ভূমিকা
নির্বাচন করার সময় একটি miniature circuit breaker (MCB) for an electrical installation, most engineers focus on the rated current—but there’s a critical variable that can drastically affect performance: ambient temperature. An MCB rated at 32A won’t necessarily carry 32A safely in all environments. In fact, at elevated temperatures, that same MCB might trip at just 28A or lower, leading to unexpected shutdowns and system failures.
Understanding MCB ambient temperature ratings and derating factors is essential for electrical professionals who need to ensure reliable protection in diverse operating conditions. Whether you’re designing a control panel for a desert climate, specifying breakers for an enclosed machinery cabinet, or troubleshooting nuisance tripping issues, temperature considerations play a defining role.
This comprehensive guide examines how ambient temperature affects MCB performance, explains the derating calculation methodology, and provides practical guidance for real-world installations. By the end, you’ll understand how to properly select and apply MCBs across varying thermal environments, ensuring both safety and operational reliability.
Understanding MCB Temperature Ratings
The Standard Reference Temperature
Every MCB is calibrated and tested at a specific reference ambient temperature, which serves as the baseline for its nominal current rating. According to IEC 60898-1—the international standard governing MCBs for household and similar installations—this reference temperature is 30°C (86°F). At this precise temperature, an MCB will perform according to its nameplate rating.
For industrial applications requiring more robust circuit breakers, such as molded case circuit breakers (MCCBs) governed by IEC 60947-2, the standard reference temperature is typically ৪০°C (১০৪°F). This higher baseline reflects the more demanding thermal environments common in industrial settings.
How MCBs Are Rated
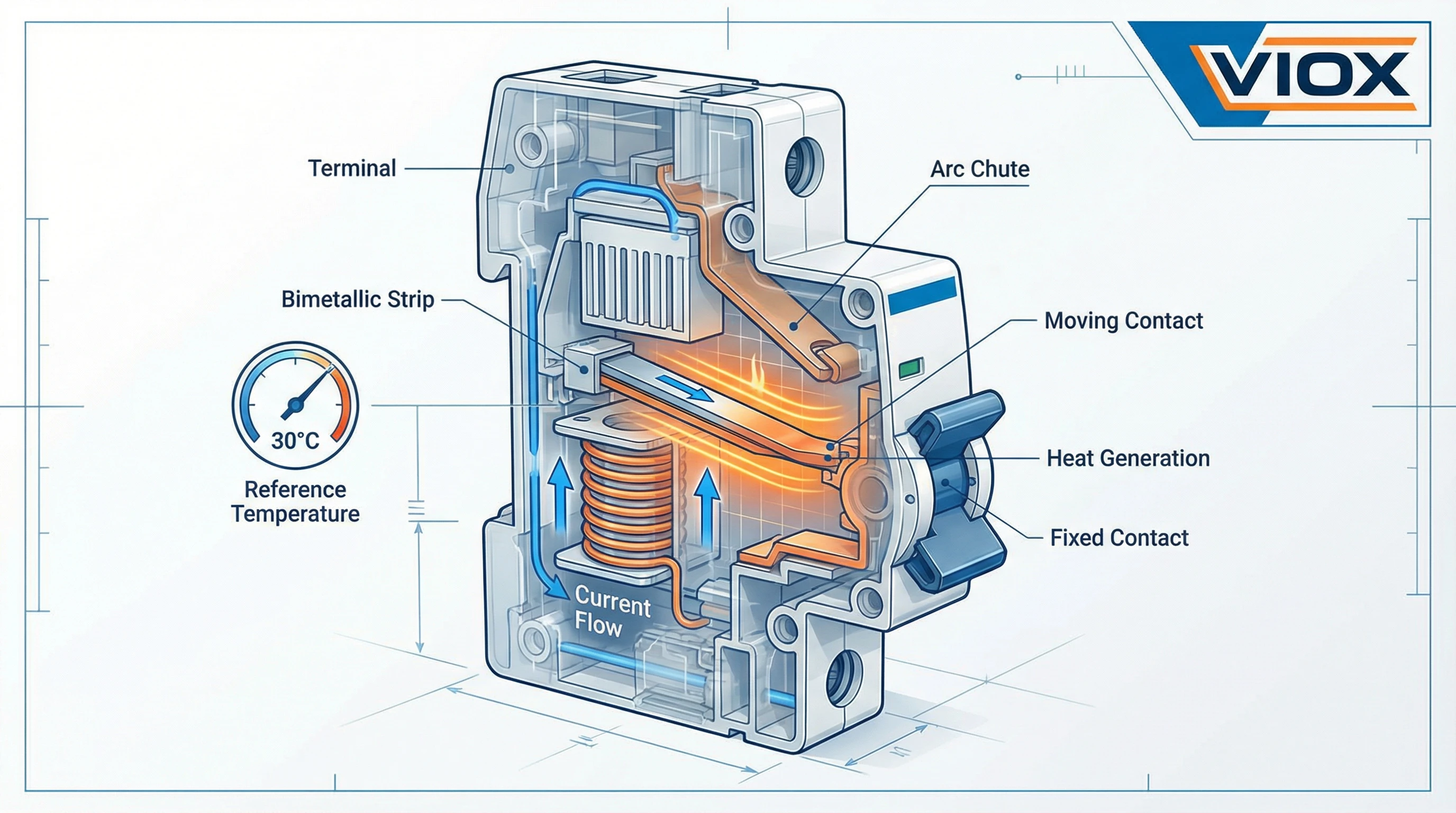
The rated current (In) marked on an MCB represents the maximum continuous current the device can carry indefinitely at the reference temperature without tripping. This rating is determined through rigorous testing where the MCB’s thermal trip element—typically a bimetallic strip—is calibrated to bend and activate the trip mechanism at specific overcurrent thresholds.
