MCB Full Form in Electrical

MCB full form is “Miniature Circuit Breaker“ – a critical electrical safety device that automatically disconnects electrical circuits when overcurrent, short circuits, or fault conditions are detected. The MCB full form represents one of the most important protective devices in modern electrical installations.
Mabilis na Sagot: MCB stands for Miniature Circuit Breaker, which protects electrical circuits from damage by automatically cutting power during dangerous electrical conditions.
Understanding the MCB full form and its applications is crucial for electrical safety, code compliance, and proper circuit protection in residential, commercial, and industrial applications.
MCB Full Form Explained: What Does MCB Stand For?
The MCB full form – Miniature Circuit Breaker – tells you exactly what this device does:
- Miniature: Compact size compared to larger circuit breakers
- Circuit: Protects electrical circuits and pathways
- Breaker: Breaks or interrupts electrical flow during faults
Other Common MCB Full Form Variations
| Abbreviation | Buong Form | Context |
|---|---|---|
| MCB | Miniature Circuit Breaker | Standard electrical term |
| MCB | Motor Circuit Breaker | Motor protection applications |
| MCB | Magnetic Circuit Breaker | Emphasizing magnetic trip mechanism |
What is MCB in Electrical Systems?
A Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB) is an automatically operated electrical switching device designed to protect electrical circuits from damage caused by overcurrent conditions, including short circuits and overload situations. Unlike traditional fuses that require replacement after operation, MCBs can be reset and reused multiple times.
Key Function: MCBs detect abnormal electrical conditions and immediately disconnect the circuit to prevent equipment damage, electrical fires, and potential electrocution hazards.
MCB vs Other Circuit Protection Devices: Complete Comparison
| Tampok | MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker) | MCCB (Molded Case Circuit Breaker) | piyus | RCD/GFCI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kasalukuyang Rating | 0.5A hanggang 125A | 100A to 2500A | 1A to 800A | 25A to 100A |
| Boltahe Rating | Up to 400V AC | Hanggang 1000V AC | Iba't-ibang | Up to 500V AC |
| Pagsira ng Kapasidad | 6kA to 25kA | 25kA to 200kA | 10kA hanggang 200kA | 6kA to 25kA |
| Oras ng Pagtugon | 0.02 to 0.05 seconds | 0.02 to 0.1 seconds | 0.001 to 1 second | 0.025 to 0.04 seconds |
| Reusability | Yes (reset after trip) | Yes (reset after trip) | No (replace after blow) | Yes (reset after trip) |
| Uri ng Proteksyon | Overcurrent & Short Circuit | Overcurrent & Short Circuit | Overcurrent & Short Circuit | Earth Fault & Residual Current |
| Gastos | Mababa hanggang Katamtaman | Katamtaman hanggang Mataas | Napakababa | Katamtaman |
| Pagpapanatili | Minimal | Regular inspection required | Replacement only | Regular testing required |
| Aplikasyon | Residential & Light Commercial | Industrial & Heavy Commercial | All applications | Safety protection only |
Mga Uri ng MCB at Ang Kanilang mga Aplikasyon
Classification by Current Characteristics
