What Is a Ground Bar Insulator Kit?
A ground bar insulator kit is an essential electrical component designed to mount a ground bar (also called a grounding bus bar) within an electrical enclosure while maintaining proper electrical isolation. These kits typically include high-quality standoff insulators, mounting brackets, and hardware that work together to create a secure, code-compliant grounding solution for electrical panels and systems.
At Viox Electric, we manufacture professional-grade ground bar insulator kits that provide reliable performance across diverse electrical applications, from residential installations to complex industrial systems.
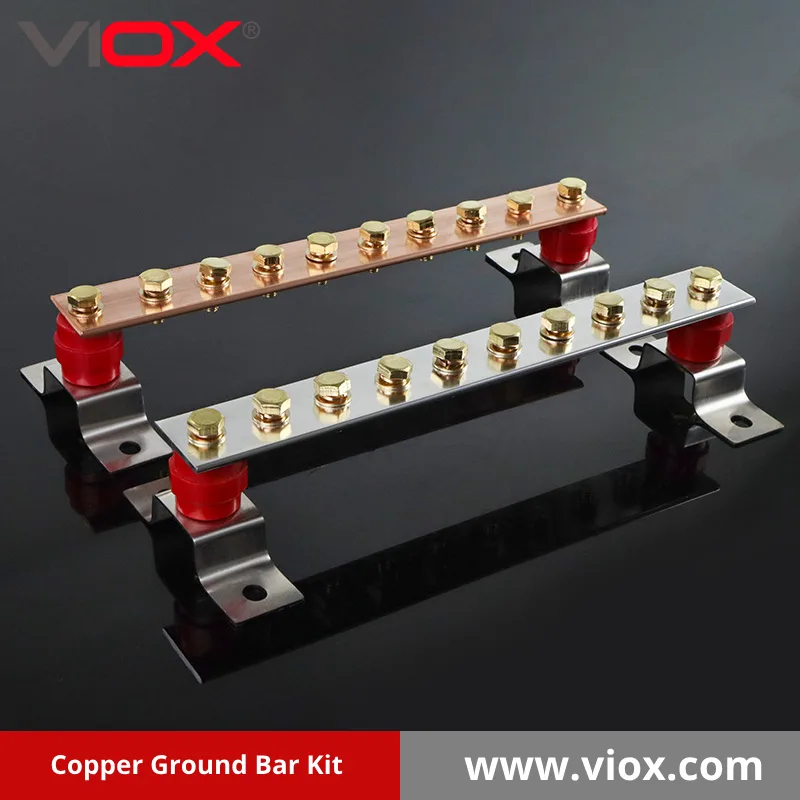

Components of a Quality Ground Bar Insulator Kit
A comprehensive ground bar insulator kit contains several key components:
Standoff Insulators (Isolators)
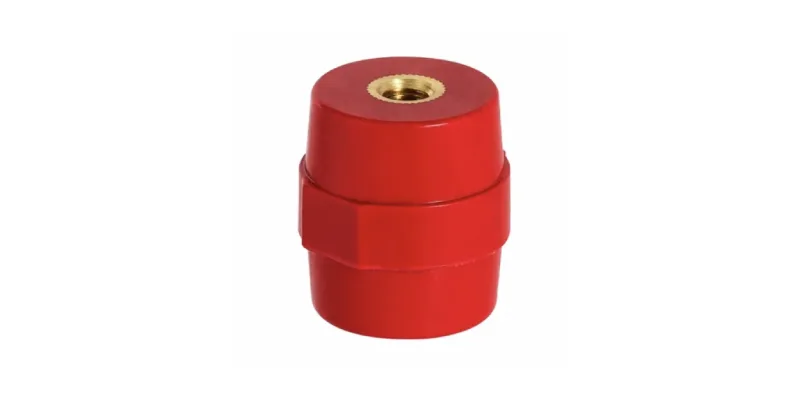

- Made from high-dielectric strength materials like thermoset polyester
- Provide physical support while preventing electrical conductivity
- Designed with threaded inserts for secure attachment
Mounting Hardware
- Durable stainless steel brackets for corrosion resistance
- Properly sized bolts, screws, and washers (typically 3/8″ or 5/8″)
- Additional center supports for longer ground bars (24″+ length)
Ground Bar Options
While some kits include only the insulators and mounting hardware, complete kits also feature:
- High-conductivity copper ground bars (99.9% pure)
- Available in various dimensions to suit different applications
- Optional plating options for enhanced corrosion resistance
Why Ground Bar Insulator Kits Are Essential
In electrical systems, proper grounding is fundamental to safety and functionality. Ground bar insulator kits serve several crucial purposes:
- Electrical Isolation: They provide necessary electrical isolation between the ground bar and the panel enclosure in specific applications, using high-quality insulators rated for appropriate voltage levels
- Code Compliance: They help ensure installations meet National Electrical Code (NEC) requirements through UL-listed components and proper configuration
- Shock Prevention: They contribute to overall electrical safety by maintaining appropriate separation between neutral and ground paths, reducing the risk of dangerous fault conditions
- System Protection: They help protect sensitive equipment by maintaining proper grounding configurations and providing clean ground paths
- Corrosion Resistance: Quality kits use corrosion-resistant materials like stainless steel brackets and optional plating on copper bars to ensure longevity in various environments
- Installation Flexibility: They allow for proper grounding solutions in diverse applications from small residential panels to large industrial and renewable energy installations
Applications in Electrical Systems
Main Service Panels vs. Subpanels
In a main service panel, the neutral bar and ground bar are typically bonded together. However, in subpanels, the National Electrical Code requires that neutral and ground conductors remain separate. This is where ground bar insulator kits become essential:
- Main Service Panels: Ground and neutral bars are usually bonded
- Subpanels: Ground bars must be bonded to the enclosure, but neutral bars must be isolated using insulator kits
Multiple Ground Bar Installations
In larger electrical panels or when adding additional circuits to existing panels, multiple ground bars may be needed:
- Ground bar insulator kits allow for expansion of grounding capacity
- They ensure proper electrical connections while maintaining code compliance
- They provide organized termination points for multiple ground wires
Specialized Electrical Applications
Ground bar insulator kits are essential in numerous specialized applications beyond standard electrical panels:
- Telecommunications Equipment: Supporting proper grounding for sensitive communications hardware
- Renewable Energy Systems: Providing robust grounding solutions for solar arrays and wind power installations
- Amateur Radio Setups: Ensuring clean ground planes for ham radio operations and reducing interference
- Data Centers: Creating reliable ground points for server racks and IT infrastructure