The bimetallic strip is the heart of an MCB’s overload protection. It consists of two different metals bonded together, each with a different coefficient of thermal expansion. When current flows through the strip, it generates heat. As temperature rises, the metals expand at different rates, causing the strip to bend. Once it bends sufficiently, it triggers the trip mechanism, disconnecting the circuit.
This elegant thermal-mechanical system works precisely at the calibrated reference temperature. However, it’s also inherently sensitive to the ambient temperature surrounding the MCB—which is where derating becomes critical.
The Temperature Range Limitation
While MCBs are typically rated for operation within a range of -20°C to +70°C, their ability to carry the rated current diminishes significantly as ambient temperature increases beyond the reference point. Conversely, in colder environments below the reference temperature, an MCB may allow slightly higher current before tripping—though this is rarely a design consideration since the connected cables and equipment have their own temperature limitations.
How Ambient Temperature Affects MCB Performance
The Physics of Thermal Tripping
The relationship between ambient temperature and MCB performance is rooted in basic thermal physics. The bimetallic strip inside an MCB must reach a specific temperature to trip. This temperature is achieved through two heat sources: the heat generated by the current flowing through the strip (I²R heating) and the heat from the surrounding environment (ambient temperature).
When ambient temperature increases, the bimetallic strip starts from a higher baseline temperature. It therefore requires less additional heating from current flow to reach its trip point. In practical terms, this means the MCB will trip at a lower current than its rated value.
Consider an MCB rated at 32A at 30°C. If that same MCB operates in a 50°C environment, the bimetallic strip begins 20°C hotter than the calibration baseline. To reach the trip temperature, it needs less current-induced heating—perhaps tripping at only 29A or 30A instead of the rated 32A.
Current Capacity Reduction
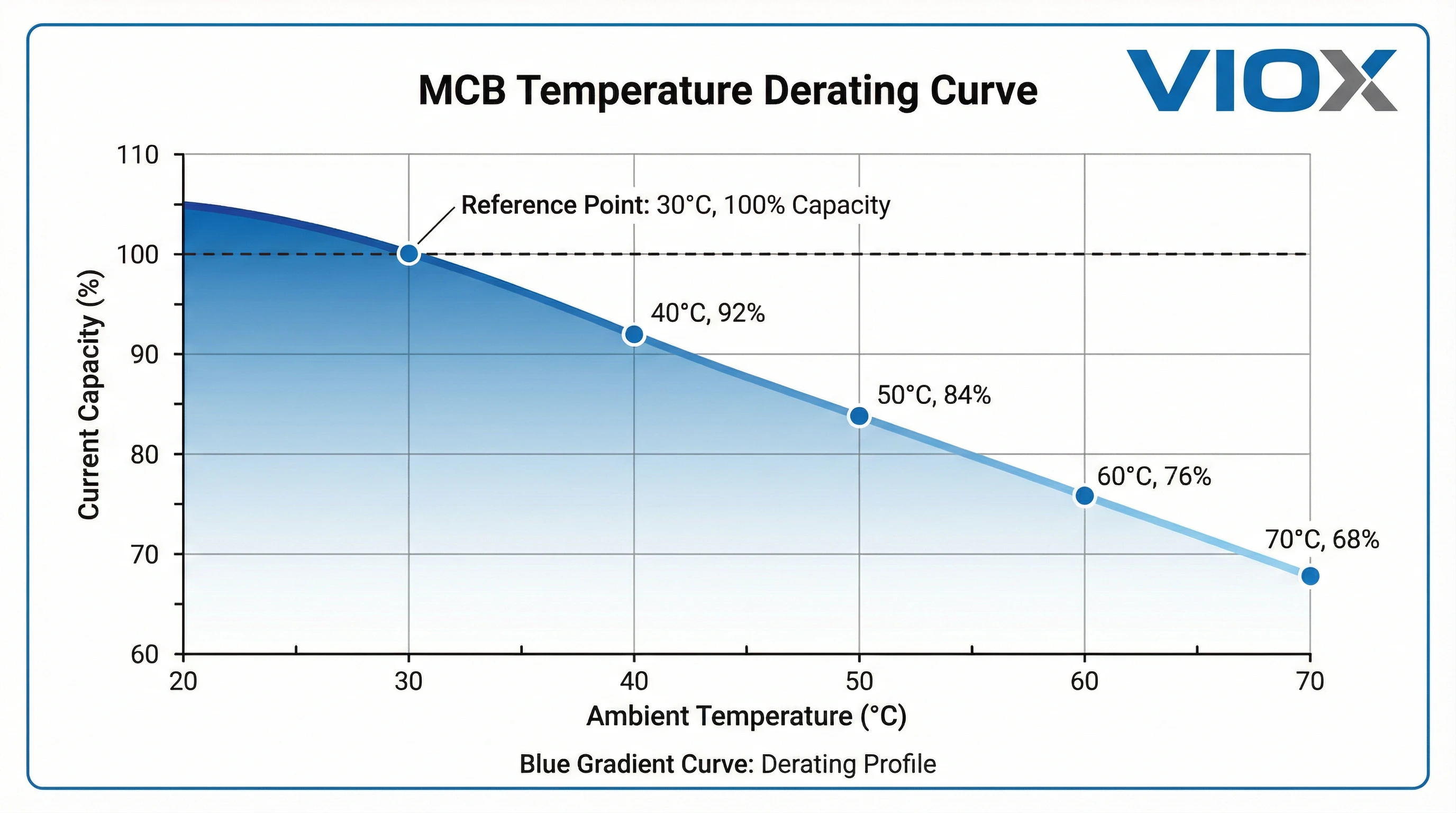
As a general rule, for thermal-magnetic MCBs, the current-carrying capacity decreases by approximately 6-10% for every 10°C rise above the reference temperature. This isn’t a linear relationship across all temperature ranges, and it varies by manufacturer and product series, but it provides a useful estimation framework.
