
တိုက်ရိုက်အဖြေ
ခရီးစဉ်အမျိုးအစားသည် IEC 60947-4-1 နှင့် NEMA စံနှုန်းများဖြင့် သတ်မှတ်ထားသော စံနှုန်းသတ်မှတ်စနစ်တစ်ခုဖြစ်ပြီး မော်တာကာကွယ်ရေးကိရိယာ (အပူလွန်ကဲဝန်ပိုအားပေးစက် သို့မဟုတ် မော်တာကာကွယ်ရေးဆားကစ်ဖြတ်စက်) သည် ၎င်း၏အဆင့်သတ်မှတ်ထားသော လျှပ်စီးကြောင်း၏ 600% (သို့မဟုတ် 7.2×) ကို ခံယူသောအခါ မော်တာကို ခရီးထွက်ပြီး ချိတ်ဆက်မှုဖြတ်တောက်ရန် အချိန်မည်မျှကြာမည်ကို သတ်မှတ်ပေးပါသည်။. အမျိုးအစားနံပါတ်သည် စက္ကန့်ပိုင်းအတွင်း အမြင့်ဆုံးခရီးစဉ်အချိန်ကို တိုက်ရိုက်ညွှန်ပြသည်—Class 10 သည် 10 စက္ကန့်အတွင်း၊ Class 20 သည် 20 စက္ကန့်အတွင်းနှင့် Class 30 သည် ဤဝန်ပိုအဆင့်တွင် 30 စက္ကန့်အတွင်း ခရီးထွက်သည်။ ဤအမျိုးအစားခွဲခြားမှုသည် ကာကွယ်ရေးကိရိယာ၏ တုံ့ပြန်ချိန်သည် မော်တာ၏ အပူပျက်စီးမှုမျဉ်းနှင့် ကိုက်ညီကြောင်း သေချာစေပြီး ပုံမှန်စတင်သည့်အခြေအနေများတွင် အနှောင့်အယှက်ဖြစ်စေသော ခရီးစဉ်ကို ရှောင်ရှားနေစဉ် ဝိုင်ယာကြိုးကာကွယ်မှုပျက်ကွက်ခြင်းကို တားဆီးပေးပါသည်။.
သော့ထုတ်ယူမှုများ
- ✅ ခရီးစဉ်အမျိုးအစား အဓိပ္ပါယ်: အမျိုးအစားနံပါတ် (5, 10, 10A, 20, 30) သည် relay ၏ လက်ရှိချိန်ညှိမှု၏ 600% (NEMA) သို့မဟုတ် 7.2× (IEC) တွင် ခရီးထွက်ရန် အမြင့်ဆုံးစက္ကန့်များကို ကိုယ်စားပြုပြီး ကာကွယ်မှုသည် မော်တာအပူကန့်သတ်ချက်များနှင့် ကိုက်ညီကြောင်း သေချာစေသည်
- ✅ NEMA နှင့် IEC စံနှုန်းများ: NEMA မော်တာများသည် ပုံမှန်အားဖြင့် Class 20 ကာကွယ်မှု (1.15 ဝန်ဆောင်မှုအချက်နှင့် ခိုင်မာသောအပူစွမ်းရည်အတွက် ဒီဇိုင်းထုတ်ထားသည်) လိုအပ်ပြီး IEC မော်တာများသည် Class 10 (1.0 ဝန်ဆောင်မှုအချက်နှင့် တင်းကျပ်သောအပူအနားသတ်များဖြင့် အသုံးချမှုအဆင့်သတ်မှတ်ထားသည်) လိုအပ်သည်
- ✅ ရွေးချယ်မှုစံနှုန်း: အမြန်တုံ့ပြန်မှုအပလီကေးရှင်းများ (ရေမြုပ်ပန့်များ၊ လေလုံအောင်ပိတ်ထားသောမော်တာများ၊ VFD-မောင်းနှင်သောမော်တာများ) အတွက် Class 10 ကိုရွေးချယ်ပါ၊ အထွေထွေရည်ရွယ်ချက် NEMA မော်တာများအတွက် Class 20 နှင့် တိုးချဲ့အရှိန်မြှင့်ချိန်လိုအပ်သော မြင့်မားသော inertia ဝန်များအတွက် Class 30 ကိုရွေးချယ်ပါ
- ✅ အပူပျက်စီးမှုမျဉ်း ကိုက်ညီမှု: ခရီးစဉ်အမျိုးအစားသည် မော်တာ၏ အပူခံနိုင်ရည်နှင့် ကိုက်ညီရမည်—မကိုက်ညီသော ကာကွယ်မှုသည် စောစီးစွာ ပျက်ကွက်ခြင်း (ကာကွယ်မှုနည်းခြင်း) သို့မဟုတ် အနှောင့်အယှက်ဖြစ်စေသော ခရီးစဉ် (ကာကွယ်မှုလွန်ကဲခြင်း) ကို ဖြစ်စေနိုင်သည်