- Industrial Control Systems: Supporting grounding requirements for manufacturing and process control equipment
- Medical Facilities: Meeting specialized grounding needs for healthcare equipment
Types of Ground Bar Insulator Kits
Ground bar insulator kits come in various configurations to accommodate different panel types and applications:
Brand-Specific Kits
- Square D/Schneider Electric: PKGTAB and similar models designed for QO and Homeline panels
- Siemens: ECINSGB series designed for specific panel configurations
- Other Manufacturers: Most major electrical equipment manufacturers offer compatible ground bar insulator kits
- Specialized Suppliers: Companies focusing exclusively on grounding solutions offering extensive customization options
Configurations and Capacities
- Bar Dimensions: Available in various thicknesses (typically 1/8″ to 1/4″), widths (2″ to 4″), and lengths (from 5″ to 72″ or more)
- Terminal Positions: Range from compact 4-position kits to extensive arrangements with over 100 termination points
- Hole Patterns: Available with round holes, slotted holes, tapped holes, or combinations for different terminal types
- Materials: Precision-manufactured from high-conductivity copper (typically 99.9% pure electrolytic tough-pitch copper)
- Surface Treatments: Available bare or with protective plating options like tin, nickel, or silver for corrosion resistance
- Mounting Options: Various bracket designs and standoff heights to accommodate different installation requirements
- Protection Accessories: Optional clear polycarbonate covers for additional insulation in specific environments
Installation Requirements
Proper installation of ground bar insulator kits is critical for electrical safety and code compliance. Key installation considerations include:
NEC Code Requirements
The National Electrical Code specifies requirements for ground bar installation, particularly in subpanels:
- NEC 250.32(B)(1) outlines requirements for separate ground and neutral conductors
- In subpanels, neutral conductors must be isolated from the enclosure while ground conductors must be bonded to it
- Ground bars in subpanels must be properly bonded to the enclosure while neutral bars must be insulated
- Grounding electrode connections must meet specific requirements in Article 250
Installation Best Practices
Following proper installation procedures ensures safety and optimal performance:
- Ensure standoff insulators are properly secured to the mounting surface
- Verify appropriate torque specifications when tightening connections
- Maintain minimum clearances between the ground bar and other conductive components
- When using protective covers, ensure proper fit and secure mounting
- Follow manufacturer-specific installation guidelines for UL compliance
- Confirm compatibility between lugs and the ground bar’s hole pattern and dimensions
Professional Installation
Due to safety considerations and code requirements, professional installation is recommended:
- Licensed electricians understand specific code requirements
- Proper installation ensures system safety and functionality
- Incorrect installation can lead to safety hazards and code violations
- Professionals can help select the appropriate kit configuration for specific applications
Selecting the Right Ground Bar Insulator Kit
When choosing a ground bar insulator kit, consider these factors:
Panel Compatibility and Configuration Needs
- Match the kit to your specific panel manufacturer and model
- Verify terminal capacity requirements based on your installation needs
- Confirm mounting compatibility with your panel enclosure
- Assess the number and type of terminations required (current and future needs)
- Consider hole patterns and spacing that accommodate your specific lug types
Material and Quality Considerations
- Choose kits made from high-conductivity copper (99.9% pure electrolytic tough-pitch copper is optimal)
- Look for UL-listed products that meet Underwriters Laboratories standards for grounding equipment
- Verify appropriate voltage ratings for insulators based on your system requirements
