The 4:45 PM Failure
Friday afternoon. The server room HVAC trips. You reset the breaker, but ten minutes later the executive floor lights flicker out. The incomer is running hot. Neutral current readings make no sense. This isn’t bad luck—it’s an under-specified distribution system collapsing under modern loads.
For facility managers and electrical engineers, this cascading failure represents a fundamental misunderstanding of three-phase power distribution. The question isn’t just “why did it fail?” It’s “how do we design a power backbone that survives commercial reality?”
The answer: properly specified TP&N (Triple Pole and Neutral) metal distribution boards. Not the bargain-basement polymer boxes. Not over-engineered switchgear. The precise middle ground that IEC 61439-3 defines as Distribution Boards for Ordinary Persons (DBO).
This guide dissects the engineering, standards, and real-world application of TP&N boards, drawing from VIOX Electric’s twenty years manufacturing these systems for commercial and industrial installations worldwide.
- Rated Current Limits: Outgoing circuits are limited to 125A, and the total assembly cannot exceed 250A at a nominal voltage of up to 300V AC to earth. This sizing makes them ideal for sub-distribution in commercial and residential contexts.
1. What is TP&N: The Four-Wire Advantage
Start with fundamentals. A standard residential setup runs Single Phase and Neutral (SPN)—one live wire, one neutral, 230V. Simple, but limited.
Um TP&N board harnesses all three phases of the supply (L1, L2, L3) plus Neutral. This “three-phase, four-wire” configuration delivers two voltage systems simultaneously:
Voltage relationships:
- Phase-to-Neutral: 230-240V (standard single-phase loads—lighting, computers, outlets)
- Phase-to-Phase: 400-415V (three-phase motors—pumps, compressors, HVAC)
- Phase-to-Neutral: 230-240V (Standard power for your laptop, lights, and coffee machine).
This is The Four-Wire Advantage. You’re not just getting more power; you’re getting architectural flexibility. A 3-phase chiller plant and a row of LED monitors can feed from the same board, provided you understand phase balancing.
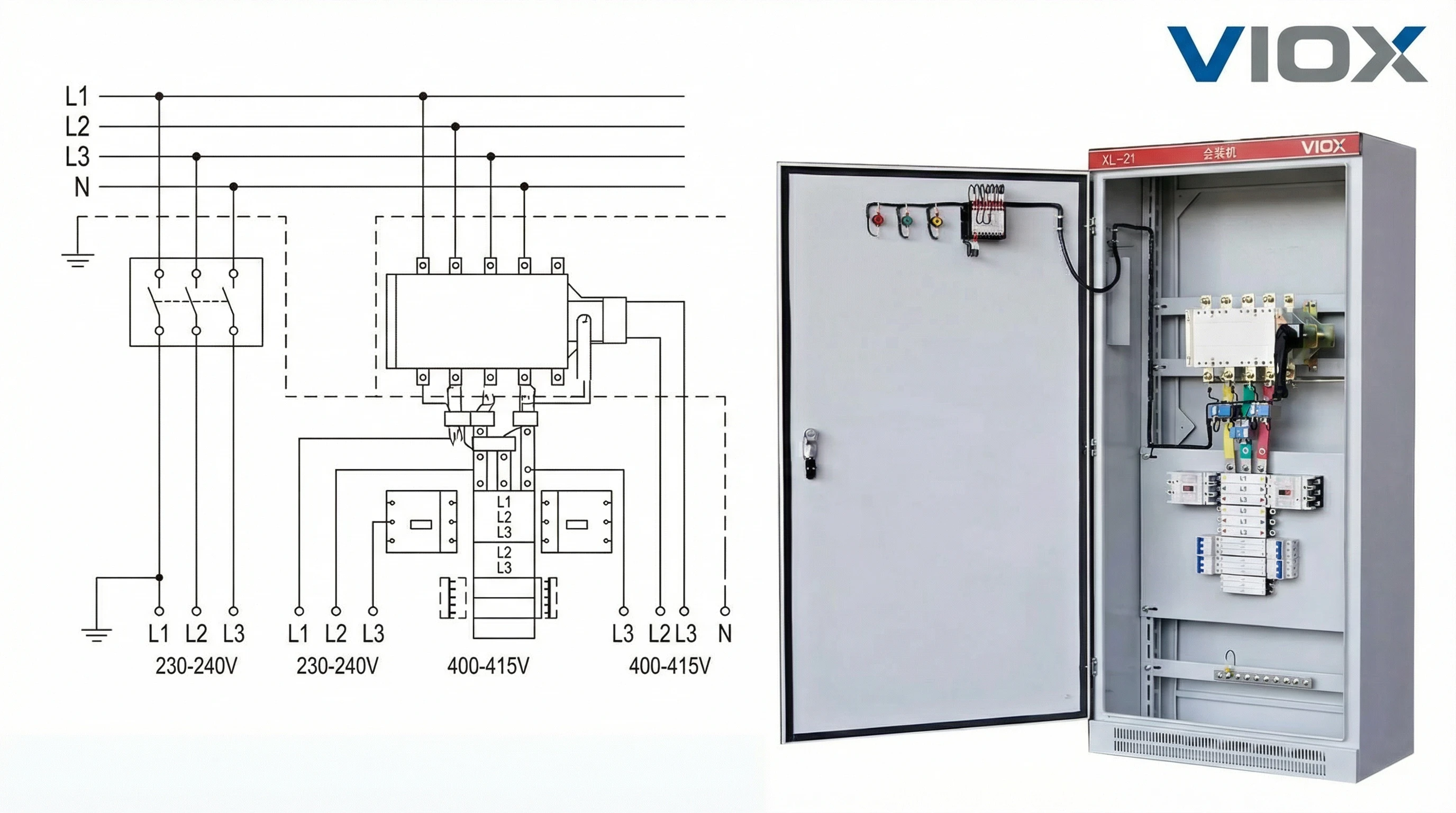
