ក ធ្នូនៅក្នុង a សៀគ្វីល្មើស គឺជាការបញ្ចេញចរន្តអគ្គិសនីដែលមានពន្លឺ—ជាបណ្តាញផ្លាស្មាដែលឡើងកម្តៅដល់ 20,000°C (36,000°F)—ដែលបង្កើតឡើងរវាងទំនាក់ទំនងដាច់ពីគ្នានៅពេលដែលឧបករណ៍បំបែកចរន្តកាត់ផ្តាច់ចរន្តនៅក្រោមបន្ទុក។ ធ្នូនេះតំណាងឱ្យបាតុភូតដ៏ខ្លាំងក្លា និងប្រើប្រាស់ថាមពលខ្លាំងបំផុតមួយនៅក្នុងវិស្វកម្មអគ្គិសនី ដែលមានសមត្ថភាពបំផ្លាញទំនាក់ទំនង បង្កជាអគ្គិភ័យ និងបណ្តាលឱ្យបរាជ័យឧបករណ៍ធ្ងន់ធ្ងរ ប្រសិនបើមិនបានគ្រប់គ្រងត្រឹមត្រូវតាមរយៈឯកទេស ទំនាក់ទំនងធ្នូ និងប្រព័ន្ធពន្លត់ធ្នូ។.
នៅ VIOX Electric ក្រុមវិស្វកររបស់យើងរចនា និងសាកល្បងឧបករណ៍បំបែកសៀគ្វីជារៀងរាល់ថ្ងៃ ដោយបានឃើញផ្ទាល់ភ្នែកពីរបៀបដែលធ្នូមានឥរិយាបថឆ្លងកាត់ប្រភេទឧបករណ៍បំបែកផ្សេងៗគ្នា—ពីឧបករណ៍បំបែកសៀគ្វីខ្នាតតូចសម្រាប់លំនៅដ្ឋាន (MCBs) ទៅឧស្សាហកម្ម ឧបករណ៍បំបែកសៀគ្វីករណីផ្សិត (MCCBs) និង ឧបករណ៍បំបែកសៀគ្វីខ្យល់ដែលមានសមត្ថភាពខ្ពស់ (ACBs). ការយល់ដឹងអំពីការបង្កើតធ្នូ តួនាទីសំខាន់នៃទំនាក់ទំនងធ្នូក្នុងការការពារទំនាក់ទំនងចម្បង និងរូបវិទ្យាដែលគ្រប់គ្រងការពន្លត់ធ្នូ គឺមានសារៈសំខាន់សម្រាប់វិស្វករអគ្គិសនី អ្នកគ្រប់គ្រងគ្រឿងបរិក្ខារ និងអ្នកដែលទទួលខុសត្រូវក្នុងការបញ្ជាក់ ឬថែទាំឧបករណ៍ការពារសៀគ្វី។.
មគ្គុទ្ទេសក៍ដ៏ទូលំទូលាយនេះពន្យល់ពីបាតុភូតធ្នូពីទស្សនៈនៃការផលិតរបស់ VIOX ដោយគ្របដណ្តប់លើរូបវិទ្យាធ្នូ (ចំណុច cathode បាតុភូត anode ឌីណាមិកផ្លាស្មា) របៀបដែលទំនាក់ទំនងធ្នូធ្វើការលះបង់ខ្លួនឯងដើម្បីការពារទំនាក់ទំនងសំខាន់ៗ លក្ខណៈវ៉ុលធ្នូ វិធីសាស្ត្រពន្លត់ឆ្លងកាត់ប្រភេទឧបករណ៍បំបែក និងលក្ខណៈវិនិច្ឆ័យនៃការជ្រើសរើសជាក់ស្តែងសម្រាប់ការការពារកំហុសធ្នូ។.
តើ Arc នៅក្នុង Circuit Breaker គឺជាអ្វី?
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេសនៃការបង្កើតធ្នូអគ្គិសនី
ធ្នូអគ្គិសនីនៅក្នុងឧបករណ៍បំបែកសៀគ្វីគឺជា ការបញ្ចេញចរន្តអគ្គិសនីដែលទ្រទ្រង់តាមរយៈខ្យល់អ៊ីយ៉ូដ (ផ្លាស្មា) ដែលកើតឡើងនៅពេលដែលទំនាក់ទំនងដាច់ពីគ្នាក្រោមបន្ទុក។ មិនដូចផ្កាភ្លើងខ្លីទេ ធ្នូគឺជាបណ្តាញផ្លាស្មាដែលបន្តដោយខ្លួនឯង ដែលផ្ទុកចរន្តសៀគ្វីពេញលេញតាមរយៈអ្វីដែលគួរតែជាគម្លាតខ្យល់អ៊ីសូឡង់។.
ធ្នូបង្កើតឡើងដោយសារតែ ចរន្តស្វែងរកដើម្បីរក្សាផ្លូវរបស់វា ទោះបីជាកម្លាំងមេកានិចទាញទំនាក់ទំនងដាច់ពីគ្នាក៏ដោយ។ នៅពេលដែលការបំបែកទំនាក់ទំនងបង្កើតគម្លាតខ្យល់ វាលអគ្គិសនីខ្លាំង (ជាញឹកញាប់លើសពី 3 លានវ៉ុលក្នុងមួយម៉ែត្រនៅពេលបំបែកដំបូង) បង្កើតអ៊ីយ៉ូដម៉ូលេគុលខ្យល់ ដោយបំបែកពួកវាទៅជាអេឡិចត្រុងសេរី និងអ៊ីយ៉ុងវិជ្ជមាន។ ឧស្ម័នអ៊ីយ៉ូដនេះ—ផ្លាស្មា—ក្លាយជាចរន្តអគ្គិសនី ដែលអនុញ្ញាតឱ្យចរន្តបន្តហូរតាមគម្លាតជាធ្នូពណ៌ស-ខៀវភ្លឺចែងចាំង។.
យោងតាមទិន្នន័យធ្វើតេស្តរបស់ VIOX ធ្នូធម្មតានៅក្នុង MCCB 600V ដែលកាត់ផ្តាច់ 10,000 អំពែរឈានដល់៖
- សីតុណ្ហភាពស្នូល៖ 15,000-20,000°C (ក្តៅជាងផ្ទៃព្រះអាទិត្យនៅ 5,500°C)
- វ៉ុលធ្នូ៖ 20-60 វ៉ុល (ប្រែប្រួលតាមប្រវែងធ្នូ និងទំហំចរន្ត)
- ដង់ស៊ីតេបច្ចុប្បន្ន៖ រហូតដល់ 10^6 A/cm² នៅចំណុច cathode
- ល្បឿនផ្លាស្មា៖ 100-1,000 ម៉ែត្រក្នុងមួយវិនាទីនៅពេលដែលជំរុញដោយម៉ាញ៉េទិច
- ការបំបែកថាមពល៖ 200-600 joules ក្នុងមួយមីលីវិនាទីសម្រាប់កំហុសចរន្តខ្ពស់
ការប្រមូលផ្តុំថាមពលខ្លាំងនេះធ្វើឱ្យការគ្រប់គ្រងធ្នូក្លាយជាបញ្ហាប្រឈមក្នុងការកំណត់វិស្វកម្មឧបករណ៍បំបែកសៀគ្វី។.
ហេតុអ្វីបានជាធ្នូបង្កើត៖ រូបវិទ្យានៅពីក្រោយការបំបែកទំនាក់ទំនង
ធ្នូគឺជាផលវិបាកដែលជៀសមិនរួចនៃការបើកសៀគ្វីដែលផ្ទុកចរន្ត។ ដំណើរការបង្កើតធ្នូធ្វើតាមគោលការណ៍រូបវិទ្យាមូលដ្ឋានទាំងនេះ៖
1. គោលការណ៍បន្តចរន្ត៖ ចរន្តអគ្គិសនីដែលហូរតាមសៀគ្វីអាំងឌុចទ័រ (ដែលរួមបញ្ចូលប្រព័ន្ធអគ្គិសនីពិតប្រាកដស្ទើរតែទាំងអស់) មិនអាចធ្លាក់ចុះដល់សូន្យភ្លាមៗបានទេ។ នៅពេលដែលទំនាក់ទំនងចាប់ផ្តើមដាច់ពីគ្នា ចរន្តត្រូវតែស្វែងរកផ្លូវមួយ—ធ្នូផ្តល់ផ្លូវនោះ។.
2. ការរឹតបន្តឹងទំនាក់ទំនង និងកំដៅក្នុងតំបន់៖ ទោះបីជាទំនាក់ទំនងហាក់ដូចជាប៉ះលើផ្ទៃមុខពេញលេញរបស់វាក៏ដោយ ចរន្តចរន្តពិតប្រាកដកើតឡើងតាមរយៈចំណុចទំនាក់ទំនងមីក្រូទស្សន៍ (asperities) ដែលភាពមិនប្រក្រតីនៃផ្ទៃធ្វើឱ្យមានទំនាក់ទំនង។ ដង់ស៊ីតេចរន្តនៅចំណុចទាំងនេះគឺខ្ពស់ខ្លាំងណាស់ បណ្តាលឱ្យមានកំដៅក្នុងតំបន់ និងការផ្សារដែកខ្នាតតូច។.
3. ការបញ្ចេញវាល និងអ៊ីយ៉ូដដំបូង៖ នៅពេលដែលទំនាក់ទំនងដាច់ពីគ្នា (ជាធម្មតាក្នុងល្បឿន 0.5-2 ម៉ែត្រក្នុងមួយវិនាទីនៅក្នុងឧបករណ៍បំបែកសៀគ្វី) តំបន់ទំនាក់ទំនងដែលថយចុះបណ្តាលឱ្យដង់ស៊ីតេចរន្តកើនឡើង។ នេះកំដៅចំណុចទំនាក់ទំនងដែលនៅសល់ដល់ 2,000-4,000°C ដោយហួតសម្ភារៈទំនាក់ទំនង។ ក្នុងពេលដំណាលគ្នា គម្លាតដែលកាន់តែធំបង្កើតវាលអគ្គិសនីខ្លាំងដែលបង្កើតអ៊ីយ៉ូដចំហាយលោហៈ និងខ្យល់ជុំវិញ។.
4. ការបង្កើតបណ្តាញផ្លាស្មា៖ នៅពេលដែលបណ្តាញផ្លាស្មាដែលមានចរន្តបង្កើតឡើង វាទ្រទ្រង់ខ្លួនឯងតាមរយៈអ៊ីយ៉ូដកម្ដៅ។ ចរន្តដែលហូរតាមផ្លាស្មាកំដៅវាកាន់តែច្រើន (កំដៅ Joule: I²R) ដែលបង្កើនអ៊ីយ៉ូដ ដែលបង្កើនចរន្ត ដែលទ្រទ្រង់ចរន្ត។ រង្វិលជុំមតិវិជ្ជមាននេះរក្សាធ្នូរហូតដល់ការត្រជាក់ខាងក្រៅ និងការពន្លូតពន្លត់វា។.
នៅក្នុងការសិក្សាកាមេរ៉ាល្បឿនលឿនរបស់ VIOX អំពីការបង្កើតធ្នូនៅក្នុងឧបករណ៍បំបែកសៀគ្វីករណីផ្សិត យើងសង្កេតឃើញការបង្កើតធ្នូកើតឡើងក្នុងរយៈពេល 0.1-0.5 មីលីវិនាទីនៃការបំបែកទំនាក់ទំនង ដោយធ្នូចាប់ផ្តើមផ្លាស់ទីភ្លាមៗក្រោមឥទ្ធិពលអេឡិចត្រូម៉ាញ៉េទិចឆ្ពោះទៅរកផ្លូវរអិលធ្នូ និងបន្ទប់ពន្លត់។.
ធ្នូទល់នឹងផ្កាភ្លើង៖ ការយល់ដឹងពីភាពខុសគ្នា
អ្នកជំនាញខាងអគ្គិសនីជួនកាលច្រឡំធ្នូ និងផ្កាភ្លើង ប៉ុន្តែពួកវាជាបាតុភូតខុសគ្នាជាមូលដ្ឋាន៖
| លក្ខណៈ | ផ្កាភ្លើង | ធ្នូ |
| រយៈពេល | បណ្តោះអាសន្ន (មីក្រូវិនាទីទៅមីលីវិនាទី) | ទ្រទ្រង់ (មីលីវិនាទីទៅវិនាទី ឬយូរជាងនេះ) |
| ថាមពល | ការបញ្ចេញថាមពលទាប | ថាមពលបន្តខ្ពស់ |
| លំហូរបច្ចុប្បន្ន | ជីពចរខ្លី ជាធម្មតា <1 អំពែរ | បន្ត, ផ្ទុកចរន្តសៀគ្វីពេញលេញ (រាប់រយទៅរាប់ពាន់អំពែរ) |
| សីតុណ្ហភាព | ក្តៅប៉ុន្តែខ្លី | ក្តៅខ្លាំង (15,000-20,000°C) |
| ទ្រទ្រង់ដោយខ្លួនឯង | ទេ—ដួលរលំភ្លាមៗ | បាទ—បន្តរហូតដល់ការរំខានខាងក្រៅ |
| សក្តានុពលនៃការខូចខាត | សំណឹកផ្ទៃតិចតួចបំផុត | សំណឹកទំនាក់ទំនងធ្ងន់ធ្ងរ ការខូចខាតឧបករណ៍ ហានិភ័យភ្លើង |
| ឧទាហរណ៍ | ការបញ្ចេញចរន្តអគ្គិសនីឋិតិវន្ត ការបើកកុងតាក់បន្ទុកស្រាល | ឧបករណ៍បំបែកសៀគ្វីកាត់ផ្តាច់ចរន្តកំហុស |
ភាពខុសគ្នាមានសារៈសំខាន់ដោយសារតែ ការទប់ស្កាត់ផ្កាភ្លើង (ដូចជា RC snubbers ឆ្លងកាត់ទំនាក់ទំនងបញ្ជូនត) និង ការពន្លត់ធ្នូ (ដូចជានៅក្នុងឧបករណ៍បំបែកសៀគ្វី) តម្រូវឱ្យមានវិធីសាស្រ្តវិស្វកម្មខុសគ្នាទាំងស្រុង។.
ទំនាក់ទំនងធ្នូទល់នឹងទំនាក់ទំនងសំខាន់ៗ៖ យន្តការការពារ
ធាតុផ្សំមួយដែលសំខាន់បំផុត ប៉ុន្តែមិនសូវយល់ច្បាស់នៅក្នុងឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វីទំនើបគឺ ទំនាក់ទំនងធ្នូអគ្គិសនី—ទំនាក់ទំនងឯកទេសដែលត្រូវបានរចនាឡើងដើម្បីការពារទំនាក់ទំនងចរន្តចម្បង (មេ) របស់ឧបករណ៍បំលែងពីការខូចខាតដោយសារធ្នូអគ្គិសនី។.
តើអ្វីទៅជាទំនាក់ទំនងធ្នូអគ្គិសនី?