Mga Type B na MCB (3-5 beses na na-rate ang kasalukuyang)
- Application: Residential lighting and general power circuits
- Trip Range: 3In to 5In (where In = rated current)
- Use Cases: LED lighting, ceiling fans, general outlets
- Proteksyon: Moderate inrush current applications
Mga Type C na MCB (5-10 beses na kasalukuyang na-rate)
- Application: Commercial and light industrial applications
- Trip Range: 5In to 10In
- Use Cases: Mga motor, transformer, fluorescent lighting
- Proteksyon: Higher inrush current tolerance
Mga Type D MCB (10-20 beses na kasalukuyang na-rate)
- Application: Industrial motors and high inrush equipment
- Trip Range: 10In to 20In
- Use Cases: Large motors, welding equipment, X-ray machines
- Proteksyon: Very high inrush current applications
Classification by Number of Poles
| Uri ng MCB | Paglalarawan | Aplikasyon | Boltahe Rating |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single Pole (1P) | Breaks one live conductor | Single-phase AC circuits | 240V AC |
| Double Pole (2P) | Breaks live and neutral | Single-phase with neutral protection | 240V AC |
| Three Pole (3P) | Breaks three live conductors | Three-phase AC circuits | 415V AC |
| Apat na Poste (4P) | Breaks three live + neutral | Tatlong yugto na may neutral | 415V AC |
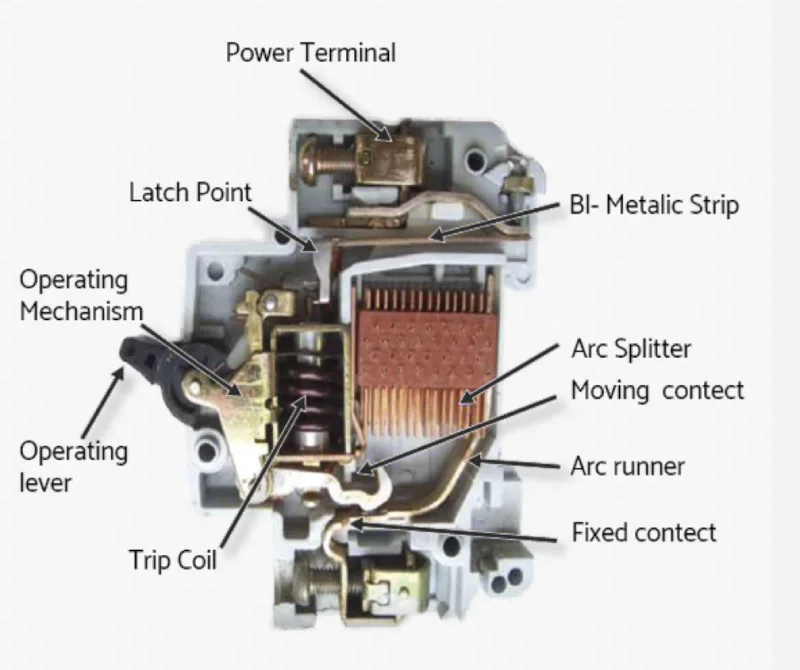
How MCBs Work: Technical Operation
Operating Mechanism
1. Thermal Protection (Sobrang karga)
- Ang bimetallic strip ay umiinit sa panahon ng matagal na overcurrent
- Strip bends and triggers trip mechanism
- Response time: 1 second to several minutes depending on overload level
2. Magnetic Protection (Short Circuit)
- Ang electromagnetic coil ay bumubuo ng magnetic field sa panahon ng mataas na kasalukuyang
- Magnetic force pulls trip mechanism instantly
- Response time: 0.02 to 0.05 seconds
3. Arc Extinction
- Arc forms when contacts separate under load
- Arc chute system extinguishes arc safely
- SF6 gas or vacuum chambers in advanced models
⚠️ Kaligtasan Babala
Always ensure power is completely disconnected before working on MCB installations. Only qualified electricians should install or replace MCBs to ensure compliance with electrical codes and safety standards.
MCB Selection Criteria: Expert Guide
Kasalukuyang Pagpili ng Rating
Step 1: Calculate Load Current
Load Current = Total Power (W) ÷ Voltage (V) For 3-phase: Load Current = Total Power (W) ÷ (√3 × Line Voltage × Power Factor)
Hakbang 2: Ilapat ang Derating Factors
- Ambient temperature derating: 0.8-1.0
- Grouping factor: 0.8-0.95
- Cable derating: As per cable manufacturer
Step 3: Select MCB Rating
- MCB rating should be ≥ 125% of calculated load current
- Must not exceed cable current carrying capacity
- Consider future load expansion (typically 20-30%)
Breaking Capacity Selection
| Uri ng Pag-install | Minimum Breaking Capacity |
|---|---|
| Residential | 6kA |
| Komersyal | 10kA |
| Pang-industriya | 25kA |
| Malakas na Pang-industriya | 50kA+ |
💡 Expert Tip
Always verify the prospective short circuit current at the point of installation using fault level calculations or measurements. The MCB breaking capacity must exceed the maximum fault current by at least 25% safety margin.
