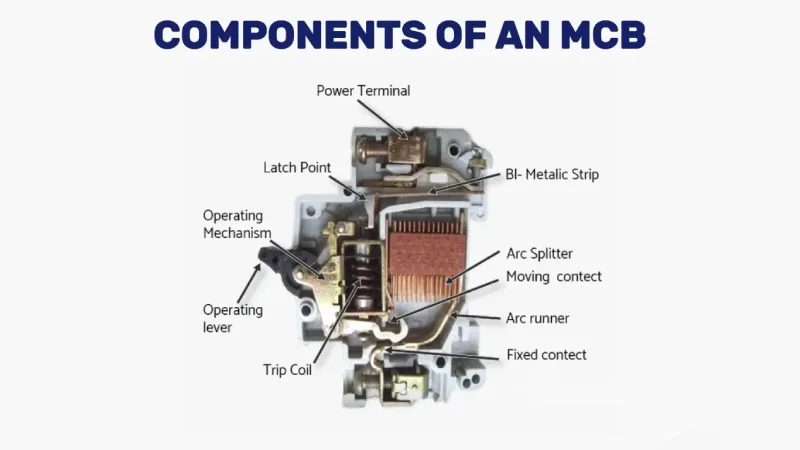
Pemutus Litar Miniatur (MCB) ialah peranti keselamatan elektrik yang dikendalikan secara automatik yang direka untuk melindungi litar elektrik daripada kerosakan yang disebabkan oleh arus berlebihan daripada beban lampau atau litar pintas. Tidak seperti fius tradisional yang perlu diganti selepas pengaktifan, MCB boleh ditetapkan semula dan digunakan semula, menjadikannya pilihan utama untuk pemasangan elektrik kediaman, komersial dan perindustrian moden.
Memahami MCB adalah penting untuk keselamatan elektrik, pematuhan kod dan membuat keputusan termaklum tentang perlindungan sistem elektrik anda. Panduan komprehensif ini merangkumi semua yang anda perlu tahu tentang MCB, daripada operasi asas hingga kriteria pemilihan profesional.
Apakah Yang Membezakan MCB Daripada Peranti Perlindungan Litar Lain?
CMB lawan. Fuse lawan RCD: Perbezaan Utama
| Ciri | CMB | Fuse | RCD/GFCI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Jenis Perlindungan | Lebihan arus (beban lampau + litar pintas) | Lebihan arus sahaja | Kebocoran bumi/kegagalan bumi |
| Kaedah Tetapkan Semula | Tetapan semula suis manual | Gantikan wayar fius/kartrij | Butang tetapan semula manual |
| Masa Tindak Balas | Serta-merta untuk litar pintas | Berbeza mengikut jenis fius | 25-40 milisaat |
| Kebolehgunaan semula | Tetapan semula tanpa had | Penggunaan tunggal sahaja | Tetapan semula tanpa had |
| Pemasangan | Snap-in ke panel | Skru masuk atau kartrij | Berwayar secara bersiri |
| kos | Permulaan lebih tinggi, jangka panjang lebih rendah | Permulaan lebih rendah, penggantian lebih tinggi | Kos permulaan tertinggi |
| Ketepatan | Ciri-ciri perjalanan yang tepat | Kurang tepat | Sangat sensitif |
Mengapa MCB Lebih Unggul untuk Aplikasi Moden
Ciri Keselamatan yang Dipertingkatkan:
- Ciri-ciri perjalanan yang tepat menghalang perjalanan gangguan
- Petunjuk visual keadaan tersandung
- Teknologi pelindapkejutan arka untuk gangguan yang selamat
- Operasi bebas suhu
Kelebihan ekonomi:
- Tiada kos penggantian selepas pengaktifan
- Mengurangkan masa henti melalui cepat set semula
- Keperluan penyelenggaraan yang lebih rendah
- Jangka hayat yang panjang (biasanya 20+ tahun)
Petua Pakar: Walaupun MCB berharga lebih tinggi pada mulanya daripada fius, ia biasanya membayar sendiri dalam tempoh 2-3 pengaktifan melalui penghapusan kos penggantian dan pengurangan masa henti.
Bagaimanakah Pemutus Litar Miniatur Berfungsi?
