Selecting the wrong DC circuit breaker size can lead to catastrophic system failures, fire hazards, and costly equipment damage in solar PV installations. Whether you’re designing systems for North American markets or international projects, understanding the critical differences between NEC 690 and IEC 60947-2 standards is essential for safe, compliant installations.
This comprehensive guide breaks down the calculation methods, safety factors, and practical applications of both standards to help electrical engineers, system designers, and installers make informed decisions.

သော့ထုတ်ယူမှုများ
- NEC 690 applies a 1.56× multiplier (125% × 125%) to short-circuit current for PV source circuits, while IEC 60947-2 uses different continuous load factors based on application type
- Voltage ratings differ significantly: NEC 690 limits residential DC systems to 600V, while IEC 60947-2 covers up to 1,500V DC for industrial applications
- Breaking capacity requirements: NEC focuses on available fault current at the installation point, while IEC 60947-2 specifies Icu (ultimate) and Ics (service) ratings
- အပူချိန် လျှော့ချခြင်း: Both standards require ambient temperature corrections, but reference temperatures differ (40°C for NEC, varies by IEC application)
- Documentation requirements: NEC 690 mandates specific labeling and placards, while IEC 62446-1 requires comprehensive commissioning reports
Understanding DC Circuit Breaker Standards: Why They Matter
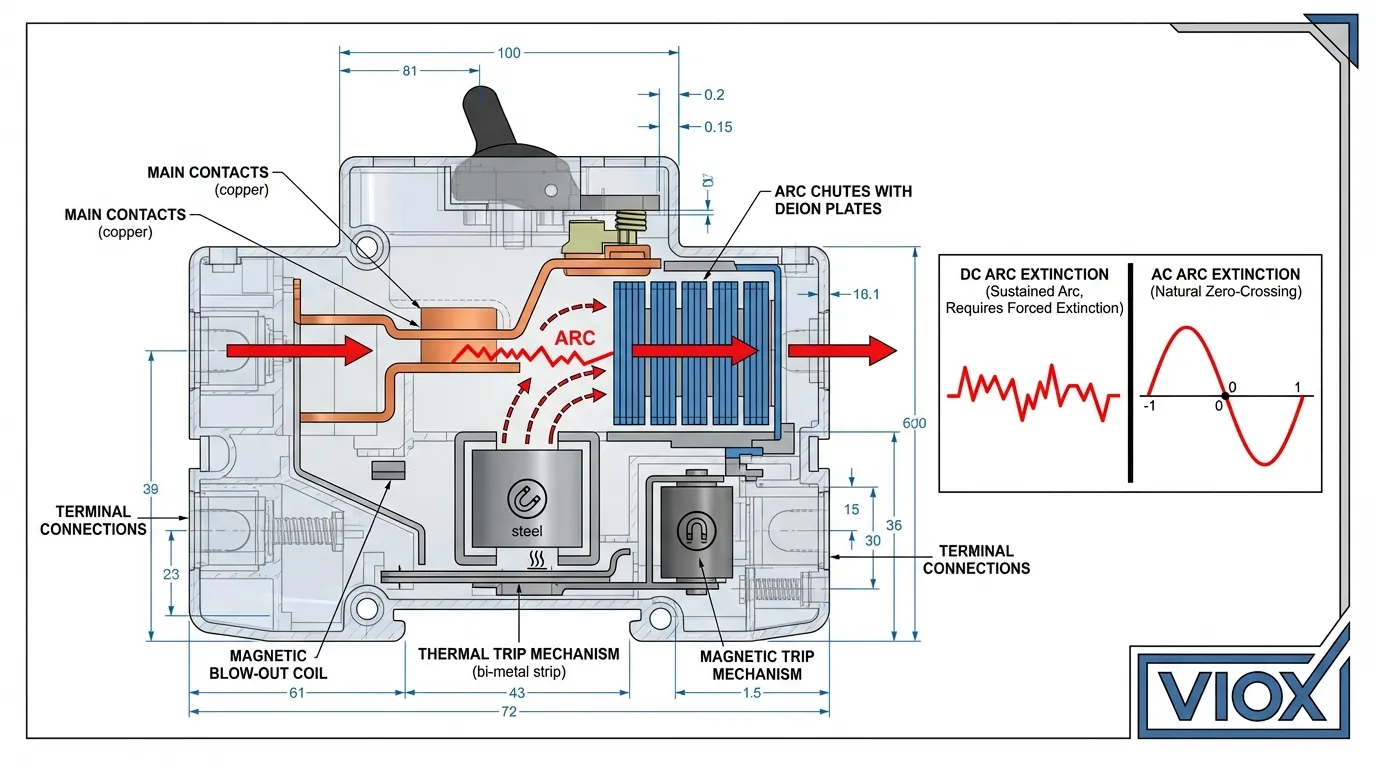
DC circuit breakers operate fundamentally differently from their AC counterparts. Unlike AC current that naturally crosses zero 100-120 times per second (aiding arc extinction), DC current maintains constant polarity, making arc interruption significantly more challenging. This physical reality drives the need for specialized sizing calculations and standards.
The National Electrical Code (NEC) Article 690 governs solar photovoltaic systems primarily in the United States and jurisdictions adopting the NEC framework. Meanwhile, IEC 60947-2 serves as the international standard for low-voltage circuit breakers used in commercial and industrial applications worldwide, including solar installations in Europe, Asia, and other regions.
Understanding both standards is crucial for manufacturers serving global markets and installers working on international projects. DC Circuit Breaker ဆိုတာဘာလဲ provides foundational knowledge on DC protection principles.