ទំនាក់ទំនងធ្នូអគ្គិសនី (ត្រូវបានគេហៅផងដែរថា arc horns ឬ arc runners នៅក្នុងឧបករណ៍បំលែងធំជាង) គឺជាទំនាក់ទំនងអគ្គិសនីបន្ទាប់បន្សំដែលត្រូវបានរចនាឡើងជាពិសេសដើម្បី:
- ទប់ទល់នឹងធ្នូអគ្គិសនីមុនគេ នៅពេលដែលទំនាក់ទំនងបើកនៅក្រោមបន្ទុក
- ទាញធ្នូអគ្គិសនីចេញ ពីទំនាក់ទំនងមេតាមរយៈមធ្យោបាយមេកានិច និងអេឡិចត្រូម៉ាញ៉េទិច
- ទប់ទល់នឹងសំណឹក ពីធ្នូអគ្គិសនីដដែលៗ តាមរយៈវត្ថុធាតុ refractory ឯកទេស
- ដឹកនាំធ្នូអគ្គិសនី ឆ្ពោះទៅបន្ទប់ពន្លត់ និង arc chutes
នៅក្នុងប្រព័ន្ធទំនាក់ទំនងឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វី អ្នកមានគូទំនាក់ទំនងពីរផ្សេងគ្នា៖
ទំនាក់ទំនងមេ (ទំនាក់ទំនងចម្បង):
- ផ្ទៃទំនាក់ទំនងធំត្រូវបានធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងសម្រាប់ភាពធន់ទ្រាំទាបក្នុងអំឡុងពេលផ្ទុកចរន្តធម្មតា
- សម្ភារៈដែលបានជ្រើសរើសសម្រាប់ចរន្តអគ្គិសនី និងភាពធន់នៃមេកានិច (ជាធម្មតា ប្រាក់-កាដមីញ៉ូមអុកស៊ីដ ប្រាក់-tungsten ឬលោហធាតុប្រាក់-នីកែល)
- ត្រូវបានរចនាឡើងដើម្បីផ្ទុកចរន្តដែលបានវាយតម្លៃជាបន្តបន្ទាប់ដោយមិនឡើងកំដៅ
- បិទមុននៅពេលដែលឧបករណ៍បំលែងបិទ; បើកចុងក្រោយនៅពេលដែលឧបករណ៍បំលែងបើកនៅពេលគ្មានបន្ទុក ឬលក្ខខណ្ឌចរន្តទាប
- មានតម្លៃថ្លៃ និងពិបាកក្នុងការជំនួសប្រសិនបើខូច
ទំនាក់ទំនងធ្នូអគ្គិសនី (ទំនាក់ទំនងបន្ទាប់បន្សំ):
- ផ្ទៃទំនាក់ទំនងតូចជាងគឺគ្រប់គ្រាន់សម្រាប់កាតព្វកិច្ចផ្ទុកធ្នូអគ្គិសនីខ្លី
- សម្ភារៈដែលបានជ្រើសរើសសម្រាប់ធន់ទ្រាំនឹងសីតុណ្ហភាពខ្ពស់ និងធន់នឹងសំណឹកធ្នូអគ្គិសនី (ទង់ដែង-tungsten, tungsten-carbide ឬលោហធាតុធន់នឹងធ្នូអគ្គិសនីឯកទេស)
- ត្រូវបានរចនាឡើងដើម្បីទប់ទល់នឹងធ្នូអគ្គិសនីខ្លាំងរយៈពេលខ្លី
- បើកមុននៅពេលដែលឧបករណ៍បំលែងធ្វើដំណើរក្រោមបន្ទុក ដោយចាប់ផ្តើមធ្នូអគ្គិសនីចេញពីទំនាក់ទំនងមេ
- ជាញឹកញាប់ត្រូវបានរួមបញ្ចូលជាមួយ arc runners ដែលផ្លាស់ទីធ្នូអគ្គិសនីដោយរូបភាពឆ្ពោះទៅតំបន់ពន្លត់
- ត្រូវបានចាត់ទុកថាជា sacrificial—ត្រូវបានរចនាឡើងដើម្បីសឹករេចរឹលបន្តិចម្តងៗ និងត្រូវបានជំនួសកំឡុងពេលថែទាំធំ
របៀបដែលទំនាក់ទំនងធ្នូអគ្គិសនីការពារឧបករណ៍បំលែង
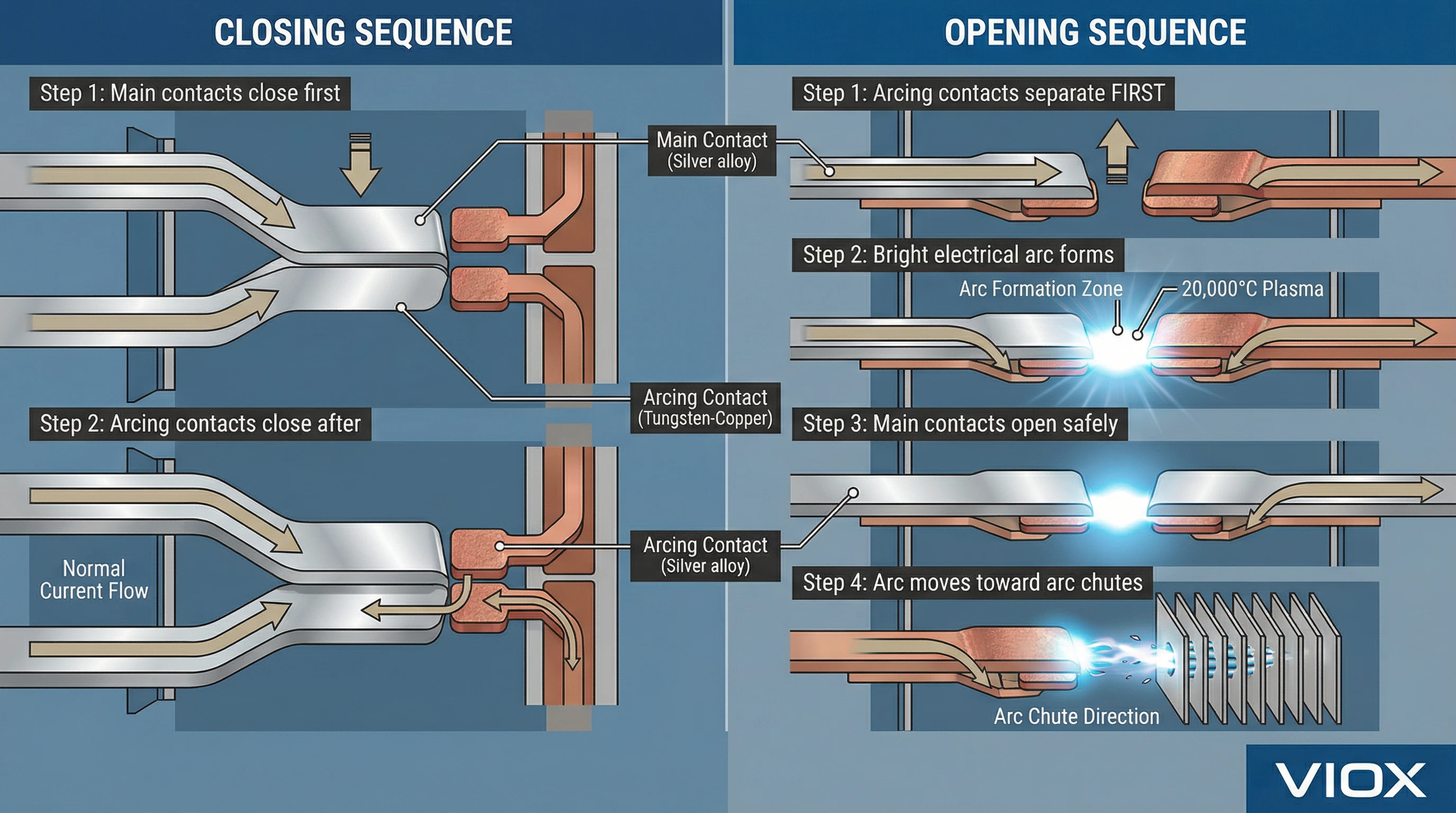
យន្តការការពារដំណើរការតាមរយៈប្រតិបត្តិការជាបន្តបន្ទាប់ដែលបានកំណត់ពេលវេលាយ៉ាងប្រុងប្រយ័ត្ន។ នៅក្នុងការរចនា VIOX MCCB លំដាប់ទំនាក់ទំនងធ្វើតាមលំនាំនេះ៖
លំដាប់បិទ (ផ្តល់ថាមពលដល់សៀគ្វី):
- ទំនាក់ទំនងមេបិទមុន ដោយបង្កើតផ្លូវចរន្ត
- ទំនាក់ទំនងធ្នូអគ្គិសនីបិទនៅពេលក្រោយ (ពួកវាភ្ជាប់ចុងក្រោយ)
- ក្នុងអំឡុងពេលប្រតិបត្តិការធម្មតា ទំនាក់ទំនងទាំងពីរសំណុំផ្ទុកចរន្ត ប៉ុន្តែទំនាក់ទំនងមេផ្ទុកភាគច្រើនដោយសារតែភាពធន់ទ្រាំទាបរបស់វា
លំដាប់បើកក្រោមបន្ទុក (រំខានចរន្ត):
- យន្តការធ្វើដំណើរដំណើរការ
- ទំនាក់ទំនងធ្នូអគ្គិសនីចាប់ផ្តើមបំបែកមុន (ពួកវាផ្តាច់មុន) ខណៈពេលដែលទំនាក់ទំនងមេនៅតែបិទ
- នៅពេលដែលគម្លាតទំនាក់ទំនងធ្នូអគ្គិសនីកាន់តែធំ ធ្នូអគ្គិសនីបង្កើតឡើងរវាងពួកវា—ប៉ុន្តែទំនាក់ទំនងមេនៅតែបិទ ដោយផ្ទុកចរន្តតាមរយៈផ្លូវលោហធាតុ
- ទំនាក់ទំនងមេបើកភ្លាមៗបន្ទាប់ពីនោះ ប៉ុន្តែនៅពេលនេះ ធ្នូអគ្គិសនីត្រូវបានបង្កើតឡើងនៅលើទំនាក់ទំនងធ្នូអគ្គិសនីរួចហើយ មិនមែនទំនាក់ទំនងមេទេ
- ទំនាក់ទំនងធ្នូអគ្គិសនីបន្តបំបែក ដោយពង្រីកធ្នូអគ្គិសនី
- កម្លាំងអេឡិចត្រូម៉ាញ៉េទិច (កម្លាំង Lorentz ពីដែនម៉ាញ៉េទិចរបស់ធ្នូអគ្គិសនី) រុញធ្នូអគ្គិសនីទៅលើ arc runners
- ធ្នូអគ្គិសនីផ្លាស់ទីទៅក្នុង arc chutes ឬបន្ទប់ពន្លត់ដែលវាត្រូវបានត្រជាក់ ពង្រីក និងពន្លត់
- ទំនាក់ទំនងមេនៅតែមិនខូចខាត ព្រោះពួកវាមិនដែលជួបប្រទះធ្នូអគ្គិសនី
ប្រតិបត្តិការផ្តាច់មុន/ភ្ជាប់ចុងក្រោយនេះមានន័យថា ទំនាក់ទំនងមេដោះស្រាយតែចរន្តផ្ទុកធម្មតាប៉ុណ្ណោះ ហើយបើកនៅក្រោមលក្ខខណ្ឌគ្មានធ្នូអគ្គិសនី, ខណៈពេលដែលទំនាក់ទំនងធ្នូអគ្គិសនីស្រូបយកថាមពលបំផ្លិចបំផ្លាញទាំងអស់នៃការបង្កើត និងរំខានធ្នូអគ្គិសនី។.
ផលប៉ះពាល់ពិភពលោកពិត៖ បទពិសោធន៍ VIOX លើទីលាន
នៅក្នុងការវិភាគរបស់ VIOX លើឧបករណ៍បំលែងដែលបានត្រឡប់មកវិញដែលបរាជ័យក្នុងការរំខានកំហុសបានត្រឹមត្រូវ យើងរកឃើញថាប្រហែល 60% នៃការបរាជ័យមហន្តរាយពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹង៖
- បាត់ ឬសឹករេចរឹលយ៉ាងធ្ងន់ធ្ងរនូវទំនាក់ទំនងធ្នូអគ្គិសនី អនុញ្ញាតឱ្យធ្នូអគ្គិសនីប៉ះទំនាក់ទំនងមេដោយផ្ទាល់
- យន្តការទំនាក់ទំនងធ្នូអគ្គិសនីមិនត្រឹមត្រូវ បណ្តាលឱ្យទំនាក់ទំនងមេបំបែកមុនពេលទំនាក់ទំនងធ្នូអគ្គិសនី
- លក្ខណៈបច្ចេកទេសសម្ភារៈខុស ដែលទំនាក់ទំនងធ្នូអគ្គិសនីប្រើលោហធាតុប្រាក់ស្តង់ដារជំនួសឱ្យសមាសធាតុ tungsten ដែលធន់នឹងធ្នូអគ្គិសនី
ការរចនា និងការថែទាំទំនាក់ទំនងធ្នូអគ្គិសនីត្រឹមត្រូវ ពង្រីកអាយុកាលប្រតិបត្តិការឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វីដោយ 3-5x នៅក្នុងកម្មវិធីដែលមានកាតព្វកិច្ចខ្ពស់។ នៅក្នុងកន្លែងសំខាន់ៗដូចជាមជ្ឈមណ្ឌលទិន្នន័យ និងមន្ទីរពេទ្យដែលឧបករណ៍បំលែងរបស់យើងការពារសៀគ្វីសុវត្ថិភាពជីវិត យើងបញ្ជាក់ប្រព័ន្ធទំនាក់ទំនងធ្នូអគ្គិសនីដែលប្រសើរឡើងជាមួយនឹងស្រទាប់ tungsten កាន់តែក្រាស់ និងវដ្តត្រួតពិនិត្យញឹកញាប់ជាងមុន (ប្រចាំឆ្នាំជំនួសឱ្យរៀងរាល់ 3-5 ឆ្នាំ)។.
រូបវិទ្យានៃការបង្កើតធ្នូអគ្គិសនី៖ Cathode Spots, Anode Phenomena និង Plasma Dynamics
ដើម្បីយល់ពិតប្រាកដពីរបៀបដែលឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វីគ្រប់គ្រងធ្នូអគ្គិសនី យើងត្រូវពិនិត្យមើលរូបវិទ្យាមូលដ្ឋានដែលគ្រប់គ្រងឥរិយាបថធ្នូអគ្គិសនី។ ផ្នែកនេះស្វែងយល់ពីរូបវិទ្យាធ្នូអគ្គិសនីនៅកម្រិតមួយលើសពីអ្វីដែលគូប្រជែងគ្របដណ្តប់ជាធម្មតា—ផ្តល់ឱ្យវិស្វករអគ្គិសនីនូវចំណេះដឹងបច្ចេកទេសស៊ីជម្រៅដើម្បីបញ្ជាក់ និងដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដែលទាក់ទងនឹងធ្នូអគ្គិសនី។.