- Select appropriately sized bars based on your system’s anticipated fault current capacity
- Consider stainless steel mounting hardware for superior corrosion resistance and durability
Environment and Application-Specific Needs
- Determine if you need standard or isolated ground bars
- Consider plating options (tin, nickel, silver) for installations in corrosive environments
- Evaluate specialized configurations for telecommunications, data centers, or renewable energy systems
- Assess the need for protective covers in high-exposure or safety-critical applications
- Consider custom options for unique installations or specialized requirements
- Evaluate temperature ranges and environmental factors that might affect insulator integrity
Benefits of Using Ground Bar Insulator Kits
Proper use of ground bar insulator kits provides numerous benefits for electrical installations:
Safety Enhancement
Ground bar insulator kits contribute significantly to electrical safety by:
- Preventing unintended current paths between neutral and ground
- Reducing shock hazards in electrical systems
- Ensuring proper fault current paths during electrical failures
Code Compliance
Using the correct ground bar insulator kits helps ensure:
- Compliance with NEC requirements for electrical installations
- Proper separation of neutral and ground in subpanels
- Meeting inspection requirements for new installations and renovations
System Performance
Beyond safety and compliance, proper ground bar installation contributes to:
- Reduced electrical noise in sensitive systems
- Proper functioning of ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs)
- Protection of equipment from potential damage
Common Applications
Ground bar insulator kits are frequently used in various settings:
Residential Applications
- Subpanels in detached garages or outbuildings
- Home workshop electrical panels
- Basement or auxiliary electrical panels
- Home entertainment systems requiring clean grounds
- Residential renewable energy installations (solar, wind)
- Amateur radio and hobbyist electronics setups
Commercial and Industrial Applications
- Distribution panels in commercial buildings
- Equipment rooms and mechanical spaces
- Retail and office electrical systems
- Manufacturing facilities with sensitive equipment
- Telecommunications infrastructure
- Control panels for industrial automation
- Power distribution units in commercial facilities
- Agricultural electrical systems
Specialized and Critical Infrastructure
- Data centers requiring isolated ground systems
- Audio/visual installations where clean grounds are critical
- Medical facilities with specific grounding requirements
- Laboratory environments with sensitive test equipment
- Broadcasting stations and recording studios
- Transportation infrastructure (airports, railways)
- Utility-scale solar arrays and wind farms
- Backup power systems and generator installations
- Maritime and marine electrical systems
Maintenance and Inspection
Once installed, ground bar insulator kits require periodic attention to ensure continued safety and performance:
Regular Inspection Protocols
- Check for secure connections and mounting at recommended intervals
- Verify insulator integrity and condition for cracks, discoloration, or deterioration
- Ensure terminal screws and mounting hardware remain tight to proper torque specifications
- Inspect copper bars for signs of oxidation, especially in non-plated installations
- Verify that protective covers (if used) remain intact and properly secured
- Confirm that separation between ground and neutral remains maintained
Environmental Considerations
- Installations in humid or corrosive environments may require more frequent inspection
- Outdoor installations should be checked after extreme weather events
- Industrial environments with vibration may need additional verification of hardware tightness
- Temperature fluctuations can affect insulator integrity and connection security
Troubleshooting and Remediation
- Address any signs of corrosion or damage promptly with appropriate cleaning or replacement
- Replace damaged insulators immediately to maintain electrical isolation
- Retorque loose connections to manufacturer specifications