The 4-Pole Incomer: Why “Floating Neutral” Destroys Equipment
Older installations use 3-pole isolators that only cut phases, leaving neutral connected. This creates the “floating neutral” hazard.
Here’s what happens: If the neutral connection opens while phases remain live, your single-phase circuits lose their voltage reference. Instead of stable 230V, voltages float wildly—potentially hitting 400V. Every computer, monitor, and LED driver on that circuit dies instantly.
Modern standards (and VIOX specification) mandate 4-pole incomers. When you isolate, everything disconnects simultaneously. No floating neutral. No voltage excursions. No equipment destruction during maintenance.
2. The 250A Ceiling: Understanding IEC 61439-3:2024
Not every distribution board is created equal. The regulatory framework matters because it defines safe application boundaries.
IEC 61439-3 covers Distribution Boards for Ordinary Persons (DBO)—assemblies where non-electricians might reset breakers or add circuits. The 2024 revision introduced crucial updates, but one constraint remains absolute:
The hard limits:
- Total assembly current: 250A maximum
- Outgoing circuits: 125A maximum per circuit
- Classificação da tensão: Up to 300V AC to earth
We call this “The 250A Ceiling.” If your load calculation demands 400A, you cannot use a TP&N distribution board. You’ve crossed into Power Switchgear territory (IEC 61439-2)—different testing requirements, professional operation, higher cost.
This ceiling is why proper load analysis matters. Oversize your incomers and you’re paying for unnecessary capacity. Undersize them and you’re designing for failure.
What Changed in the 2024 Revision?
The standout addition is Annex BB addressing Prosumer Electrical Installations (PEI). Distribution boards are no longer passive consumers. They now manage:
- Bidirectional power flows from solar PV and battery storage
- Dual-source capability handling utility and local generation
- Anti-islanding protection preventing backfeed during grid failures
- Smart monitoring integration with energy management systems
The 2024 updates recognize that modern boards sit at the intersection of consumption and generation.