Cathode Phenomena: ប្រភពថាមពលរបស់ធ្នូអគ្គិសនី
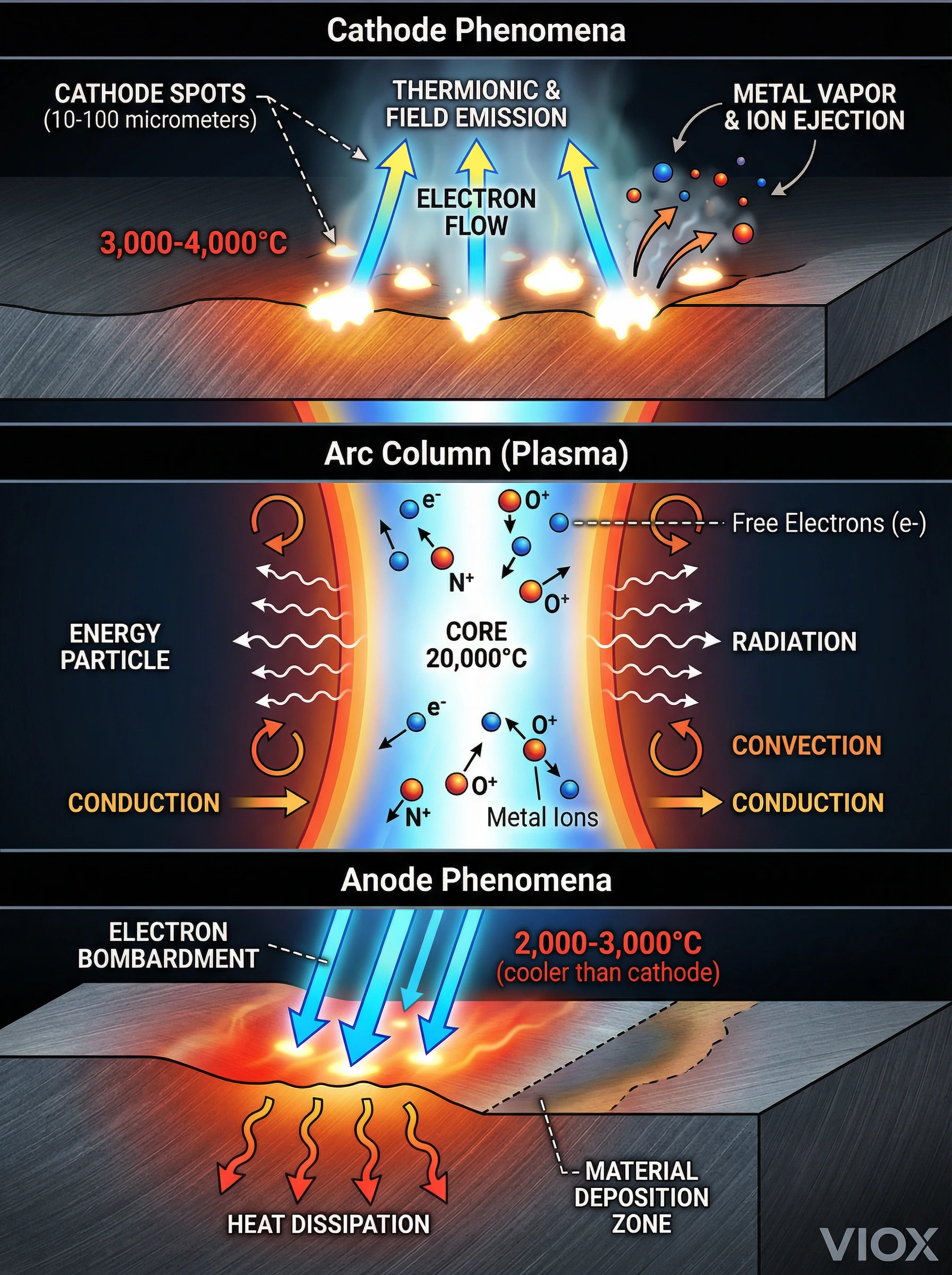
នេះ។ cathode (អេឡិចត្រូតអវិជ្ជមាន) គឺជាកន្លែងដែលអេឡិចត្រុងមានប្រភពនៅក្នុងធ្នូអគ្គិសនី។ មិនដូចចរន្តស្ថិរភាពដែលចរន្តហូរស្មើៗគ្នាទេ cathodes ធ្នូអគ្គិសនីប្រមូលផ្តុំដង់ស៊ីតេចរន្តយ៉ាងខ្លាំងទៅក្នុងតំបន់សកម្មតូចៗដែលគេហៅថា cathode spots.
លក្ខណៈនៃ Cathode Spot (ពីការវាស់វែងមន្ទីរពិសោធន៍ VIOX)៖
- ទំហំ៖ អង្កត់ផ្ចិត 10-100 មីក្រូម៉ែត្រ
- ដង់ស៊ីតេបច្ចុប្បន្ន៖ 10^6 ទៅ 10^9 A/cm² (លានទៅពាន់លានអំពែរក្នុងមួយសង់ទីម៉ែត្រការ៉េ)
- សីតុណ្ហភាព៖ 3,000-4,000°C នៅលើផ្ទៃកាតូត
- អាយុកាល៖ មីក្រូវិនាទី—ចំណុចរលត់ និងបង្កើតឡើងវិញយ៉ាងឆាប់រហ័ស ដែលផ្តល់ឱ្យធ្នូនូវរូបរាងភ្លឹបភ្លែតៗលក្ខណៈរបស់វា
- ការបញ្ចេញសារធាតុ៖ ចំណុចកាតូតធ្វើឱ្យសារធាតុអេឡិចត្រូតហួត បញ្ចេញចំហាយលោហៈ អ៊ីយ៉ុង និងដំណក់ទឹកតូចៗទៅក្នុងជួរធ្នូ
ចំណុចកាតូតដំណើរការតាមរយៈ ការបញ្ចេញកំដៅ និង ការបញ្ចេញវាល:
- ការបញ្ចេញកំដៅ៖ កំដៅខ្លាំងនៅចំណុចទំនាក់ទំនងមីក្រូទស្សន៍ផ្តល់ថាមពលកម្ដៅដើម្បីបញ្ចេញអេឡិចត្រុងពីផ្ទៃលោហៈ ដោយយកឈ្នះលើមុខងារការងារ (ថាមពលចង)។ សម្រាប់ទំនាក់ទំនងទង់ដែង មុខងារការងារ ≈ 4.5 eV ដែលតម្រូវឱ្យមានសីតុណ្ហភាព >2,000 K សម្រាប់ការបញ្ចេញយ៉ាងសំខាន់។.
- ការបញ្ចេញវាល៖ វាលអេឡិចត្រូតខ្លាំងនៅលើផ្ទៃកាតូត (10^8 ទៅ 10^9 V/m) ទាញអេឡិចត្រុងចេញពីលោហៈតាមរយៈការឆ្លងកាត់កង់ទិច សូម្បីតែនៅសីតុណ្ហភាពទាបក៏ដោយ។ ការបញ្ចេញវាលគ្របដណ្តប់លើកន្លែងទំនេរ និងឧបករណ៍បំបែក SF6 ដែលកម្លាំងវាលខ្ពស់អាចត្រូវបានរក្សា។.
ផលប៉ះពាល់នៃការជ្រើសរើសសម្ភារៈ៖ សំណឹកកាតូតគឺជាយន្តការពាក់ចម្បងសម្រាប់ទំនាក់ទំនងធ្នូ។ VIOX បញ្ជាក់ សមាសធាតុ tungsten-copper (ជាធម្មតា tungsten 75%, copper 25%) សម្រាប់ទំនាក់ទំនងធ្នូ ពីព្រោះ៖
- ចំណុចរលាយខ្ពស់របស់ Tungsten (3,422°C) កាត់បន្ថយអត្រាហួត
- មុខងារការងារខ្ពស់របស់ Tungsten (4.5 eV) កាត់បន្ថយការបញ្ចេញកំដៅ ធ្វើឱ្យចំណុចកាតូតមានស្ថេរភាព
- ទង់ដែងផ្តល់នូវចរន្តអគ្គិសនី និងចរន្តកំដៅដើម្បីរំសាយកំដៅ
- សមាសធាតុនេះទប់ទល់នឹងសំណឹកបានល្អជាង 3-5 ដង ជាងទំនាក់ទំនងទង់ដែង ឬប្រាក់សុទ្ធ
បាតុភូត Anode: ការរំសាយកំដៅ និងការផ្ទេរសម្ភារៈ
នេះ។ anode (អេឡិចត្រូតវិជ្ជមាន) ទទួលលំហូរអេឡិចត្រុងពីកាតូត។ អាកប្បកិរិយា Anode ខុសគ្នាជាមូលដ្ឋានពីអាកប្បកិរិយាកាតូត៖
លក្ខណៈ Anode:
- យន្តការកំដៅ៖ ការទម្លាក់គ្រាប់បែកដោយអេឡិចត្រុងល្បឿនលឿនពីកាតូត ដែលបំប្លែងថាមពល kinetic ទៅជាកំដៅនៅពេលប៉ះទង្គិច
- សីតុណ្ហភាព៖ ចំណុច Anode ជាធម្មតាត្រជាក់ជាងចំណុចកាតូត 500-1,000°C
- ដង់ស៊ីតេបច្ចុប្បន្ន៖ សាយភាយជាងកាតូត—រាលដាលលើផ្ទៃធំជាង
- ការផ្ទេរសម្ភារៈ៖ នៅក្នុងធ្នូ DC សម្ភារៈច្រេះពីកាតូត និងដាក់នៅលើ anode បង្កើតបានជា “លោហៈដែលបានផ្ទេរ” លក្ខណៈដែលបានសង្កេតឃើញនៅក្នុងទំនាក់ទំនងដែលខូចដោយធ្នូ
ក្នុង សៀគ្វី AC (ភាគច្រើននៃកម្មវិធីឧបករណ៍បំបែកសៀគ្វី) ប៉ូលផ្លាស់ប្តូរ 50-60 ដងក្នុងមួយវិនាទី ដូច្នេះទំនាក់ទំនងនីមួយៗឆ្លាស់គ្នារវាងកាតូត និង anode ។ ប៉ូលឆ្លាស់គ្នានេះពន្យល់ពីមូលហេតុដែលទំនាក់ទំនងឧបករណ៍បំបែកសៀគ្វី AC បង្ហាញលំនាំសំណឹកឯកសណ្ឋានជាងឧបករណ៍បំបែក DC ដែលសំណឹកកាតូតគ្របដណ្តប់។.
ជួរធ្នូ: រូបវិទ្យាប្លាស្មានៅក្នុងសកម្មភាព
នេះ។ ជួរធ្នូ គឺជាបណ្តាញប្លាស្មាភ្លឺដែលភ្ជាប់កាតូត និង anode ។ នេះគឺជាកន្លែងដែលភាគច្រើននៃថាមពលធ្នូរលាយបាត់។.
លក្ខណៈសម្បត្តិប្លាស្មា:
- សមាសភាព៖ ចំហាយលោហៈអ៊ីយ៉ូដពីសំណឹកអេឡិចត្រូត + ខ្យល់អ៊ីយ៉ូដ (អាសូត អុកស៊ីហ្សែនក្លាយជាអ៊ីយ៉ុង N+, O+ បូកនឹងអេឡិចត្រុងសេរី)
- ទម្រង់សីតុណ្ហភាព៖ 15,000-20,000°C នៅស្នូល កាត់បន្ថយកាំទៅគែម
- ចរន្តអគ្គិសនី៖ 10^3 ទៅ 10^4 siemens/meter—ចរន្តខ្ពស់ អាចប្រៀបធៀបទៅនឹងលោហៈខ្សោយ
- ចរន្តកំដៅ៖ ខ្ពស់—ប្លាស្មាចម្លងកំដៅទៅខ្យល់ជុំវិញយ៉ាងមានប្រសិទ្ធភាព
- ការបញ្ចេញពន្លឺ៖ ពន្លឺពណ៌ស-ខៀវខ្លាំងពីការរំភើបចិត្ត និងការផ្សំឡើងវិញ (អេឡិចត្រុងត្រឡប់ទៅសភាពដើមវិញបញ្ចេញ photons)
តុល្យភាពថាមពលនៅក្នុងជួរធ្នូ:
ជួរធ្នូត្រូវតែរក្សាតុល្យភាពកម្ដៅរវាងការបញ្ចូលថាមពល (កំដៅ Joule: V_arc × I) និងការបាត់បង់ថាមពល (វិទ្យុសកម្ម ចរន្តកំដៅ ចរន្ត)៖
- ការបញ្ចូលថាមពល៖ P_in = V_arc × I (ជាធម្មតា 20-60V × 1,000-50,000A = 20 kW ទៅ 3 MW)
- ការបាត់បង់វិទ្យុសកម្ម៖ ប្លាស្មាសីតុណ្ហភាពខ្ពស់បញ្ចេញកាំរស្មី UV និងពន្លឺដែលអាចមើលឃើញ (Stefan-Boltzmann: P ∝ T^4)
- ការបាត់បង់ចរន្តកំដៅ៖ ប្លាស្មាកើនឡើងដោយសារតែការអណ្តែត (ឧស្ម័នក្តៅ) ហើយត្រូវបានផ្លុំដោយកម្លាំងម៉ាញ៉េទិច
- ការបាត់បង់ចរន្ត៖ កំដៅត្រូវបានដឹកនាំទៅអេឡិចត្រូត ជញ្ជាំងបន្ទប់ធ្នូ និងឧស្ម័នជុំវិញ
នៅពេលដែលការបាត់បង់ថាមពលលើសពីការបញ្ចូលថាមពល (ដូចជានៅពេលដែលធ្នូត្រូវបានពន្លូត ឬត្រជាក់យ៉ាងឆាប់រហ័ស) សីតុណ្ហភាពប្លាស្មាធ្លាក់ចុះ អ៊ីយ៉ូដថយចុះ ភាពធន់កើនឡើង ហើយធ្នូរលត់។.
លក្ខណៈវ៉ុលធ្នូ: គន្លឹះក្នុងការកំណត់ចរន្ត
ប៉ារ៉ាម៉ែត្រធ្នូដ៏សំខាន់បំផុតមួយសម្រាប់ការអនុវត្តឧបករណ៍បំបែកសៀគ្វីគឺ វ៉ុលធ្នូ—ការធ្លាក់ចុះវ៉ុលឆ្លងកាត់ធ្នូពីកាតូតទៅ anode ។.