উদাহরণস্বরূপ:
- An MCB at 40°C (10°C above the 30°C reference) might operate at roughly 94% of its rated capacity
- At 50°C (20°C above reference), capacity drops to approximately 88-90%
- At 60°C (30°C above reference), capacity may be reduced to 80-85%
Failure Modes from Inadequate Derating
When MCBs operate in higher ambient temperatures without proper derating consideration, two primary failure modes emerge:
বিরক্তিকর ট্রিপিং: The MCB trips during normal operation because the actual current, while within the nameplate rating, exceeds the temperature-adjusted capacity. This leads to unexpected downtime, productivity losses, and frustration for operators who see no apparent overload.
Premature Aging: If the MCB is consistently operated near its temperature-derated limit in a hot environment, the internal components experience accelerated thermal stress. This degrades the bimetallic strip calibration over time, reducing the device’s service life and potentially compromising protection reliability.
Both scenarios undermine the fundamental purpose of the MCB: reliable, predictable circuit protection.
Derating Factors Explained
What Is a Derating Factor?
A derating factor (also called a temperature correction factor or ambient temperature correction factor) is a multiplier applied to an MCB’s nominal rating to determine its effective current-carrying capacity at a specific ambient temperature. This factor is always less than or equal to 1.0 for temperatures at or above the reference temperature.
The mathematical relationship is straightforward:
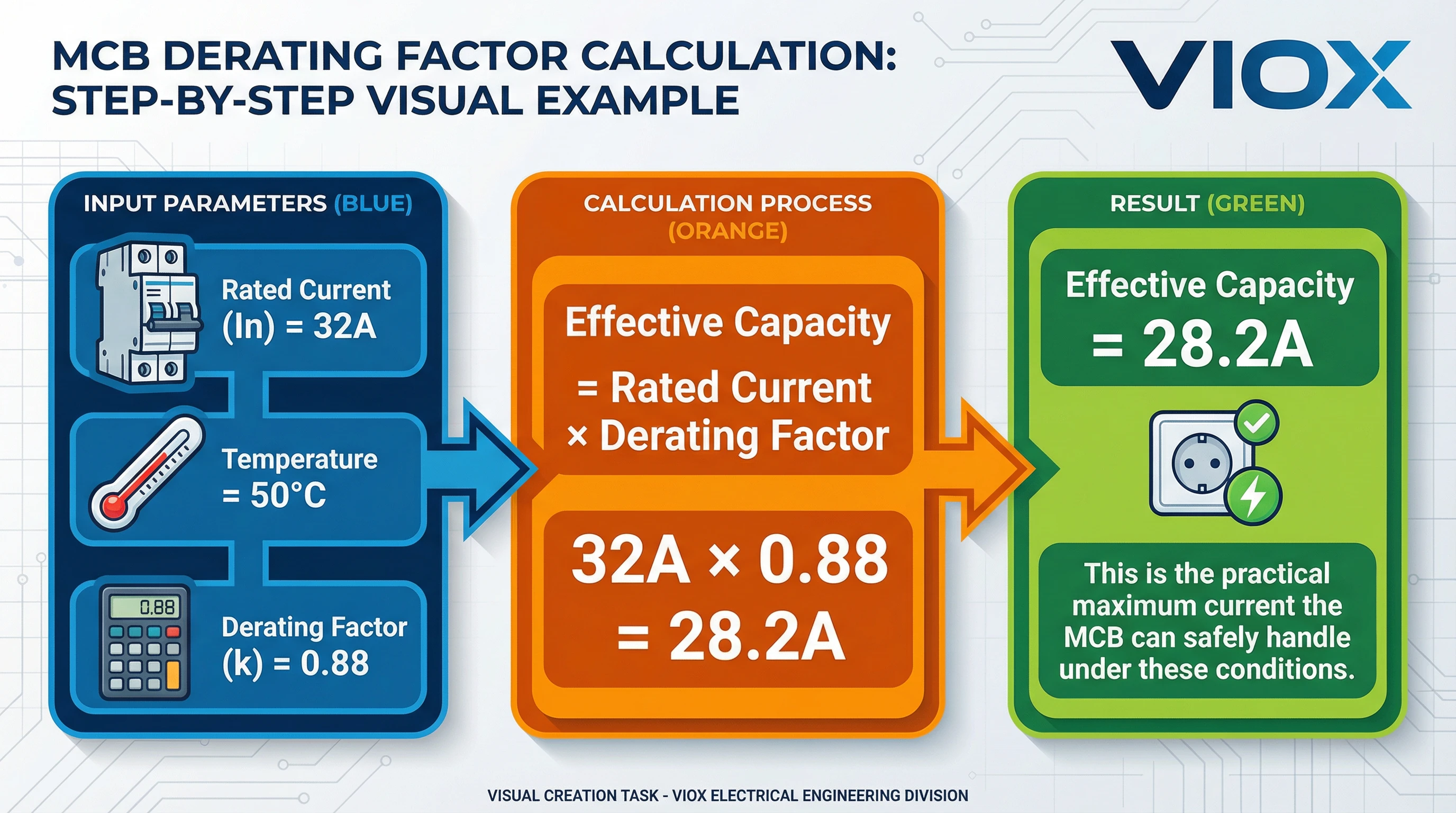
Effective Current Capacity = Rated Current × Derating Factor
For example, if a 25A MCB has a derating factor of 0.88 at 50°C:
- Effective capacity = 25A × 0.88 = 22A
This means that in a 50°C environment, the MCB should not be loaded beyond 22A to ensure reliable operation without nuisance tripping.