Regional Compliance: BIS and Global Standards
In India, Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) compliance is mandatory. BIS adopts IEC standards with local modifications—IS/IEC 61439 series. Manufacturers must provide type-test reports and routine verification records.
The global trend is convergence. “Locally fabricated” boxes without proper testing are disappearing. Type-tested, certified systems are becoming the norm, driven by insurance requirements and liability concerns.
3. Key Components: Anatomy of a Metal-Clad System
A TP&N board isn’t a box of breakers. It’s an engineered assembly managing heat, electromagnetic forces, and fault currents. Understanding each component’s role prevents specification errors.
The Metal Enclosure: Containment and Protection
Por que metal em vez de polímero?
Durante um curto-circuito catastrófico, as temperaturas do arco atingem milhares de graus em milissegundos. Invólucros termoplásticos podem derreter ou romper, permitindo que o fogo escape. Invólucros de metal — aço galvanizado com revestimento em pó — atuam como vasos de contenção.
Benefícios secundários:
- Proteção contra impacto: As classificações IK lidam com impactos de empilhadeiras e quedas de ferramentas que racham o plástico
- Blindagem EMC: O metal atua como uma gaiola de Faraday, reduzindo a interferência eletromagnética
- Dissipação térmica: O metal conduz o calor para longe dos disjuntores; o plástico o isola