NEC 690: Solar PV Circuit Breaker Sizing Method
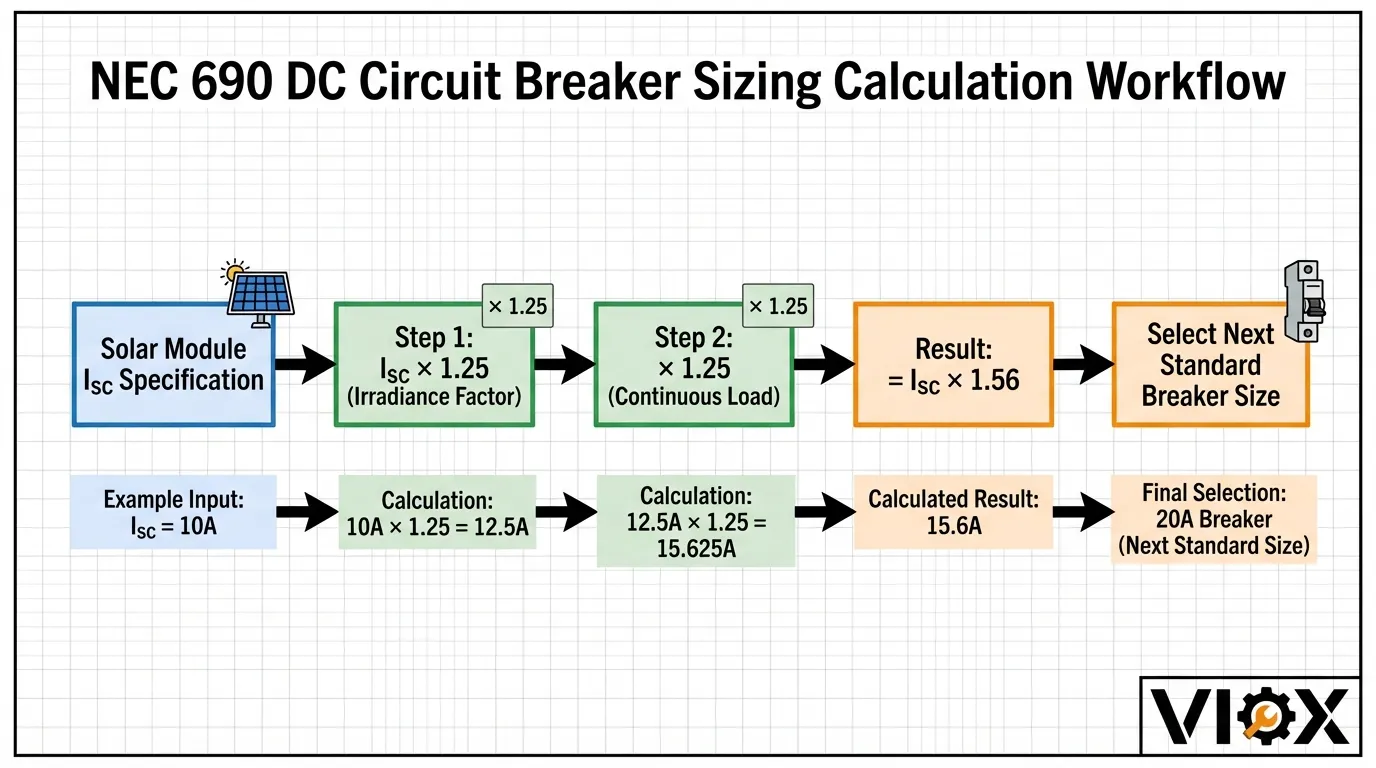
The 1.56× Multiplier Explained
NEC 690.8(A)(1) establishes the foundation for DC circuit breaker sizing in solar applications. The calculation applies two consecutive 125% safety factors:
Step 1: Account for Enhanced Irradiance
The first 125% factor addresses the “edge of cloud” effect, where solar modules can produce current exceeding their rated short-circuit current (Isc) under certain atmospheric conditions.
Step 2: Continuous Load Factor
The second 125% factor accounts for continuous operation, as PV systems can generate power for three or more consecutive hours during peak sunlight.
Combined Calculation:
Maximum Current = Isc × 1.25 × 1.25 = Isc × 1.56
Practical NEC 690 Sizing Example
System Specifications:
- Solar module Isc: 10.5A
- Number of parallel strings: 2
- Operating voltage: 48V DC
Calculation Steps:
- Calculate total short-circuit current:
Total Isc = 10.5A × 2 strings = 21A - Apply NEC 690.8 multiplier:
Required breaker rating = 21A × 1.56 = 32.76A - Select standard breaker size:
Next standard size = 40A DC circuit breaker - Verify conductor ampacity:
Conductor must handle ≥ 32.76A after temperature/conduit fill corrections
This methodology ensures the breaker won’t nuisance-trip during normal high-irradiance conditions while providing adequate overload protection. How to Choose the Right DC Circuit Breaker offers additional selection criteria.
NEC 690 Voltage Considerations
NEC 690.7 requires calculating maximum system voltage using temperature-corrected open-circuit voltage (Voc). For residential installations, NEC limits DC voltage to 600V for one- and two-family dwellings, though commercial systems can operate at higher voltages with proper safeguards.
Temperature Correction Formula:
Voc(max) = Voc(STC) × [1 + (Tmin – 25°C) × Temperature Coefficient]
Where Tmin is the lowest expected ambient temperature at the installation site.
IEC 60947-2: Industrial DC Circuit Breaker Standards

Scope and Application
IEC 60947-2 applies to circuit breakers with main contacts intended for circuits not exceeding:
- 1,000V AC
- 1,500V DC
This standard covers molded case circuit breakers (MCCBs) and other industrial-grade protection devices, making it suitable for large-scale solar installations, battery energy storage systems (BESS), and DC microgrids. Understanding IEC 60947-2 compares this standard with residential MCB requirements.
IEC Current Rating Categories
IEC 60947-2 defines several current ratings that differ from NEC terminology:
နှုန်းလက်ရှိလည်ပတ်(ဆိုလိုသည်မှာ):
The current the breaker can carry continuously at a specified ambient temperature (typically 40°C for enclosed installations, 25°C for open air).
အပူစီးကြောင်း (Ith):
အပူချိန်မြင့်တက်မှု ကန့်သတ်ချက်ထက် မကျော်လွန်ဘဲ ဘရိတ်ကာသည် ၎င်း၏အကာအတွင်း၌ သယ်ဆောင်နိုင်သော အမြင့်ဆုံး စီးကြောင်းဖြစ်သည်။.
သမားရိုးကျ လွတ်လပ်သောလေ အပူစီးကြောင်း (Ithe):
25°C တွင် လွတ်လပ်သောလေထဲ၌ DIN ရထားလမ်းပေါ်တွင် တပ်ဆင်ထားသည့်အခါ စီးကြောင်းအဆင့်သတ်မှတ်ချက်ဖြစ်သည်။.