- ✅ အေးသော vs. ပူသော စတင်အပြုအမူ: ခရီးစဉ်မျဉ်းများသည် အအေးစတင်သည့်အခြေအနေများ (ပတ်ဝန်းကျင်အပူချိန်တွင် မော်တာ၊ ခရီးစဉ်ကြာချိန်ကို လက်ခံနိုင်သည်) နှင့် ပူသောပြန်လည်စတင်သည့်အခြေအနေများ (လည်ပတ်အပူချိန်အနီးရှိ မော်တာ၊ ပိုမိုမြန်ဆန်သောကာကွယ်မှုလိုအပ်သည်) နှစ်ခုလုံးအတွက် ထည့်သွင်းတွက်ချက်သည်
ခရီးစဉ်အမျိုးအစားကို နားလည်ခြင်း- မော်တာကာကွယ်ရေး၏ အခြေခံအုတ်မြစ်
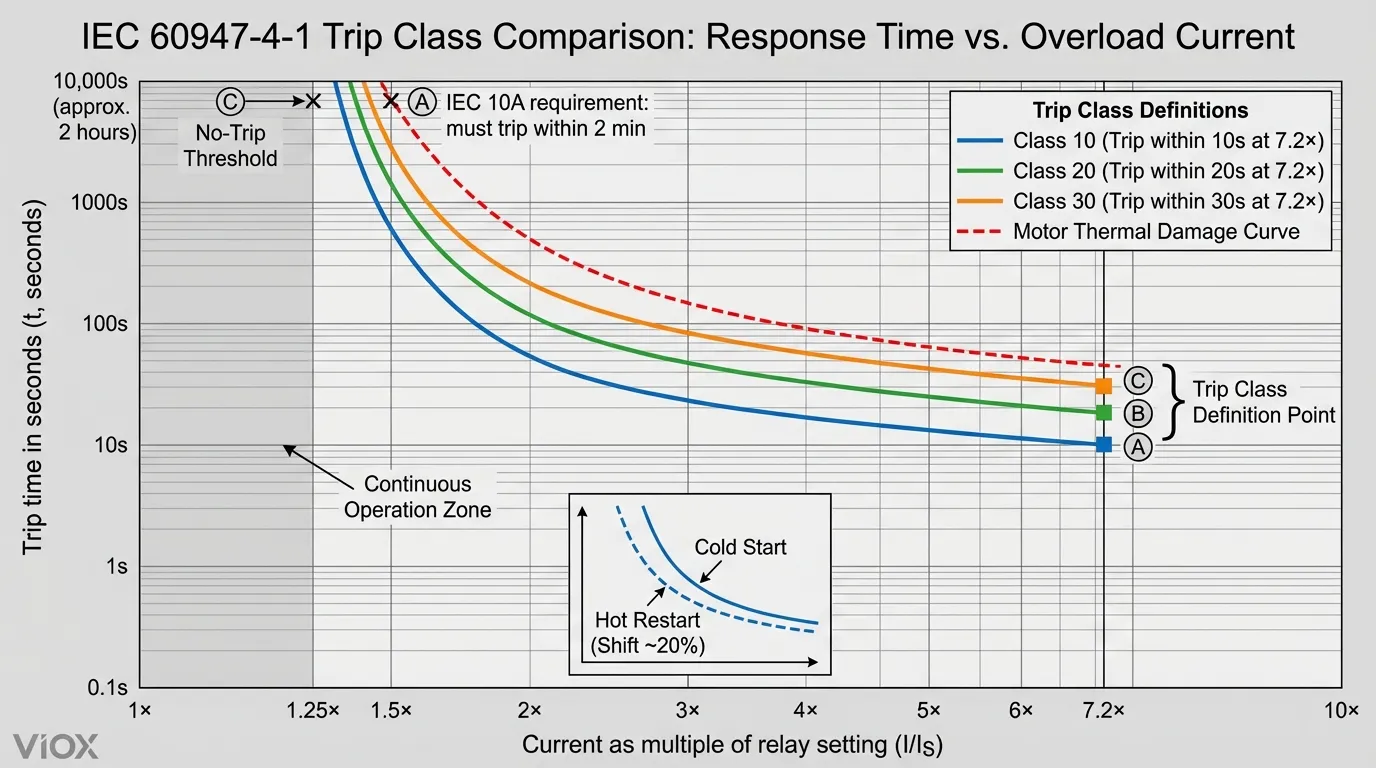
ခရီးစဉ်အမျိုးအစားသည် အမှန်တကယ်ဘာကိုဆိုလိုသနည်း
ခရီးစဉ်အမျိုးအစားသည် ရိုးရိုးအချိန်သတ်မှတ်ချက်တစ်ခုမဟုတ်ပါ—၎င်းသည် ကာကွယ်ရေးကိရိယာ၏ တုံ့ပြန်မှုလက္ခဏာများနှင့် အပူဖိစီးမှုကို ခံနိုင်ရည်ရှိသော မော်တာ၏စွမ်းရည်ကြားတွင် ဂရုတစိုက်အင်ဂျင်နီယာလုပ်ထားသော ဆက်စပ်မှုကို ကိုယ်စားပြုသည်။ IEC 60947-4-1 အရ ခရီးစဉ်အမျိုးအစားသည် ပြီးပြည့်စုံသော ကာကွယ်မှုမျဉ်းကို တည်ထောင်သည့် အရေးကြီးသော လည်ပတ်မှုအမှတ်နှစ်ခုကို သတ်မှတ်သည်-
မူလအဓိပ္ပါယ်အမှတ် (မြင့်မားသောလျှပ်စီးကြောင်း):
- NEMA စံနှုန်း: relay ချိန်ညှိမှု၏ 600% တွင် အမျိုးအစားအချိန် (စက္ကန့်) အတွင်း ခရီးထွက်ပါ
- IEC စံနှုန်း: relay ချိန်ညှိမှု၏ 7.2× တွင် အမျိုးအစားအချိန် (စက္ကန့်) အတွင်း ခရီးထွက်ပါ
ဒုတိယအဓိပ္ပါယ်အမှတ် (အလယ်အလတ်ဝန်ပို):
- ချိန်ညှိမှု၏ 125% တွင်: ၂ နာရီအတွင်း ခရီးမထွက်ရ (အအေးစတင်)
- ချိန်ညှိမှု၏ 150% တွင်: အမျိုးအစားအပေါ်အခြေခံ၍ သတ်မှတ်ထားသောအချိန်အတွင်း ခရီးထွက်ရမည် (IEC 10A: <2 မိနစ်)
ဤနှစ်ထပ်အမှတ်အသားသည် မော်တာ၏ အပူပျက်စီးမှုပရိုဖိုင်ကို ထင်ဟပ်စေသော ပြောင်းပြန်အချိန်လက္ခဏာမျဉ်းကို ဖန်တီးသည်—ဝန်ပိုမြင့်လေ၊ ခရီးစဉ်တုံ့ပြန်မှု မြန်လေဖြစ်သည်။.
ခရီးစဉ်အမျိုးအစား ရွေးချယ်မှုနောက်ကွယ်ရှိ ရူပဗေဒ
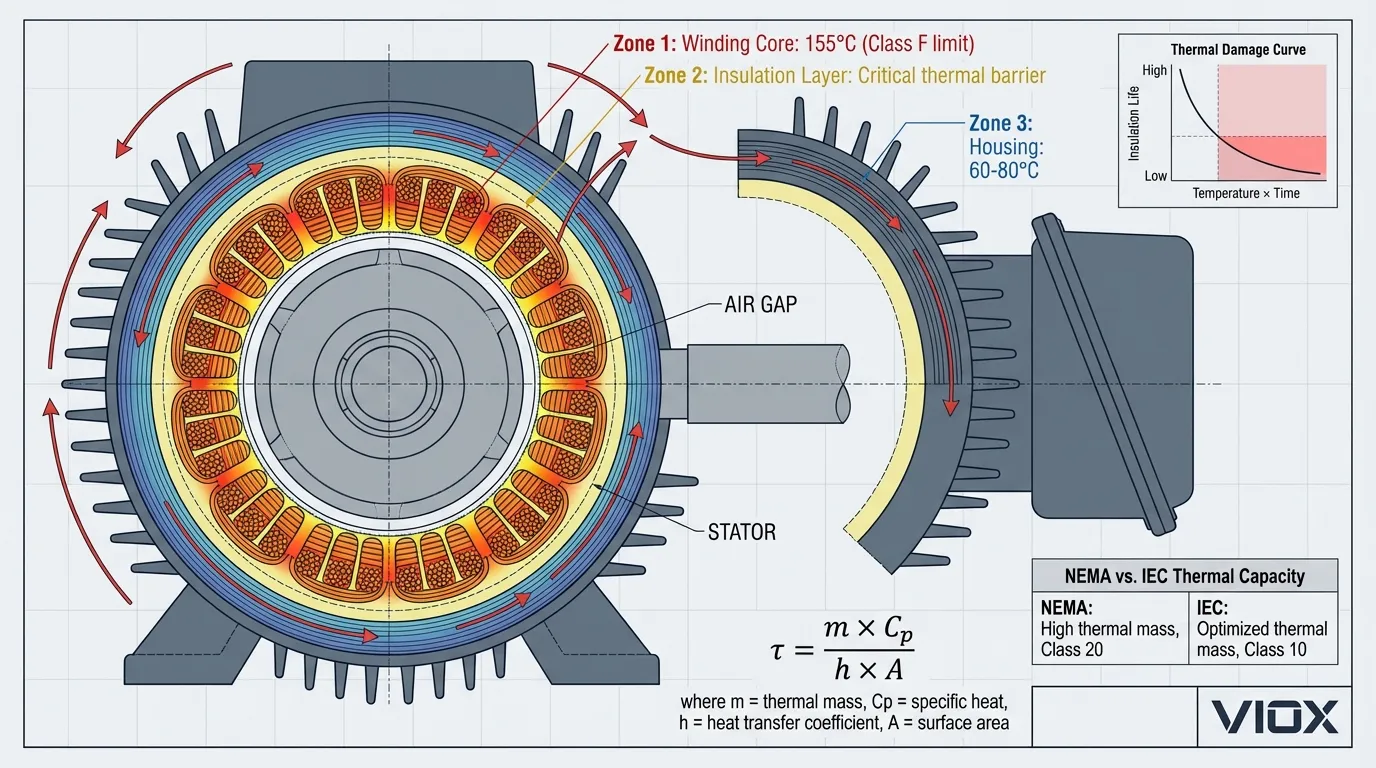
မော်တာဝိုင်ယာကြိုးကာကွယ်မှုသည် “10 ဒီဂရီစည်းမျဉ်း” ကိုလိုက်နာသည်—အဆင့်သတ်မှတ်ထားသောအပူချိန်ထက် 10°C မြင့်တက်တိုင်း ကာကွယ်မှုသက်တမ်းသည် တစ်ဝက်ကျဆင်းသွားသည်။ ဝန်ပိုအခြေအနေများတွင်၊ I2ဝိုင်ယာကြိုးများတွင် R အပူပေးခြင်းသည် လက်ရှိနှင့်အတူ ထပ်တိုး၍ တိုးလာသည်။ ခရီးစဉ်အမျိုးအစားသည် စုဆောင်းထားသော အပူစွမ်းအင် (∫ I²·t dt) သည် မော်တာ၏ အပူခံနိုင်ရည်ထက် မကျော်လွန်မီ ကာကွယ်ရေးကိရိယာသည် ပါဝါကို အနှောင့်အယှက်ပေးကြောင်း သေချာစေရမည်။.