As classificações IP são importantes:
- IP30: Instalações internas padrão (espaços com controle climático)
- IP43/IP54: Ambientes semi-externos ou empoeirados
- IP65: Áreas costeiras, plantas químicas, instalações externas
Combine o invólucro com o ambiente. Uma placa IP30 em um cais à beira-mar se torna sucata corroída em meses.
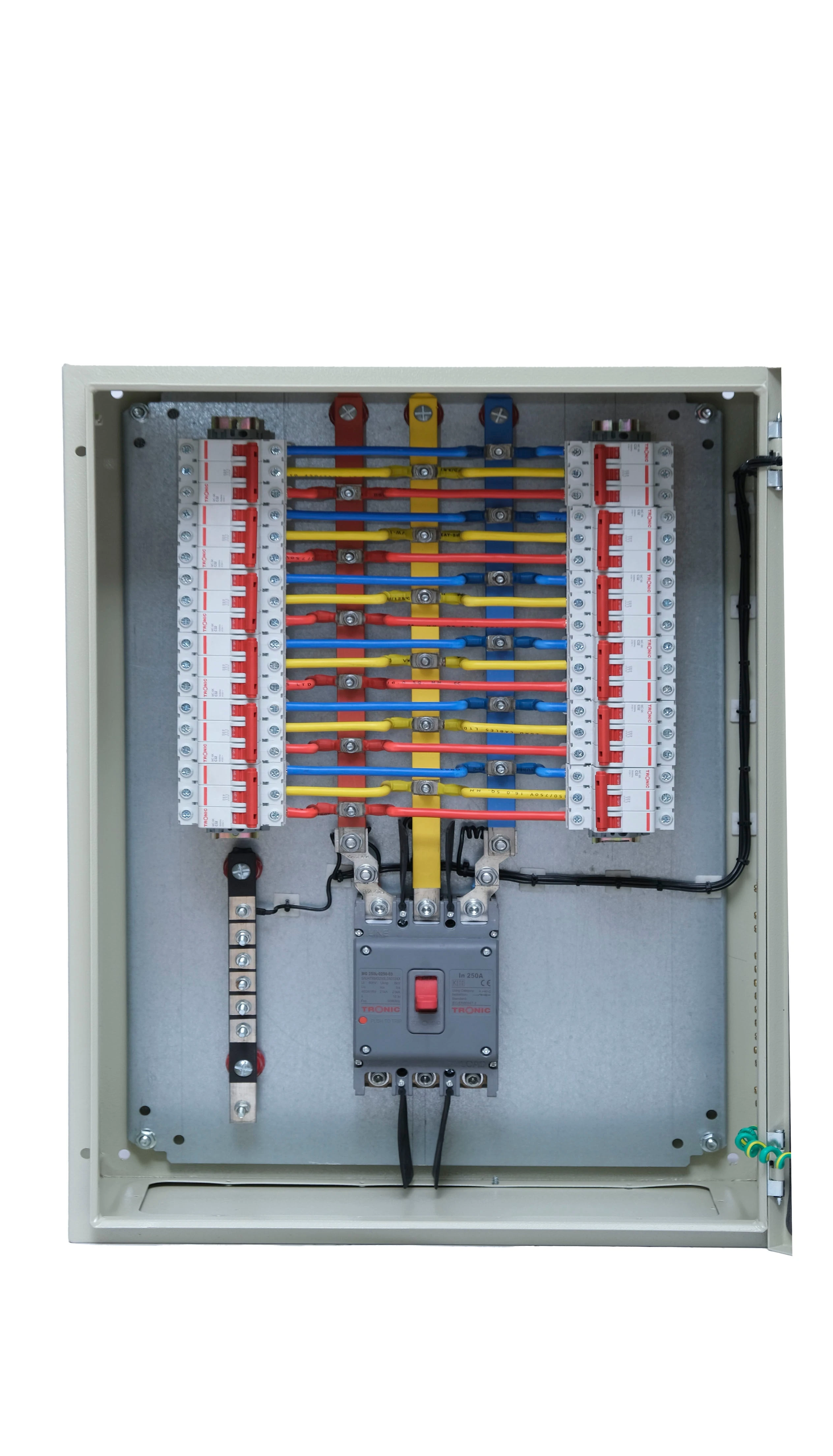
O Sistema de Barramento: Coluna Vertebral de Alta Condutividade
As barras de barramento são barras de cobre que distribuem energia do alimentador para os dispositivos de saída. Na configuração TP&N: quatro barras distintas (L1, L2, L3, N).
Seleção de materiais:
A VIOX usa cobre eletrolítico estanhado. Por que o revestimento de estanho? O cobre oxida. A oxidação cria resistência. A resistência gera calor. O calor acelera a oxidação. Este ciclo de feedback positivo termina em fuga térmica. O revestimento de estanho quebra o ciclo.
Resistência a curto-circuito:
Durante as falhas, as forças eletromagnéticas tentam separar as barras de barramento. Os suportes de montagem devem manter as barras rígidas contra quilo-ampères de força. Suportes mal projetados significam barras de barramento deformadas e folgas comprometidas.
- Ensaios de resistência de isolamento: Use um megôhmetro para verificar se a resistência de isolamento entre as fases e entre as fases e a terra atende aos valores mínimos (normalmente > 1 MΩ para novas instalações).