IEC 60947-2 အရွယ်အစား သတ်မှတ်ခြင်းဆိုင်ရာ နည်းလမ်း
NEC ၏ 1.56× မြှောက်ကိန်းနှင့်မတူဘဲ IEC 60947-2 သည် ဒီဇိုင်နာများအား အောက်ပါအချက်များကို ထည့်သွင်းစဉ်းစားရန် လိုအပ်သည်-
- စဉ်ဆက်မပြတ် လျှပ်စစ်စီးကြောင်း (ပုံမှန်အခြေအနေအောက်တွင် လည်ပတ်နေသော လျှပ်စစ်စီးကြောင်း)
- ပတ်ဝန်းကျင် အပူချိန် လျှော့ချခြင်း (ကိုးကားအပူချိန်သည် တပ်ဆင်မှုအပေါ်မူတည်၍ ကွဲပြားသည်)
- အသုံးပြုမှု အမျိုးအစား (AC အတွက် AC-21A, AC-22A, AC-23A; DC အတွက် DC-21A, DC-22A, DC-23A)
- ဝါယာရှော့ဖြစ်ခြင်းကို ဖြတ်တောက်နိုင်စွမ်း (Icu နှင့် Ics အဆင့်သတ်မှတ်ချက်များ)
အခြေခံ IEC အရွယ်အစား သတ်မှတ်ခြင်းဆိုင်ရာ ဖော်မြူလာ:
Breaker Ie ≥ (စဉ်ဆက်မပြတ် လျှပ်စစ်စီးကြောင်း) / (အပူချိန် လျှော့ချခြင်းဆိုင်ရာ အချက်)
IEC ဖြတ်တောက်နိုင်စွမ်း လိုအပ်ချက်များ
IEC 60947-2 သည် အရေးကြီးသော ဖြတ်တောက်နိုင်စွမ်း အဆင့်သတ်မှတ်ချက် နှစ်ခုကို သတ်မှတ်သည်-
Icu (အမြင့်ဆုံး ဝါယာရှော့ဖြစ်ခြင်းကို ဖြတ်တောက်နိုင်စွမ်း):
ဘရိတ်ကာသည် တစ်ကြိမ် ဖြတ်တောက်နိုင်သော အမြင့်ဆုံး ချို့ယွင်းချက် လျှပ်စစ်စီးကြောင်းဖြစ်သည်။ ဤစမ်းသပ်မှုအပြီးတွင် ဘရိတ်ကာသည် ဆက်လက်အသုံးပြုရန် မသင့်တော်ပါ။.
Ics (ဝန်ဆောင်မှု ဝါယာရှော့ဖြစ်ခြင်းကို ဖြတ်တောက်နိုင်စွမ်း):
ဘရိတ်ကာသည် အကြိမ်ပေါင်းများစွာ ဖြတ်တောက်နိုင်ပြီး ဆက်လက်အသုံးပြုနိုင်သော ချို့ယွင်းချက် လျှပ်စစ်စီးကြောင်းအဆင့်ဖြစ်သည်။ ယေဘုယျအားဖြင့် Icu ၏ ရာခိုင်နှုန်း (25%, 50%, 75% သို့မဟုတ် 100%) အဖြစ် ဖော်ပြသည်။.
ယုံကြည်စိတ်ချရသော ကာကွယ်မှုအတွက် ဘရိတ်ကာ၏ Icu အဆင့်သတ်မှတ်ချက်သည် တပ်ဆင်သည့်နေရာ၌ ရရှိနိုင်သော အမြင့်ဆုံး ချို့ယွင်းချက် လျှပ်စစ်စီးကြောင်းထက် ကျော်လွန်ရမည်ဖြစ်ပြီး Ics သည် ချို့ယွင်းချက်ဖြစ်ပွားပြီးနောက် ဆက်လက်လည်ပတ်ရန်အတွက် မျှော်လင့်ထားသော ချို့ယွင်းချက် လျှပ်စစ်စီးကြောင်းထက် ကျော်လွန်ရမည်ဖြစ်သည်။.
နှိုင်းယှဉ်သုံးသပ်ခြင်း- NEC 690 နှင့် IEC 60947-2
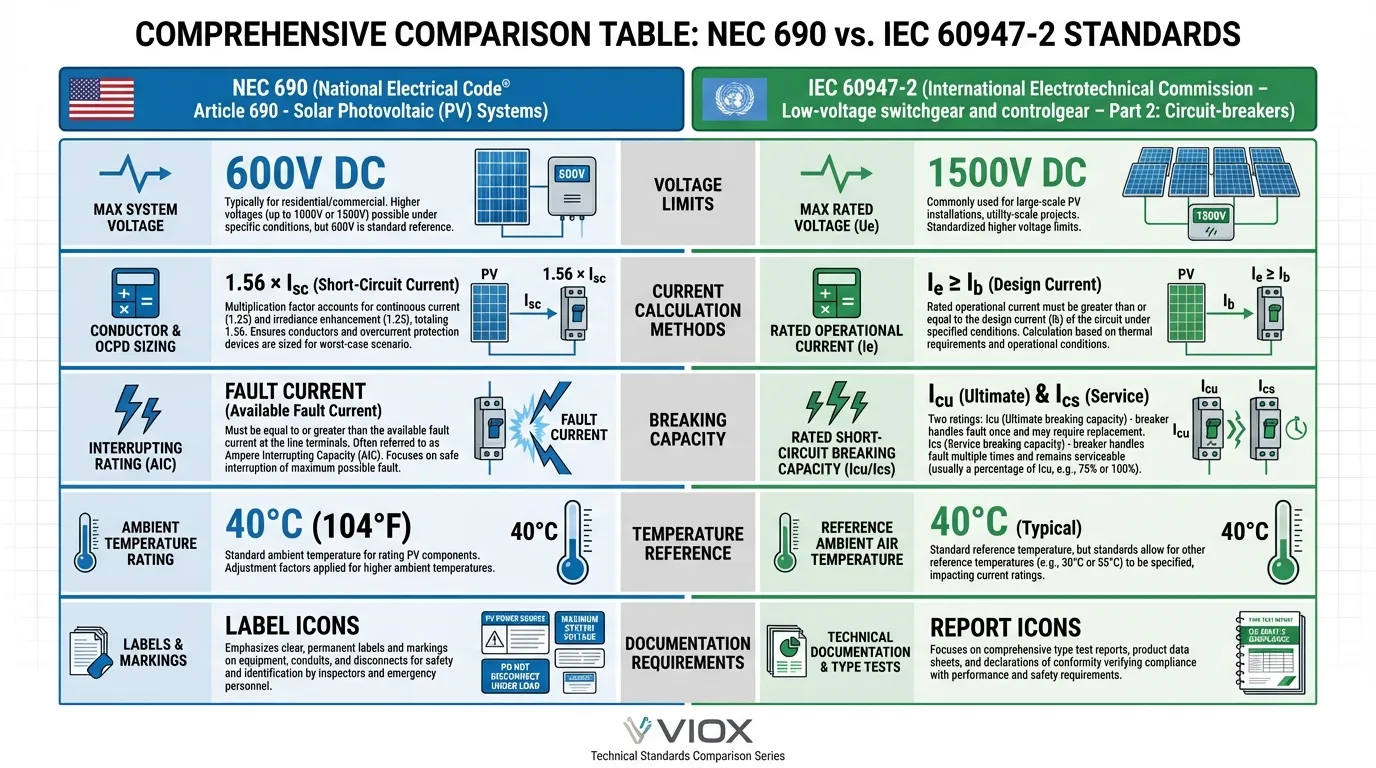
| ဇာတိ | NEC 690 (ဆိုလာ PV) | IEC 60947-2 (Industrial) |
|---|---|---|
| မူလတန်းလျှောက်လွှာ | ဆိုလာ ဓာတ်အားလျှပ်စစ်စနစ်များ (USA) | စက်မှု/စီးပွားဖြစ် ဗို့အားနိမ့်စနစ်များ (နိုင်ငံတကာ) |
| အမြင့်ဆုံး DC ဗို့အား | 600V (လူနေအိမ်), 1,000V (စီးပွားဖြစ်) | 1,500V DC |
| လျှပ်စစ်စီးကြောင်း တွက်ချက်ခြင်း | Isc × 1.56 (ပုံသေ မြှောက်ကိန်း) | စဉ်ဆက်မပြတ် ဝန်အား + လျှော့ချခြင်းအပေါ် အခြေခံ၍ Ie |
| အပူချိန် ကိုးကားချက် | 40°C ပတ်ဝန်းကျင် (NEC 310.15) | 40°C အကာအကွယ်, 25°C လွတ်လပ်သောလေ |
| ေဆးေၾ | ရရှိနိုင်သော ချို့ယွင်းချက် လျှပ်စစ်စီးကြောင်းအပေါ် အခြေခံသည် | Icu (အမြင့်ဆုံး) နှင့် Ics (ဝန်ဆောင်မှု) အဆင့်သတ်မှတ်ချက်များ |
| Continuous Load Factor | 1.56× မြှောက်ကိန်းထဲသို့ 125% ထည့်သွင်းထားသည် | တာဝန်ကျမှုစက်ဝန်းအပေါ် အခြေခံ၍ သီးခြားစီ အသုံးပြုသည် |
| အသုံးချမှု အမျိုးအစားများ | သတ်မှတ်မထားပါ (PV-သီးသန့်) | DC-21A, DC-22A, DC-23A ကို သတ်မှတ်ထားသည် |
| စမ်းသပ်စံနှုန်းများ | UL 489 (USA), UL 1077 (နောက်ဆက်တွဲ) | IEC 60947-2 စမ်းသပ်မှု အစီအစဉ်များ |