အပူချိန်အချိန် အဆက်အသွယ်ဆက်ဆံရေး-
τမော်တာ > τလွှင် × ဘေးကင်းလုံခြုံရေးအနားသတ်
Where:
- τမော်တာ = မော်တာအပူချိန်အချိန် အဆက်အသွယ် (ပုံမှန်အားဖြင့် အလုံပိတ်မော်တာများအတွက် 30-60 မိနစ်)
- τလွှင် = Relay အပူချိန်အချိန် အဆက်အသွယ် (အမျိုးအစားအလိုက် ကွဲပြားသည်)
- ဘေးကင်းလုံခြုံရေးအနားသတ် = ပတ်ဝန်းကျင်အပြောင်းအလဲများအတွက် ပုံမှန်အားဖြင့် 1.2-1.5×
စံခရီးစဉ်အမျိုးအစားများ- ပြီးပြည့်စုံသော နှိုင်းယှဉ်မှု
IEC 60947-4-1 ခရီးစဉ်အမျိုးအစားများ
| ခရီးစဉ်အမျိုးအစား | 7.2× I တွင် ခရီးစဉ်အချိန်r | ပံုမွန္အသံုးခ်ျခင္း | မော်တာအမျိုးအစား လိုက်ဖက်ညီမှု |
|---|---|---|---|
| Class 5 | ≤5 စက္ကန့် | အပူချိန်ထိလွယ်သော မော်တာများအတွက် အလွန်မြန်ဆန်သော ကာကွယ်မှု | လေလုံအောင်ပိတ်ထားသော ဖိအားပေးစက်များ၊ သေးငယ်သော ရေမြုပ်ပန့်များ |
| Class 10 | ≤10 စက္ကန့် | စံ IEC မော်တာများ၊ VFD အပလီကေးရှင်းများ | IEC ဒီဇိုင်း N မော်တာများ၊ တုပအအေးခံထားသော မော်တာများ၊ အမြန်တုံ့ပြန်မှုဝန်များ |
| Class 10A | 7.2× တွင် ≤10 စက္ကန့် 1.5× တွင် ≤2 မိနစ် |
ပူသောပြန်လည်စတင်သည့်အခြေအနေများအတွက် မြှင့်တင်ထားသော ကာကွယ်မှု | မကြာခဏ စတင်/ရပ်တန့်စက်ဝန်းများပါရှိသော IEC မော်တာများ |
| Class 20 | ≤20 စက္ကန့် | အထွေထွေရည်ရွယ်ချက် NEMA မော်တာများ | 1.15 SF ပါရှိသော NEMA ဒီဇိုင်း A/B မော်တာများ၊ စံစက်မှုအပလီကေးရှင်းများ |
| Class 30 | ≤30 စက္ကန့် | မြင့်မားသော inertia၊ တိုးချဲ့အရှိန်မြှင့်ဝန်များ | စက်မှုလုပ်ငန်းသုံးမော်တာများ၊ ကြိတ်စက်များ၊ ကြီးမားသော ပန်ကာများ၊ ဗဟိုခွာအားစက်များ |
NEMA ခရီးစဉ်အမျိုးအစား စံနှုန်းများ
NEMA စံနှုန်းများသည် IEC အဓိပ္ပါယ်များနှင့် ကိုက်ညီသော်လည်း ရည်ညွှန်းအမှတ်အဖြစ် 7.2× အစား 600% (6×) ကို အသုံးပြုသည်။ လက်တွေ့ကွာခြားချက်မှာ အရေးမပါပါ—စနစ်နှစ်ခုစလုံးသည် တူညီသော ကာကွယ်မှုမျဉ်းများကို ထုတ်လုပ်သည်။.
NEMA သီးသန့်အချက်အလက်များ:
- Class 20 လွှမ်းမိုးမှု: NEMA မော်တာများ၏ ~85% သည် စံသတ်မှတ်ထားသော 1.15 service factor နှင့် ခိုင်မာသော အပူဒီဇိုင်းကြောင့် Class 20 ကာကွယ်မှုအတွက် ဒီဇိုင်းထုတ်ထားပါသည်။
- Locked-Rotor Time: NEMA MG-1 သည် မော်တာ ≤500 HP များအား ပုံမှန်လည်ပတ်အပူချိန်တွင် ≥12 စက္ကန့်ကြာ Locked-Rotor current ကို ခံနိုင်ရည်ရှိရန် လိုအပ်ပြီး Class 20 ကာကွယ်မှုနှင့် ကိုက်ညီပါသည်။
- Service Factor Interaction: 1.15 SF ရှိသော မော်တာများသည် 115% ဆက်တိုက် Overload ကို ကိုင်တွယ်နိုင်ပြီး ဤစွမ်းဆောင်ရည်ကို အနှောင့်အယှက်မဖြစ်စေသော Trip Curves များ လိုအပ်ပါသည်။
Trip Class ရွေးချယ်မှု လမ်းညွှန်: ကာကွယ်မှုကို Application နှင့် ကိုက်ညီစေခြင်း
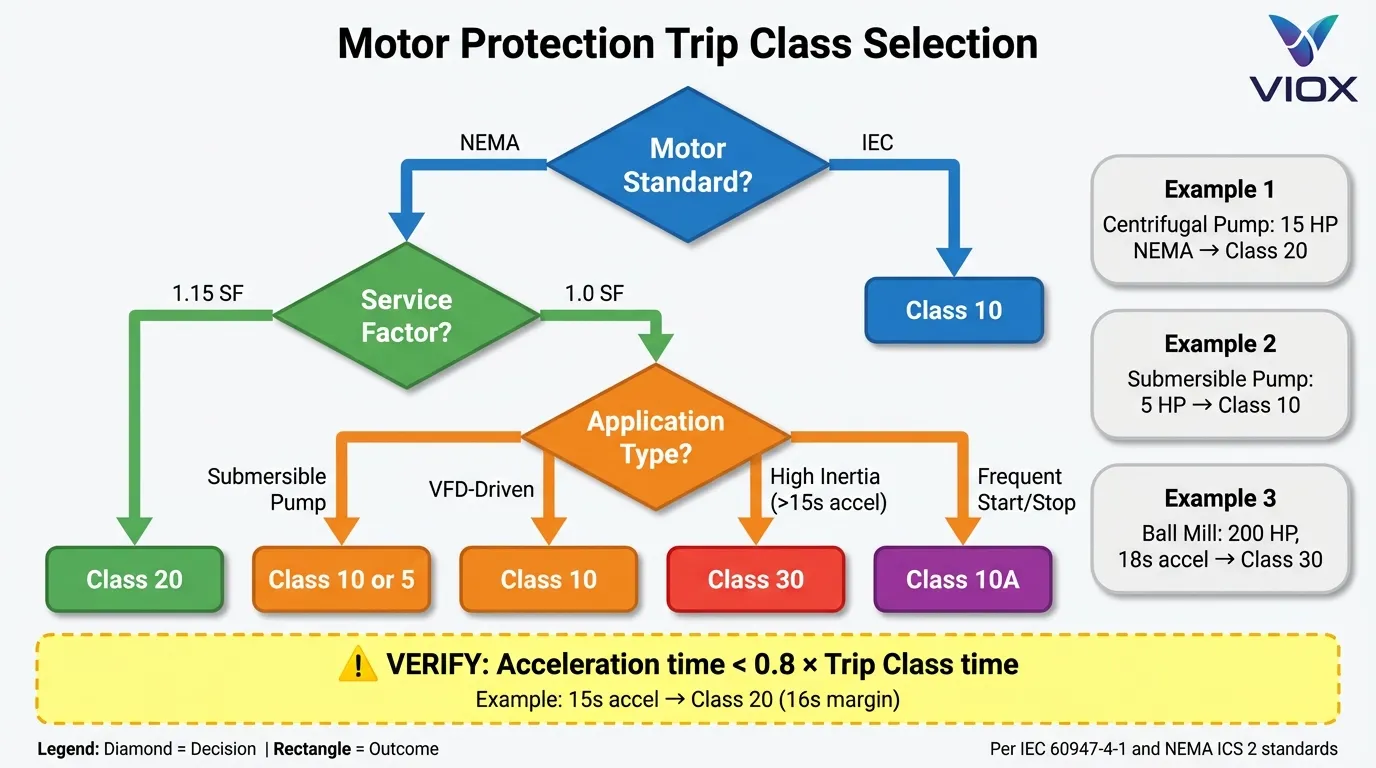
ဆုံးဖြတ်ချက်ဇယား: သင်လိုအပ်သော Trip Class ကဘာလဲ။
| မော်တာ၏ လက္ခဏာရပ် | အကြံပြုထားသော Trip Class | အကြောင်းပြချက် |
|---|---|---|
| NEMA Design A/B, 1.15 SF | Class 20 | စံအပူစွမ်းရည်၊ 12-20 စက္ကန့် Locked-Rotor ခံနိုင်ရည် |
| IEC Design N, 1.0 SF | Class 10 | Application-rated, တင်းကျပ်သောအပူအနားသတ်များ၊ 10 စက္ကန့် Locked-Rotor ခံနိုင်ရည် |
| ရေငုပ်စုပ်စက်မော်တာများ | Class 10 သို့မဟုတ် Class 5 | အရည်အေး၊ စီးဆင်းမှုရပ်တန့်သောအခါ အပူချိန်လျင်မြန်စွာမြင့်တက်ခြင်း |
| VFD-driven မော်တာများ | Class 10 | အရှိန်နည်းချိန်တွင် အအေးခံနိုင်စွမ်းလျော့နည်းခြင်း၊ Inverter-fed ဖြစ်သောအခါ Service Factor မရှိခြင်း |
| High-inertia loads (>5 စက္ကန့် အရှိန်မြှင့်ခြင်း) | Class 30 | စတင်ချိန်ကြာမြင့်ခြင်း၊ Nuisance Tripping ကိုကာကွယ်ခြင်း |
| မကြာခဏ Start/Stop (>10 cycles/hour) | Class 10A | Hot-restart ကာကွယ်မှု၊ 150% တွင် 2 မိနစ် Trip |
| Hermetically Sealed မော်တာများ | Class 5 သို့မဟုတ် Class 10 | ပြင်ပအအေးခံစနစ်မရှိခြင်း၊ အပူချိန်လျင်မြန်စွာမြင့်တက်ခြင်း |
အရေးကြီးသော Application အခြေအနေများ
အခြေအနေ ၁: 15 HP NEMA မော်တာပါရှိသော Centrifugal Pump
မော်တာ သတ်မှတ်ချက်များ:
- Full-Load Current (FLA): 20A
- Service Factor: 1.15