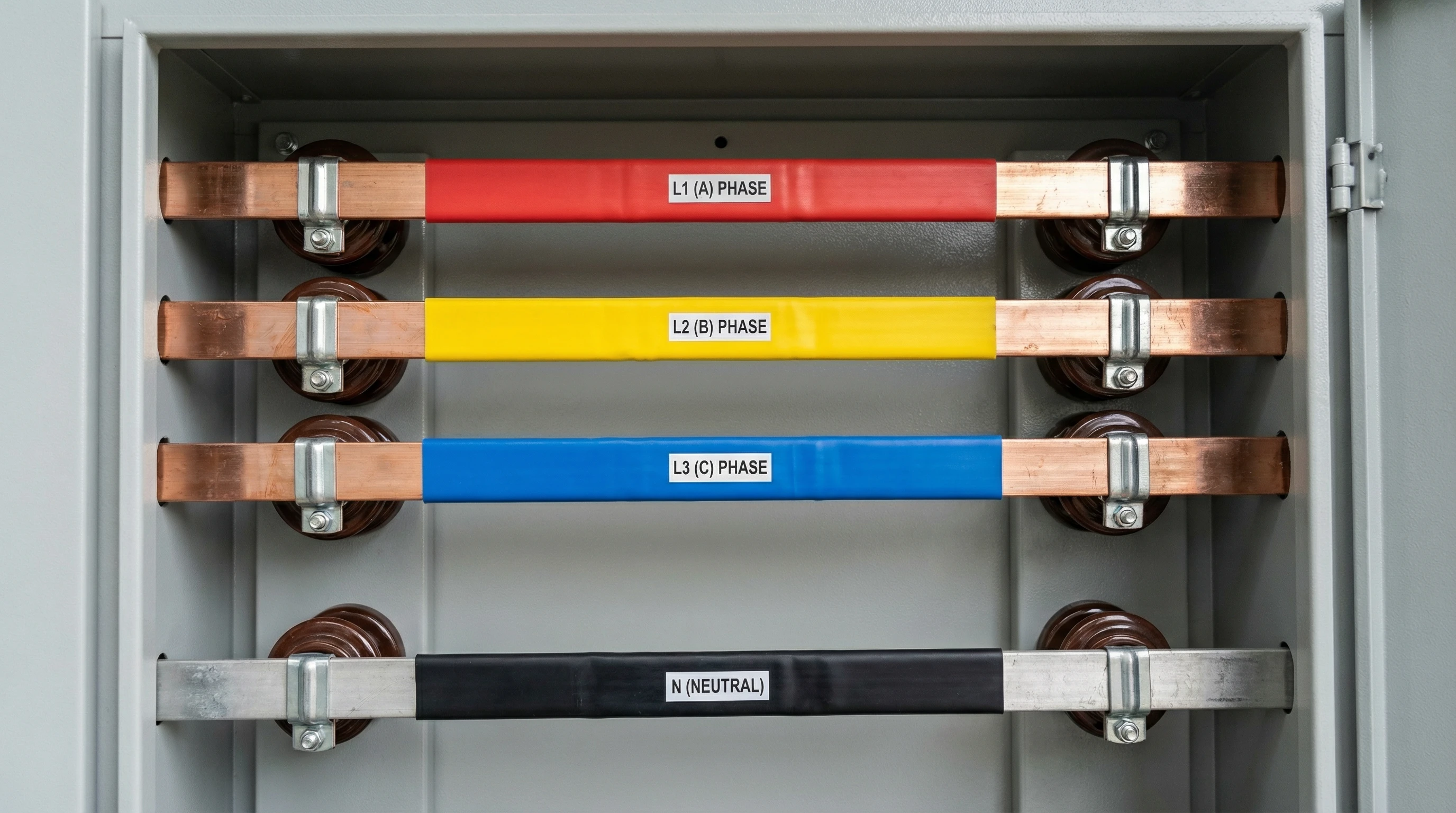

A Barra Neutra: A Vítima Silenciosa de Harmônicos
Aqui está um fato que surpreende os engenheiros juniores: a corrente neutra pode exceder a corrente de fase.
Na era das cargas resistivas (lâmpadas incandescentes, aquecedores), a corrente neutra era baixa. Cargas não lineares modernas — drivers de LED, fontes de alimentação chaveadas, VFDs — geram harmônicos que se acumulam no condutor neutro.
A resposta da engenharia: As placas TP&N devem ter barras neutras classificadas para pelo menos 100% da corrente de fase. Subdimensione isso e você caçará o cheiro de plástico queimado por semanas.