How Derating Factors Are Determined
Derating factors are not theoretical calculations—they’re empirically derived through extensive testing by manufacturers. Each MCB product series undergoes thermal testing across a range of ambient temperatures to measure actual trip characteristics. The results are compiled into derating tables or curves specific to that product line.
This is why it’s critical to consult the manufacturer’s technical documentation rather than relying solely on generic industry rules of thumb. Different MCB designs, internal component layouts, and thermal management features can result in varying derating characteristics even for breakers with the same nominal rating.
The Derating Curve
Manufacturers typically present derating information in two formats: tabular data and graphical curves. A derating curve plots ambient temperature on the X-axis against either the derating factor or the effective current capacity on the Y-axis.
These curves reveal important characteristics:
- The relationship is generally non-linear, with steeper capacity reduction at higher temperatures
- Some MCB designs show more gradual derating, while others drop off more sharply
- The curves may flatten at very high temperatures, approaching the MCB’s absolute maximum operating limit
Practical Calculation Examples
Example 1: Basic Derating
You need to install an MCB in a control panel where the internal ambient temperature reaches 55°C. The circuit requires continuous protection for a 30A load. The manufacturer’s data shows a derating factor of 0.85 at 55°C.
- Required MCB rating = Load Current ÷ Derating Factor
- Required MCB rating = 30A ÷ 0.85 = 35.3A
- Select the next standard size: 40A MCB
Example 2: Verification Approach
You’ve specified a 63A MCB for an application. The expected ambient is 60°C. The manufacturer’s table shows this MCB can carry 54A at 60°C (derating factor of approximately 0.86).
If your actual load is 58A:
- 58A > 54A (তাপমাত্রা-সমন্বিত ক্ষমতা)
- এই অ্যাপ্লিকেশনের জন্য 63A MCB অপর্যাপ্ত; 80A তে আপগ্রেড করুন
উদাহরণ 3: বিপরীত গণনা
একটি বিদ্যমান ইনস্টলেশনে 32A MCB ব্যবহৃত হয়। বৈদ্যুতিক ঘেরের ভিতরে গ্রীষ্মের তাপমাত্রা 65°C এ পৌঁছায়। 65°C এ প্রস্তুতকারকের ডি-রেটিং ফ্যাক্টর 0.78 ব্যবহার করে:
- কার্যকরী ক্ষমতা = 32A × 0.78 = 25A
- সর্বাধিক নিরাপদ অবিচ্ছিন্ন লোড: 25A
এই উদাহরণগুলি প্রমাণ করে যে কেন MCB নির্বাচনের একটি অবিচ্ছেদ্য অংশ তাপমাত্রা ডি-রেটিং হওয়া উচিত, কোনো গৌণ বিষয় নয়।.