- Locked-Rotor Current: 120A (6× FLA)
- အရှိန်မြှင့်ချိန်: 3 စက္ကန့်
သုံးသပ်ချက်-
- Locked-Rotor ကြာချိန် (3s) < Class 20 Trip Time (20s) → ✅ Nuisance Tripping မရှိပါ။
- NEMA Design B မော်တာ → Class 20 စံ
- 1.15 SF သည် Trip မဖြစ်ဘဲ 23A ဆက်တိုက် ခွင့်ပြုသည်။
ရွေးချယ်မှု: Class 20 Thermal Overload Relay, 20A တွင် သတ်မှတ်ထားသည်။
အခြေအနေ ၂: 5 HP မော်တာပါရှိသော Submersible Well Pump
မော်တာ သတ်မှတ်ချက်များ:
- Full-Load Current: 14A
- Service Factor: 1.0 (Submersible အတွက် SF မရှိပါ)
- Locked-Rotor Current: 84A (6× FLA)
- အအေးခံခြင်း: ရေစီးဆင်းမှုအပေါ် မူတည်သည်။
သုံးသပ်ချက်-
- ရေစီးဆင်းမှု ဆုံးရှုံးခြင်း = အပူလွန်ကဲခြင်း (ပြင်ပအအေးခံစနစ်မရှိခြင်း)
- Burnout ကိုကာကွယ်ရန် လျင်မြန်သောကာကွယ်မှု လိုအပ်သည်။
- ထုတ်လုပ်သူသည် Class 10 ကာကွယ်မှုကို သတ်မှတ်သည်။
ရွေးချယ်မှု: Class 10 Thermal Overload Relay, 14A တွင် သတ်မှတ်ထားသည်။
အခြေအနေ ၃: 200 HP မော်တာပါရှိသော Ball Mill (High Inertia)
မော်တာ သတ်မှတ်ချက်များ:
- Full-Load Current: 240A
- အရှိန်မြှင့်ချိန်: 18 စက္ကန့်
- Locked-Rotor Current: 1,440A (6× FLA)
- Load အမျိုးအစား: High Inertia, Mechanical Time Constant >10s
သုံးသပ်ချက်-
- အရှိန်မြှင့်ချိန် (18s) > Class 20 Trip Time (20s) → ⚠️ Marginal
- အရှိန်မြှင့်ချိန် (18s) < Class 30 Trip Time (30s) → ✅ Safe Margin
- High Inertia သည် Extended Starting Allowance လိုအပ်သည်။
ရွေးချယ်မှု: Class 30 Thermal Overload Relay, 240A တွင် သတ်မှတ်ထားသည်။
NEMA နှင့် IEC မော်တာကာကွယ်မှု: အခြေခံကွာခြားချက်များကို နားလည်ခြင်း
ဒီဇိုင်းအတွေးအခေါ် နှိုင်းယှဉ်ခြင်း
| ရှုထောင့် | NEMA မော်တာများ | IEC မော်တာများ |
|---|---|---|
| ဒီဇိုင်းချဉ်းကပ်ပုံ | Conservative, Versatility အတွက် Over-designed | Application-specific, တိကျသော Duty အတွက် Optimized |
| Service Factor | Typically 1.15 (15% continuous overload capacity) | Typically 1.0 (no overload margin) |
| Thermal Capacity | High thermal mass, robust insulation systems | Optimized thermal design, minimal excess capacity |
| Standard Trip Class | Class 20 (20 seconds at 600% FLA) | Class 10 (10 seconds at 7.2× Ir) |
| Locked-Rotor Withstand | ≥12 seconds (NEMA MG-1 for ≤500 HP) | ~10 seconds (IEC 60034-12) |
| လျှပ်ကာ အတန်းအစား | Typically Class F (155°C) with Class B rise | Typically Class F with Class F rise |
| လက်ရှိစတင်ခြင်း။ | 6-7× FLA (NEMA Design B) | 5-8× In (IEC Design N) |
Why IEC Motors Require Faster Protection
IEC motors are designed with tighter thermal margins because they’re engineered for specific applications rather than general-purpose use. This “application rating” philosophy means:
- No Service Factor Buffer: An IEC motor rated for 10 kW delivers exactly 10 kW continuously—no 15% overload margin like NEMA 1.15 SF motors
- Optimized Cooling: Cooling systems are sized precisely for rated load, not over-designed
- Faster Thermal Response: Lower thermal mass means temperature rises more quickly during overload
- Global Efficiency Standards: IEC IE3/IE4 efficiency requirements drive tighter thermal designs
Practical implication: Using a Class 20 relay on an IEC motor can allow 10-20 seconds of damaging overload before tripping—potentially exceeding the motor’s 10-second thermal limit.
Cold Start vs. Hot Restart: The Hidden Complexity
Thermal State Impact on Trip Behavior
Trip class specifications are based on cold-start conditions—the motor and protection device are both at ambient temperature. However, real-world applications involve hot restarts after recent operation, fundamentally changing the protection dynamics.