| စာတမ်းပြုစုခြင်း။ | NEC 690.53 အရ တံဆိပ်များ | IEC 62446-1 အရ စတင်လည်ပတ်ခြင်း |
| ညှိနှိုင်းဆောင်ရွက်ခြင်း | NEC 240.12 အရ ရွေးချယ်နိုင်မှု | IEC 60947-2 Annex A အရ ခွဲခြားသတ်မှတ်ခြင်း |
လက်တွေ့ အရွယ်အစား သတ်မှတ်ခြင်းဆိုင်ရာ ဥပမာများ- ဘေးချင်းယှဉ် နှိုင်းယှဉ်ခြင်း
ဥပမာ ၁- လူနေအိမ် ဆိုလာ အခင်းအကျင်း
စနစ် ပါရာမီတာများ:
- Module Isc: 9.5A
- အပြိုင်ရှိ ကြိုးများ: 3
- စနစ် ဗို့အား: 400V DC
- တည်နေရာ: Phoenix, AZ (အပူချိန်မြင့်မား)
- တပ်ဆင်ခြင်း: အမိုးပေါ်ရှိ ပြွန်
NEC 690 တွက်ချက်ခြင်း:
- စုစုပေါင်း Isc = 9.5A × 3 = 28.5A
- NEC မြှောက်ကိန်း = 28.5A × 1.56 = 44.46A
- စံ ဘရိတ်ကာ = 50A DC ဘရိတ်ကာ
- ဝါယာကြိုး: 90°C တွင် #8 AWG (50A) အပူချိန် ပြုပြင်မှုနှင့်အတူ
IEC 60947-2 တွက်ချက်ခြင်း:
- စဉ်ဆက်မပြတ် လျှပ်စစ်စီးကြောင်း = 28.5A (Isc ကို ကိုးကားချက်အဖြစ်)
- အပူချိန် လျှော့ချခြင်း (50°C ပတ်ဝန်းကျင်): 0.88 အချက်
- Required Ie = 28.5A / 0.88 = 32.4A
- Selected breaker: 40A MCCB (IEC rated)
- Verify Icu ≥ available fault current
အဓိကကွာခြားချက်- NEC’s conservative 1.56× multiplier results in a larger breaker (50A vs 40A), providing additional safety margin for extreme irradiance conditions common in desert climates.
Example 2: Commercial Battery Storage System
စနစ် ပါရာမီတာများ:
- Battery bank: 500V DC nominal
- အများဆုံးသွင်းလက်ရှိ:၁၀၀A
- Maximum discharge current: 150A
- Fault current available: 8,000A
NEC 690 Approach (if applicable):
For battery circuits, NEC 690 doesn’t directly apply, but NEC 706 (Energy Storage Systems) would govern:
- Continuous current = 150A (higher of charge/discharge)
- Apply 125% factor = 150A × 1.25 = 187.5A
- စံ ဘရိတ်ကာ = 200A DC breaker
IEC 60947-2 Approach:
- Rated operational current (Ie) = 150A
- Select breaker with Ie ≥ 150A
- Verify Icu ≥ 8,000A (8kA)
- Verify Ics ≥ 4,000A (50% of Icu minimum)
- Selected breaker: 160A MCCB with 10kA Icu rating
အဓိကကွာခြားချက်- IEC allows more precise sizing based on actual operational current without the fixed 1.56× multiplier, but requires detailed fault current analysis and breaking capacity verification.
Temperature Derating: Critical Considerations
Both standards require temperature corrections, but methodologies differ:
NEC 310.15 Temperature Correction
NEC provides temperature correction factors in Table 310.15(B)(1):
| ပတ်ဝန်းကျင် အပူချိန် | Correction Factor (90°C conductor) |
|---|---|
| 30°C | 1.04 |
| 40°C | 1.00 |
| 50°C | 0.82 |
| 60°C | 0.58 |
လျှောက်လွှာ Multiply conductor ampacity by correction factor, then verify breaker rating doesn’t exceed corrected ampacity.
IEC 60947-2 Temperature Derating
IEC breakers are rated at specific reference temperatures (typically 40°C for enclosed, 25°C for free air). Manufacturers provide derating curves for different ambient conditions.