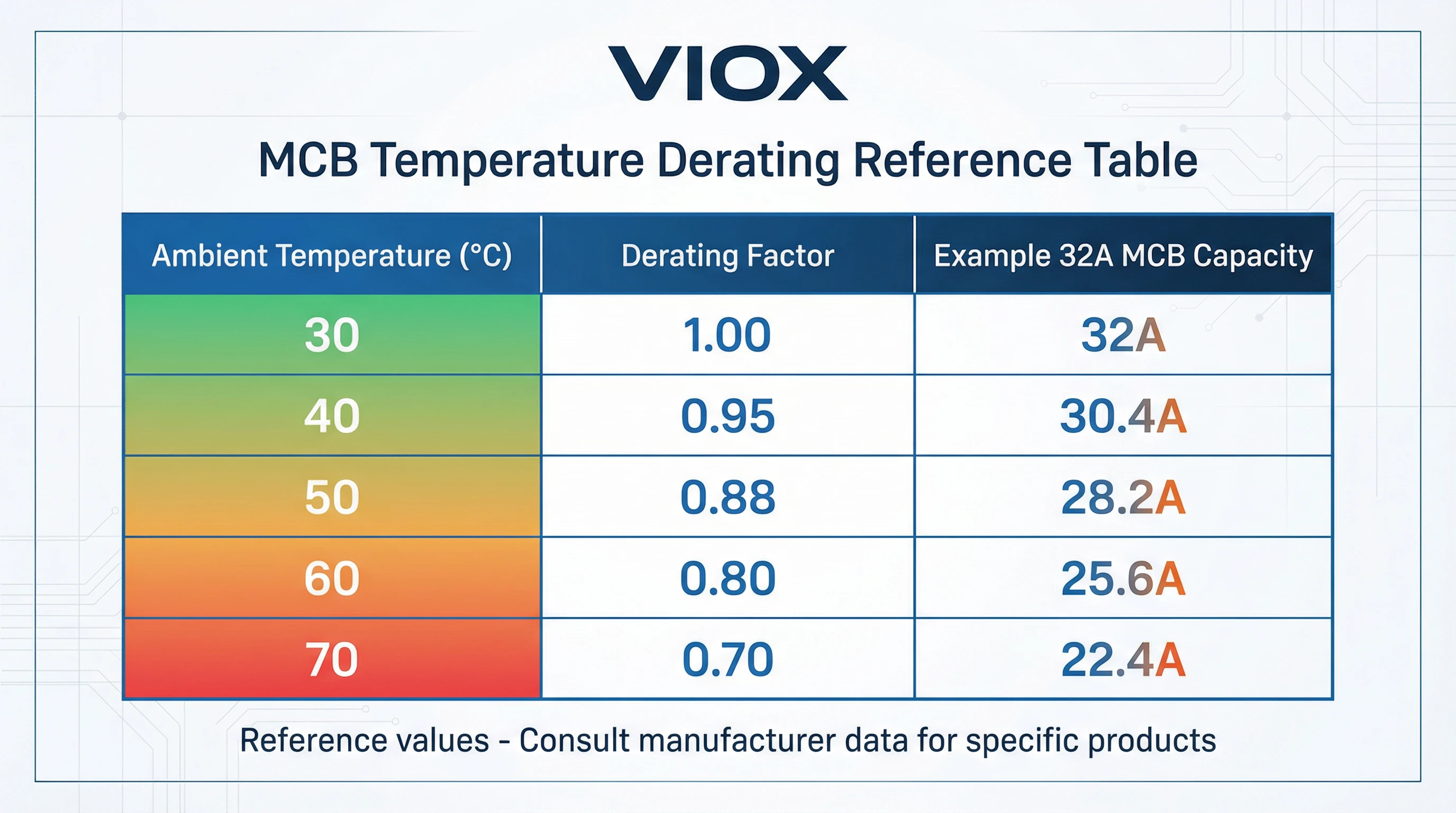
স্ট্যান্ডার্ড ডি-রেটিং টেবিল এবং নির্দেশিকা
সাধারণ ডি-রেটিং মান
যদিও নির্দিষ্ট ডি-রেটিং ফ্যাক্টর প্রস্তুতকারক এবং পণ্যের লাইন অনুসারে পরিবর্তিত হয়, তবে শিল্পের ডেটা সামঞ্জস্যপূর্ণ প্যাটার্ন প্রকাশ করে। 30°C এ ক্যালিব্রেটেড থার্মাল-ম্যাগনেটিক MCB-এর জন্য (IEC 60898-1 অনুযায়ী), সাধারণ ডি-রেটিং ফ্যাক্টরগুলি হল:
| পরিবেষ্টিত তাপমাত্রা | সাধারণ ডি-রেটিং ফ্যাক্টর | উদাহরণ: 32A MCB কার্যকরী ক্ষমতা |
|---|---|---|
| 30°C (রেফারেন্স) | 1.00 | ৩২এ |
| 40°C | 0.94 – 0.97 | 30A – 31A |
| 50°C | 0.88 – 0.95 | 28A – 30A |
| 60°C | 0.76 – 0.90 | 24A – 29A |
| 70°C | 0.64 – 0.85 | 20A – 27A |
MCB এবং এমসিসিবি 40°C এ ক্যালিব্রেটেড (IEC 60947-2 অনুযায়ী), সেই অনুযায়ী বেসলাইন পরিবর্তিত হয়:
| পরিবেষ্টিত তাপমাত্রা | সাধারণ ডি-রেটিং ফ্যাক্টর | উদাহরণ: 100A MCCB কার্যকরী ক্ষমতা |
|---|---|---|
| 40°C (রেফারেন্স) | 1.00 | ১০০এ |
| 50°C | 0.90 – 0.94 | 90A – 94A |
| 60°C | 0.80 – 0.87 | 80A – 87A |
| 70°C | 0.70 – 0.80 | 70A – 80A |
এই পরিসীমা বিভিন্ন প্রস্তুতকারকের পণ্যের নকশার মধ্যে তারতম্য প্রতিফলিত করে। উন্নত তাপ ব্যবস্থাপনার সাথে প্রিমিয়াম MCB সিরিজগুলি উচ্চ তাপমাত্রায় আরও ভাল পারফরম্যান্স দেখাতে পারে।.
প্রস্তুতকারক-নির্দিষ্ট ডেটা
শীর্ষস্থানীয় নির্মাতারা তাদের প্রযুক্তিগত ক্যাটালগগুলিতে বিস্তারিত ডি-রেটিং তথ্য সরবরাহ করে:
ABB S200 সিরিজ (30°C রেফারেন্স): একটি 80A MCB-এর জন্য, বিভিন্ন তাপমাত্রায় সর্বাধিক অপারেটিং কারেন্ট প্রায় 50°C তাপমাত্রায় 77.6A, 60°C তাপমাত্রায় 75.2A এবং 70°C তাপমাত্রায় 72.8A।.
Schneider Electric Acti9 সিরিজ: 40°C এ ক্যালিব্রেটেড একটি 160A থার্মাল-ম্যাগনেটিক ব্রেকার 50°C তাপমাত্রায় 150A, 60°C তাপমাত্রায় 140A এবং 70°C তাপমাত্রায় 130A কার্যকরী ক্ষমতা দেখায়—যা প্রতি 10°C বৃদ্ধিতে প্রায় 10A হ্রাস প্রদর্শন করে।.
Eaton এবং Siemens: উভয় প্রস্তুতকারকই পণ্য-নির্দিষ্ট ডকুমেন্টেশন পরামর্শ করার উপর জোর দেন, কারণ তাদের বিস্তৃত MCB পোর্টফোলিওতে ডি-রেটিং বৈশিষ্ট্যগুলি উল্লেখযোগ্যভাবে পরিবর্তিত হয়।.
IEC স্ট্যান্ডার্ডস গাইডেন্স
IEC 60898-1 এবং IEC 60947-2 টেস্টিং প্রোটোকল এবং রেফারেন্স তাপমাত্রা প্রতিষ্ঠা করে কিন্তু নির্দিষ্ট ডি-রেটিং মান নির্ধারণ করে না। পরিবর্তে, নির্মাতাদের তাদের পণ্যের প্রকার পরীক্ষার ভিত্তিতে এই ডেটা সরবরাহ করতে হবে। স্ট্যান্ডার্ডগুলির প্রয়োজন MCB গুলিকে তাদের নির্দিষ্ট তাপমাত্রা পরিসীমা জুড়ে নিরাপদে কাজ করতে হবে, তবে চরম তাপমাত্রায় কর্মক্ষমতা হ্রাস প্রত্যাশিত এবং অ্যাপ্লিকেশন ইঞ্জিনিয়ারিংয়ে এটি অবশ্যই বিবেচনা করতে হবে।.