Cold Start Characteristics:
- Motor windings at ambient temperature (~40°C)
- Full thermal capacity available
- Longer acceptable overload duration
- Trip curve follows published specifications
Hot Restart Characteristics:
- Motor windings near operating temperature (~120-155°C)
- Reduced thermal capacity (already partially “used”)
- Shorter safe overload duration
- Trip curve shifts left (faster tripping)
IEC Class 10A: The Hot-Restart Solution
IEC 60947-4-1 defines Class 10A specifically to address hot-restart protection inadequacies in standard Class 10/20 relays. The key difference:
| အခြေအနေ | Standard Class 20 | IEC Class 10A |
|---|---|---|
| At 7.2× Ir (cold) | ≤20 စက္ကန့် | ≤10 စက္ကန့် |
| At 1.5× Ir (hot) | ~8 minutes | ≤2 minutes |
| လျှောက်လွှာ | အထွေထွေရည်ရွယ်ချက် | Frequent start/stop, cyclic duty |
Why this matters: A motor running at full load reaches thermal equilibrium at ~120°C (Class F insulation). If it trips on overload and immediately restarts, a 150% overload can damage insulation within 2 minutes. Standard Class 20 relays may take 4-8 minutes to trip at this level, allowing thermal damage. Class 10A ensures protection within 2 minutes.
Motor Protection Circuit Breakers (MPCBs) vs. Thermal Overload Relays
Technology Comparison
| အင်္ဂါ | Thermal Overload Relay (TOR) | Motor Protection Circuit Breaker (MPCB) |
|---|---|---|
| ခရီးယန္တရား | Bimetallic strip or eutectic alloy heating | Magnetic (instantaneous) + thermal (overload) |
| Trip Class Availability | (ကိရိယာတစ်ခုချင်းအလိုက်) သတ်မှတ်ပြီးသား သို့မဟုတ် ချိန်ညှိနိုင်သော (အီလက်ထရောနစ်) | သတ်မှတ်ပြီးသား သို့မဟုတ် ချိန်ညှိနိုင်သော (အီလက်ထရောနစ် ထရစ်ယူနစ်များ) |
| Short-Circuit ကာကွယ်မှု | ❌ မရပါ (သီးခြား ဘရိတ်ကာ/ဖျူး လိုအပ်သည်) | ✅ ရပါသည် (ပေါင်းစပ်ထားသော သံလိုက် ထရစ်) |
| Phase Loss Detection | ✅ ရပါသည် (3-အဆင့် ဒီဇိုင်းတွင် မူလပါရှိသည်) | ✅ ရပါသည် (အီလက်ထရောနစ် မော်ဒယ်များ) |
| ချိန်ညှိမှု | လက်ရှိ ဆက်တင် ချိန်ညှိနိုင်သည်၊ အတန်းအစားကို များသောအားဖြင့် သတ်မှတ်ထားသည် | လက်ရှိ + အတန်းအစား ချိန်ညှိနိုင်သည် (အီလက်ထရောနစ် မော်ဒယ်များ) |
| ပြန်လည်သတ်မှတ်ခြင်းနည်းလမ်း | လက်ဖြင့် သို့မဟုတ် အလိုအလျောက် | လက်ဖြင့် (ထရစ်-ဖရီး ယန္တရား) |
| ပံုမွန္အသံုးခ်ျခင္း | ကွန်တက်တာအခြေခံ စတင်စက်များ၊ IEC အသုံးချမှုများ | သီးခြား မော်တာကာကွယ်မှု၊ NEMA/IEC ပေါင်းစပ် |
| စံနှုန်းများ | IEC 60947-4-1 (TOR), NEMA ICS 2 | IEC 60947-4-1 (MPSD), IEC 60947-2 (ဘရိတ်ကာ) |
နည်းပညာတစ်ခုစီကို ဘယ်အချိန်မှာ အသုံးပြုမလဲ
Thermal Overload Relay များကို အောက်ပါအခြေအနေများတွင် ရွေးချယ်ပါ-
- ကွန်တက်တာအခြေခံ မော်တာ စတင်စက်များကို အသုံးပြုခြင်း (စံ IEC/NEMA ဖွဲ့စည်းပုံများ)
- အထက်ပိုင်း ဆားကစ် ဘရိတ်ကာ သို့မဟုတ် ဖျူးများမှ ပေးထားသော ဝါယာရှော့ကာကွယ်မှု
- ကုန်ကျစရိတ်သက်သာသော အသုံးချပရိုဂရမ်များ
- ရှိပြီးသား ကွန်တက်တာ စနစ်များတွင် အစားထိုး/ပြန်လည်တပ်ဆင်ခြင်း
Motor Protection Circuit Breaker များကို အောက်ပါအခြေအနေများတွင် ရွေးချယ်ပါ-
- ကိရိယာတစ်ခုတည်းတွင် ပေါင်းစပ်ထားသော ကာကွယ်မှု (အိုဗာလုဒ် + ဝါယာရှော့) လိုအပ်ခြင်း
- နေရာ အကန့်အသတ်ရှိခြင်း (MPCB သည် ကွန်တက်တာ + TOR + ဘရိတ်ကာထက် ပိုမိုကျစ်လစ်သည်)
- ကွန်တက်တာမပါဘဲ တိုက်ရိုက်စတင်ခြင်း (DOL)
- မကြာခဏ လက်ဖြင့် ပြောင်းရန် လိုအပ်ခြင်း (MPCB တွင် ဖြုတ်တပ်နိုင်သော လုပ်ဆောင်ချက် ပါရှိသည်)
အဖြစ်များသော ထရစ်အတန်းအစား ရွေးချယ်မှု အမှားများနှင့် ဖြေရှင်းနည်းများ
အမှား ၁: IEC မော်တာများတွင် Class 20 ကာကွယ်မှုကို အသုံးပြုခြင်း
လက္ခဏာ: မော်တာသည် စောစီးစွာ ပျက်စီးခြင်း၊ ဝိုင်ယာကြိုး အကာအကွယ်များ ပျက်စီးခြင်း၊ ထရစ် မဖြစ်ပေါ်ခြင်း
အကြောင်းရင်းခံ: IEC မော်တာကို Class 10 ကာကွယ်မှု (၁၀ စက္ကန့် အပူချိန်ကန့်သတ်ချက်) အတွက် ဒီဇိုင်းထုတ်ထားသော်လည်း Class 20 relay (၂၀ စက္ကန့် ထရစ်ချိန်) ဖြင့် ကာကွယ်ထားသည်။ ၁၀ စက္ကန့် ကွာဟချက်သည် အပူကြောင့် ပျက်စီးမှုကို ခွင့်ပြုသည်။.
ဖြေရှင်းနည်း:
- မော်တာ ထုတ်လုပ်သူ၏ ထရစ်အတန်းအစား လိုအပ်ချက်ကို အမြဲစစ်ဆေးပါ (မော်တာ မှတ်တမ်း သို့မဟုတ် နာမည်ပြားကို စစ်ဆေးပါ)
- NEMA မော်တာများကို IEC နှင့် ညီမျှသော မော်တာများနှင့် အစားထိုးသည့်အခါ ထရစ်အတန်းအစား လိုက်ဖက်ညီမှုကို စစ်ဆေးပါ
- လိုက်လျောညီထွေဖြစ်စေရန် ချိန်ညှိနိုင်သော ထရစ်အတန်းအစားပါရှိသော အီလက်ထရောနစ် အိုဗာလုဒ် relay များကို အသုံးပြုပါ
အမှား ၂: Class 10 Relay သည် NEMA မော်တာများတွင် အနှောင့်အယှက်ဖြစ်စေသော ထရစ်ကို ဖြစ်စေခြင်း
လက္ခဏာ: မော်တာသည် ပုံမှန်စတင်ချိန်အတွင်း ထရစ်ဖြစ်သည်၊ အထူးသဖြင့် မြင့်မားသော အင်နာရှားဝန်များနှင့်
အကြောင်းရင်းခံ: ၁၈ စက္ကန့် အရှိန်မြှင့်ချိန်ရှိသော NEMA Design B မော်တာကို Class 10 relay (၁၀ စက္ကန့် ထရစ်) ဖြင့် ကာကွယ်ထားသည်။ လော့ခ်ချထားသော ရိုတာလျှပ်စီးကြောင်း (6× FLA) သည် မော်တာ အရှိန်အပြည့်မရရှိမီ ထရစ်အမှတ်ကို ကျော်လွန်သွားသည်။.