Typical IEC Derating:
- 30°C: 1.05× rated current
- 40°C: 1.00× rated current (reference)
- 50°C: 0.86× rated current
- 60°C: 0.71× rated current
For solar installations in hot climates, temperature derating can significantly impact breaker selection. Circuit Breaker Altitude Derating Guide covers additional environmental factors.
Breaking Capacity and Fault Current Analysis
NEC Approach: Available Fault Current
NEC 110.9 requires that “equipment intended to interrupt current at fault levels shall have an interrupting rating sufficient for the nominal circuit voltage and the current that is available at the line terminals of the equipment.”
Calculation Method:
- Determine maximum available fault current from utility/source
- Calculate fault current contribution from solar array
- Sum total available fault current
- Select breaker with interrupting rating ≥ total fault current
Solar PV Fault Current:
Maximum fault current from PV ≈ Isc × 1.25 × number of parallel strings
IEC 60947-2 Approach: Icu and Ics Ratings
IEC requires both ultimate (Icu) and service (Ics) breaking capacity verification:
Icu Selection:
Breaker Icu ≥ Maximum prospective short-circuit current
Ics Selection:
Breaker Ics ≥ Expected fault current for continued operation
- Ics = 100% Icu: Full service capacity
- Ics = 75% Icu: High service capacity
- Ics = 50% Icu: Moderate service capacity
- Ics = 25% Icu: Limited service capacity
For critical installations, selecting breakers with Ics = 100% Icu ensures the breaker remains fully operational after clearing fault currents. Circuit Breaker Ratings ICU ICS ICW ICM provides detailed explanations of these ratings.
ညှိနှိုင်းမှုနှင့် ရွေးချယ်မှု
NEC Selectivity Requirements
NEC 240.12 addresses selective coordination for emergency systems, legally required standby systems, and critical operations power systems. For solar installations:
- အောက်ပိုင်း breaker ခရီးထွက်သည့်အခါ ပင်မ breaker သည် ပိတ်ထားရမည်
- အချိန်-လက်ရှိ ကွေးညွှတ်မှုများကို ခွဲခြမ်းစိတ်ဖြာရမည်
- စီးရီးအဆင့်သတ်မှတ်ထားသော စနစ်များကို သတ်မှတ်ထားသောအခြေအနေများအောက်တွင် ခွင့်ပြုထားသည်
IEC ခွဲခြားဆက်ဆံမှု လိုအပ်ချက်များ
IEC 60947-2 Annex A သည် အသေးစိတ်ခွဲခြားဆက်ဆံမှု (ရွေးချယ်နိုင်မှု) ဇယားများနှင့် တွက်ချက်နည်းများကို ပေးသည်-
စုစုပေါင်း ခွဲခြားဆက်ဆံမှု-
အောက်ပိုင်းကိရိယာမှ ရှင်းလင်းထားသော ချို့ယွင်းချက်များအတွက် အထက်ပိုင်းကိရိယာသည် အလုပ်မလုပ်ပါ။
တစ်စိတ်တစ်ပိုင်း ခွဲခြားဆက်ဆံမှု-
သတ်မှတ်ထားသော လက်ရှိအဆင့် (ခွဲခြားဆက်ဆံမှုကန့်သတ်ချက်) အထိ ခွဲခြားဆက်ဆံမှု
စွမ်းအင် ခွဲခြားဆက်ဆံမှု-
ဖြတ်သန်းခွင့်စွမ်းအင် (I²t) လက္ခဏာများအပေါ် အခြေခံသည်။
အကာအကွယ်အဆင့်များစွာပါရှိသော ကြီးမားသော ဆိုလာတပ်ဆင်မှုများအတွက်၊ သင့်လျော်သော ညှိနှိုင်းမှုသည် အနှောင့်အယှက်ဖြစ်စေသော ခရီးစဉ်ကို တားဆီးပြီး စနစ်ရရှိနိုင်မှုကို ထိန်းသိမ်းပေးသည်။. Breaker ရွေးချယ်နိုင်မှု ညှိနှိုင်းမှု လမ်းညွှန်ချက်ဆိုသည်မှာ အဘယ်နည်း ညှိနှိုင်းမှုမူများကို အသေးစိတ်ရှင်းပြသည်။.
ဆိုလာအသုံးချမှုများအတွက် အထူးထည့်သွင်းစဉ်းစားမှုများ
ဝင်ရိုးစွန်းနှင့် DC Arc ငြိမ်းသတ်ခြင်း
ဆိုလာအသုံးချမှုများအတွက် DC circuit breaker များသည် ထူးခြားသောစိန်ခေါ်မှုများကို ကိုင်တွယ်ဖြေရှင်းရမည်-
Arc ငြိမ်းသတ်ရန် ခက်ခဲခြင်း-
DC arcs များသည် AC ကဲ့သို့ သုညဖြတ်ကျော်တွင် သဘာဝအတိုင်း မငြိမ်းသတ်ပါ။ Breakers များသည် အသုံးပြုသည်-
- သံလိုက်မှုတ်ထုတ်သည့် coils များ
- Deion plates ပါသော Arc chutes များ
- အဆက်အသွယ်ခွဲထွက်ခြင်း တိုးလာခြင်း
ဝင်ရိုးစွန်း ထည့်သွင်းစဉ်းစားမှုများ-
DC breaker အချို့သည် ဝင်ရိုးစွန်းအထိမခံပါ။. Polarity DC Circuit Breaker လမ်းညွှန် သင့်လျော်သော တပ်ဆင်မှု ဦးတည်ချက်ကို လွှမ်းခြုံထားသည်။.
String နှင့် Array-Level ကာကွယ်ရေး
String-Level ကာကွယ်ရေး (NEC 690.9):
- ကြိုးတစ်ချောင်းလျှင် တစ်ဦးချင်း breaker
- တစ်ခုတည်းသောကြိုးကို သီးခြားခွဲထုတ်ခွင့်ပြုသည်။
- အစိတ်အပိုင်းအရေအတွက်နှင့် ကုန်ကျစရိတ် မြင့်မားသည်။
Array-Level ကာကွယ်ရေး-
- အပြိုင်ကြိုးများစွာအတွက် တစ်ခုတည်းသော breaker
- သင့်လျော်သော conductor အရွယ်အစား လိုအပ်သည်။
- ကုန်ကျစရိတ်သက်သာသော်လည်း granular ထိန်းချုပ်မှုနည်းသည်။
Rapid Shutdown Compliance
NEC 690.12 (2017 နှင့် နောက်ပိုင်း) သည် လျင်မြန်စွာပိတ်ခြင်းလုပ်ဆောင်နိုင်စွမ်းကို မဖြစ်မနေလိုအပ်သည်-
- ဗို့အားကို စက္ကန့် 30 အတွင်း ≤ 80V သို့ လျှော့ချပါ။
- DC breaker အချို့သည် လျင်မြန်စွာပိတ်ခြင်းစနစ်များနှင့် ပေါင်းစပ်ထားသည်။
- breaker နေရာချထားမှုနှင့် စနစ်ဒီဇိုင်းကို ထိခိုက်စေသည်။
Rapid Shutdown နှင့် DC Disconnect Safety Guide မတူညီသော လိုက်နာမှုနည်းလမ်းများကို နှိုင်းယှဉ်သည်။.