কখন আরও রক্ষণশীল ফ্যাক্টর প্রয়োগ করতে হবে
কিছু পরিস্থিতিতে, আরও রক্ষণশীল ডি-রেটিং প্রয়োগ করা বিচক্ষণতার কাজ:
- মিশন-ক্রিটিক্যাল অ্যাপ্লিকেশন যেখানে কোনো প্রকার সমস্যা সৃষ্টি হওয়ার মারাত্মক পরিণতি হতে পারে
- দুর্বল তাপমাত্রা পর্যবেক্ষণ সহ ইনস্টলেশন যেখানে প্রকৃত পরিবেষ্টিত তাপমাত্রা ডিজাইন অনুমানের চেয়ে বেশি হতে পারে
- পুরাতন ইনস্টলেশন যেখানে MCB ক্যালিব্রেশন বহু বছরের পরিষেবাতে সরে যেতে পারে
- বিস্তৃত তাপমাত্রা ওঠানামা সহ পরিবেশ যা বার বার তাপীয় সাইক্লিংয়ের মাধ্যমে বাইমেটালিক স্ট্রিপের উপর চাপ সৃষ্টি করে
ব্যবহারিক প্রয়োগ এবং ইনস্টলেশন বিবেচ্য বিষয়
বাস্তব ইনস্টলেশনে পরিবেষ্টিত তাপমাত্রা নির্ধারণ করা
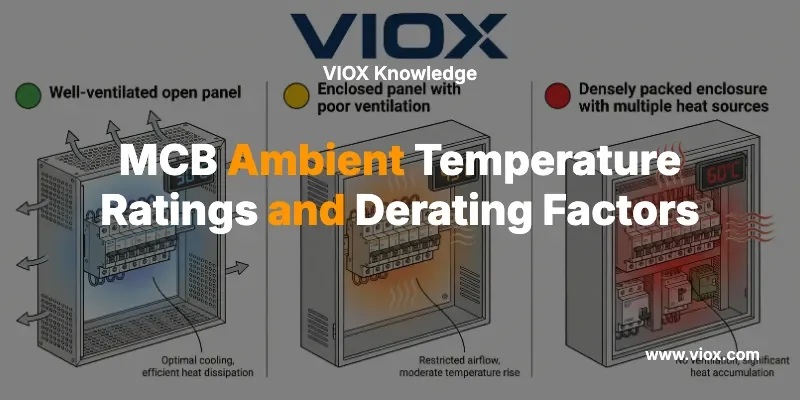
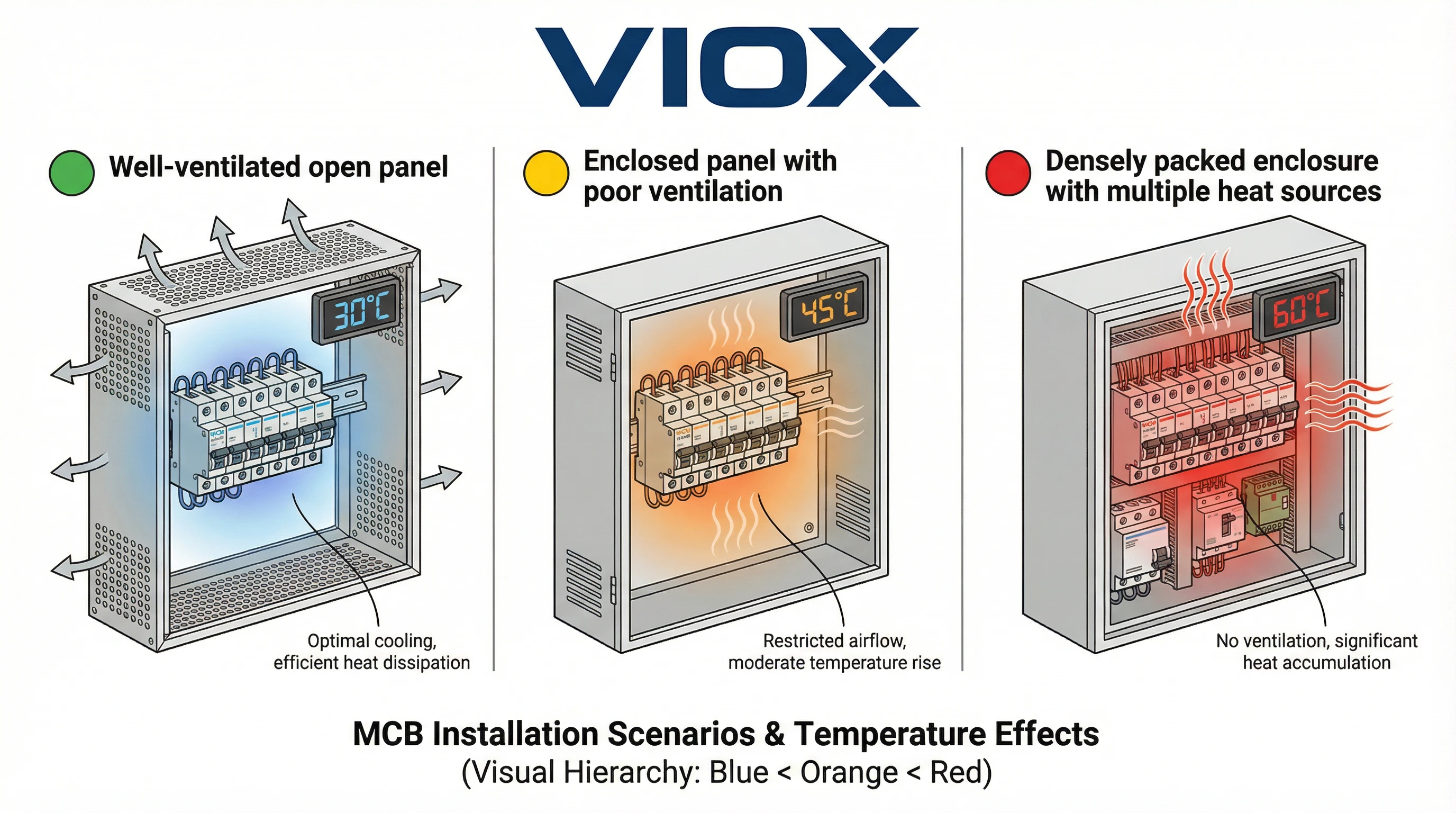
একটি গুরুত্বপূর্ণ বিষয় যা প্রায়শই ভুল বোঝা হয়: MCB ডি-রেটিংয়ের উদ্দেশ্যে পরিবেষ্টিত তাপমাত্রা হল not ঘরের তাপমাত্রা। এটি MCB এর ঠিক চারপাশের বাতাসের তাপমাত্রা। আবদ্ধ ইনস্টলেশনে, এটি সাধারণ পরিবেশের চেয়ে উল্লেখযোগ্যভাবে বেশি হতে পারে।.