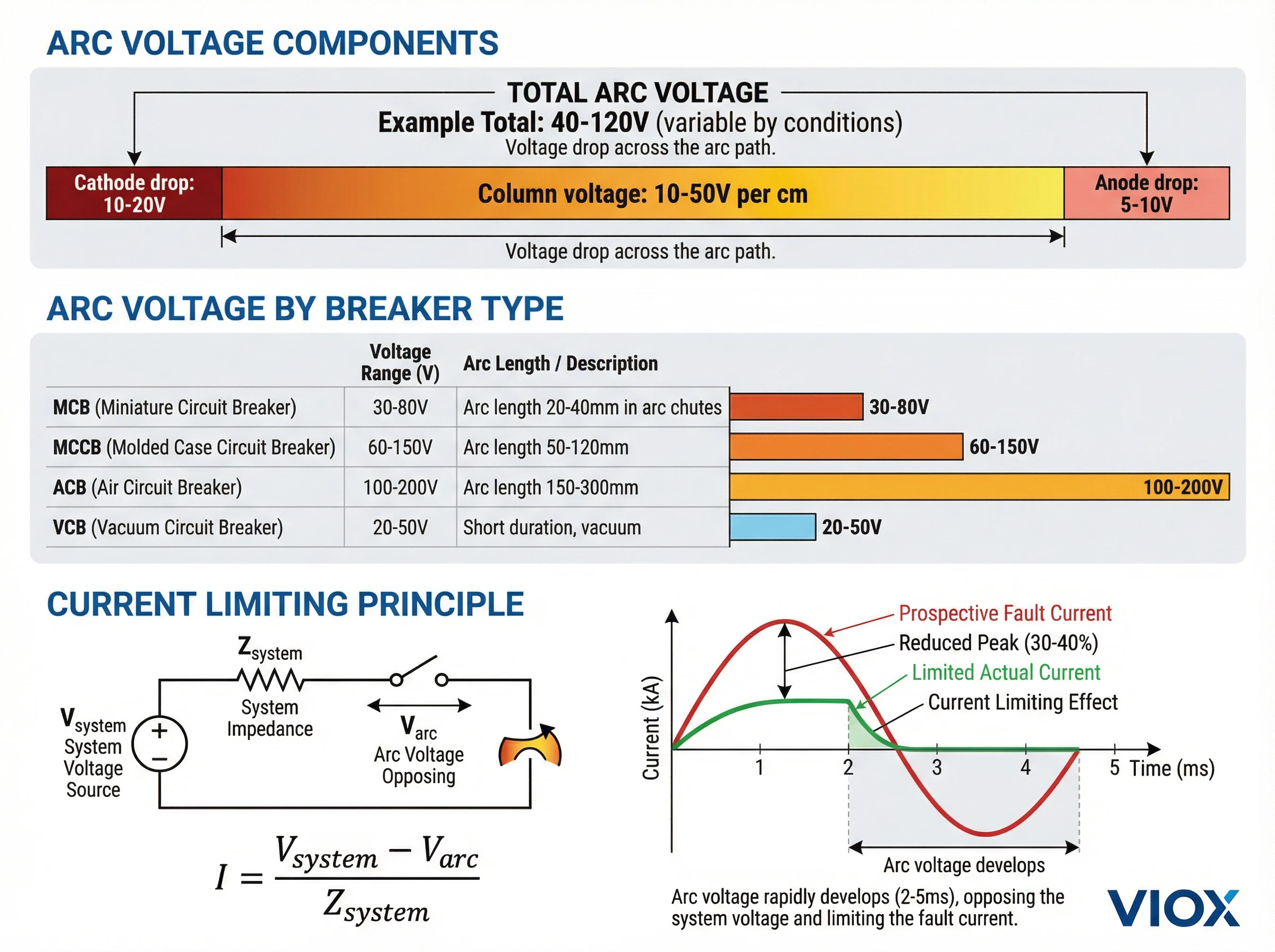
សមាសភាគវ៉ុលធ្នូ:
V_arc = V_cathode + V_column + V_anode
កន្លែងណា៖
- V_cathode: ការធ្លាក់ចុះវ៉ុលកាតូត (ជាទូទៅ 10-20V) - ថាមពលដែលត្រូវការដើម្បីទាញយកអេឡិចត្រុងចេញពីកាតូត
- V_column: ការធ្លាក់ចុះវ៉ុលជួរឈរ (ប្រែប្រួលតាមប្រវែងធ្នូ: ~10-50V ក្នុងមួយសង់ទីម៉ែត្រនៃប្រវែងធ្នូ)
- V_anode: ការធ្លាក់ចុះវ៉ុលអាណូត (ជាទូទៅ 5-10V) - ថាមពលដែលបាត់បង់នៅពេលអេឡិចត្រុងប៉ះអាណូត
វ៉ុលធ្នូសរុប នៅក្នុងឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វី VIOX កំឡុងពេលរំខានកំហុស:
| ប្រភេទឧបករណ៍បំបែក | គម្លាតធ្នូដំបូង | ប្រវែងធ្នូបន្ទាប់ពីផ្លុំចេញ | វ៉ុលធ្នូធម្មតា |
| MCB (ខ្នាតតូច) | 2-4 មម | 20-40 មម (នៅក្នុងរន្ធធ្នូ) | 30-80V |
| MCCB (ករណីផ្សិត) | 5-10 មម | 50-120 មម (នៅក្នុងរន្ធធ្នូ) | 60-150V |
| ACB (ឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វីខ្យល់) | 10-20 មម | 150-300 មម (ស្នែងធ្នូដែលបានពង្រីក) | 100-200V |
| VCB (ខ្វះចន្លោះ) | 5-15 មម | គ្មានការពន្លូត (ខ្វះចន្លោះ) | 20-50V (ទាបដោយសារតែរយៈពេលខ្លី) |
វ៉ុលធ្នូ និងការកំណត់ចរន្ត:
វ៉ុលធ្នូគឺជាយន្តការដែល ឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វីកំណត់ចរន្ត កាត់បន្ថយចរន្តកំហុសក្រោមទំហំដែលរំពឹងទុក។ ប្រព័ន្ធអាចត្រូវបានគំរូដូចជា:
V_system = I × Z_system + V_arc
រៀបចំឡើងវិញ:
I = (V_system – V_arc) / Z_system
ដោយការអភិវឌ្ឍវ៉ុលធ្នូខ្ពស់យ៉ាងឆាប់រហ័ស (តាមរយៈការពន្លូតធ្នូ ការត្រជាក់ និងអន្តរកម្មបន្ទះបំបែក) ឧបករណ៍បំលែងកាត់បន្ថយវ៉ុលជំរុញសុទ្ធ ដែលកំណត់ចរន្ត។ MCCB ដែលកំណត់ចរន្តរបស់ VIOX អភិវឌ្ឍវ៉ុលធ្នូចំនួន 120-180V ក្នុងរយៈពេល 2-3 មិល្លីវិនាទី ដោយកាត់បន្ថយចរន្តកំហុសកំពូលទៅ 30-40% នៃតម្លៃដែលរំពឹងទុក។.
ការវាស់វែងវ៉ុលធ្នូ: កំឡុងពេលធ្វើតេស្តសៀគ្វីខ្លីនៅក្នុងមន្ទីរពិសោធន៍ 65 kA របស់ VIOX យើងវាស់វ៉ុលធ្នូដោយប្រើប្រដាប់ស្ទង់ឌីផេរ៉ង់ស្យែលវ៉ុលខ្ពស់ និងការទទួលបានទិន្នន័យល្បឿនលឿន (អត្រាគំរូ 1 MHz)។ រលកវ៉ុលធ្នូបង្ហាញពីការកើនឡើងយ៉ាងឆាប់រហ័សនៅពេលដែលទំនាក់ទំនងដាច់ពីគ្នា បន្ទាប់មកការប្រែប្រួលលក្ខណៈនៅពេលដែលធ្នូផ្លាស់ទីឆ្លងកាត់រន្ធធ្នូ បន្ទាប់មកការដួលរលំភ្លាមៗដល់សូន្យនៅពេលសូន្យចរន្តនៅពេលដែលធ្នូរលត់។.
វិធីសាស្រ្តពន្លត់ធ្នូឆ្លងកាត់ប្រភេទឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វី
បច្ចេកវិទ្យាឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វីផ្សេងៗគ្នាប្រើប្រាស់យុទ្ធសាស្រ្តពន្លត់ធ្នូខុសៗគ្នា ដែលនីមួយៗត្រូវបានធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរសម្រាប់ថ្នាក់វ៉ុលជាក់លាក់ ការវាយតម្លៃចរន្ត និងតម្រូវការកម្មវិធី។.
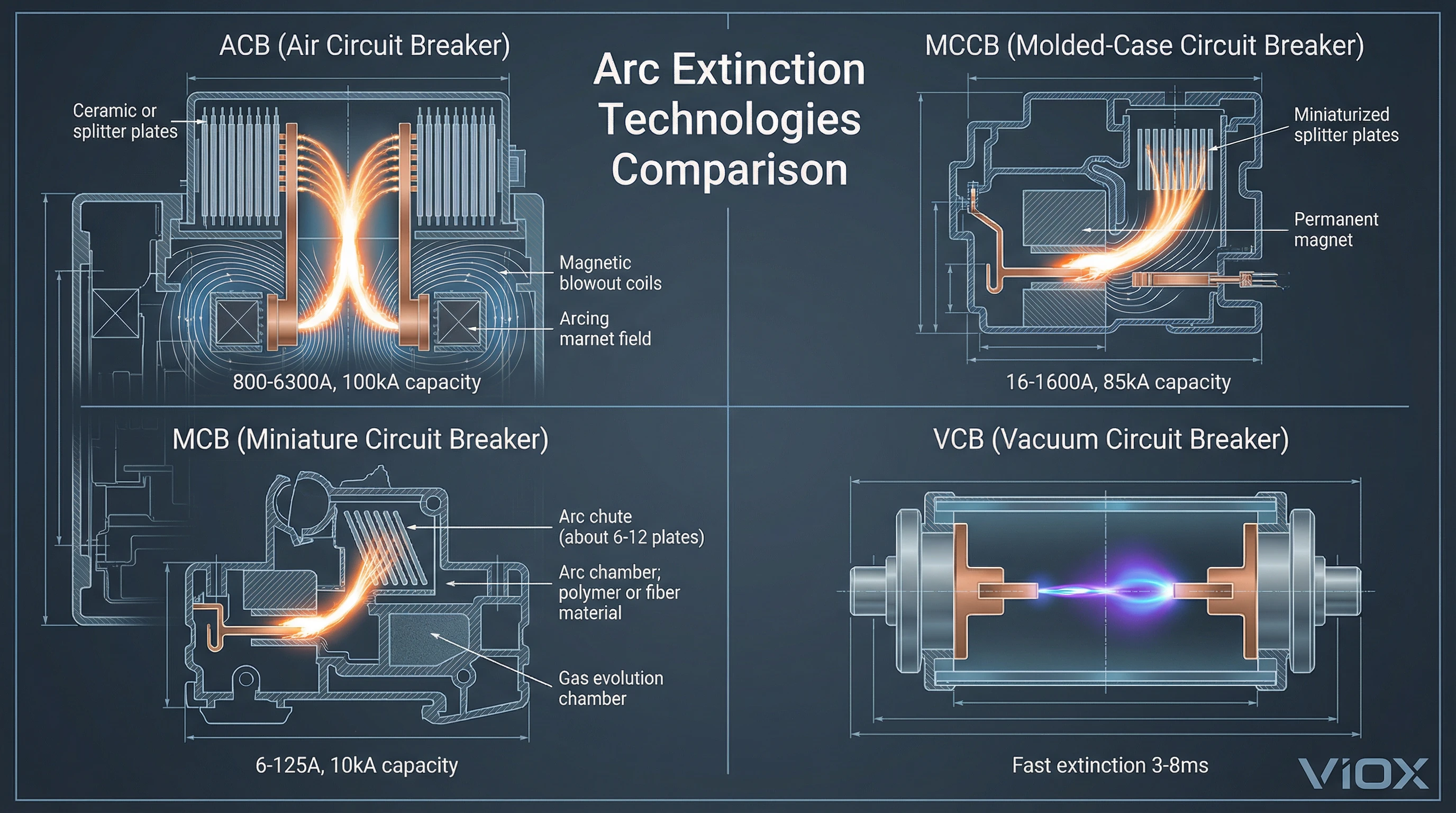
ឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វីខ្យល់ (ACBs): ផ្លុំម៉ាញ៉េទិច និងរន្ធធ្នូ
ឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វីខ្យល់ គឺជាកម្លាំងពលកម្មបែបប្រពៃណីសម្រាប់កម្មវិធីឧស្សាហកម្មធំៗ (ទំហំស៊ុម 800-6300A សមត្ថភាពរំខានរហូតដល់ 100 kA)។ ពួកវាពន្លត់ធ្នូនៅក្នុងខ្យល់បើកចំហដោយប្រើកម្លាំងមេកានិច និងអេឡិចត្រូម៉ាញ៉េទិច។.
យន្តការពន្លត់ធ្នូ:
- ការផ្ទុះម៉ាញេទិក: មេដែកអចិន្ត្រៃយ៍ ឬឧបករណ៏អេឡិចត្រូម៉ាញ៉េទិចបង្កើតវាលម៉ាញ៉េទិចកាត់កែងទៅនឹងផ្លូវធ្នូ។ ចរន្តធ្នូធ្វើអន្តរកម្មជាមួយវាលនេះ បង្កើតកម្លាំង Lorentz: F = I × L × B
- ទិសដៅកម្លាំង: កាត់កែងទៅទាំងចរន្ត និងវាលម៉ាញ៉េទិច (ច្បាប់ដៃស្តាំ)
- ទំហំ: សមាមាត្រទៅនឹងចរន្តធ្នូ - ចរន្តកំហុសខ្ពស់ត្រូវបានផ្លុំលឿនជាង
- ផលប៉ះពាល់: បើកបរធ្នូឡើងលើ និងឆ្ងាយពីទំនាក់ទំនងក្នុងល្បឿន 50-200 m/s
- អ្នករត់ធ្នូ: ធ្នូត្រូវបានរុញទៅលើទង់ដែង ឬដែកដែលបានពង្រីក ដែលពន្លូតផ្លូវធ្នូ បង្កើនវ៉ុល និងភាពធន់របស់ធ្នូ។.
- រន្ធធ្នូ (ឧបករណ៍បំបែកធ្នូ): ធ្នូចូលទៅក្នុងបន្ទប់ដែលមានបន្ទះដែកប៉ារ៉ាឡែលច្រើន (ជាធម្មតា 10-30 បន្ទះដែលមានចន្លោះពី 2-8 មម) ។ ធ្នូគឺ:
- បំបែក ទៅជាធ្នូស៊េរីច្រើន (មួយរវាងគូនៃបន្ទះនីមួយៗ)
- ត្រជាក់ ដោយការប៉ះកម្ដៅជាមួយបន្ទះដែក
- ពន្លូត នៅពេលដែលវាលាតសន្ធឹងលើផ្ទៃបន្ទះ
- គម្លាតនីមួយៗបន្ថែម ~20-40V ទៅវ៉ុលធ្នូ ដូច្នេះ 20 បន្ទះ = 400-800V វ៉ុលធ្នូសរុប
- Deionization: ការរួមបញ្ចូលគ្នានៃការត្រជាក់ និងការឆ្លងកាត់សូន្យចរន្ត (នៅក្នុងប្រព័ន្ធ AC) អនុញ្ញាតឱ្យខ្យល់ deionize ការពារការវាយប្រហារធ្នូម្តងទៀត។.
ការរចនា VIOX ACB: ACBs ស៊េរី VAB របស់យើងប្រើធរណីមាត្ររន្ធធ្នូដែលបានធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរជាមួយនឹងបន្ទះបំបែកដែលមានចន្លោះជិត (3-5 មម) និងមេដែកអចិន្ត្រៃយ៍ដែលមានកម្លាំងខ្ពស់ដែលបង្កើតកម្លាំងវាល 0.3-0.8 Tesla ។ ការរចនានេះពន្លត់ធ្នូរហូតដល់ 100 kA យ៉ាងគួរឱ្យទុកចិត្តក្នុងរយៈពេល 12-18 មិល្លីវិនាទី។.
ឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វីករណី (MCCBs): បំពង់ពន្លត់ធ្នូខ្នាតតូច
MCCBs គឺជាឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វីឧស្សាហកម្មទូទៅបំផុត (16-1600A) ដែលត្រូវការប្រព័ន្ធពន្លត់ធ្នូខ្នាតតូចដែលសមស្របសម្រាប់ករណីផ្សិតដែលបានបិទជិត។.
យុទ្ធសាស្ត្រពន្លត់ធ្នូ:
MCCBs ប្រើគោលការណ៍ស្រដៀងគ្នាទៅនឹង ACBs ប៉ុន្តែនៅក្នុងបន្ទប់ធ្នូខ្នាតតូចដែលបានធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើង:
- ការរចនាបន្ទប់ធ្នូ: លំនៅដ្ឋានធន់នឹងធ្នូដែលបានផ្សិតរួមបញ្ចូលគ្នា (ជាញឹកញាប់ជាសមាសធាតុប៉ូលីអេស្ទែរ) ដែលផ្ទុកធ្នូ និងដឹកនាំឧស្ម័ន
- ការផ្ទុះម៉ាញេទិក: មេដែកអចិន្ត្រៃយ៍តូច ឬឧបករណ៏ផ្លុំដែលផ្ទុកចរន្ត
- បំពង់ពន្លត់ធ្នូខ្នាតតូច: បន្ទះបំបែក 8-20 នៅក្នុងបរិមាណកំណត់
- ការបញ្ចេញសម្ពាធឧស្ម័ន: ការបញ្ចេញខ្យល់ដែលបានគ្រប់គ្រងអនុញ្ញាតឱ្យមានការធូរស្រាលសម្ពាធខណៈពេលដែលការពារការឆេះខាងក្រៅ
MCCB កំណត់ចរន្ត: ស៊េរី CLM របស់ VIOX ប្រើការរចនាបន្ទប់ធ្នូដែលបានពង្រឹង:
- គម្លាតតឹង: បន្ទះបំបែកមានគម្លាត 2-3mm (ធៀបនឹង 4-6mm នៅក្នុង MCCBs ស្តង់ដារ)
- ផ្លូវបន្ថែម: ធ្នូត្រូវបានបង្ខំឱ្យធ្វើដំណើរ 80-120mm តាមរយៈបំពង់ធ្នូរាងពស់
- ការអភិវឌ្ឍវ៉ុលលឿន: វ៉ុលធ្នូរឈានដល់ 120-180V ក្នុងរយៈពេល 2ms
- អនុញ្ញាតឱ្យឆ្លងកាត់ថាមពល: កាត់បន្ថយមកត្រឹម 20-30% នៃ I²t ដែលរំពឹងទុក
ការរចនាកំណត់ចរន្តទាំងនេះការពារឧបករណ៍អេឡិចត្រូនិកដែលងាយរងគ្រោះ កាត់បន្ថយគ្រោះថ្នាក់នៃការឆាបឆេះធ្នូ និងកាត់បន្ថយភាពតានតឹងផ្នែកមេកានិចនៅលើរបារឡានក្រុង និងឧបករណ៍ប្តូរ។.
ឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វីខ្នាតតូច (MCBs): ការគ្រប់គ្រងធ្នូកម្ដៅ និងម៉ាញេទិក
MCBs (ឧបករណ៍បំលែងលំនៅដ្ឋាន/ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម 6-125A) ប្រើការពន្លត់ធ្នូសាមញ្ញដែលសមស្របសម្រាប់ចរន្តកំហុសទាប និងការសាងសង់ប៉ូលតែមួយតូច។.
លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃការពន្លត់ធ្នូ:
- កំណាត់ធ្នូ: បន្ទះបំបែក 6-12 នៅក្នុងបន្ទប់ផ្សិតតូចមួយ
- ការផ្ទុះម៉ាញេទិក: មេដែកអចិន្ត្រៃយ៍តូច ឬអ្នករត់ធ្នូម៉ាញ៉េទិច
- ការវិវត្តន៍ឧស្ម័ន: កំដៅធ្នូធ្វើឱ្យហួតសរសៃ ឬសមាសធាតុបំពង់ធ្នូ polymer បង្កើតឧស្ម័ន deionizing (អ៊ីដ្រូសែនពីការរលាយ polymer) ដែលជួយធ្វើឱ្យត្រជាក់ និងពន្លត់ធ្នូ
ការរចនា VIOX MCB (ស៊េរី VOB4/VOB5):
- បំពង់ធ្នូត្រូវបានសាកល្បងរហូតដល់ 10,000 ប្រតិបត្តិការរំខានក្នុងមួយ IEC 60898-1
- ធ្នូត្រូវបានពន្លត់ក្នុងរយៈពេល 8-15 ms សម្រាប់ចរន្តកំហុសដែលបានវាយតម្លៃ (6 kA ឬ 10 kA)
- ការទប់ស្កាត់ធ្នូខាងក្នុងត្រូវបានផ្ទៀងផ្ទាត់ដើម្បីការពារការឆេះខាងក្រៅ
ឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វីខ្វះចន្លោះ (VCBs): ការពន្លត់ធ្នូលឿនក្នុងខ្វះចន្លោះ
ឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វីខ្វះចន្លោះ ប្រើវិធីសាស្រ្តខុសគ្នាទាំងស្រុង: លុបបំបាត់មធ្យមទាំងស្រុង។ ទំនាក់ទំនងដំណើរការនៅក្នុងដបខ្វះចន្លោះដែលបានផ្សាភ្ជាប់ (សម្ពាធ 10^-6 ទៅ 10^-7 Torr) ។.
យន្តការពន្លត់ធ្នូ:
នៅក្នុងខ្វះចន្លោះ មិនមានឧស្ម័នដើម្បីធ្វើឱ្យអ៊ីយ៉ូដទេ។ នៅពេលដែលទំនាក់ទំនងដាច់ពីគ្នា:
- ធ្នូដែក: ធ្នូដំបូងមានតែចំហាយដែកអ៊ីយ៉ូដពីផ្ទៃទំនាក់ទំនងប៉ុណ្ណោះ។
- ការពង្រីកយ៉ាងឆាប់រហ័ស: ចំហាយដែកពង្រីកទៅក្នុងខ្វះចន្លោះ និងខាប់នៅលើផ្ទៃត្រជាក់ (ខែល និងទំនាក់ទំនង)
- Deionization លឿន: នៅសូន្យបច្ចុប្បន្ន អ៊ីយ៉ុង និងអេឡិចត្រុងដែលនៅសេសសល់បញ្ចូលគ្នាឡើងវិញ ឬដាក់ក្នុងរយៈពេលមីក្រូវិនាទី
- ការងើបឡើងវិញនៃ dielectric ខ្ពស់: គម្លាតខ្វះចន្លោះទទួលបានកម្លាំង dielectric ពេញលេញស្ទើរតែភ្លាមៗ
- ការផុតពូជនៃធ្នូ: ជាធម្មតាក្នុងរយៈពេល 3-8 មិល្លីវិនាទី (1/2 ទៅ 1 វដ្តនៅ 50/60 Hz)
គុណសម្បត្តិនៃ VCB:
- ការសឹករេចរឹលតិចតួចបំផុត (មានតែចំហាយដែក គ្មានប្រតិកម្មឧស្ម័ន)
- ការរំខានលឿនណាស់ (3-8 ms)
- អាយុកាលទំនាក់ទំនងយូរ (100,000+ ប្រតិបត្តិការ)
- មិនចាំបាច់ថែទាំ (បិទជិតសម្រាប់អាយុកាល)
- ទំហំបង្រួម
ដែនកំណត់:
- មានតម្លៃថ្លៃជាងឧបករណ៍បំបែកខ្យល់
- វ៉ុលមានកំណត់ (ជាធម្មតា 1-38 kV; មិនសមស្របសម្រាប់កម្មវិធីវ៉ុលទាប)
- សក្តានុពលសម្រាប់វ៉ុលលើស (ចរន្តកាត់) នៅក្នុងកម្មវិធីមួយចំនួន
VIOX ផលិត VCBs (ឧបករណ៍ទំនាក់ទំនងខ្វះចន្លោះស៊េរី VVB) សម្រាប់ការគ្រប់គ្រងម៉ូទ័រវ៉ុលមធ្យម និងកម្មវិធីប្តូរ capacitor ដែលអាយុកាលវែង និងការថែទាំតិចតួចបំផុតរបស់ពួកគេបង្ហាញអំពីភាពត្រឹមត្រូវនៃតម្លៃបុព្វលាភ។.
ឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វី SF6: ការពន្លត់ធ្នូសម្ពាធខ្ពស់
ឧបករណ៍បំបែក SF6 ប្រើឧស្ម័ន sulfur hexafluoride ដែលមានលក្ខណៈសម្បត្តិពន្លត់ធ្នូពិសេស:
- Dielectric កម្លាំង: 2-3x ខ្យល់នៅសម្ពាធដូចគ្នា
- អេឡិចត្រូត: SF6 ចាប់យកអេឡិចត្រុងដោយឥតគិតថ្លៃ ដោយធ្វើឱ្យធ្នូចុះខ្សោយយ៉ាងឆាប់រហ័ស
- ចរន្តកំដៅ: ធ្វើឱ្យត្រជាក់ប្លាស្មាធ្នូប្រកបដោយប្រសិទ្ធភាព
ការផុតពូជ Arc:
ធ្នូបង្កើតជា SF6 ដែលមានសម្ពាធ (2-6 bar) ។ នៅសូន្យបច្ចុប្បន្ន SF6 យកកំដៅចេញយ៉ាងឆាប់រហ័ស និងចាប់យកអេឡិចត្រុង ដែលអនុញ្ញាតឱ្យការងើបឡើងវិញនៃ dielectric ក្នុងរយៈពេលមីក្រូវិនាទី។ ប្រើជាចម្បងនៅក្នុងកម្មវិធីវ៉ុលខ្ពស់ (>72 kV) និងឧបករណ៍បំបែកវ៉ុលមធ្យមមួយចំនួន។.
ការពិចារណាអំពីបរិស្ថាន: SF6 គឺជាឧស្ម័នផ្ទះកញ្ចក់ដ៏ខ្លាំងក្លា (23,500× CO2 លើសពី 100 ឆ្នាំ) ដែលនាំឱ្យមានការផ្លាស់ប្តូរឧស្សាហកម្មឆ្ពោះទៅរកខ្វះចន្លោះ និងជម្រើសជំនួសខ្យល់។ VIOX មិនផលិតឧបករណ៍បំបែក SF6 ទេ ដោយផ្តោតលើបច្ចេកវិទ្យាខ្យល់ និងខ្វះចន្លោះដែលមិនប៉ះពាល់ដល់បរិស្ថាន។.
ការវាយតម្លៃធន់នឹងធ្នូ និងស្តង់ដាររបស់ឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វី
ការជ្រើសរើសឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វីតម្រូវឱ្យមានការយល់ដឹងអំពីការវាយតម្លៃទាក់ទងនឹងធ្នូដែលបានធ្វើស្តង់ដារដែលកំណត់សមត្ថភាពរបស់ឧបករណ៍បំលែងក្នុងការរំខានចរន្តកំហុសដោយសុវត្ថិភាព។ ការវាយតម្លៃទាំងនេះប្រែប្រួលរវាងតំបន់ និងអង្គការស្តង់ដារ ប៉ុន្តែទាំងអស់ដោះស្រាយសំណួរសំខាន់ដូចគ្នា៖ តើឧបករណ៍បំលែងនេះអាចពន្លត់ធ្នូដោយសុវត្ថិភាពនៅពេលរំខានចរន្តកំហុសអតិបរមាដែលមានដែរឬទេ?
សមត្ថភាពរំខាន (Breaking Capacity)
សមត្ថភាពរំខាន គឺជាចរន្តកំហុសអតិបរមាដែលឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វីអាចរំខានដោយសុវត្ថិភាពដោយមិនមានការខូចខាត ឬបរាជ័យ។ ការវាយតម្លៃនេះតំណាងឱ្យសេណារីយ៉ូដ៏អាក្រក់បំផុត៖ សៀគ្វីខ្លី (កំហុស impedance សូន្យ) កើតឡើងនៅស្ថានីយឧបករណ៍បំលែង។.
ស្តង់ដារ IEC (IEC 60947-2 សម្រាប់ MCCB):
- Icu (សមត្ថភាពបំបែកសៀគ្វីខ្លីចុងក្រោយ)៖ ចរន្តកំហុសអតិបរមាដែលឧបករណ៍បំលែងអាចរំខានបានម្តង។ បន្ទាប់ពីការរំខាន Icu ឧបករណ៍បំលែងអាចតម្រូវឱ្យមានការត្រួតពិនិត្យ ឬការជំនួស។ បង្ហាញជា kA (គីឡូអំពែរ)។.
- Ics (សមត្ថភាពបំបែកសៀគ្វីខ្លីសេវាកម្ម)៖ ចរន្តកំហុសដែលឧបករណ៍បំលែងអាចរំខានបានច្រើនដង (ជាធម្មតា 3 ប្រតិបត្តិការ) ហើយបន្តដំណើរការជាធម្មតា។ ជាធម្មតា 25%, 50%, 75% ឬ 100% នៃ Icu ។.
ស្តង់ដារ UL/ANSI (UL 489 សម្រាប់ MCCB):
- Interrupting Rating (IR or AIC)៖ ការវាយតម្លៃតែមួយដែលបង្ហាញជាអំពែរ (ឧទាហរណ៍ 65,000 A ឬ “65kA”)។ ឧបករណ៍បំលែងត្រូវតែរំខានកម្រិតចរន្តនេះ ហើយឆ្លងកាត់ការធ្វើតេស្តជាបន្តបន្ទាប់ដោយមិនបរាជ័យ។ ជាទូទៅអាចប្រៀបធៀបទៅនឹង IEC Icu ។.
ជួរផលិតផល VIOX:
| ប្រភេទឧបករណ៍បំបែក | ទំហំស៊ុមធម្មតា | ជួរសមត្ថភាពរំខាន VIOX | ការអនុលោមតាមស្តង់ដារ |
| MCB | 6-63A | 6 kA, 10 kA | IEC 60898-1, EN 60898-1 |
| MCCB | 16-1600A | 35 kA, 50 kA, 65 kA, 85 kA | IEC 60947-2, UL 489 |
| ACB | 800-6300A | 50 kA, 65 kA, 80 kA, 100 kA | IEC 60947-2, UL 857 |
ការណែនាំអំពីការជ្រើសរើស៖ សមត្ថភាពរំខានរបស់ឧបករណ៍បំលែងត្រូវតែលើសពី ចរន្តកំហុសដែលអាចប្រើបាន (ត្រូវបានគេហៅផងដែរថា ចរន្តសៀគ្វីខ្លីដែលមានសក្តានុពល) នៅចំណុចដំឡើង។ ចរន្តកំហុសនេះត្រូវបានគណនាដោយផ្អែកលើសមត្ថភាពឧបករណ៍បំលែងរបស់ក្រុមហ៊ុនផ្គត់ផ្គង់, impedances ខ្សែ និង impedance ប្រភព។ ការដំឡើងឧបករណ៍បំលែងដែលមានសមត្ថភាពរំខានមិនគ្រប់គ្រាន់ បណ្តាលឱ្យមានការបរាជ័យយ៉ាងធ្ងន់ធ្ងរក្នុងអំឡុងពេលមានកំហុស—ធ្នូមិនអាចពន្លត់បាន, ឧបករណ៍បំលែងផ្ទុះ និងភ្លើង/របួសកើតឡើង។.
VIOX ណែនាំឱ្យមានរឹមសុវត្ថិភាព៖ បញ្ជាក់ឧបករណ៍បំលែងដែលត្រូវបានវាយតម្លៃយ៉ាងហោចណាស់ 125% នៃចរន្តកំហុសដែលអាចប្រើបានដែលបានគណនា ដើម្បីគណនាសម្រាប់ការផ្លាស់ប្តូរប្រព័ន្ធឧបករណ៍ប្រើប្រាស់ និងភាពមិនច្បាស់លាស់នៃការគណនា។.
ការវាយតម្លៃចរន្តទប់ទល់រយៈពេលខ្លី
សម្រាប់ ការសម្របសម្រួលជ្រើសរើស នៅក្នុងប្រព័ន្ធការពារ cascaded ឧបករណ៍បំលែងមួយចំនួន (ជាពិសេស ACBs និង MCCB ដែលមាន electronic-trip) រួមបញ្ចូលការកំណត់ការពន្យាពេលរយៈពេលខ្លី ដែលទប់ទល់នឹងចរន្តកំហុសដោយចេតនាសម្រាប់រយៈពេលខ្លី (0.1-1.0 វិនាទី) ដើម្បីអនុញ្ញាតឱ្យឧបករណ៍បំលែងនៅផ្នែកខាងក្រោមធ្វើដំណើរមុន។.
Icw (IEC 60947-2)៖ ការវាយតម្លៃចរន្តទប់ទល់រយៈពេលខ្លី។ ឧបករណ៍បំលែងអាចផ្ទុកចរន្តកំហុសនេះសម្រាប់រយៈពេលដែលបានបញ្ជាក់ (ឧទាហរណ៍ 1 វិនាទី) ដោយមិនធ្វើដំណើរ ឬខូចខាត ដែលអនុញ្ញាតឱ្យមានការសម្របសម្រួលជាមួយឧបករណ៍នៅផ្នែកខាងក្រោម។.
ម៉ូដែល VIOX ACB ជាមួយ LSI (Long-time, Short-time, Instantaneous) trip units ផ្តល់នូវការកំណត់រយៈពេលខ្លីដែលអាចលៃតម្រូវបាន (0.1-0.4s) និងការវាយតម្លៃ Icw នៃ 30-85 kA ដែលអនុញ្ញាតឱ្យមានការសម្របសម្រួលជ្រើសរើសនៅក្នុងប្រព័ន្ធចែកចាយឧស្សាហកម្ម។.