Conductor အရွယ်အစား ပေါင်းစပ်ခြင်း
သင့်လျော်သော DC circuit breaker အရွယ်အစားသည် conductor ampacity နှင့် ညှိနှိုင်းရမည်-
NEC Conductor အရွယ်အစား
- အနည်းဆုံး ampacity ကို တွက်ချက်ပါ-
Ampacity ≥ Isc × 1.56 - ပြင်ဆင်ချက်အချက်များ လျှောက်ထားပါ-
- အပူချိန်ပြင်ဆင်ချက် (NEC 310.15(B)(1))
- Conduit ဖြည့်ညှိနှိုင်းမှု (NEC 310.15(B)(3)(a))
- breaker ကာကွယ်ရေးကို စစ်ဆေးပါ-
Breaker အဆင့်သတ်မှတ်ချက် ≤ Conductor ampacity (ပြင်ဆင်ပြီးနောက်)
IEC Conductor အရွယ်အစား
- ဒီဇိုင်းလက်ရှိ (Ib) ကို ဆုံးဖြတ်ပါ-
Ib = စဉ်ဆက်မပြတ်လည်ပတ်နေသော လက်ရှိ - breaker အဆင့်သတ်မှတ်ချက် (In) ကို ရွေးချယ်ပါ-
In ≥ Ib - conductor ampacity (Iz) ကို ရွေးချယ်ပါ-
Iz ≥ In - ပြင်ဆင်ချက်အချက်များ လျှောက်ထားပါ-
- ပတ်ဝန်းကျင်အပူချိန် (IEC 60364-5-52)
- အုပ်စုဖွဲ့အချက်
- တပ်ဆင်နည်း
50 Amp Wire အရွယ်အစား ရွေးချယ်မှု လမ်းညွှန် လက်တွေ့ကျသော conductor အရွယ်အစား ဥပမာများကို ပေးသည်။.
အဖြစ်များသော Sizing အမှားများနှင့်၎င်းတို့ကိုရှောင်ရှားရန်နည်းလမ်း
အမှား 1: 125% အချက်ကို နှစ်ဆရေတွက်ခြင်း
မမှန်ကန်သော ချဉ်းကပ်မှု-
- တွက်ချက်ပါ- Isc × 1.56 = 15.6A
- Apply additional 125%: 15.6A × 1.25 = 19.5A ❌
Correct Approach:
- NEC 690.8 already includes continuous load factor
- Use: Isc × 1.56 = 15.6A
- Select next standard size: 20A ✓
အမှား ၂- အပူချိန်လျှော့ချခြင်းကို လျစ်လျူရှုခြင်း
ပြဿနာ-
Selecting #12 AWG (25A at 90°C) for a 20A breaker in 60°C ambient without temperature correction.
Corrected ampacity:
25A × 0.58 (60°C factor) = 14.5A (insufficient for 20A breaker)
ဖြေရှင်းချက်:
Use #10 AWG (35A × 0.58 = 20.3A) ✓
Mistake 3: Inadequate Breaking Capacity
ဇာတ်လမ်း-
Installing a 6kA breaker where available fault current is 8kA
အကျိုးဆက်-
Breaker may fail catastrophically during fault, causing fire hazard
ဖြေရှင်းချက်:
Calculate maximum fault current including all sources, select breaker with Icu ≥ total fault current
Mistake 4: Mixing AC and DC Ratings
Critical Error:
Using AC-rated breaker for DC application
Why It Fails:
- AC breakers rely on zero-crossing for arc extinction
- DC arc sustains indefinitely without proper interruption mechanism
- Can result in breaker failure and fire
ဖြေရှင်းချက်:
Always specify DC-rated breakers for solar PV and battery systems. DC vs AC Circuit Breakers Essential Differences explains the critical distinctions.
Compliance and Documentation Requirements
NEC 690 Documentation
Required Labels (NEC 690.53):
- အများဆုံးစနစ်ဗို့အား
- Maximum circuit current
- Maximum OCPD rating
- Short-circuit current rating
Placard Requirements:
- Location of DC disconnects
- Rapid shutdown button location
- အရေးပေါ် ဆက်သွယ်ရန် အချက်အလက်
IEC Commissioning Documentation
IEC 62446-1 Requirements:
- System design documentation
- Component specifications
- Test results (insulation resistance, polarity, earth continuity)
- I-V curve measurements
- Protective device settings
- As-built drawings
For international projects, maintaining both NEC labels and IEC commissioning reports ensures compliance across jurisdictions.
Selecting the Right Standard for Your Project
Use NEC 690 When:
- Installing in USA, Canada, or NEC-adopting jurisdictions
- Designing residential solar systems
- Working with UL-listed equipment
- Project requires AHJ approval under NEC framework
- Utility interconnection follows IEEE 1547
Use IEC 60947-2 When:
- Installing in Europe, Asia, Middle East, or IEC-adopting regions
- Designing large commercial/industrial systems
- Working with CE-marked equipment
- Project specifications require IEC compliance
- Integrating with IEC 61727 utility interface
Dual Compliance Approach:
For manufacturers serving global markets:
- Design to the more stringent requirement
- Obtain both UL and IEC certifications
- Provide documentation for both standards
- Use conservative sizing that satisfies both frameworks
Many modern DC circuit breakers carry dual ratings (UL 489 and IEC 60947-2), simplifying specification for international projects. တရုတ်နိုင်ငံရှိ ထိပ်တန်း Circuit Breaker ထုတ်လုပ်သူ ၁၀ ဦး lists suppliers offering dual-certified products.