একটি 25°C শীতাতপ নিয়ন্ত্রিত কক্ষে থাকা একটি কন্ট্রোল প্যানেলের অভ্যন্তরীণ তাপমাত্রা 45°C বা তার বেশি হতে পারে অন্যান্য সরঞ্জাম দ্বারা উত্পন্ন তাপ, ঘেরের উপর সৌর লোডিং বা অপর্যাপ্ত বায়ুচলাচলের কারণে। MCB যেখানে মাউন্ট করা আছে সেই ঘেরের ভিতরের প্রকৃত তাপমাত্রা সর্বদা পরিমাপ করুন বা গণনা করুন।.
ঘেরের প্রভাব এবং তাপ জমা হওয়া
বৈদ্যুতিক ঘের স্থানীয় গরম অঞ্চল তৈরি করে। তাপের উৎসগুলির মধ্যে রয়েছে:
- পাওয়ার সাপ্লাই এবং ট্রান্সফরমার ক্রমাগত তাপ উৎপন্ন করে
- VFDs (ভেরিয়েবল ফ্রিকোয়েন্সি ড্রাইভ) সুইচিং ক্ষতির সাথে
- কন্টাক্টর এবং রিলে এনার্জাইজড কয়েল সহ
- MCB নিজেরাই I²R ক্ষতিতে অবদান রাখে
পর্যাপ্ত বায়ুচলাচল ছাড়া একটি ঘনভাবে প্যাক করা প্যানেলে, অভ্যন্তরীণ তাপমাত্রা বাহ্যিক পরিবেষ্টিত তাপমাত্রা থেকে 20-30°C বেশি হতে পারে। বায়ুচলাচল পাখা, হিট সিঙ্ক এবং সঠিক ব্যবধান অপরিহার্য প্রশমন কৌশল।.
গ্রুপিং ফ্যাক্টর এবং একাধিক MCB
যখন একাধিক MCB খুব কাছাকাছি পাশাপাশি মাউন্ট করা হয়, তখন তাদের সম্মিলিত তাপীয় আউটপুট পারস্পরিক গরম করার প্রভাব তৈরি করে। এর জন্য একটি অতিরিক্ত প্রয়োজনীয় গ্রুপিং ফ্যাক্টর বা অ্যারেঞ্জমেন্ট ফ্যাক্টর পরিবেষ্টিত তাপমাত্রা ডিরেটিংয়ের উপরে প্রয়োগ করতে হয়।.
উদাহরণস্বরূপ, IEC 60947-2 স্বীকৃতি দেয় যে একটি আবদ্ধ স্থানে সারিবদ্ধভাবে মাউন্ট করা সার্কিট ব্রেকারগুলি বিচ্ছিন্ন ইউনিটের চেয়ে বেশি অপারেটিং তাপমাত্রা অনুভব করে। কিছু প্রস্তুতকারক নির্দিষ্ট নির্দেশনা প্রদান করে: 3-6টি সংলগ্ন MCB-এর একটি সারির জন্য তাপমাত্রা সংশোধনের বাইরে অতিরিক্ত 5-10% ডিরেটিং-এর প্রয়োজন হতে পারে।.
ক্রমবর্ধমান প্রভাব যথেষ্ট হতে পারে:
- পরিবেষ্টিত তাপমাত্রা ডিরেটিং: 0.90 (50°C তাপমাত্রায়)
- গ্রুপিং ফ্যাক্টর: 0.95 (4টি সংলগ্ন MCB-এর জন্য)
- সম্মিলিত ফ্যাক্টর: 0.90 × 0.95 = 0.855
- একটি 32A MCB কার্যকরভাবে হয়ে যায়: 32A × 0.855 = 27.4A ক্ষমতা
বায়ুচলাচল এবং তাপীয় ব্যবস্থাপনা
সঠিক আবদ্ধ স্থান নকশা MCB-এর তাপীয় কার্যকারিতাকে উল্লেখযোগ্যভাবে প্রভাবিত করে:
প্রাকৃতিক পরিচলন: MCB সারির উপরে এবং নীচে পর্যাপ্ত স্থান নিশ্চিত করুন। গরম বাতাস অবশ্যই উপরের ভেন্ট থেকে বের হতে হবে এবং ঠান্ডা বাতাস নীচ থেকে প্রবেশ করতে হবে।.
জোরপূর্বক বায়ুচলাচল: উচ্চ-ঘনত্বের ইনস্টলেশন বা গরম পরিবেশে, গ্রহণযোগ্য অভ্যন্তরীণ তাপমাত্রা বজায় রাখার জন্য আকারের বায়ুচলাচল পাখা নির্দিষ্ট করুন। একটি সাধারণ নির্দেশিকা হল আবদ্ধ স্থানের অভ্যন্তরীণ তাপমাত্রা বাইরের পরিবেষ্টিত তাপমাত্রার থেকে 10-15°C এর মধ্যে রাখা।.