ថាមពលឧប្បត្តិហេតុ Arc Flash និងស្លាកសញ្ញា
លើសពីការវាយតម្លៃរបស់ឧបករណ៍បំលែងផ្ទាល់, គ្រោះថ្នាក់ arc flash តម្រូវការដាក់ស្លាក (យោងតាម NEC 110.16, NFPA 70E និង IEEE 1584) តម្រូវឱ្យឧបករណ៍អគ្គិសនីបង្ហាញ ចរន្តកំហុសដែលអាចប្រើបាន និង ពេលវេលាបោសសំអាត ដើម្បីបើកដំណើរការព្រំដែន arc flash និងការគណនាថាមពលឧប្បត្តិហេតុ។.
VIOX ដឹកជញ្ជូនឧបករណ៍បំលែងទាំងអស់ជាមួយនឹងឯកសារដើម្បីគាំទ្រការដាក់ស្លាក arc flash៖
- ការវាយតម្លៃចរន្តកំហុសអតិបរមាដែលអាចប្រើបាន
- ពេលវេលាជម្រះធម្មតានៅកម្រិតចរន្តកំហុសផ្សេងៗគ្នា (ពីខ្សែកោងពេលវេលា-ចរន្ត)
- អនុញ្ញាតឱ្យឆ្លងកាត់តម្លៃ I²t សម្រាប់ឧបករណ៍បំលែងកម្រិតចរន្ត
អ្នកម៉ៅការអគ្គិសនី និងវិស្វករប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យនេះជាមួយនឹងកម្មវិធីគណនា arc flash ដើម្បីកំណត់ថាមពលឧប្បត្តិហេតុ (cal/cm²) និងបង្កើតចម្ងាយធ្វើការប្រកបដោយសុវត្ថិភាព និងតម្រូវការ PPE ។.
ការធ្វើតេស្តនិងវិញ្ញាបនប័ត្រ
ឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វី VIOX ទាំងអស់ឆ្លងកាត់ការធ្វើតេស្ត និងវិញ្ញាបនប័ត្រភាគីទីបី ដើម្បីផ្ទៀងផ្ទាត់ដំណើរការរំខានធ្នូ៖
ការធ្វើតេស្តប្រភេទ (យោងតាម IEC 60947-2 និង UL 489)៖
- លំដាប់តេស្តសៀគ្វីខ្លី៖ ឧបករណ៍បំលែងរំខានចរន្តកំហុសដែលបានវាយតម្លៃច្រើនដង (“O-t-CO” sequence: Open, time delay, Close-Open) ដើម្បីផ្ទៀងផ្ទាត់ទំនាក់ទំនង arcing និងភាពធន់នៃបន្ទប់ធ្នូ
- ការធ្វើតេស្តកើនឡើងសីតុណ្ហភាព៖ បញ្ជាក់ថាទំនាក់ទំនង arcing និងបន្ទប់ធ្នូមិនឡើងកំដៅខ្លាំងពេកក្នុងអំឡុងពេលប្រតិបត្តិការធម្មតា
- ការធ្វើតេស្ត endurance៖ ប្រតិបត្តិការមេកានិច 4,000-10,000 បូកនឹងប្រតិបត្តិការអគ្គិសនីដែលបានវាយតម្លៃ ផ្ទៀងផ្ទាត់អាយុកាលទំនាក់ទំនង
- ការធ្វើតេស្ត Dielectric៖ ការធ្វើតេស្តវ៉ុលខ្ពស់បញ្ជាក់ថាអ៊ីសូឡង់ដែលខូចដោយធ្នូររក្សាបាននូវគម្លាត
ការធ្វើតេស្តជាប្រចាំ (គ្រប់អង្គភាពផលិតកម្ម)៖
- ការផ្ទៀងផ្ទាត់ចរន្តធ្វើដំណើរ
- ការវាស់វែងធន់នឹងទំនាក់ទំនង
- ការត្រួតពិនិត្យមើលឃើញនៃទំនាក់ទំនង arcing និង arc chutes
- ការធ្វើតេស្ត Hi-pot dielectric
ប្រព័ន្ធគ្រប់គ្រងគុណភាពរបស់ VIOX (ISO 9001:2015 certified) តម្រូវឱ្យមានការយកគំរូតាមបាច់ និងការធ្វើតេស្តយោងតាម IEC 60947-2 Annex B ជាមួយនឹងការតាមដានពេញលេញពីសមាសធាតុបន្ទប់ធ្នូរហូតដល់ការផ្គុំចុងក្រោយ។.
ការជ្រើសរើសឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វីសម្រាប់ដំណើរការធ្នូ និងកម្មវិធី
ការជ្រើសរើសឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វីត្រឹមត្រូវដោយពិចារណាលើឥរិយាបថធ្នូ ធានាបាននូវការរំខានប្រកបដោយសុវត្ថិភាព និងអាចទុកចិត្តបានពេញមួយអាយុកាលនៃការដំឡើង។ អនុវត្តតាមវិធីសាស្រ្តជាប្រព័ន្ធនេះ៖
ជំហានទី 1: កំណត់ចរន្តកំហុសដែលអាចប្រើបាន
គណនា ឬវាស់ស្ទង់ចរន្តកាត់សៀគ្វីខ្លីនៅចំណុចដំឡើងឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វី។ វិធីសាស្រ្ត:
វិធីសាស្រ្តគណនា:
- ទទួលបានកម្រិត kVA និង impedance របស់ឧបករណ៍បំលែងចរន្ត (ជាទូទៅ 4-8%)
- គណនាផ្លាស់ទីកំហុសបច្ចុប្បន្ន៖I_fault=kVA/(√៣×V×Z%)
- បន្ថែម impedance ខ្សែពីឧបករណ៍បំលែងទៅទីតាំងឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វី
- គណនាប្រភពស្របគ្នា (ម៉ាស៊ីនភ្លើង, ឧបករណ៍បញ្ជូនផ្សេងទៀត)
វិធីសាស្រ្តវាស់ស្ទង់:
ប្រើឧបករណ៍វិភាគចរន្តកំហុស ឬឧបករណ៍វាស់ស្ទង់ចរន្តកាត់សៀគ្វីខ្លីនៅចំណុចដំឡើង (តម្រូវឱ្យមានការធ្វើតេស្តដោយគ្មានថាមពល ឬឧបករណ៍ផ្ទាល់ពិសេស)។.
វិធីសាស្រ្តទិន្នន័យឧបករណ៍ប្រើប្រាស់:
ស្នើសុំទិន្នន័យចរន្តកំហុសដែលមានពីឧបករណ៍ប្រើប្រាស់អគ្គិសនីសម្រាប់ច្រកចូលសេវាកម្ម។.
សម្រាប់កម្មវិធីអតិថិជន VIOX ធម្មតា:
- លំនៅដ្ឋាន: 10-22 kA ធម្មតា
- អគារពាណិជ្ជកម្ម: 25-42 kA ធម្មតា
- គ្រឿងបរិក្ខារឧស្សាហកម្ម: 35-100 kA (រហូតដល់ 200 kA នៅជិតឧបករណ៍បំលែងធំ)
ជំហានទី 2: ជ្រើសរើសសមត្ថភាពរំខានជាមួយនឹងរឹមសុវត្ថិភាព
ជ្រើសរើសកម្រិត Icu/AIC របស់ឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វី ≥ 1.25 × ចរន្តកំហុសដែលអាចប្រើបាន។.
ឧទាហរណ៍: ចរន្តកំហុសដែលអាចប្រើបាន = 38 kA → បញ្ជាក់ឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វីដែលមានកម្រិត ≥ 48 kA → MCCB ស៊េរី VIOX VPM1 ដែលមានកម្រិត 50 kA គឺសមរម្យ។.
ជំហានទី 3: វាយតម្លៃថាមពលធ្នូ និងដែនកំណត់ចរន្ត
សម្រាប់ការការពារឧបករណ៍ដែលងាយរងគ្រោះ (គ្រឿងអេឡិចត្រូនិច, ឧបករណ៍បញ្ជាប្រេកង់អថេរ, ប្រព័ន្ធគ្រប់គ្រង), ពិចារណា ឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វីកំណត់ចរន្ត ដែលកាត់បន្ថយថាមពលដែលអនុញ្ញាតឱ្យឆ្លងកាត់:
ដំណើរការកំណត់ចរន្ត: MCCB ស៊េរី VIOX CLM ជាមួយនឹងបំពង់ធ្នូកំណត់ចរន្តសម្រេចបាន:
- ចរន្តអនុញ្ញាតឱ្យឆ្លងកាត់កំពូល: 30-45% នៃចរន្តកំហុសដែលរំពឹងទុក
- I²t អនុញ្ញាតឱ្យឆ្លងកាត់: 15-25% នៃថាមពល I²t ដែលរំពឹងទុក
- ដែនកំណត់កើតឡើងក្នុងរយៈពេល 2-5 ms ដំបូង (តិចជាង 1/4 វដ្តនៅ 60 Hz)
ការកាត់បន្ថយថាមពលយ៉ាងខ្លាំងនេះការពារខ្សែ, បារឡាន, និងឧបករណ៍ពីភាពតានតឹងកម្ដៅ និងមេកានិច។.
ជំហានទី 4: ពិចារណាអំពីសុវត្ថិភាពពន្លឺផ្លេកបន្ទោរ និងលទ្ធភាពទទួលបាន
នៅទីតាំងដែលកម្មករត្រូវចូលប្រើឧបករណ៍ដែលមានថាមពល:
- បញ្ជាក់ឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វីជាមួយនឹងស្រោមការពារធ្នូ ឬយន្តការដាក់ធ្នើរពីចម្ងាយ
- ប្រើអង្គភាពធ្វើដំណើរអេឡិចត្រូនិចជាមួយនឹងការចាក់សោរតំបន់ជ្រើសរើស (ZSI) សម្រាប់ការសម្អាតកំហុសលឿនជាងមុន
- ពិចារណាបញ្ជូនតពន្លឺផ្លេកបន្ទោរជាមួយនឹងការរកឃើញអុបទិកសម្រាប់ការធ្វើដំណើរលឿនបំផុត (2-5 ms)
- ដំឡើងស្លាកសញ្ញាព្រមានពន្លឺផ្លេកបន្ទោរ និងបង្កើតនីតិវិធីសុវត្ថិភាពយោងតាម NFPA 70E
ម៉ូដែល VIOX ACB ជាមួយនឹងយន្តការទាញចេញអនុញ្ញាតឱ្យដកឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វីចេញ ខណៈពេលដែលរក្សាការតម្រឹមបន្ទប់ធ្នូ និងសុវត្ថិភាព—សំខាន់សម្រាប់ការថែទាំនៅក្នុងប្រព័ន្ធថាមពលខ្ពស់។.
ជំហានទី 5: បញ្ជាក់សម្ភារៈទំនាក់ទំនងធ្នូ និងចន្លោះពេលថែទាំ
សម្រាប់កម្មវិធីដែលមានកាតព្វកិច្ចខ្ពស់ (ការប្តូរញឹកញាប់, បរិស្ថានចរន្តកំហុសខ្ពស់):
ទំនាក់ទំនងធ្នូដែលបានពង្រឹង: បញ្ជាក់សមាសភាព tungsten-copper ជាមួយនឹងម៉ាស់កើនឡើង
ចន្លោះពេលត្រួតពិនិត្យ: ការណែនាំរបស់ VIOX ផ្អែកលើកម្មវិធី:
| វដ្តកាតព្វកិច្ច | ការត្រួតពិនិត្យក្នុងមួយឆ្នាំ | អាយុកាលរំពឹងទុកនៃទំនាក់ទំនងធ្នូ |
| ពន្លឺ (លំនៅដ្ឋាន, ការិយាល័យពាណិជ្ជកម្ម) | 0 (មើលឃើញតែប៉ុណ្ណោះ) | 20-30 ឆ្នាំ |
| មធ្យម (លក់រាយ, ឧស្សាហកម្មស្រាល) | ជារៀងរាល់ ៣-៥ ឆ្នាំ | 10-20 ឆ្នាំ។ |
| ធ្ងន់ (ការផលិត, ការចាប់ផ្តើមដដែលៗ) | ប្រចាំឆ្នាំ | ៥-១០ ឆ្នាំ។ |
| ធ្ងន់ធ្ងរ (ឧបករណ៍ប្តូរសំខាន់, ការប៉ះពាល់កំហុសខ្ពស់) | រៀងរាល់ 6 ខែម្តង | 2-5 ឆ្នាំ ឬបន្ទាប់ពីកំហុសធំ |
ជំហានទី 6: ផ្ទៀងផ្ទាត់ការសម្របសម្រួល និងការជ្រើសរើស
គ្រោងខ្សែកោងពេលវេលា-ចរន្ត ដើម្បីធានាបាននូវការសម្របសម្រួលធ្នូ-កំហុសត្រឹមត្រូវ:
- ឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វីនៅផ្នែកខាងលើមិនគួរធ្វើដំណើរមុនឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វីនៅផ្នែកខាងក្រោមក្នុងអំឡុងពេលមានកំហុស
- រឹមពេលវេលាគ្រប់គ្រាន់ (ជាធម្មតា 0.2-0.4 វិនាទី) រវាងខ្សែកោង
- គណនាពេលវេលាធ្នូរបស់ឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វី និងផលប៉ះពាល់នៃការកំណត់ចរន្ត
VIOX ផ្តល់ទិន្នន័យ TCC (ខ្សែកោងពេលវេលា-ចរន្ត) និងកម្មវិធីសម្របសម្រួលដើម្បីសម្រួលដល់ការវិភាគការជ្រើសរើស។.
ការថែទាំ, ការត្រួតពិនិត្យ និងការដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដែលទាក់ទងនឹងធ្នូ
ការថែទាំត្រឹមត្រូវពង្រីកអាយុកាលទំនាក់ទំនងធ្នូ, រក្សាសមត្ថភាពរំខាន, និងការពារការបរាជ័យដែលទាក់ទងនឹងធ្នូ។.