ဖြေရှင်းနည်း:
- အမှန်တကယ် အရှိန်မြှင့်ချိန်ကို တွက်ချက်ပါ- taccel = (J · ω) / (Tမော်တာ – Tload)
- သေချာအောင်လုပ်ပါ: taccel < 0.8 × tခရီးသင်တန်း (20% ဘေးကင်းလုံခြုံရေးအနားသတ်)
- ဤကိစ္စအတွက်: Class 20 သို့မဟုတ် Class 30 relay ကိုသုံးပါ
အမှား ၃: အပူချိန်ပြန်စသည့် အခြေအနေများကို လျစ်လျူရှုခြင်း
လက္ခဏာ: အအေးစတင် ကာကွယ်မှု မှန်ကန်သော်လည်း အကြိမ်များစွာ လျင်မြန်စွာ စတင်/ရပ်တန့်ပြီးနောက် မော်တာ ပျက်စီးခြင်း
အကြောင်းရင်းခံ: မကြာခဏ လည်ပတ်ခြင်းသည် မော်တာကို မြင့်မားသောအပူချိန်တွင် ထိန်းထားသည်။ စံ Class 20 relay သည် 150% အိုဗာလုဒ် (အပူချိန်အခြေအနေ) တွင် ၈ မိနစ်ခွင့်ပြုသော်လည်း မော်တာသည် ၂ မိနစ်သာ ခံနိုင်ရည်ရှိသည်။.
ဖြေရှင်းနည်း:
- တစ်နာရီလျှင် >6 ကြိမ် စတင်သည့် အသုံးချမှုများအတွက်: IEC Class 10A ကာကွယ်မှုကို အသုံးပြုပါ
- အနည်းဆုံး ပိတ်ချိန်နှောင့်နှေးမှုများကို အကောင်အထည်ဖော်ပါ (စတင်မှုများကြားတွင် မော်တာကို အေးစေရန် ခွင့်ပြုပါ)
- မော်တာ အပူချိန်မှတ်တမ်းကို ခြေရာခံသည့် အပူပုံစံအခြေခံ အီလက်ထရောနစ် relay များကို ထည့်သွင်းစဉ်းစားပါ
အမှား ၄: Relay လျှပ်စီးကြောင်း ဆက်တင်ကို အရွယ်အစားကြီးမြင့်စွာ သတ်မှတ်ခြင်း
လက္ခဏာ: မော်တာသည် အဆက်မပြတ် ပူနေသည်၊ နောက်ဆုံးတွင် လျှပ်ကာပျက်စီးခြင်း၊ relay သည် ဘယ်တော့မှ ထရစ်မဖြစ်ပါ
အကြောင်းရင်းခံ: Relay ကို 20A မော်တာအတွက် 25A (FLA ၏ 125%) သို့ သတ်မှတ်ထားသည်။ အဆက်မပြတ် 23A ဝန် (မော်တာ FLA ၏ 115%) သည် relay ထရစ်အမှတ်သို့ ဘယ်တော့မှ မရောက်ပါ။.
ဖြေရှင်းနည်း:
- relay လျှပ်စီးကြောင်းကို မော်တာ နာမည်ပြား FLA (ဝန်ဆောင်မှုအချက် လျှပ်စီးကြောင်းမဟုတ်) သို့ သတ်မှတ်ပါ
- 1.15 SF ရှိသော 20A မော်တာအတွက်: relay ကို 23A မဟုတ်ဘဲ 20A သို့ သတ်မှတ်ပါ
- 125% (25A) တွင် Relay ထရစ်မျဉ်းကွေးသည် အနှောင့်အယှက်ဖြစ်စေသော ထရစ်မဖြစ်ပေါ်ဘဲ ဝန်ဆောင်မှုအချက် လည်ပတ်မှုကို ခွင့်ပြုလိမ့်မည်
အီလက်ထရောနစ်နှင့် အပူချိန် ထရစ်အတန်းအစား နည်းပညာ
Bimetallic/Eutectic Alloy Thermal Relay များ
၎င်းတို့အလုပ်လုပ်ပုံ-
- လျှပ်စီးကြောင်းသည် အပူပေးသည့်ဒြပ်စင်မှတဆင့် စီးဆင်းသည်
- Bimetallic အကွက်သည် မတူညီသော အပူချိန်ပြန့်ကားမှုကြောင့် ကွေးသွားသည်
- ကွေးညွှတ်မှုအမှတ်သို့ရောက်ရှိသောအခါ စက်ပိုင်းဆိုင်ရာချိတ်ဆက်မှုသည် relay အဆက်အသွယ်များကို ထရစ်ဖြစ်စေသည်
ထရစ်အတန်းအစား လက္ခဏာများ:
- သတ်မှတ်ထားသော ထရစ်အတန်းအစား (ကိရိယာတစ်ခုချင်းအလိုက်၊ ပြောင်းလဲ၍မရပါ)
- ပတ်ဝန်းကျင် အပူချိန် လျော်ကြေးပေးခြင်း (bimetallic အကွက်သည် မူလအားဖြင့် လျော်ကြေးပေးသည်)
- အပူမှတ်ဉာဏ် (ထရစ်ဖြစ်ပြီးနောက် အပူကို ထိန်းသိမ်းထားသည်၊ ပြန်လည်စတင်ချိန်ကို ထိခိုက်စေသည်)
- ခရီးစဉ်မျဉ်းကွေး တိကျမှု: ±10-20% (စက်ပိုင်းဆိုင်ရာ ခံနိုင်ရည်)
အားသာချက်များ
- ပြင်ပပါဝါ မလိုအပ်ပါ။
- လျှပ်စစ်ဆူညံသံ/EMI ကို ခုခံနိုင်စွမ်းရှိသည်။
- ရိုးရှင်းပြီး သက်သေပြပြီးသော နည်းပညာ
- ကုန်ကျစရိတ်သက်သာတယ်။
အားနည်းချက်များ-
- ခရီးစဉ်အတန်းအစား သတ်မှတ်ထားသည် (relay အမျိုးအစားများစွာကို သိုလှောင်ထားရမည်)
- လျင်မြန်သောအလွန်အကျွံဝန်များအတွက် တုံ့ပြန်မှုနှေးကွေးသည်။
- အချိန်ကြာလာသည်နှင့်အမျှ စက်ပိုင်းဆိုင်ရာ ဝတ်ဆင်မှု
- အကန့်အသတ်ရှိသော ရောဂါရှာဖွေနိုင်စွမ်း
အီလက်ထရောနစ် အလွန်အကျွံဝန်အားပေးစက်များ
၎င်းတို့အလုပ်လုပ်ပုံ-
- လက်ရှိထရန်စဖော်မာ (CTs) သည် မော်တာလျှပ်စီးကြောင်းကို တိုင်းတာသည်။
- မိုက်ခရိုပရိုဆက်ဆာသည် အပူပုံစံကို တွက်ချက်သည်- θ(t) = θ0 + ∫ [(I2 – Iအဆင့်သတ်မှတ်သည်။2) / τ] dt
