមាន)៖ ប្រចាំខែ
- ធ្វើតេស្តអគ្គិសនី៖ តាមការណែនាំរបស់អ្នកផលិត
- ផ្លាស់ប្តូរ៖ បន្ទាប់ពីមានហេតុការណ៍លំហូរភ្លើងធ្ងន់ធ្ងរ ឬនៅពេលដែលសូចនាករបង្ហាញពីការបរាជ័យ
- អាយុកាលសេវាកម្មធម្មតា៖ 10-25 ឆ្នាំ អាស្រ័យលើការប៉ះពាល់នឹងលំហូរភ្លើង
កត់ត្រាសកម្មភាពថែទាំទាំងអស់ និងឧបករណ៍រាប់ហេតុការណ៍លំហូរភ្លើង (ប្រសិនបើមាន) ដើម្បីតាមដានសុខភាពឧបករណ៍។.
5. តើមានអ្វីកើតឡើងប្រសិនបើឧបករណ៍ទប់រន្ទះ ឬ SPD បរាជ័យ?
របៀបបរាជ័យប្រែប្រួលតាមការរចនា៖
បរាជ័យដោយសុវត្ថិភាព (ពេញចិត្ត)៖
- ឧបករណ៍ផ្តាច់កម្តៅដែលបានសាងសង់រួចជាស្រេចដំណើរការ
- ឧបករណ៍ក្លាយជាសៀគ្វីបើកចំហ
- សូចនាករមើលឃើញ/អគ្គិសនី បង្ហាញសញ្ញានៃការបរាជ័យ
- ប្រព័ន្ធបន្តដំណើរការ ប៉ុន្តែគ្មានការការពារលំហូរភ្លើង
បរាជ័យដោយគ្រោះមហន្តរាយ៖
- លក្ខខណ្ឌសៀគ្វីខ្លីអាចកើតឡើង
- ការការពារចរន្តលើសនៅផ្នែកខាងលើ (ហ្វុយស៊ីប/អ្នកបំបែក) គួរតែញែកឧបករណ៍
- ហានិភ័យនៃអគ្គីភ័យ ប្រសិនបើការការពារកម្តៅមិនគ្រប់គ្រាន់
ឧបករណ៍ដែលមានគុណភាពពីក្រុមហ៊ុនផលិតដែលគួរឱ្យទុកចិត្តដូចជា VIOX Electric រួមបញ្ចូលយន្តការការពារសុវត្ថិភាពច្រើន រួមទាំងឧបករណ៍ផ្តាច់កម្តៅ សម្ពាធធូរស្រាល និងសូចនាករកំហុស ដើម្បីធានាបាននូវរបៀបបរាជ័យដោយសុវត្ថិភាព។.
6. តើខ្ញុំត្រូវការការការពាររន្ទះទេ ប្រសិនបើកន្លែងរបស់ខ្ញុំមានខ្សែថាមពលក្រោមដី?
បាទ/ចាស ការការពាររន្ទះនៅតែមានសារៈសំខាន់ ទោះបីជាមានខ្សែក្រោមដីក៏ដោយ។ ខណៈពេលដែលខ្សែក្រោមដីលុបបំបាត់ហានិភ័យនៃការវាយប្រហារដោយផ្ទាល់ទៅលើខ្សែថាមពល រន្ទះនៅតែអាចប៉ះពាល់ដល់កន្លែងរបស់អ្នកតាមរយៈ៖
- ការវាយប្រហារទៅលើរចនាសម្ព័ន្ធអគារដោយខ្លួនឯង
- លំហូរភ្លើងដែលបណ្តាលមកពីការវាយប្រហារលើដីក្បែរនោះ រីករាលដាលតាមរយៈដី
- លំហូរភ្លើងចូលតាមរយៈខ្សែទូរគមនាគមន៍ បំពង់ទឹក ឬឧបករណ៍ចម្លងផ្សេងទៀត
- ភាពប្រែប្រួលប្តូរពីប្រតិបត្តិការបណ្តាញអគ្គិសនី
ដំឡើង Type 2 SPDs ជាការការពារអប្បបរមា។ ពិចារណា Type 1 SPDs ប្រសិនបើអគាររបស់អ្នកមានប្រព័ន្ធការពាររន្ទះខាងក្រៅ ឬស្ថិតនៅក្នុងតំបន់ដែលមានហានិភ័យខ្ពស់។.