Advanced Topics: Battery Storage and Microgrids
Battery Circuit Protection
Battery energy storage systems present unique challenges:
အားသွင်း/ထုတ်လွှတ်မှု မညီမျှခြင်း-
- အားသွင်းလျှပ်စီးကြောင်း- ပုံမှန်အားဖြင့် inverter/charger မှ ကန့်သတ်ထားသည်။
- ထုတ်လွှတ်လျှပ်စီးကြောင်း- သိသိသာသာ ပိုမိုမြင့်မားနိုင်သည်။
- အားသွင်းခြင်း သို့မဟုတ် ထုတ်လွှတ်ခြင်း၏ အမြင့်ဆုံးအတွက် breaker အရွယ်အစားကို သတ်မှတ်ပါ။
Inrush Current-
- Capacitive load များသည် မြင့်မားသော inrush ကို ဖန်တီးသည်။
- D-curve breaker များ သို့မဟုတ် soft-start circuit များ လိုအပ်နိုင်သည်။
Fault Current Contribution-
- ဘက်ထရီများသည် အလွန်မြင့်မားသော fault current များကို ထုတ်ပေးနိုင်သည်။
- ဂရုတစိုက် breaking capacity analysis လိုအပ်သည်။
BESS High Breaking Capacity တွင် Standard DC Breaker များ အဘယ်ကြောင့် ကျရှုံးရသနည်း။ ဘက်ထရီ-သီးသန့် ကာကွယ်ရေးဆိုင်ရာ စိန်ခေါ်မှုများကို ဖြေရှင်းပေးသည်။.
DC Microgrid Applications
Multi-source DC စနစ်များသည် ခေတ်မီသော ကာကွယ်ရေး ညှိနှိုင်းမှုကို လိုအပ်သည်-
Source ညှိနှိုင်းမှု:
- Solar PV contribution
- Battery contribution
- Utility-tied rectifier contribution
- Generator contribution
Bidirectional Power Flow-
- Breaker များသည် လျှပ်စီးကြောင်းကို နှစ်ဖက်စလုံးတွင် ဖြတ်တောက်နိုင်ရမည်။
- non-symmetric breaker များအတွက် Polarity ထည့်သွင်းစဉ်းစားမှုများ
Grounding Schemes-
- Solidly grounded systems
- High-resistance grounded systems
- Ungrounded systems (IEC အရ IT systems)
DC Circuit Protection အတွက် အနာဂတ်ရေစီးကြောင်းများ
Solid-State Circuit Breakers
ပေါ်ထွက်လာသော solid-state နည်းပညာသည်-
- ပိုမိုမြန်ဆန်သော ဖြတ်တောက်ချိန်များ (microseconds vs. milliseconds)
- စက်ပိုင်းဆိုင်ရာ ဝတ်ဆင်မှု မရှိပါ။
- တိကျသော current limiting
- စမတ်ဂရစ်စနစ်များနှင့် ပေါင်းစပ်ခြင်း။
Solid State Circuit Breaker SSCB Nvidia Tesla Switch ဤပေါ်ထွက်လာသော နည်းပညာကို စူးစမ်းလေ့လာသည်။.
Smart Breakers နှင့် IoT Integration
နောက်မျိုးဆက် DC breaker များတွင်-
- အချိန်နှင့်တပြေးညီ လက်ရှိစောင့်ကြည့်ခြင်း။
- ကြိုတင်ပြင်ဆင်ထိန်းသိမ်းမှု သတိပေးချက်များ
- Remote trip/close capability
- အဆောက်အဦစီမံခန့်ခွဲမှုစနစ်များနှင့်ပေါင်းစပ်
Standards Harmonization
NEC နှင့် IEC စံနှုန်းများကို ညှိရန် ကြိုးပမ်းမှုများ ဆက်လက်လုပ်ဆောင်နေသည်-
- IEC/UL 61730 သည် solar module safety ကို ညှိနှိုင်းပေးသည်။
- DC protection ကွာဟချက်များကို ဖြေရှင်းရန် ပူးတွဲလုပ်ငန်းအဖွဲ့များ
- စမ်းသပ်မှုရလဒ်များကို အပြန်အလှန်အသိအမှတ်ပြုမှု တိုးမြှင့်ခြင်း
အတိုချုပ် မေးလေ့ရှိသောမေးခွန်းများ ကဏ္ဍ
မေး- NEC နှင့် IEC projects နှစ်ခုလုံးအတွက် တူညီသော breaker အရွယ်အစား သတ်မှတ်နည်းကို သုံးနိုင်ပါသလား။
ဖြေ- မရပါ။ NEC 690 သည် solar PV circuit များအတွက် fixed 1.56× multiplier လိုအပ်ပြီး IEC 60947-2 သည် သီးခြား derating factors ပါသော continuous load current ကို အသုံးပြုသည်။ သင့်တရားစီရင်ပိုင်ခွင့်ကို အုပ်ချုပ်သည့် စံနှုန်းကို အမြဲတမ်း အသုံးပြုပါ။ နိုင်ငံတကာ projects များအတွက် နည်းလမ်းနှစ်ခုလုံးကို အသုံးပြု၍ တွက်ချက်ပြီး ပိုမိုတင်းကျပ်သော ရလဒ်ကို ရွေးချယ်ပါ။.
မေး- IEC breaker များတွင် Icu နှင့် Ics ratings များအကြား ကွာခြားချက်ကဘာလဲ။
ဖြေ- Icu (ultimate breaking capacity) သည် breaker တစ်ကြိမ် ဖြတ်တောက်နိုင်သည့် အမြင့်ဆုံး fault current ဖြစ်ပြီး Ics (service breaking capacity) သည် ၎င်းသည် အကြိမ်ပေါင်းများစွာ ဖြတ်တောက်နိုင်ပြီး လည်ပတ်နိုင်သည့် fault level ဖြစ်သည်။ Ics သည် ပုံမှန်အားဖြင့် Icu ၏ 25-100% ဖြစ်သည်။ အရေးကြီးသော applications များအတွက် Ics = 100% Icu ပါသော breaker များကို ရွေးချယ်ပါ။.
မေး- NEC အောက်တွင် battery circuit များသို့ 1.56× multiplier ကို အသုံးပြုရန် လိုအပ်ပါသလား။
ဖြေ- မလိုအပ်ပါ။ NEC 690.8 multiplier သည် PV source နှင့် output circuit များအတွက် သီးခြားသက်ရောက်ပါသည်။ Battery circuit များသည် NEC 706 (Energy Storage Systems) အောက်တွင် ကျရောက်ပြီး continuous load များအတွက် 125% (1.25×) လိုအပ်သော်လည်း နောက်ထပ် irradiance factor မလိုအပ်ပါ။ သင့်သီးခြား application အတွက် သက်ဆိုင်ရာ code article ကို အမြဲစစ်ဆေးပါ။.