- တွက်ချက်ထားသော အပူချိန်သည် သတ်မှတ်ထားသော အကန့်အသတ်ထက် ကျော်လွန်သောအခါ ခရီးထွက်သည်။
ထရစ်အတန်းအစား လက္ခဏာများ:
- ရွေးချယ်နိုင်သော ခရီးစဉ်အတန်းအစား (Class 5, 10, 10A, 15, 20, 30 via DIP switch သို့မဟုတ် software)
- ဒစ်ဂျစ်တယ် အပူပုံစံ (မော်တာအပူချိန်ကို အဆက်မပြတ် ခြေရာခံသည်)
- အပူချိန်ပြန်စခြင်းလျော်ကြေး (ပါဝါဆုံးရှုံးပြီးနောက် အပူချိန်အခြေအနေကို မှတ်မိသည်)
- ခရီးစဉ်မျဉ်းကွေး တိကျမှု: ±5% (ဒစ်ဂျစ်တယ် တိကျမှု)
အားသာချက်များ
- စက်တစ်ခုတည်းသည် ခရီးစဉ်အတန်းအစားများစွာကို လွှမ်းခြုံထားသည် (စာရင်းကို လျှော့ချပေးသည်)
- အဆင့်မြင့် ရောဂါရှာဖွေခြင်း (လက်ရှိမညီမျှခြင်း၊ အဆင့်ဆုံးရှုံးခြင်း၊ မြေပြင်ချို့ယွင်းခြင်း)
- ဆက်သွယ်ရေးစွမ်းရည် (Modbus, Profibus, EtherNet/IP)
- ပရိုဂရမ်ပြုလုပ်နိုင်သော အင်္ဂါရပ်များ (နှိုးစက်အကန့်အသတ်များ၊ ခရီးစဉ်နှောင့်နှေးခြင်း)
အားနည်းချက်များ-
- ထိန်းချုပ်ပါဝါထောက်ပံ့မှု လိုအပ်သည်။
- ပိုမိုရှုပ်ထွေးသည် (ကနဦးကုန်ကျစရိတ် မြင့်မားသည်)
- လျှပ်စစ်ဆူညံသံကို ခံနိုင်ရည်ရှိသည် (သင့်လျော်သော မြေစိုက်ခြင်း လိုအပ်သည်)
- Firmware အပ်ဒိတ်များ လိုအပ်နိုင်ပါသည်။
ခရီးစဉ်အတန်းအစားနှင့် မော်တာညှိနှိုင်းမှု- အမျိုးအစား ၁ နှင့် အမျိုးအစား ၂
IEC 60947-4-1 ညှိနှိုင်းမှု အမျိုးအစားများ
မော်တာကာကွယ်ရေးစနစ်များသည် ဘေးကင်းလုံခြုံသော ချို့ယွင်းမှုအနှောင့်အယှက်ကို သေချာစေရန်အတွက် တိုတောင်းသောဆားကစ်ကာကွယ်ရေးကိရိယာများ (ဖျူးစ်များ သို့မဟုတ် ဆားကစ်ဘရိတ်ကာများ) နှင့် ညှိနှိုင်းဆောင်ရွက်ရမည်။ ခရီးစဉ်အတန်းအစားသည် ဤညှိနှိုင်းမှုကို ထိခိုက်စေသည်-
အမျိုးအစား ၁ ညှိနှိုင်းမှု-
- တိုတောင်းသောဆားကစ်အခြေအနေများအောက်တွင်၊ ဆက်သွယ်သူ သို့မဟုတ် စတင်သူသည် ပျက်စီးမှုကို ခံနိုင်ရည်ရှိနိုင်သည်။
- လူပုဂ္ဂိုလ်များ သို့မဟုတ် တပ်ဆင်မှုအတွက် အန္တရာယ်မရှိပါ။
- ပြန်လည်စတင်ခြင်းမပြုမီ ပြုပြင်ခြင်း သို့မဟုတ် အစားထိုးခြင်း လိုအပ်နိုင်ပါသည်။
- ခရီးစဉ်အတန်းအစား သက်ရောက်မှု: အနည်းဆုံး—အလွန်အကျွံဝန်မဟုတ်ဘဲ တိုတောင်းသောဆားကစ်ကာကွယ်ရေးကို အာရုံစိုက်သည်။
အမျိုးအစား ၂ ညှိနှိုင်းမှု-
- တိုတောင်းသောဆားကစ်အခြေအနေများအောက်တွင်၊ ဆက်သွယ်သူ သို့မဟုတ် စတင်သူအား ပျက်စီးမှုမရှိပါ (ဖြစ်နိုင်ချေရှိသော ဆက်သွယ်မှုဂဟေဆော်ခြင်းမှလွဲ၍)
- လူပုဂ္ဂိုလ်များ သို့မဟုတ် တပ်ဆင်မှုအတွက် အန္တရာယ်မရှိပါ။
- ချို့ယွင်းချက်ရှင်းလင်းပြီးနောက် ဝန်ဆောင်မှုအတွက် အဆင်သင့်ဖြစ်နေသော စက်ပစ္စည်း
- ခရီးစဉ်အတန်းအစား သက်ရောက်မှု: အရေးပါသည်—ဆက်သွယ်သူအဆက်အသွယ်များ မကပ်မီ အလွန်အကျွံဝန်အားပေးစက်သည် ခရီးထွက်ရမည်။
ညှိနှိုင်းမှု ဥပမာ-
| မော်တာ FLA | ခရီးစဉ်အမျိုးအစား | အထက်ပိုင်း ဖျူးစ် | ညှိနှိုင်းမှု အမျိုးအစား | အမြင့်ဆုံး ချို့ယွင်းချက် လျှပ်စီးကြောင်း |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 32A | Class 10 | 63A gG ဖျူးစ် | အမျိုးအစား ၂ | 50 kA |
| 32A | Class 20 | 63A gG ဖျူးစ် | အမျိုးအစား ၂ | 50 kA |
| 32A | Class 30 | 80A gG ဖျူးစ် | အမျိုးအစား ၁ | 50 kA |
အဓိက ထိုးထွင်းသိမြင်မှု: နှေးကွေးသော ခရီးစဉ်အတန်းအစားများ (Class 30) သည် ညှိနှိုင်းမှုကိုရရှိရန် ကြီးမားသောဖျူးစ်များ လိုအပ်နိုင်ပြီး အမျိုးအစား ၂ စွမ်းဆောင်ရည်ကို ထိခိုက်စေနိုင်သည်။ ထုတ်လုပ်သူများသည် ခရီးစဉ်အတန်းအစားတစ်ခုစီအတွက် အမြင့်ဆုံးဖျူးစ်အရွယ်အစားကို သတ်မှတ်ပေးသည့် ညှိနှိုင်းမှုဇယားများကို ပေးထားသည်။.