- Verify continued compliance with current electrical codes during inspections
- Document all maintenance activities for compliance and warranty purposes
- Consider periodic thermal scanning in critical applications to identify potential hot spots
Conclusion
Ground bar insulator kits play a vital role in electrical safety, code compliance, and system performance across a wide range of applications. These precision-engineered components—combining high-conductivity copper bars, sturdy insulators, and durable mounting hardware—create the foundation for proper electrical grounding in everything from residential subpanels to sophisticated industrial and renewable energy installations.
By properly isolating ground bars in appropriate applications, these kits help ensure electrical systems function safely and effectively. The range of available configurations—with variations in dimensions, hole patterns, plating options, and accessory components—allows for customized solutions to match specific requirements in virtually any electrical installation scenario.
Whether installed in a home workshop, telecommunications facility, or utility-scale solar farm, understanding the purpose, selection criteria, and proper application of ground bar insulator kits is essential for anyone working with electrical systems. The quality of these components directly impacts not only code compliance but the long-term safety and reliability of the entire electrical system.
For specific installation requirements or technical specifications, always consult a licensed electrician and refer to current National Electrical Code provisions. Proper grounding is not just about compliance—it’s about creating safer, more reliable electrical systems for homes, businesses, and critical infrastructure.
FAQs
Q: Do I need a ground bar insulator kit for my main service panel?
A: Typically, no. In main service panels, the neutral and ground are bonded together. The insulator kits are primarily used in subpanels where separation is required by the National Electrical Code.
Q: Can I install a ground bar insulator kit myself?
A: While it’s technically possible, electrical work involving panels should generally be performed by qualified professionals to ensure safety and code compliance. Improper installation can create serious safety hazards.
Q: How do I know if my subpanel needs an insulated ground bar?
A: According to the NEC, subpanels generally require ground bars that are bonded to the enclosure while neutral bars must be isolated. A licensed electrician can assess your specific situation and code requirements for your location.
Q: Can I use any ground bar insulator kit with my panel?
A: No, you should use kits specifically designed for your panel’s make and model to ensure proper fit and function. Consider factors like mounting hole patterns, voltage ratings, and terminal compatibility with your specific application.
Q: How many terminal positions do I need on my ground bar?
A: Calculate based on the number of circuits requiring ground connections, plus at least 25% extra positions for future expansion. For specialized applications like telecommunications or data centers, you may need additional capacity.
Q: Does the material of the ground bar matter?
A: Yes, high-conductivity copper (99.9% pure) provides optimal electrical performance. The bar thickness should be appropriate for the anticipated fault current, and plating options should be considered for corrosive environments.
Q: What’s the difference between a ground bar kit and an insulator kit?
A: A complete ground bar kit typically includes the copper bar, insulators, mounting hardware, and sometimes protective covers. An insulator kit may only include the standoff insulators and mounting hardware, requiring separate purchase of the copper bar.
Q: Are there special requirements for outdoor or high-humidity installations?
A: Yes, for these environments, consider tin-plated copper bars and stainless steel hardware for superior corrosion resistance. Some installations may also benefit from protective polycarbonate covers.
Related
VIOX Customizable Busbar/Busbar Insulator Stand-Off Bracket
How to Determine the Quality of a Busbar Insulator