Prinsip Operasi
MCB beroperasi pada dua mekanisme perlindungan utama:
- **热保护(过载)**
- Jalur dwilogam memanas semasa arus lampau berterusan
- Jalur membengkok dan melepaskan mekanisme perjalanan
- Menyediakan ciri-ciri masa songsang (arus lebih tinggi = perjalanan lebih cepat)
- Perlindungan Magnetik (Litar Pintas)
- Gegelung elektromagnet mencipta medan magnet semasa arus kerosakan tinggi
- Daya magnet serta-merta melepaskan mekanisme perjalanan
- Menyediakan perlindungan serta-merta untuk litar pintas
Ciri-ciri Perjalanan Dijelaskan
| Tahap Semasa | Masa Perjalanan | Kaedah Perlindungan |
|---|---|---|
| 100-113% daripada penarafan | Tiada perjalanan (toleransi) | tiada |
| 113-145% daripada penarafan | 1+ jam | terma |
| 145-300% daripada penarafan | 1-60 minit | terma |
| 300%+ daripada penarafan | serta merta | Magnetik |
Amaran Keselamatan: Jangan sekali-kali cuba mengubah suai atau memintas ciri-ciri perjalanan MCB. Ini boleh mengakibatkan bahaya kebakaran, kerosakan peralatan dan pelanggaran kod.
Jenis MCB dan Aplikasinya
Jenis MCB mengikut Ciri-ciri Perjalanan
MCB Jenis B (3-5 kali arus berkadar)
- Terbaik untuk: Litar kediaman, lampu, outlet umum
- Julat perjalanan: 3-5 × In (arus berkadar)
- Aplikasi: Rumah, pejabat, komersial ringan
- Pematuhan kod: Memenuhi NEC Keperluan Artikel 240
MCB Jenis C (5-10 kali arus terperingkat)
- Terbaik untuk: Litar motor, transformer, lampu pendaflour
- Julat perjalanan: 5-10 × In
- Aplikasi: Peralatan HVAC, jentera perindustrian
- Ciri khas: Mengendalikan arus permulaan motor
MCB Jenis D (10-20 kali arus terperingkat)
- Terbaik untuk: Peralatan perindustrian berat, mesin kimpalan
- Julat perjalanan: 10-20 × In
- Aplikasi: Motor besar, transformer, proses perindustrian
- Keperluan: Biasanya memerlukan penilaian kejuruteraan
Penarafan MCB dan Kapasiti Arus
| Penilaian Semasa (A) | Aplikasi Biasa | Saiz Wayar (AWG) | Jenis Panel |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6-10A | Litar lampu | 14-12 | Kediaman |
| 15-20A | Outlet umum, perkakas kecil | 12-10 | Kediaman/Komersial |
| 25-30A | Perkakas besar, HVAC | 10-8 | Kediaman/Komersial |
| 40-63A | Sub-panel, peralatan besar | 8-4 | Komersial/Perindustrian |
| 80-100A | Suapan utama, beban besar | 4-2/0 | Perindustrian |
Kriteria Pemilihan MCB: Cara Memilih MCB yang Betul
Proses Pemilihan Langkah demi Langkah
Langkah 1: Tentukan Keperluan Beban
- Kira jumlah beban litar (watt ÷ voltan = ampere)
- Tambah margin keselamatan 25% untuk beban berterusan
- Pertimbangkan keperluan pengembangan masa hadapan
- Semak ampacity wayar maksimum
Langkah 2: Pilih Jenis yang Sesuai
- Jenis B: Kebanyakan aplikasi kediaman dan komersial ringan
- Jenis C: Beban motor dan peralatan induktif
- Jenis D: Aplikasi perindustrian berat sahaja
Langkah 3: Sahkan Pematuhan Kod
- Pastikan penarafan sepadan dengan ampacity wayar (NEC Jadual 310.15(B)(16))
- Sahkan AFCI/GFCI keperluan untuk lokasi tertentu
- Semak pindaan dan keperluan tempatan
Langkah 4: Pertimbangkan Ciri Khas
- Keupayaan Pemutus Litar Arus Kerosakan Arka (AFCI)
- Perlindungan Pemutus Litar Kerosakan Tanah (GFCI)
- Keupayaan pintar/bersambung untuk pemantauan
Kriteria Pemilihan Profesional
Pertimbangan Keselamatan:
- Jangan sesekali membesarkan penarafan MCB melebihi kapasiti wayar
- Pertimbangkan penurunan suhu ambien
- Nilaikan arus kerosakan yang tersedia di titik pemasangan
- Pastikan penyelarasan yang betul dengan perlindungan huluan
Penunjuk Kualiti:
- Penyenaraian UL 489 untuk Amerika Utara
- IEC 60898 pematuhan untuk piawaian antarabangsa
- Pengeluar reputasi dan terma jaminan
- Kapasiti pemutusan yang mencukupi untuk pemasangan
Petua Pakar: Sentiasa rujuk kod elektrik tempatan dan pertimbangkan untuk mengupah juruelektrik berlesen untuk pemilihan MCB dalam aplikasi kediaman komersial atau kompleks.