မေး- voltage နှင့် current ratings များ လုံလောက်ပါက DC applications များအတွက် AC-rated breaker ကို သုံးနိုင်ပါသလား။
ဖြေ- ဘယ်တော့မှ မသုံးပါနဲ့။ AC breaker များသည် arcs များကို ငြိမ်းသတ်ရန် alternating current ၏ သဘာဝ zero-crossing ကို အားကိုးသည်။ DC current သည် constant polarity ကို ထိန်းသိမ်းထားပြီး အထူး arc interruption mechanisms များ လိုအပ်သည်။ DC applications များအတွက် AC breaker များကို အသုံးပြုခြင်းသည် ဆိုးရွားသော ချို့ယွင်းမှုနှင့် မီးဘေးအန္တရာယ်များ ဖြစ်ပေါ်စေနိုင်သည်။ သင့်လျော်သော voltage ratings များပါသော DC-rated breaker များကို အမြဲသတ်မှတ်ပါ။.
မေး- breaker ရွေးချယ်မှုအတွက် ရရှိနိုင်သော fault current ကို မည်သို့ဆုံးဖြတ်မည်နည်း။
ဖြေ- grid-tied systems များအတွက် interconnection ၏အချက်တွင် utility ၏ရရှိနိုင်သော fault current ကိုရယူပါ။ သင်၏ PV array မှ fault current contribution ကိုထည့်ပါ (ခန့်မှန်းခြေအားဖြင့် Isc × 1.25 × parallel strings အရေအတွက်)။ Battery systems များအတွက် အမြင့်ဆုံး short-circuit current အတွက် ထုတ်လုပ်သူ၏ data ကို တိုင်ပင်ပါ။ စုစုပေါင်းတွက်ချက်ထားသော fault current ထက်ကျော်လွန်သော Icu (IEC) သို့မဟုတ် interrupting rating (NEC) ပါသော breaker ကို ရွေးချယ်ပါ။.
မေး- solar rooftop installations များတွင် conductor derating အတွက် မည်သည့်အပူချိန်ကို သုံးသင့်သနည်း။
ဖြေ- rooftops များပေါ်တွင် conduit-mounted conductors များအတွက် ပတ်ဝန်းကျင်အပူချိန်သည် နေရောင်ခြည် တိုက်ရိုက်ထိတွေ့ပါက 60-70°C ထက် ကျော်လွန်နိုင်သည်။ ဒေသဆိုင်ရာ ရာသီဥတု data နှင့် NEC 310.15(B)(3)(c) ကို rooftop temperature adders များအတွက် အသုံးပြုပါ (ပုံမှန်အားဖြင့် ပတ်ဝန်းကျင်ထက် +33°C)။ Conservative designs များသည် သဲကန္တာရ ရာသီဥတုများ သို့မဟုတ် လေဝင်လေထွက် မကောင်းသော အမည်းရောင် ခေါင်မိုးများအတွက် 70°C ပတ်ဝန်းကျင်ကို အသုံးပြုသည်။.
နိဂုံး- လုံခြုံပြီး လိုက်နာမှုရှိသော DC Protection ကို သေချာစေခြင်း
သင့်လျော်သော DC circuit breaker အရွယ်အစား သတ်မှတ်ခြင်းသည် လုံခြုံပြီး ယုံကြည်စိတ်ချရသော solar PV နှင့် energy storage installations များအတွက် အခြေခံဖြစ်သည်။ NEC 690 သို့မဟုတ် IEC 60947-2 စံနှုန်းများအောက်တွင် လုပ်ဆောင်သည်ဖြစ်စေ တွက်ချက်နည်းစနစ်များ၊ safety factors များနှင့် breaking capacity လိုအပ်ချက်များကို နားလည်ခြင်းသည် သင့်စနစ်များသည် စက်ပစ္စည်းများနှင့် ဝန်ထမ်းများကို ကာကွယ်ပေးကြောင်း သေချာစေသည်။.
မှတ်သားထားရမည့် အဓိကမူများ-
- မှန်ကန်သော စံနှုန်းကို အသုံးပြုပါ။ သင့်တရားစီရင်ပိုင်ခွင့်နှင့် application အတွက်
- အပူချိန် derating ကို ဘယ်တော့မှ မကျော်ပါနဲ့။ – ၎င်းသည် conductor protection အတွက် အရေးကြီးသည်။
- Breaking capacity ကို စစ်ဆေးပါ ရရှိနိုင်သော အမြင့်ဆုံး fault current မှ
- DC-rated breaker များကို သုံးပါ။ – DC applications များအတွက် AC breaker များကို ဘယ်တော့မှ အစားမထိုးပါနဲ့။
- စေ့စေ့စပ်စပ် မှတ်တမ်းတင်ပါ။ – သင့်လျော်သော labeling နှင့် commissioning records များသည် မရှိမဖြစ်လိုအပ်သည်။
အရင်းအမြစ်များစွာ၊ battery storage သို့မဟုတ် နိုင်ငံတကာ လိုက်နာမှုလိုအပ်ချက်များ ပါဝင်သော ရှုပ်ထွေးသော installations များအတွက် အတွေ့အကြုံရှိသော လျှပ်စစ်အင်ဂျင်နီယာများနှင့် တိုင်ပင်ခြင်းနှင့် နာမည်ကောင်းရှိသော ထုတ်လုပ်သူများထံမှ စက်ပစ္စည်းများကို အသုံးပြုခြင်းသည် သင့်ကာကွယ်ရေးစနစ်များသည် လိုအပ်သည့်အခါ ဒီဇိုင်းထုတ်ထားသည့်အတိုင်း လုပ်ဆောင်ကြောင်း သေချာစေသည်။.
VIOX Electric သည် NEC နှင့် IEC စံနှုန်းများနှင့် ကိုက်ညီသော DC circuit breaker များ၏ ကျယ်ပြန့်သော အကွာအဝေးကို ပေးဆောင်ထားပြီး သင့်လျော်သော application အတွက် တင်းကျပ်သော စမ်းသပ်မှုများနှင့် နည်းပညာဆိုင်ရာ ပံ့ပိုးမှုများဖြင့် ကျောထောက်နောက်ခံပြုထားသည်။ သင်သည် လူနေအိမ်သုံး solar arrays သို့မဟုတ် ကြီးမားသော battery storage systems များကို ဒီဇိုင်းဆွဲသည်ဖြစ်စေ သင့်လျော်သော circuit protection သည် တိကျသော အရွယ်အစား တွက်ချက်မှုများနှင့် အရည်အသွေးမြင့် အစိတ်အပိုင်းများဖြင့် စတင်သည်။.