Dispositivos de Proteção em Trilho DIN: A Coordenação é Fundamental
As saídas acomodam dispositivos modulares de acordo com os padrões IEC:
- MCBs (IEC 60898-1): Protegem os circuitos contra sobrecargas e curtos-circuitos
- RCDs (IEC 61008): Detectam fuga de corrente para a terra, previnem choque elétrico
- RCBOs (IEC 61009): Proteção combinada contra sobrecorrente + corrente residual
- AFDDs (IEC 62606): Detecção de arco voltaico para prevenção de incêndio
Dica profissional: A coordenação do dispositivo é importante. O MCB upstream deve ser seletivo com a proteção downstream. Se uma falha no Andar 3 desarmar o alimentador principal em vez do disjuntor do andar, você perdeu a seletividade. Revise as curvas de tempo-corrente durante a especificação.
Dispositivos de Proteção contra Surtos (SPDs): A Apólice de Seguro
Sobretensões transitórias de raios ou comutação da rede elétrica destroem eletrônicos sensíveis. SPDs integrados fixam picos de tensão em níveis seguros.
A seleção do SPD depende da exposição:
- Tipo 1: Exposição direta a raios (alimentador principal do edifício)
- Tipo 2: Distribuição padrão do edifício (aplicação da placa TP&N)
- Tipo 3: Proteção final do circuito (equipamento sensível)
4. Aplicações: Onde as Placas TP&N se Mostram Essenciais
As placas TP&N aparecem onde a carga excede a capacidade monofásica ou o balanceamento de fase se torna crítico.
- Cenário: Uma casa moderna tem um carregador de EV de 22kW, uma bomba de calor e uma sauna elétrica.
Residencial: A Evolução do Prosumidor
Dez anos atrás, TP&N em residencial era raro. Hoje é padrão para construções modernas com:
- Carregadores de EV de 22kW (requerem alimentação trifásica)
- Bombas de calor multi-cabeça (sistemas de 10-15kW)
- Solar FV + armazenamento de bateria (fluxo de energia bidirecional)
- Saunas elétricas e aquecedores de água instantâneos
- Mandatos de eficiência energética: Iniciativas governamentais impulsionam sistemas de distribuição mais eficientes.
Não se pode despejar 40kW de carga em uma fase. As placas TP&N permitem a distribuição de carga: carregador de EV em L1, bomba de calor em L2, cargas da casa em L3. Equilíbrio restaurado.
- HVAC: Grandes unidades de tratamento de ar precisam do impulso de 415V da energia trifásica para iniciar seus compressores sem diminuir a intensidade das luzes em todo o edifício.
- Projetos Modulares e Compactos: Restrições de espaço em edifícios urbanos impulsionam a demanda por placas TP&N compactas que mantêm a funcionalidade completa em um espaço menor.
Em torres de escritórios, complexos de varejo e hotéis, as placas TP&N são cavalos de batalha de distribuição.
Cargas típicas:
- Sistemas HVAC: Chillers centrais e unidades de tratamento de ar precisam de 415V trifásico
- Elevadores e escadas rolantes: Alto torque de partida exige trifásico
- Circuitos de iluminação: Escalonado entre as fases (Linha A→L1, Linha B→L2, Linha C→L3) para evitar desequilíbrio do transformador e efeitos estroboscópicos
O Jogo do Equilíbrio de Fase: A distribuição adequada reduz a corrente neutra, minimiza o estresse do transformador e diminui as perdas de energia. Cargas desequilibradas desperdiçam dinheiro.

- Material da Barra Coletora: Cobre eletrolítico de alta pureza com revestimento de estanho
5. As Normas Que Importam: “O Limite de 250A”
Fábricas e oficinas exigem invólucros de metal. Poeira, óleo, impactos—as placas TP&N alimentam Centros de Controle de Motores (CCMs) em condições adversas.
Considerações críticas:
- A rotação de fase importa. Se um motor de bomba funcionar para trás devido a fases trocadas, é catastrófico
- A rotulagem clara simplifica o comissionamento e a manutenção
- Invólucros IP54/IP65 lidam com ambientes industriais
Ecossistema Abrangente de Produtos
6. Vantagens do TP&N Revestido de Metal Sobre Alternativas
Por que pagar mais por metal quando o plástico é mais barato? Porque as especificações devem abordar a realidade, não as condições de laboratório.