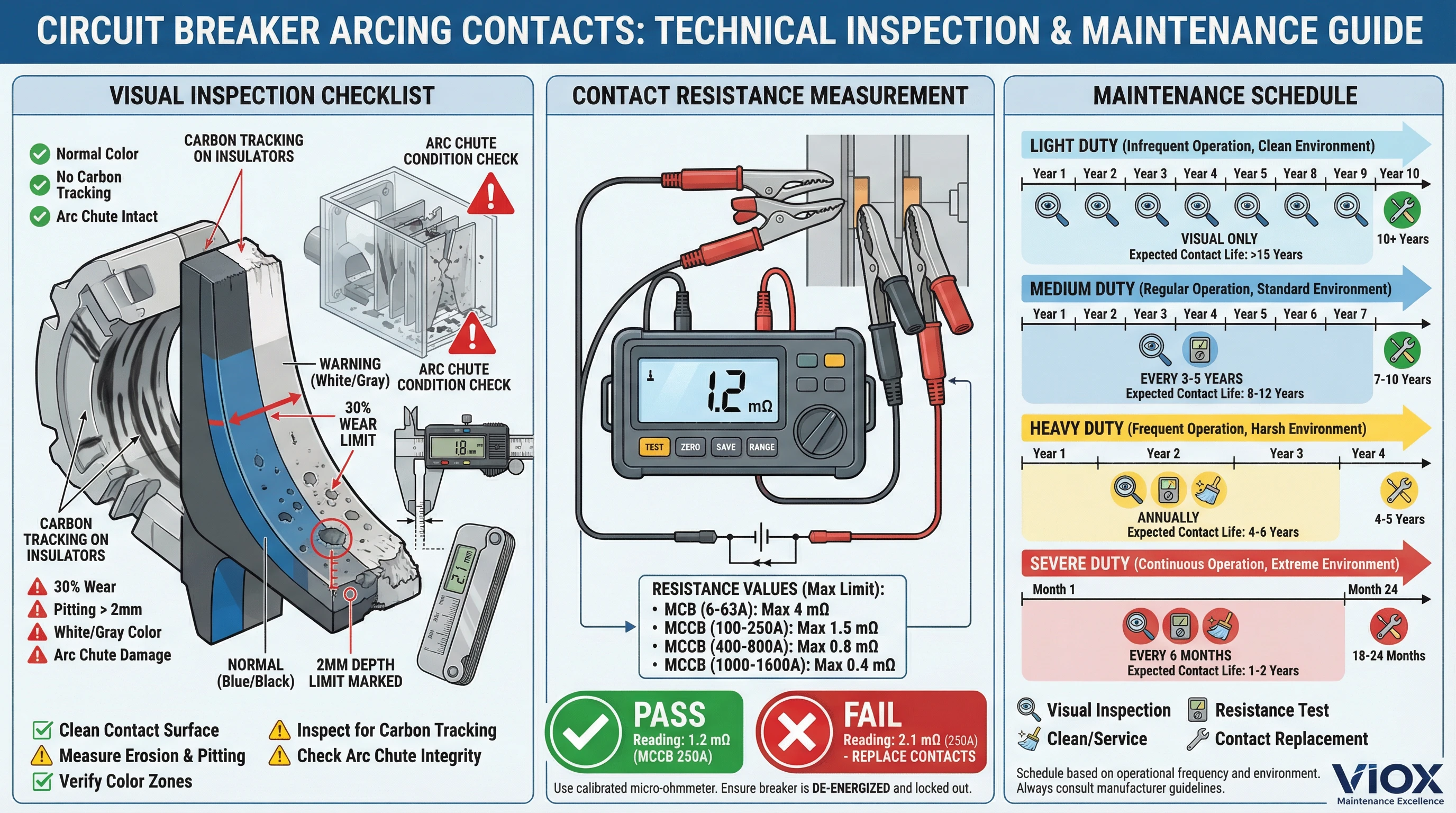
ការត្រួតពិនិត្យមើលឃើញនៃទំនាក់ទំនងធ្នូ
អនុវត្តការត្រួតពិនិត្យមើលឃើញក្នុងអំឡុងពេលថែទាំដែលបានកំណត់ពេល (ឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វីត្រូវបានបិទថាមពល និងដកចេញ):
អ្វីដែលត្រូវរកមើល:
- ការ erosion ទំនាក់ទំនង: ការបាត់បង់សម្ភារៈពីគន្លឹះទំនាក់ទំនងធ្នូ—អាចទទួលយកបានប្រសិនបើ <30% នៃសម្ភារៈដើមនៅសល់
- ការរលេះរលួយ និងការកើតរណ្ដៅ៖ រណ្ដៅជ្រៅបង្ហាញពីការឆាបឆេះខ្លាំង; ជំនួសប្រសិនជម្រៅរណ្ដៅ > 2mm
- ការប្រែពណ៌៖ ការកត់សុីពណ៌ខៀវ/ខ្មៅគឺជារឿងធម្មតា; សំណល់ពណ៌ស/ប្រផេះបង្ហាញពីកំដៅខ្លាំងពេក
- ចរន្តកាបូន៖ ផ្លូវកាបូនចម្លងនៅលើអ៊ីសូឡង់ពីផ្លាស្មាម៉ាស៊ីន - សម្អាតឬជំនួសផ្នែកដែលរងផលប៉ះពាល់
- ការខូចទ្រង់ទ្រាយ ឬរលាយ៖ បង្ហាញពីថាមពលម៉ាស៊ីនខ្លាំងពេក ឬការរលត់ម៉ាស៊ីនបរាជ័យ - ជំនួសឧបករណ៍បំលែង
- ការខូចខាតបន្ទប់ពន្លត់ធ្នូអគ្គីសនី៖ បន្ទះបំបែកខូច របាំងរលាយ ឬការប្រមូលផ្តុំកំទេចកំទី - សម្អាត ឬជំនួសបន្ទប់ធ្នូ
ឧបករណ៍ត្រួតពិនិត្យ VIOX៖ រង្វាស់កម្រាស់ទំនាក់ទំនង និងគំរូកំណត់ការពាក់ អាចរកបានសម្រាប់ម៉ូដែល MCCB/ACB ទាំងអស់ដើម្បីកំណត់បរិមាណសំណឹក។.
ការវាស់ស្ទង់ភាពធន់ទ្រាំទំនាក់ទំនង
វាស់ភាពធន់ទ្រាំឆ្លងកាត់បង្គោលនីមួយៗដោយប្រើមីក្រូអូមម៉ែត្រ (អូមម៉ែត្រធន់ទ្រាំទាបឌីជីថល)៖
តម្លៃដែលអាចទទួលយកបាន (ឧបករណ៍បំលែង VIOX យោងតាម IEC 60947-2)៖
| ទំហំស៊ុមឧបករណ៍បំលែង | ភាពធន់ទ្រាំទំនាក់ទំនងថ្មី | អតិបរមាដែលអាចអនុញ្ញាតបាន |
| MCB (6-63A) | 0.5-2 mΩ | 4 mΩ |
| MCCB (100-250A) | 0.1-0.5 mΩ | 1.5 mΩ |
| MCCB (400-800A) | 0.05-0.2 mΩ | 0.8 mΩ |
| MCCB (1000-1600A) | 0.02-0.1 mΩ | 0.4 mΩ |
| ACB (1600-3200A) | 0.01-0.05 mΩ | 0.2 mΩ |
ការកើនឡើងភាពធន់ទ្រាំទំនាក់ទំនងបង្ហាញពី៖
- សំណឹកទំនាក់ទំនងម៉ាស៊ីន
- ការចម្លងរោគ ឬការកត់សុីទំនាក់ទំនងសំខាន់
- ការកាត់បន្ថយសម្ពាធទំនាក់ទំនង (ប្រភពទឹកដែលពាក់)
- ការខុសប្រក្រតី
ប្រសិនបើភាពធន់ទ្រាំលើសពីអតិបរមាដែលអាចអនុញ្ញាតបាន សូមជំនួសទំនាក់ទំនងម៉ាស៊ីន ឬឧបករណ៍បំលែងទាំងមូល អាស្រ័យលើម៉ូដែល និងលទ្ធភាពជួសជុល។.
ការដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដែលទាក់ទងនឹងធ្នូអគ្គីសនី
បញ្ហា៖ ឧបករណ៍បំលែងធ្វើដំណើរភ្លាមៗនៅពេលបិទលើបន្ទុក
- ដែលអាចធ្វើមូលហេតុ៖ សៀគ្វីខ្លីនៅផ្នែកខាងក្រោម (ផ្ទៀងផ្ទាត់ជាមួយការធ្វើតេស្តមេហ្គាអូមម៉ែត្រ), ការកំណត់ដំណើរកំសាន្តភ្លាមៗទាបពេក, ទំនាក់ទំនងម៉ាស៊ីនដែលពាក់ដែលបណ្តាលឱ្យមានភាពធន់ទ្រាំដំបូងខ្ពស់ និងចរន្តចូល
- ដំណោះស្រាយ៖ ញែកបន្ទុកផ្នែកខាងក្រោម, សាកល្បងភាពបន្តនៃសៀគ្វី, ត្រួតពិនិត្យទំនាក់ទំនងម៉ាស៊ីន
បញ្ហា៖ ធ្នូអគ្គីសនីដែលអាចមើលឃើញក្នុងអំឡុងពេលប្រតិបត្តិការធម្មតា
- ដែលអាចធ្វើមូលហេតុ៖ ទំនាក់ទំនងសំខាន់មិនបិទត្រឹមត្រូវ (ទំនាក់ទំនងម៉ាស៊ីនផ្ទុកចរន្តបន្ត), ការតភ្ជាប់រលុងនៅស្ថានីយឧបករណ៍បំលែង, ការចម្លងរោគទំនាក់ទំនងកាត់បន្ថយចរន្តអគ្គិសនី, ការខុសប្រក្រតីមេកានិច
- ដំណោះស្រាយ៖ បិទថាមពលភ្លាមៗ ហើយត្រួតពិនិត្យ។ ធ្នូអគ្គីសនីក្នុងអំឡុងពេលប្រតិបត្តិការធម្មតាបង្ហាញពីការបរាជ័យជិតមកដល់ - ជំនួសឧបករណ៍បំលែង។.
បញ្ហា៖ ឧបករណ៍បំលែងបរាជ័យក្នុងការរំខានកំហុស
- ដែលអាចធ្វើមូលហេតុ៖ ចរន្តកំហុសលើសពីកម្រិតរំខាន (ធ្នូមិនអាចពន្លត់បាន), សំណឹកទំនាក់ទំនងម៉ាស៊ីនធ្ងន់ធ្ងរ, ការខូចខាត ឬការស្ទះបន្ទប់ធ្នូ, ការចម្លងរោគនៅក្នុងរន្ធធ្នូ (ភាគល្អិតលោហៈខ្លីបន្ទះបំបែក)
- ដំណោះស្រាយ៖ ជំនួសឧបករណ៍បំលែងភ្លាមៗ។ ការបរាជ័យក្នុងការរំខានបង្ហាញពីគ្រោះថ្នាក់សុវត្ថិភាពធ្ងន់ធ្ងរ។.
បញ្ហា៖ ក្លិនឆេះ ឬផ្សែងចេញពីឧបករណ៍បំលែងកំឡុងពេលរំខានកំហុស
- ដែលអាចធ្វើមូលហេតុ៖ ផលិតផលធ្នូធម្មតា (អូហ្សូន, NOx) ប្រសិនបើកើតឡើងម្តងក្នុងអំឡុងពេលការដកកំហុស, Pyrolysis អ៊ីសូឡង់សរីរាង្គប្រសិនបើថាមពលធ្នូច្រើនហួសប្រមាណ, កំដៅផ្នែកខាងក្នុង
- ដំណោះស្រាយ៖ ប្រសិនបើព្រឹត្តិការណ៍តែមួយក្នុងអំឡុងពេលការដកកំហុស សូមអនុវត្តការត្រួតពិនិត្យក្រោយការរំខាន យោងតាម IEC 60947-2 (មើលឃើញ ភាពធន់ទ្រាំ, dielectric) ។ ប្រសិនបើធ្វើម្តងទៀត ឬក្នុងអំឡុងពេលប្រតិបត្តិការធម្មតា សូមជំនួសឧបករណ៍បំលែង។.
ពេលណាត្រូវជំនួសឧបករណ៍បំលែងបន្ទាប់ពីការប៉ះពាល់នឹងធ្នូ
VIOX ណែនាំឱ្យជំនួសឧបករណ៍បំលែងក្រោមលក្ខខណ្ឌទាំងនេះ៖
- ការរំខាននៃ ≥80% នៃ Icu ដែលបានវាយតម្លៃ៖ ការរំខានតែមួយដងនៅជិតសមត្ថភាពបណ្តាលឱ្យមានសំណឹកទំនាក់ទំនងម៉ាស៊ីនធ្ងន់ធ្ងរ
- ការរំខានច្រើនដង ≥50% Icu៖ ការខូចខាតកកកុញលើសពីអាយុកាលរចនា
- សំណឹកទំនាក់ទំនងដែលអាចមើលឃើញ >30%៖ សម្ភារៈមិនគ្រប់គ្រាន់នៅសល់សម្រាប់ការរំខាននាពេលអនាគតដែលអាចទុកចិត្តបាន
- ភាពធន់ទ្រាំទំនាក់ទំនងលើសពីអតិបរមា៖ បង្ហាញពីផ្លូវចរន្តដែលខូច
- ការខូចខាតបន្ទប់ធ្នូ៖ បន្ទះបំបែកខូច គ្រឿងផ្សំរលាយ
- អាយុ >20 ឆ្នាំក្នុងការប្រើប្រាស់៖ ទោះបីជាគ្មានកំហុសក៏ដោយ ការចាស់នៃសម្ភារៈប៉ះពាល់ដល់ការរលត់នៃធ្នូអគ្គិសនី
អតិថិជនពាណិជ្ជកម្ម/ឧស្សាហកម្ម VIOX ភាគច្រើនអនុវត្ត វដ្តនៃការជំនួស 25 ឆ្នាំ សម្រាប់ MCCB សំខាន់ៗ ដោយមិនគិតពីស្ថានភាពដែលអាចមើលឃើញ ធានាបាននូវការរំខានធ្នូអគ្គិសនីដែលអាចទុកចិត្តបាននៅពេលចាំបាច់។.
សំណួរដែលសួរញឹកញាប់៖ ធ្នូអគ្គិសនីនៅក្នុងឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វី
ហេតុអ្វីបានជាចរន្តអគ្គិសនីលោត (arcs) នៅក្នុងឧបករណ៍បំបែកសៀគ្វីមានគ្រោះថ្នាក់ខ្លាំងម្ល៉េះ?
ធ្នូអគ្គិសនីនៅក្នុងឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វីមានគ្រោះថ្នាក់ ពីព្រោះវាឡើងដល់សីតុណ្ហភាព 20,000°C — ក្តៅជាងផ្ទៃព្រះអាទិត្យ — បង្កើតជាភ្លើង ផ្ទុះ និងគ្រោះថ្នាក់ចរន្តអគ្គិសនីខ្លាំង។ ផ្លាស្មារបស់ធ្នូអគ្គិសនីអាចបញ្ឆេះសម្ភារៈងាយឆេះនៅក្បែរនោះភ្លាមៗ បង្កឲ្យធាតុដែកហួត និងបង្កើតរលកសម្ពាធលើសពី 10 bar (145 psi) ដែលបណ្តាលឲ្យប្រអប់ផ្ទុះ។ ឧប្បត្តិហេតុឆាបឆេះធ្នូអគ្គិសនី បណ្តាលឲ្យរលាកធ្ងន់ធ្ងរ ពិការភ្នែកជាអចិន្ត្រៃយ៍ដោយសារពន្លឺកាំរស្មី UV ខ្លាំង និងខូចខាតការស្តាប់ដោយសារសំឡេងផ្ទុះ (140+ dB)។ លើសពីនេះ ធ្នូអគ្គិសនីបង្កើតឧស្ម័នពុល រួមទាំងអូហ្សូន អុកស៊ីដអាសូត និងកាបូនម៉ូណូអុកស៊ីត។ បើគ្មានទំនាក់ទំនងធ្នូអគ្គិសនី និងប្រព័ន្ធរំលត់ធ្នូអគ្គិសនីត្រឹមត្រូវ ធ្នូអគ្គិសនីដែលមិនអាចគ្រប់គ្រងបានអាចរីករាលដាលតាមរយៈប្រព័ន្ធអគ្គិសនី បណ្តាលឲ្យមានការបរាជ័យជាបន្តបន្ទាប់ និងការខូចខាតទូទាំងបរិវេណ។.
តើធ្នូអគ្គិសនីមានរយៈពេលប៉ុន្មាននៅក្នុងឧបករណ៍បំបែកសៀគ្វីកំឡុងពេលរំខានដល់កំហុស?
ឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វីទំនើបរំលត់ធ្នូអគ្គិសនីក្នុងរយៈពេល 8-20 មីលីវិនាទី នៅក្នុងប្រព័ន្ធ AC (ជាធម្មតានៅត្រង់ចំណុចសូន្យនៃចរន្តទីមួយ ឬទីពីរ)។ VIOX MCCB ដែលមានបំពង់រំលត់ធ្នូអគ្គិសនីដែលបានធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើង សម្រេចបាននូវការរំខានក្នុងរយៈពេល 10-16 ms នៅចរន្តកំហុសដែលបានវាយតម្លៃ។ ឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វីខ្វះចន្លោះលឿនជាង (3-8 ms) ដោយសារតែការរលត់នៃធ្នូអគ្គិសនីយ៉ាងឆាប់រហ័សនៅក្នុងខ្វះចន្លោះ។ ទោះជាយ៉ាងណាក៏ដោយ ប្រសិនបើសមត្ថភាពរំខានរបស់ឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វីលើស ឬបន្ទប់ធ្នូអគ្គិសនីខូច ធ្នូអគ្គិសនីអាចនៅតែបន្តរាប់រយមីលីវិនាទី ឬយូរជាងនេះ បញ្ចេញថាមពលយ៉ាងច្រើន និងបណ្តាលឲ្យមានការបរាជ័យដ៏មហន្តរាយ។ រយៈពេលនៃធ្នូអគ្គិសនីមានទំនាក់ទំនងដោយផ្ទាល់ទៅនឹងការបញ្ចេញថាមពល៖ E = V × I × t ដូច្នេះការរលត់លឿនកាត់បន្ថយការខូចខាត និងគ្រោះថ្នាក់យ៉ាងខ្លាំង។.