សេចក្តីសន្និដ្ឋាន៖ ការប្តេជ្ញាចិត្តរបស់ VIOX Electric ចំពោះការការពារលំហូរភ្លើងដ៏ទូលំទូលាយ
ការយល់ដឹងពីភាពខុសគ្នារវាងឧបករណ៍ទប់លំហូរភ្លើង និងឧបករណ៍ទប់រន្ទះ គឺជាមូលដ្ឋានគ្រឹះសម្រាប់ការរចនាប្រព័ន្ធការពារអគ្គិសនីប្រកបដោយប្រសិទ្ធភាព។ ខណៈពេលដែលឧបករណ៍ទប់រន្ទះបម្រើជាខ្សែការពារដំបូងប្រឆាំងនឹងការវាយប្រហារដោយរន្ទះដោយផ្ទាល់ និងលំហូរថាមពលខ្ពស់នៅច្រកចូលសេវាកម្ម ឧបករណ៍ទប់លំហូរភ្លើងផ្តល់នូវការការពារបន្ទាប់បន្សំដ៏សំខាន់ប្រឆាំងនឹងភាពប្រែប្រួលនៃប្រតិបត្តិការ និងវ៉ុលលើសដែលបណ្តាលមកពីបណ្តាញចែកចាយកន្លែងរបស់អ្នក។.
យុទ្ធសាស្ត្រការពារលំហូរភ្លើងដ៏ទូលំទូលាយតម្រូវឱ្យមានការដាក់ពង្រាយបច្ចេកវិទ្យាទាំងពីរដែលបានសម្របសម្រួល កំណត់យ៉ាងត្រឹមត្រូវតាម IEC 61643-11, IEEE C62.11 និងស្តង់ដារក្នុងតំបន់ដែលអាចអនុវត្តបាន។ ការជ្រើសរើសត្រូវគិតគូរពីកម្រិតវ៉ុល សមត្ថភាពចរន្តបញ្ចេញ កម្រិតការពារវ៉ុល និងតម្រូវការកម្មវិធីជាក់លាក់។.
VIOX អគ្គិសនី មានឯកទេសក្នុងការផលិតឧបករណ៍ទប់រន្ទះ និងឧបករណ៍ការពារលំហូរភ្លើងដែលមានគុណភាពខ្ពស់ ដែលត្រូវបានរចនាឡើងដើម្បីបំពេញតាមស្តង់ដារអន្តរជាតិយ៉ាងតឹងរ៉ឹង។ ផលប័ត្រផលិតផលរបស់យើងរួមមាន៖
- ឧបករណ៍ទប់រន្ទះអុកស៊ីដលោហៈសម្រាប់ថ្នាក់វ៉ុលទាំងអស់
- Type 1, Type 2, និង Type 3 ឧបករណ៍ការពារលំហូរភ្លើង
- ដំណោះស្រាយការពារលំហូរភ្លើងដែលបានសម្របសម្រួលសម្រាប់កម្មវិធីឧស្សាហកម្ម ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម និងថាមពលកកើតឡើងវិញ
- ការរចនាតាមតម្រូវការសម្រាប់តម្រូវការការពារឯកទេស
ក្រុមបច្ចេកទេសរបស់យើងផ្តល់នូវការពិគ្រោះយោបល់ពីអ្នកជំនាញ ដើម្បីជួយអ្នកក្នុងការរចនាយុទ្ធសាស្ត្រការពារស៊ីជម្រៅដ៏ល្អប្រសើរ ដែលសម្របទៅនឹងទម្រង់ហានិភ័យជាក់លាក់របស់កន្លែងអ្នក និងតម្រូវការប្រតិបត្តិការ។ កុំសម្រុះសម្រួលលើការការពារប្រព័ន្ធអគ្គិសនី—ចាប់ដៃគូជាមួយ VIOX Electric សម្រាប់ដំណោះស្រាយការពារលំហូរភ្លើងដែលអាចទុកចិត្តបាន និងមានការបញ្ជាក់។.
ទាក់ទង VIOX Electric today សម្រាប់ការវាយតម្លៃប្រព័ន្ធការពារលម្អិត និងស្វែងយល់ពីរបៀបដែលបច្ចេកវិទ្យាឧបករណ៍ទប់កម្រិតខ្ពស់របស់យើង អាចការពារហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធសំខាន់ៗរបស់អ្នកប្រឆាំងនឹងការវាយប្រហារដោយរន្ទះ និងហេតុការណ៍លំហូរភ្លើង។.