အတွင်းပိုင်းလင့်ခ်များနှင့် ဆက်စပ်အရင်းအမြစ်များ
မော်တာကာကွယ်ရေးစနစ်များနှင့် ဆက်စပ်လျှပ်စစ်အစိတ်အပိုင်းများကို ပြည့်စုံစွာနားလည်သဘောပေါက်ရန်အတွက်၊ ဤ VIOX နည်းပညာလမ်းညွှန်များကို လေ့လာပါ-
- Thermal Overload Relays ဟူသည် အဘယ်နည်း- မော်တော်ကာကွယ်ရေးကိရိယာများအတွက် လမ်းညွှန်ချက်အပြည့်အစုံ – အပူလွန်ကဲသောဝန်အားပေးစက်နည်းပညာ၊ အမျိုးအစားများနှင့် ရွေးချယ်မှုစံနှုန်းများအကြောင်း နက်ရှိုင်းစွာလေ့လာပါ။
- NEMA Class 20 နှင့် IEC Class 10 အလွန်အကျွံဝန်အားပေးစက် လမ်းညွှန် – NEMA နှင့် IEC မော်တာကာကွယ်ရေးစံနှုန်းများ၏ အသေးစိတ် နှိုင်းယှဉ်ချက်
- Contactor နှင့် Motor Starter- အဓိက ကွာခြားချက်များကို နားလည်ခြင်း – ဆက်သွယ်သူများနှင့် အလွန်အကျွံဝန်အားပေးစက်များသည် မော်တာထိန်းချုပ်မှုတွင် မည်သို့အတူတကွလုပ်ဆောင်သည်ကို လေ့လာပါ။
- Motor Power ကိုအခြေခံ၍ Contactors နှင့် Circuit Breakers ကိုရွေးချယ်နည်း – ပြီးပြည့်စုံသော မော်တာကာကွယ်ရေးစနစ်များအတွက် လက်တွေ့ကျသော အရွယ်အစားလမ်းညွှန်
- ဆက်သွယ်သူများအတွက် လျှပ်စစ်စံနှုန်းများ- AC1, AC2, AC3, AC4 အသုံးပြုမှု အမျိုးအစားများကို နားလည်ခြင်း – IEC 60947-4-1 အသုံးပြုမှု အမျိုးအစားများအတွက် ပြည့်စုံသော လမ်းညွှန်
အမေးများသောမေးခွန်းများ- ခရီးစဉ်အတန်းအစား ရွေးချယ်ခြင်းနှင့် အသုံးချခြင်း
Q1: Class 20 အတွက် အဆင့်သတ်မှတ်ထားသော NEMA မော်တာတွင် Class 10 အလွန်အကျွံဝန်အားပေးစက်ကို သုံးနိုင်ပါသလား။
တဲ့: နည်းပညာအရ ဟုတ်ပါတယ်၊ ဒါပေမယ့် အသုံးချမှုအများစုအတွက် မထောက်ခံပါဘူး။ Class 10 relay သည် ပိုမိုမြန်ဆန်သောကာကွယ်မှု (အလားအလာကောင်းမွန်သည်) ကိုပေးစွမ်းနိုင်သော်လည်း၊ ပုံမှန်စတင်ချိန်အတွင်း အနှောင့်အယှက်ဖြစ်စေနိုင်သည်၊ အထူးသဖြင့် inertia မြင့်မားသောဝန်များ သို့မဟုတ် အရှိန်မြှင့်ချိန် > 8 စက္ကန့်ရှိသော မော်တာများအတွက်ဖြစ်သည်။ NEMA မော်တာသည် Class 20 ကာကွယ်မှု (600% FLA တွင် 20 စက္ကန့်ခံနိုင်ရည်) နှင့်ဆက်စပ်သောအပူဖိစီးမှုကို ဘေးကင်းစွာကိုင်တွယ်နိုင်ရန် ဒီဇိုင်းထုတ်ထားသောကြောင့် Class 10 ကိုအသုံးပြုခြင်းသည် ဘေးကင်းလုံခြုံရေးအပိုအနားသတ်ကို မပေးစွမ်းနိုင်ပါ—၎င်းသည် မလိုလားအပ်သောခရီးစဉ်များ၏အန္တရာယ်ကို တိုးစေပါသည်။ ခြွင်းချက်- မော်တာထုတ်လုပ်သူသည် Class 10 (ဥပမာ- VFD လည်ပတ်မှု သို့မဟုတ် အထူးတာဝန်စက်ဝန်းများအတွက်) ကို အထူးအကြံပြုပါက ၎င်းတို့၏လမ်းညွှန်မှုကို လိုက်နာပါ။.
Q2: မော်တာအမည်ပြားက ၎င်းကိုမသတ်မှတ်ပါက မှန်ကန်သော ခရီးစဉ်အတန်းအစားကို မည်သို့ဆုံးဖြတ်မည်နည်း။
တဲ့: ဤဆုံးဖြတ်ချက်သစ်ပင်ကို လိုက်နာပါ-
- မော်တာမူရင်းကို စစ်ဆေးပါ။: NEMA motors (North American) → Class 20; IEC motors (European/Asian) → Class 10
- Check service factor: 1.15 SF → Class 20; 1.0 SF → Class 10
- Check application type:
- Submersible pumps → Class 10 or Class 5
- VFD-driven motors → Class 10
- High-inertia loads (acceleration >15s) → Class 30
- General industrial → Class 20
- Consult manufacturer: When in doubt, contact the motor manufacturer with the motor serial number—they can provide the recommended trip class based on design specifications.
Q3: What happens if I use the wrong trip class?
တဲ့: Two failure modes:
- Under-protection (Class too slow): Motor experiences thermal damage before relay trips. Example: Class 20 relay on Class 10 motor allows 10-20 seconds of damaging overload. Result: Shortened motor life, insulation breakdown, eventual failure.
- Over-protection (Class too fast): Relay trips during normal operation, causing nuisance shutdowns. Example: Class 10 relay on high-inertia load with 18-second acceleration. Result: Motor never reaches full speed, production downtime, frustrated operators who may bypass protection (dangerous).
Q4: Do electronic overload relays provide better protection than thermal relays?
တဲ့: Not necessarily “better,” but more flexible and precise. Electronic relays offer:
- Adjustable trip class (one device = multiple applications)
- ပိုမိုတိကျမှု (±5% vs. ±15% for thermal)
- Advanced diagnostics (current imbalance, ground fault, thermal state)
- ဆက်သွယ်ရေး (remote monitoring, predictive maintenance)
However, thermal relays have advantages:
- ပြင်ပပါဝါ မလိုအပ်ပါ။ (self-powered by motor current)
- Immune to electrical noise (important in harsh EMI environments)
- ကုန်ကျစရိတ်သက်သာတယ်။ (for simple, fixed applications)
ထောက်ခံချက်: Use electronic relays for critical applications, variable loads, or where diagnostics/communication are needed. Use thermal relays for cost-sensitive, fixed-duty applications where simplicity is valued.
Q5: How does ambient temperature affect trip class performance?
တဲ့: Ambient temperature directly impacts trip time because both the motor and protection device are affected:
Motor side:
- Higher ambient → Less thermal capacity available → Faster temperature rise
- Standard rating: 40°C ambient (IEC/NEMA)
- Derating required above 40°C (typically 1% per °C above 40°C)
Relay side:
- Bimetallic relays: Inherently compensate (bimetallic strip responds to ambient + load heating)
- Electronic relays: Require ambient compensation setting (many have built-in temperature sensors)
ဥပမာ: A motor in a 50°C ambient (10°C above standard) has ~10% less thermal capacity. The relay must be set 10% lower (18A instead of 20A for a 20A motor) OR the motor must be derated to 18A continuous operation. Trip class remains the same, but the current threshold changes.
နိဂုံး
Trip Class is far more than a simple timing specification—it represents the critical link between motor thermal characteristics and protection device response. Understanding the nuances of Class 5, 10, 10A, 20, and 30 protection enables engineers to design motor control systems that prevent both catastrophic failures and costly nuisance tripping.
Key design principles to remember:
- Match protection to motor design: NEMA motors (Class 20) and IEC motors (Class 10) have fundamentally different thermal capacities—mismatched protection compromises safety or reliability
- Consider real-world duty cycles: Cold-start specifications don’t tell the whole story—hot-restart conditions (frequent cycling) may require faster protection (Class 10A)
- Verify acceleration time compatibility: Calculate actual motor acceleration time and ensure it’s less than 80% of the trip class time to prevent nuisance tripping
- Leverage modern technology: Electronic overload relays with adjustable trip classes provide flexibility, diagnostics, and precision that fixed thermal relays cannot match
- အထက်ပိုင်းကာကွယ်ရေးနှင့် ညှိနှိုင်းဆောင်ရွက်ခြင်း: Trip class selection affects Type 1/Type 2 coordination with fuses and circuit breakers—consult manufacturer coordination tables
As motor efficiency standards tighten globally (IEC IE4, IE5 on the horizon), thermal margins continue to shrink, making proper trip class selection more critical than ever. The trend toward IEC-style application-rated motors—even in North American markets—means engineers must understand both NEMA and IEC protection philosophies to specify systems that deliver long-term reliability.
VIOX Electric အကြောင်း: VIOX Electric is a leading B2B manufacturer of electrical equipment, specializing in motor protection circuit breakers (MPCBs), thermal overload relays, contactors, and comprehensive motor control solutions for industrial and commercial applications. Our engineering team provides technical support for motor protection system design, trip class selection, and coordination studies. ကြှနျုပျတို့ကိုဆကျသှယျရနျ for application-specific guidance and product selection assistance.