Garis Panduan Pemasangan dan Penyelenggaraan MCB
Keperluan Pemasangan
Senarai Semak Pra-Pemasangan:
- [ ] Sahkan kuasa DIMATIKAN dan dikunci
- [ ] Sahkan keserasian MCB dengan pengeluar panel
- [ ] Semak kelegaan yang mencukupi mengikut NEC 110.26
- [ ] Pastikan pembumian dan ikatan yang betul
- [ ] Sahkan sambungan wayar ketat dan selamat
Langkah Pemasangan:
- Matikan kuasa utama di panel servis
- Tanggalkan penutup panel mengikut prosedur keselamatan
- Masukkan MCB ke dalam slot yang sesuai (reka bentuk snap-in)
- Sambungkan wayar litar ke terminal MCB (wayar panas sahaja)
- Sahkan sambungan selamat dengan ujian tarikan lembut
- Labelkan litar dengan jelas dan kekal
- Operasi ujian sebelum menghidupkan litar
Penyelenggaraan dan Pengujian
Pemeriksaan Visual Bulanan:
- Periksa tanda-tanda terlalu panas (perubahan warna, bau terbakar)
- Sahkan semua label boleh dibaca dan tepat
- Cari sambungan longgar atau kakisan
- Pastikan akses panel jelas dan tidak terhalang
Prosedur Pengujian Tahunan:
- Matikan litar pada MCB
- Uji operasi dengan menekan butang ujian (jika dilengkapi)
- Trip dan set semula MCB secara manual
- Periksa operasi lancar dan penglibatan positif
- Sahkan fungsi litar selepas set semula
Amaran Keselamatan: Jika MCB trip berulang kali, jangan teruskan menetapkannya semula. Ini menunjukkan masalah elektrik yang serius yang memerlukan perhatian profesional segera.
Penyelesaian Masalah MCB Biasa
MCB Sentiasa Trip
Kemungkinan Punca dan Penyelesaian:
| Masalah | Kemungkinan Punca | Penyelesaian |
|---|---|---|
| Trip serta-merta pada set semula | Litar pintas | Hubungi juruelektrik dengan segera |
| Trip selepas beberapa minit | Keadaan beban lampau | Kurangkan beban litar |
| Trip rawak | Sambungan longgar | Ketatkan semua sambungan |
| Trip semasa permulaan motor | Jenis MCB yang salah | Naik taraf kepada MCB Jenis C |
MCB Tidak Boleh Diset Semula
Langkah Penyelesaian Masalah:
- Pastikan MCB dimatikan sepenuhnya sebelum mencuba set semula
- Periksa kerosakan yang boleh dilihat pada perumah MCB
- Sahkan tiada wayar longgar dalam panel
- Uji dengan MCB yang baik jika ada
- Gantikan MCB jika disyaki kegagalan mekanikal
Penyelesaian Trip Mengganggu
Pembaikan Biasa:
- Lampu pendaflour: Gunakan MCB Jenis C dan bukannya Jenis B
- Litar motor: Sahkan kaedah permulaan dan jenis MCB yang betul
- Beban elektronik: Pertimbangkan MCB khusus untuk beban bukan linear
- Pelbagai beban kecil: Semak jumlah pengiraan ampere litar
Keselamatan dan Pematuhan Kod
Keperluan Kod Elektrik Kebangsaan (NEC).
Artikel NEC Utama untuk MCB:
- Perkara 240: Keperluan Perlindungan Arus Lebih
- Artikel 210: Keperluan Litar Cabang
- Perkara 408: Keperluan Papan Suis dan Papan Panel
- Perkara 110: Keperluan am untuk pemasangan elektrik
Perkara Pematuhan Kritikal:
- Penarafan MCB tidak boleh melebihi ampacity wayar
- Perlindungan AFCI diperlukan di kebanyakan kawasan kediaman
- Perlindungan GFCI diperlukan di lokasi basah/lembap
- Pelabelan dan pengenalan yang betul adalah wajib
Amalan Terbaik Keselamatan
Perkara yang Perlu Dilakukan:
- Sentiasa gunakan prosedur kunci keluar/tag keluar
- Uji MCB setiap tahun atau selepas sebarang kerja elektrik
- Pastikan panel elektrik bersih dan mudah diakses
- Gunakan hanya aksesori yang diluluskan pengeluar
- Kekalkan kelegaan yang mencukupi di sekeliling panel
Perkara yang Tidak Boleh Dilakukan:
- Jangan sekali-kali menggunakan MCB sebagai suis untuk operasi rutin
- Jangan abaikan keadaan trip berulang
- Jangan sekali-kali mengubah suai atau mengganggu mekanisme MCB
- Jangan gunakan jenis MCB yang salah untuk aplikasi
- Jangan sekali-kali memasang MCB melebihi kapasiti pemutusnya
Syor Profesional: Untuk sebarang kerja elektrikal yang melebihi penggantian MCB yang mudah, rujuk kepada juruelektrik berlesen untuk memastikan pematuhan kod dan keselamatan.