Mga Alituntunin sa Pag-install at Pag-wire
Standard Wiring Practices
Single Pole MCB Connection:
- Connect incoming live wire to MCB input terminal
- Connect outgoing live wire to MCB output terminal
- Neutral wire bypasses MCB (connects directly in distribution board)
- Earth wire connects directly to earth bar
Three Pole MCB Connection:
- Connect all three phase wires to respective MCB input terminals
- Connect load phase wires to MCB output terminals
- Maintain proper phase sequence (R-Y-B)
- Use appropriate cable size for each phase
⚠️ Code Compliance Requirements
IEC 60898 Standards:
- MCBs must comply with IEC 60898-1 for AC applications
- Mandatory short circuit and overload testing
- Temperature rise limits and insulation requirements
National Electrical Code (NEC) mga Kinakailangan:
- Article 240: Overcurrent Protection requirements
- Section 240.4: Protection of conductors
- Section 240.6: Standard ampere ratings
Installation Standards:
- Minimum clearances: 50mm on all sides
- Ambient temperature rating: -25°C to +70°C
- IP20 minimum protection rating for indoor use
Mga Karaniwang Problema at Pag-troubleshoot
Frequent MCB Tripping Issues
Problema:
MCB trips immediately after reset
Dahilan:
Short circuit in downstream wiring
Solusyon:
- Disconnect all loads from the circuit
- Test insulation resistance using megger
- Identify and repair short circuit location
- Replace damaged cables if necessary
Problema:
MCB trips after some time under load
Dahilan:
Overload condition or loose connections
Solusyon:
- Calculate actual load vs MCB rating
- Check all terminal connections for tightness
- Verify cable size adequacy for the load
- Redistribute loads or upgrade MCB rating if needed
Problema:
MCB doesn’t trip during fault conditions
Dahilan:
MCB failure or incorrect rating
Solusyon:
- Test MCB using appropriate test equipment
- Replace MCB if faulty
- Verify breaking capacity is adequate for installation
🔧 Propesyonal na Rekomendasyon
MCB testing should be performed annually in commercial installations and every 3 years in residential applications using calibrated test equipment. Any MCB that fails to trip within specified time-current characteristics should be replaced immediately.
MCB Specifications and Standards
Technical Specifications Table
| Parameter | Value Range | Pamantayang Sanggunian |
|---|---|---|
| Na-rate na Kasalukuyan | 0.5A hanggang 125A | IEC 60898-1 |
| Na-rate na Boltahe | 230V to 400V AC | IEC 60898-1 |
| Dalas | 50Hz to 60Hz | IEC 60898-1 |
| Pagsira ng Kapasidad | 6kA to 25kA | IEC 60898-1 |
| Buhay ng Elektrisidad | 10,000 operations | IEC 60898-1 |
| Buhay Mekanikal | 20,000 operations | IEC 60898-1 |
| Saklaw ng Temperatura | -25°C hanggang +70°C | IEC 60898-1 |
| Insulation Voltage | 500V AC for 1 minute | IEC 60898-1 |
Marking and Identification
Mandatory Markings:
- Manufacturer name or trademark
- Type designation and model number
- Rated current and voltage
- Pagsira ng kapasidad
- Trip characteristic (B, C, or D)
- Standards compliance (IEC 60898)
Mga Pagsasaalang-alang sa Kaligtasan at Pinakamahuhusay na Kasanayan
Installation Safety
Bago ang Pag-install:
- Verify power isolation using approved voltage tester
- Check MCB compatibility with existing equipment
- Ensure adequate breaking capacity for installation
- Verify ambient temperature rating
During Installation:
- Gumamit ng naaangkop na personal protective equipment (PPE)
- Sundin ang mga pamamaraan ng lockout/tagout
- Maintain proper torque on terminal connections
- Verify correct cable sizing and routing
Pagkatapos ng Pag-install:
- Test MCB operation using appropriate test equipment
- Verify correct labeling and circuit identification
- Document installation details and test results
- Provide operation instructions to end users
⚠️ Kritikal Na Kaligtasan Tandaan
MCBs provide protection against overcurrent conditions but do not protect against electric shock or earth faults. Install RCDs (Residual Current Devices) for comprehensive electrical safety protection.