តើអ្វីជាភាពខុសគ្នារវាង contact សម្រាប់ផ្កាភ្លើង (arcing contacts) និង contact មេ (main contacts) នៅក្នុងឧបករណ៍ breaker?
ទំនាក់ទំនងធ្នូអគ្គិសនី និងទំនាក់ទំនងមេដើរតួនាទីខុសគ្នានៅក្នុងឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វី។. ទំនាក់ទំនងមេ គឺជាទំនាក់ទំនងផ្ទៃធំ ដែលមានភាពធន់ទ្រាំទាប ដែលត្រូវបានធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងដើម្បីផ្ទុកចរន្តដែលបានវាយតម្លៃជាបន្តបន្ទាប់ ជាមួយនឹងកំដៅតិចបំផុត។ ពួកវាប្រើប្រាស់សម្ភារៈដែលមានតម្លៃថ្លៃ (យ៉ាន់ស្ព័រប្រាក់) សម្រាប់ចរន្តអគ្គិសនី និងភាពធន់។. ទំនាក់ទំនងធ្នូអគ្គិសនី គឺជាទំនាក់ទំនងបន្ទាប់បន្សំតូចជាង ដែលធ្វើពីវត្ថុធាតុធន់នឹងធ្នូអគ្គិសនី (ទង់ស្តែន-ទង់ដែង) ដែលត្រូវបានរចនាឡើងដើម្បីទប់ទល់នឹងធ្នូអគ្គិសនីដែលបំផ្លិចបំផ្លាញកំឡុងពេលរំខាន។ ភាពខុសគ្នាដ៏សំខាន់គឺពេលវេលា៖ ទំនាក់ទំនងធ្នូអគ្គិសនីបើកមុនគេ (បំបែកមុនគេ) នៅពេលដែលឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វីធ្វើដំណើរ ដោយទាញធ្នូអគ្គិសនីចេញពីទំនាក់ទំនងមេ។ ប្រតិបត្តិការបំបែកមុនគេ/បង្កើតចុងក្រោយនេះការពារទំនាក់ទំនងមេពីការខូចខាតដោយធ្នូអគ្គិសនី ពន្យារអាយុជីវិតឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វីដោយ 3-5 ដង បើប្រៀបធៀបទៅនឹងការរចនាទំនាក់ទំនងតែមួយ។ ការធ្វើតេស្ត VIOX បង្ហាញថា 60-70% នៃការបរាជ័យឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វីមិនគ្រប់ខែ បណ្តាលមកពីការបាត់ ឬសឹករេចរឹលនៃទំនាក់ទំនងធ្នូអគ្គិសនី ដែលអនុញ្ញាតឲ្យធ្នូអគ្គិសនីធ្វើឲ្យខូចខាតទំនាក់ទំនងមេ។.
តើអ្នកអាចឃើញធ្នូអគ្គិសនីបង្កើតនៅខាងក្នុងឧបករណ៍កាត់សៀគ្វីបានទេ?
អ្នកមិនគួរមើលការបង្កើតធ្នូអគ្គិសនីដោយចេតនាទេ ព្រោះកាំរស្មី UV ខ្លាំង និងពន្លឺដែលអាចមើលឃើញ (ប្រៀបធៀបទៅនឹងពន្លឺធ្នូអគ្គិសនីនៃការផ្សារដែក) អាចបណ្តាលឲ្យខូចខាតរីទីណាជាអចិន្ត្រៃយ៍ក្នុងរយៈពេលប៉ុន្មានមីលីវិនាទី — ស្ថានភាពមួយហៅថា “ភ្នែកធ្នូអគ្គិសនី” ឬ photokeratitis ។ កំឡុងពេលប្រតិបត្តិការធម្មតា ឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វីត្រូវបានបិទជិត ហើយធ្នូអគ្គិសនីកើតឡើងនៅខាងក្នុងបន្ទប់ធ្នូអគ្គិសនី ដែលមើលមិនឃើញដោយប្រតិបត្តិករ។ VIOX ប្រើកាមេរ៉ាល្បឿនលឿន ជាមួយនឹងតម្រងត្រឹមត្រូវនៅក្នុងមន្ទីរពិសោធន៍ធ្វើតេស្ត 65 kA របស់យើង ដើម្បីសិក្សាអំពីឥរិយាបថធ្នូអគ្គិសនីដោយសុវត្ថិភាព។ នៅពេលធ្វើការជាក់ស្តែង ប្រសិនបើអ្នកឃើញធ្នូអគ្គិសនី ឬពន្លឺភ្លឹបភ្លែតៗចេញពីឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វីកំឡុងពេលប្រតិបត្តិការធម្មតា (មិនមែនកំឡុងពេលសម្អាតកំហុសទេ) សូមផ្តាច់ថាមពលឧបករណ៍ភ្លាមៗ — ធ្នូអគ្គិសនីដែលអាចមើលឃើញបង្ហាញពីការបរាជ័យដ៏មហន្តរាយដែលជិតមកដល់។ កំឡុងពេលសម្អាតកំហុស ពន្លឺភ្លឹបភ្លែតៗខាងក្នុងខ្លីដែលអាចមើលឃើញតាមរយៈបង្អួចសញ្ញា គឺជារឿងធម្មតាសម្រាប់ការរំខានចរន្តខ្ពស់។.
តើវ៉ុលធ្នូមានឥទ្ធិពលយ៉ាងដូចម្តេចទៅលើការកំណត់ចរន្តរបស់ឧបករណ៍បំបែកសៀគ្វី?
វ៉ុលធ្នូអគ្គិសនី គឺជាយន្តការសំខាន់ដែលអនុញ្ញាតឲ្យឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វីកំណត់ចរន្តកាត់បន្ថយចរន្តកំហុសក្រោមកម្រិតរំពឹងទុក។ នៅពេលដែលធ្នូអគ្គិសនីពន្លូតតាមរយៈការផ្លុំចេញដោយម៉ាញ៉េទិច និងធ្វើដំណើរឆ្លងកាត់បំពង់រំលត់ធ្នូអគ្គិសនី វ៉ុលធ្នូអគ្គិសនីកើនឡើងយ៉ាងឆាប់រហ័ស (ជាធម្មតា 80-200V នៅក្នុងបន្ទប់ធ្នូអគ្គិសនី VIOX MCCB)។ វ៉ុលនេះផ្ទុយនឹងវ៉ុលប្រព័ន្ធ កាត់បន្ថយវ៉ុលសុទ្ធដែលមានដើម្បីជំរុញចរន្តកំហុស៖ I_actual = (V_system – V_arc) / Z_system ។ ដោយការអភិវឌ្ឍវ៉ុលធ្នូអគ្គិសនីខ្ពស់យ៉ាងឆាប់រហ័សក្នុងរយៈពេល 2-5 មីលីវិនាទី ឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វីកំណត់ចរន្ត សម្រេចបាននូវចរន្តអនុញ្ញាតអតិបរមាត្រឹមតែ 30-40% នៃកម្រិតកំហុសដែលរំពឹងទុក។ VIOX CLM series MCCB ប្រើប្រាស់បន្ទះបំបែកចន្លោះតូចចង្អៀត (2mm) និងផ្លូវបំពង់រំលត់ធ្នូអគ្គិសនីដែលបានពង្រីក (80-120mm) ដើម្បីបង្កើនវ៉ុលធ្នូអគ្គិសនី ការពារឧបករណ៍នៅផ្នែកខាងក្រោមពីកំដៅ (I²t) និងភាពតានតឹងផ្នែកមេកានិច (I_peak²) កំឡុងពេលមានកំហុស។.
តើអ្វីដែលធ្វើឲ្យសៀគ្វីដាច់ចរន្តអគ្គិសនីធ្ងន់ធ្ងរជាងនេះ?
ភាពធ្ងន់ធ្ងរនៃធ្នូអគ្គិសនីកើនឡើងជាមួយនឹងកត្តាច្រើន៖ ចរន្តកំហុសខ្ពស់ជាង (ថាមពលបញ្ចូលកាន់តែច្រើន), រយៈពេលធ្នូអគ្គិសនីយូរជាង (ការពន្យារពេលការរលត់), សមត្ថភាពរំខានមិនគ្រប់គ្រាន់ (ឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វីមានទំហំតូចពេកសម្រាប់ចរន្តកំហុសដែលមាន), ទំនាក់ទំនងធ្នូអគ្គិសនីកខ្វក់ ឬសឹករេចរឹល (ការបង្កើតធ្នូអគ្គិសនីមិនទៀងទាត់), គ្រឿងបន្លាស់ដែលសឹករេចរឹល (កាត់បន្ថយសម្ពាធទំនាក់ទំនង បំពង់រំលត់ធ្នូអគ្គិសនីខូច), ការដំឡើងមិនត្រឹមត្រូវ (ស្ថានីយរលុងបណ្តាលឲ្យមានធ្នូអគ្គិសនីខាងក្រៅ) និង លក្ខខណ្ឌបរិស្ថាន (សំណើមខ្ពស់កាត់បន្ថយកម្លាំង dielectric កម្ពស់ខ្ពស់កាត់បន្ថយដង់ស៊ីតេខ្យល់ដែលប៉ះពាល់ដល់ការត្រជាក់ធ្នូអគ្គិសនី)។ នៅក្នុងការវិភាគរបស់ VIOX លើឧប្បត្តិហេតុធ្នូអគ្គិសនីធ្ងន់ធ្ងរ មូលហេតុទូទៅបំផុតគឺការដំឡើងឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វីដែលមានសមត្ថភាពរំខានមិនគ្រប់គ្រាន់សម្រាប់ចរន្តកំហុសដែលមាន — នៅពេលដែលកំហុសដែលរំពឹងទុកលើសពីកម្រិត Icu របស់ឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វី ធ្នូអគ្គិសនីមិនអាចរលត់បានទេ ហើយការបរាជ័យដ៏មហន្តរាយក៏កើតឡើង។ ត្រូវប្រាកដថាផ្ទៀងផ្ទាត់ចរន្តកំហុសដែលមានជានិច្ច និងបញ្ជាក់ឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វីដែលមានកម្រិត ≥125% ខាងលើតម្លៃនោះ។.
តើឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វី AFCI ខុសពីឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វីស្តង់ដារយ៉ាងដូចម្តេចក្នុងការរកឃើញធ្នូអគ្គីសនី?
Arc Fault Circuit Interrupters (AFCIs) detect dangerous parallel arcs (line-to-neutral or line-to-ground arcing from damaged wiring, loose connections, or frayed cords) that standard breakers cannot detect because these arcs draw insufficient current to trip overcurrent protection. AFCIs use advanced electronics to analyze current waveforms for the characteristic high-frequency signatures (typically 20-100 kHz) produced by arcing—irregular, chaotic patterns distinct from normal load currents. When the AFCI detects arc signatures exceeding threshold levels and duration, it trips to prevent electrical fires. Standard circuit breakers only detect series arcs (arcs in the intentional current path during interruption) when they trip to clear faults; they cannot detect parallel arcs in branch wiring. VIOX industrial/commercial breakers focus on high-energy series arc interruption, while residential AFCI breakers (outside our product range) specialize in detecting low-energy parallel arcs that cause fires.
តើនឹងមានអ្វីកើតឡើងប្រសិនបើឧបករណ៍បំបែកសៀគ្វីមិនអាចពន្លត់ធ្នូអគ្គិសនីបាន?
ប្រសិនបើឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វីបរាជ័យក្នុងការរំលត់ធ្នូអគ្គិសនី ការបរាជ័យដ៏មហន្តរាយនឹងកើតឡើងក្នុងរយៈពេលប៉ុន្មានវិនាទី។ ធ្នូអគ្គិសនីដែលនៅតែបន្តកើតឡើង បន្តទាញចរន្តកំហុស (ដែលអាចរាប់ម៉ឺនអំពែរ) បញ្ចេញថាមពលយ៉ាងច្រើន (មេហ្គាជូលក្នុងមួយវិនាទី) ដែល៖ 1) ធ្វើឲ្យគ្រឿងបន្លាស់ខាងក្នុងរបស់ឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វីហួត និងរលាយ បង្កើតជាចំហាយលោហៈដែលបញ្ជូនចរន្តអគ្គិសនី ដែលរីករាលដាលធ្នូអគ្គិសនីពាសពេញប្រអប់។ 2) បង្កើតសម្ពាធខ្លាំង (20+ bar) ដែលធ្វើឲ្យប្រអប់ឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វីផ្ទុះ បាញ់លោហៈរលាយ និងផ្លាស្មាចេញទៅខាងក្រៅ។ 3) បញ្ឆេះសម្ភារៈជុំវិញ — ខ្សែ ខ្សែការពារ រចនាសម្ព័ន្ធអគារ — បណ្តាលឲ្យមានភ្លើងអគ្គិសនី។ 4) បង្កើតធ្នូអគ្គិសនីពីដំណាក់កាលមួយទៅដំណាក់កាលមួយ ឬពីដំណាក់កាលមួយទៅដី នៅក្នុងឧបករណ៍នៅផ្នែកខាងលើ បង្កឲ្យមានការបរាជ័យជាបន្តបន្ទាប់។ និង 5) បង្កគ្រោះថ្នាក់ឆាបឆេះធ្នូអគ្គិសនីខ្លាំងដល់បុគ្គលិកដែលនៅក្បែរនោះ ជាមួយនឹងថាមពលនៃឧប្បត្តិហេតុលើសពី 100 cal/cm²។ នេះជាមូលហេតុដែលការបញ្ជាក់សមត្ថភាពរំខានត្រឹមត្រូវមានសារៈសំខាន់។ ការធ្វើតេស្តយ៉ាងម៉ត់ចត់របស់ VIOX យោងតាម IEC 60947-2 ផ្ទៀងផ្ទាត់ថាម៉ូដែលឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វីនីមួយៗរំលត់ធ្នូអគ្គិសនីដោយអាចទុកចិត្តបានរហូតដល់កម្រិត Icu ដែលបានវាយតម្លៃ ក្រោមលក្ខខណ្ឌដ៏អាក្រក់បំផុត។.
សេចក្តីសន្និ
ធ្នូអគ្គិសនីគឺជាកម្លាំងបំផ្លិចបំផ្លាញ ប៉ុន្តែជាមួយនឹងទំនាក់ទំនងធ្នូអគ្គិសនី និងប្រព័ន្ធរំលត់ធ្នូអគ្គិសនីដែលត្រូវបានរចនាឡើងយ៉ាងជាក់លាក់ ពួកវាអាចត្រូវបានគ្រប់គ្រង។ ការយល់ដឹងអំពីរូបវិទ្យានៃធ្នូអគ្គិសនី — ពីចំណុច cathode ដល់ឌីណាមិកផ្លាស្មា — អនុញ្ញាតឲ្យវិស្វករជ្រើសរើសឧបករណ៍ការពារត្រឹមត្រូវ និងថែទាំវាសម្រាប់សុវត្ថិភាព និងភាពអាចទុកចិត្តបាន។ VIOX Electric បន្តធ្វើឲ្យបច្ចេកវិទ្យាគ្រប់គ្រងធ្នូអគ្គិសនីកាន់តែប្រសើរឡើង ធានាថាឧបករណ៍បំលែងសៀគ្វីរបស់យើងផ្តល់នូវការការពារដ៏ប្រសើរសម្រាប់ហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធអគ្គិសនីដ៏សំខាន់របស់អ្នក។.