Panduan Rujukan Pantas
Carta Pantas Pemilihan MCB
| Permohonan | Jenis MCB | Penilaian Biasa | Keperluan Khas |
|---|---|---|---|
| Litar lampu | Jenis B | 15-20A | AFCI di bilik tidur/ruang tamu |
| Outlet am | Jenis B | 15-20A | GFCI di lokasi basah |
| Perkakas dapur | Jenis B | 20A | GFCI untuk outlet atas meja |
| peralatan HVAC | Jenis C | Setiap peralatan | Saiz mengikut spesifikasi pengeluar |
| Motor (am) | Jenis C | FLA motor 125% | Pertimbangkan kaedah permulaan motor |
| Kimpalan/perindustrian | Jenis D | Setiap kiraan beban | Penilaian kejuruteraan diperlukan |
Maklumat Hubungan Kecemasan
Bila Perlu Memanggil Juruelektrik:
- MCB tersandung serta-merta selepas ditetapkan semula
- Bau terbakar atau kerosakan yang boleh dilihat
- Pelbagai MCB tersandung serentak
- Pemasangan litar baharu
- Peningkatan atau pengubahsuaian panel
Sering Bertanya Soalan-Soalan
Apakah perbezaan antara pemutus litar dan MCB?
MCB ialah jenis pemutus litar tertentu yang direka untuk kadar arus yang lebih rendah (biasanya sehingga 100A) dalam aplikasi kediaman dan komersial ringan. Semua MCB ialah pemutus litar, tetapi bukan semua pemutus litar ialah MCB.
Berapa lama MCB biasanya bertahan?
MCB berkualiti biasanya bertahan 20-30 tahun dengan penyelenggaraan yang betul. Walau bagaimanapun, ia harus diuji setiap tahun dan diganti jika ia menunjukkan tanda-tanda haus, gagal ujian, atau telah tertakluk kepada pelbagai keadaan kerosakan.
Bolehkah saya menggantikan fius dengan MCB?
Ya, tetapi ia memerlukan pengubahsuaian atau penggantian panel. MCB dan fius mempunyai sistem pemasangan yang berbeza, jadi anda biasanya memerlukan panel baharu yang direka untuk MCB. Kerja ini harus dilakukan oleh juruelektrik berlesen.
Mengapa MCB saya tersandung apabila saya menghidupkan peralatan tertentu?
Ini biasanya menunjukkan sama ada litar yang terlebih beban atau peralatan dengan arus permulaan yang tinggi (seperti motor). Penyelesaiannya mungkin menaik taraf kepada MCB Jenis C, menggunakan litar khusus, atau menservis peralatan tersebut.
Adakah selamat untuk menetapkan semula MCB yang tersandung?
Ya, jika ia kekal ditetapkan semula dan tidak tersandung lagi serta-merta. Walau bagaimanapun, jika MCB tersandung berulang kali, jangan terus menetapkannya semula – ini menunjukkan masalah serius yang memerlukan perhatian profesional.
Apakah perbezaan antara jenis MCB B, C dan D?
Perbezaannya ialah dalam ciri-ciri tersandung magnetiknya: Jenis B tersandung pada 3-5 kali arus berkadar, Jenis C pada 5-10 kali, dan Jenis D pada 10-20 kali. Ini menentukan berapa banyak arus lebih sementara yang boleh dikendalikannya sebelum tersandung.
Adakah MCB melindungi daripada kejutan elektrik?
Tidak, MCB standard hanya melindungi daripada arus lebih. Untuk perlindungan kejutan, anda memerlukan perlindungan GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter) atau RCD (Residual Current Device), yang boleh digabungkan dengan MCB dalam beberapa produk.
Bagaimanakah saya tahu saiz MCB yang saya perlukan?
Saiz MCB harus sepadan dengan ampacity wayar litar dan keperluan beban. Untuk litar 15A dengan wayar 14 AWG, gunakan MCB 15A. Jangan sekali-kali menggunakan MCB yang lebih besar daripada yang boleh dikendalikan oleh wayar dengan selamat.
Perundingan Pakar Tersedia: Untuk projek elektrikal yang kompleks, peningkatan panel, atau kebimbangan keselamatan, sentiasa berunding dengan juruelektrik berlesen yang boleh memastikan pemasangan yang betul, pematuhan kod dan keselamatan optimum untuk aplikasi khusus anda.
Berkaitan
Panduan Lengkap Simbol Pemutus Litar