Cost Analysis and Selection Factors
Initial Cost Comparison
| Uri ng MCB | Price Range (USD) | Kaangkupan ng Application | Lifecycle Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard MCB | $5 – $25 | Basic residential/commercial | Mababa |
| Mataas na Kapasidad ng Pagsira | $15 – $50 | Mga aplikasyon sa industriya | Katamtaman |
| Electronic MCB | $50 – $200 | Precision applications | High initial, low maintenance |
| Smart MCB | $100 – $500 | IoT and monitoring systems | High initial, reduced downtime |
💰 Cost Optimization Tips
- Select appropriate breaking capacity (don’t over-specify)
- Consider bulk purchasing for multiple installations
- Factor in long-term reliability and maintenance costs
- Evaluate smart MCB benefits for critical applications
Mga Uso at Teknolohiya sa Hinaharap
Smart MCB Technology
- IoT connectivity for remote monitoring
- Mahuhulaang mga kakayahan sa pagpapanatili
- Energy measurement and reporting
- Mobile app integration for real-time status
Mga Tampok ng Advanced na Proteksyon
- Arc fault detection at pagkagambala
- Ground fault protection integration
- Communication protocols (Modbus, BACnet)
- Data logging and analysis capabilities
Mabilis na Gabay sa Sanggunian
MCB Rating Selection Checklist
- [ ] Calculate maximum load current
- [ ] Apply appropriate derating factors
- [ ] Select MCB rating ≥ 125% of load current
- [ ] Verify cable capacity exceeds MCB rating
- [ ] Confirm breaking capacity for installation
- [ ] Check type characteristic (B, C, or D)
- [ ] Verify voltage and frequency ratings
- [ ] Consider future load expansion
Mga Pamamaraang Pang-emergency
- MCB Won’t Reset: Check for short circuit, remove all loads, inspect wiring
- Madalas na Pag-trip: Verify load calculations, check connections, test insulation
- No Power After Reset: Check downstream connections, verify MCB operation
- Burning Smell: Immediately disconnect power, inspect for damage, replace if needed
Frequently Asked Questions About MCB Full Form
What is the MCB full form in electrical?
MCB full form is Miniature Circuit Breaker. It’s an automatic electrical switch designed to protect electrical circuits from damage caused by overcurrent conditions including short circuits and overloads.
What does MCB stand for in electrical engineering?
In electrical engineering, MCB stands for Miniature Circuit Breaker – a protective device that combines overcurrent protection with the ability to be reset and reused after operation, unlike traditional fuses.
What is the difference between MCB full form and other circuit breakers?
While MCB stands for Miniature Circuit Breaker (for smaller applications), MCCB stands for Molded Case Circuit Breaker (for larger industrial applications), and ACB stands for Air Circuit Breaker (for very high current applications).
Why is it called a Miniature Circuit Breaker?
The “miniature” in MCB full form refers to its compact size compared to larger industrial circuit breakers, making it ideal for residential and light commercial applications where space is limited.
What is the difference between MCB and MCCB?
MCBs are designed for lower current ratings (up to 125A) and residential/light commercial use, while MCCBs handle higher currents (100A to 2500A) for industrial applications. MCCBs also offer adjustable trip settings and higher breaking capacities.
How do I know if my MCB is faulty?
Signs of MCB failure include: failure to trip during overload, inability to reset after tripping, physical damage or burning marks, loose or corroded terminals, and inconsistent operation. Professional testing is recommended for verification.
Can I replace an MCB with a higher rating?
Only if the downstream wiring and components can safely handle the increased current. The cable current carrying capacity must exceed the new MCB rating, and proper load calculations must be performed.
How often should MCBs be tested?
Residential installations: Every 3 years. Commercial installations: Annually. Industrial installations: Every 6 months or as per maintenance schedule. Critical applications may require more frequent testing.
What causes MCBs to trip frequently?
Common causes include: actual overload conditions, loose terminal connections, damaged cables, moisture ingress, ambient temperature issues, and MCB wear or failure.
Pinoprotektahan ba ng mga MCB laban sa electric shock?
No, standard MCBs only protect against overcurrent and short circuits. For electric shock protection, install RCDs (Residual Current Devices) or combination RCBO units.
Conclusion: Understanding MCB Full Form and Applications
The MCB full form – Miniature Circuit Breaker – represents one of the most critical electrical safety devices in modern installations. Understanding what MCB stands for and how these devices function ensures electrical safety, code compliance, and reliable circuit protection.
Key Takeaways About MCB Full Form:
- MCB stands for Miniature Circuit Breaker – essential for electrical protection
- The “miniature” designation refers to compact size for residential/commercial use
- MCB full form encompasses automatic overcurrent and short circuit protection
- Professional installation and regular testing ensure optimal MCB performance
- Combining MCBs with RCDs provides comprehensive electrical protection
For complex electrical installations or questions about MCB full form applications, always consult qualified electrical engineers or certified electricians to ensure safety and code compliance.
Rekomendasyon ng Dalubhasa: Understanding the MCB full form is just the beginning – proper selection, installation, and maintenance of Miniature Circuit Breakers requires detailed knowledge of electrical codes, load calculations, and safety standards for optimal electrical system protection.
Kaugnay
Ano ang Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB): Kumpletong Gabay para sa Kaligtasan at Pagpili