তাপীয় বাধা: ব্যাফেল বা পৃথক কম্পার্টমেন্ট ব্যবহার করে MCB বিভাগ থেকে উচ্চ-তাপ উপাদান (VFD, পাওয়ার সাপ্লাই) আলাদা করুন।.
কেবল ডিরেটিং সমন্বয়
একটি গুরুত্বপূর্ণ কিন্তু প্রায়শই উপেক্ষিত বিষয়: MCB-এর সাথে সংযুক্ত কেবলগুলিরও তাপমাত্রা ডিরেটিং প্রয়োজন। সামগ্রিক সার্কিট সুরক্ষা স্কিমটি কেবল তার দুর্বলতম উপাদানের মতোই নির্ভরযোগ্য।.
যদি একটি MCB তাপমাত্রার জন্য 28A-এ ডিরেট করা হয় কিন্তু সংযুক্ত কেবল (যা তাপমাত্রার ডিরেটিং সাপেক্ষে) একই পরিবেশে নিরাপদে শুধুমাত্র 26A বহন করতে পারে, তবে সার্কিটটি 26A-এর মধ্যে সীমাবদ্ধ থাকবে—28A নয়। সর্বদা MCB এবং কেবল ডিরেটিং গণনা সমন্বয় করুন।.
উচ্চতা বিবেচনা
2,000 মিটারের বেশি উচ্চতায়, বাতাসের ঘনত্ব হ্রাস পায়, যা শীতল করার কার্যকারিতা কমিয়ে দেয়। এর জন্য অতিরিক্ত ডিরেটিং-এর প্রয়োজন হতে পারে, যা সাধারণত উচ্চ-উচ্চতার অ্যাপ্লিকেশনগুলির জন্য প্রস্তুতকারকের নথিতে নির্দিষ্ট করা হয়।.
উপসংহার
পরিবেষ্টিত তাপমাত্রা MCB নির্বাচন এবং প্রয়োগের ক্ষেত্রে একটি গুরুত্বপূর্ণ কিন্তু প্রায়শই কম মূল্যায়ন করা বিষয়। যদিও একটি MCB-এর নেমপ্লেট রেটিং প্রয়োজনীয় তথ্য সরবরাহ করে, তবে এটি শুধুমাত্র স্ট্যান্ডার্ড রেফারেন্স তাপমাত্রায় কর্মক্ষমতা উপস্থাপন করে—সাধারণত আবাসিক/বাণিজ্যিক ডিভাইসের জন্য 30°C বা শিল্প অ্যাপ্লিকেশনের জন্য 40°C।.
বাস্তব-বিশ্বের ইনস্টলেশনে, বিশেষ করে বৈদ্যুতিক আবদ্ধ স্থান বা চ্যালেঞ্জিং তাপীয় পরিবেশে, একটি MCB-এর কার্যকর কারেন্ট-বহন ক্ষমতা উল্লেখযোগ্যভাবে হ্রাস করা যেতে পারে। তাপমাত্রা ডিরেটিং উপেক্ষা করলে উপদ্রবপূর্ণ ট্রিপিং, আপোস করা সুরক্ষা নির্ভরযোগ্যতা এবং অকাল সরঞ্জাম ব্যর্থতা দেখা দিতে পারে।.
বৈদ্যুতিক পেশাদারদের জন্য মূল বিষয়গুলি:
- শুধুমাত্র ঘরের তাপমাত্রা নয়, MCB অবস্থানে প্রকৃত পরিবেষ্টিত তাপমাত্রা সর্বদা নির্ধারণ করুন
- জেনেরিক নির্দেশিকাগুলির উপর সম্পূর্ণরূপে নির্ভর না করে প্রস্তুতকারক-নির্দিষ্ট ডিরেটিং টেবিলগুলি দেখুন
- একাধিক সংলগ্ন MCB-এর জন্য তাপমাত্রা ডিরেটিং এবং গ্রুপিং ফ্যাক্টর উভয়ই প্রয়োগ করুন
- কেবল কারেন্ট-বহন ক্ষমতা হ্রাসের সাথে MCB ডিরেটিং সমন্বয় করুন
- তাপ জমাট বাঁধা পরিচালনা করতে পর্যাপ্ত বায়ুচলাচল সহ আবদ্ধ স্থান ডিজাইন করুন
VIOX-এ, আমরা আমাদের সমস্ত MCB পণ্য লাইনের জন্য বিস্তারিত তাপমাত্রা ডিরেটিং কার্ভ এবং অ্যাপ্লিকেশন নির্দেশিকা সহ ব্যাপক প্রযুক্তিগত ডকুমেন্টেশন সরবরাহ করি। আমাদের ইঞ্জিনিয়ারিং সহায়তা দল জটিল ইনস্টলেশনগুলিতে সহায়তা করার জন্য উপলব্ধ যেখানে তাপীয় ব্যবস্থাপনা গুরুত্বপূর্ণ। পরিবেষ্টিত তাপমাত্রার জন্য সঠিক MCB নির্বাচন নিশ্চিত করে যে আপনার বৈদ্যুতিক সুরক্ষা ব্যবস্থা নির্ভরযোগ্য, দীর্ঘমেয়াদী কর্মক্ষমতা সরবরাহ করে ঠিক যখন এটির সবচেয়ে বেশি প্রয়োজন।.
VIOX MCB-এর জন্য প্রযুক্তিগত বৈশিষ্ট্য, ডিরেটিং টেবিল এবং অ্যাপ্লিকেশন সহায়তার জন্য, আমাদের পণ্যের ক্যাটালগ দেখুন বা আমাদের প্রযুক্তিগত দলের সাথে যোগাযোগ করুন।.