Capacidade de Potência e Escalabilidade Superiores
O fornecimento trifásico fornece até três vezes a potência do monofásico para o mesmo tamanho de condutor. Para instalações que planejam expansão—adicionando racks de servidor, máquinas ou inquilinos—as placas TP&N oferecem folga sem atualizações de serviço dispendiosas.
- Circuitos de Saída: Máximo de 125A por circuito.
- Tensão: Até 300V AC para a terra.
Distribuição equilibrada da carga
Cargas desequilibradas causam ineficiência e superaquecimento. As placas TP&N permitem um projeto de circuito inteligente: distribua as cargas monofásicas uniformemente entre L1, L2, L3. Isso reduz a corrente neutra (crítico devido a problemas harmônicos de LEDs e cargas eletrônicas) e evita a sobrecarga do transformador.
Eficiência Operacional Aprimorada
Motores trifásicos superam os equivalentes monofásicos:
- Operação mais suave com menos vibração
- Menor necessidade de manutenção
- Maior eficiência (bombas, compressores, HVAC)
A economia de energia ao longo da vida útil justifica o investimento inicial.
Contenção de Incêndio e Segurança
Arcos de falha são violentos—pulverizando cobre fundido e gás ionizado. Os invólucros de metal contêm esse caos, impedindo que falhas internas se tornem incêndios externos no edifício. Isso não é teórico; é a diferença entre uma interrupção incômoda e uma reclamação de seguro.
Recursos de Proteção Específicos da VIOX
Nossas placas integram:
- Barras neutras e de terra totalmente blindadas reduzindo o risco de contato acidental durante a manutenção
- Montagem robusta da barra coletora minimizando o afrouxamento do ciclo térmico—um modo de falha comum em montagens baratas
- Pontos de conexão calibrados prevenindo “a armadilha do torque”
7. Requisitos de Instalação: Evitando Falhas de Sexta-Feira à Tarde
Você pode comprar a melhor placa disponível, mas uma instalação ruim garante o fracasso. Geralmente às 16h45 de sexta-feira.
A Armadilha do Torque: Assassino Número Um
Conexões soltas destroem mais placas de distribuição do que raios.
A física: Conexão solta → aumento da resistência → geração de calor → expansão térmica → conexão mais solta. Este ciclo de feedback positivo termina em terminais derretidos.
A correção: Chaves de torque calibradas. Não seu pulso. Não “apertado o suficiente”. Os fabricantes especificam valores de torque (normalmente 10-12 Nm para terminais MCB). Use-os.
Estratégia de Equilíbrio de Fase
Antes de energizar:
- Mapear cargas: Documentar quais cargas se conectam a quais fases
- Calcular distribuição: Almejar ±10% de equilíbrio de corrente entre as fases
- Medir durante a operação: Use medidores de pinça na carga de pico. Se L1 puxar 80A enquanto L3 puxar 10A, mova os circuitos
- Documentar: Afixe o cronograma do circuito na porta. Disjuntores não marcados são dores de cabeça futuras
Lista de Verificação de Testes de Pré-Comissionamento
Conclua estes testes antes de energizar:
✓ Inspeção visual: Verifique as classificações do dispositivo, as terminações dos cabos, sem detritos
✓ Resistência de isolamento: Use megôhmetro. Mínimo 1 MΩ entre fases e para terra para novas instalações
✓ Teste funcional: Desarme manualmente cada dispositivo de proteção
✓ Verificação da rotação de fase: Use o indicador de sequência de fase para verificar a ordem L1-L2-L3 (a rotação incorreta faz com que os motores funcionem ao contrário)
✓ Teste de RCD: Teste na corrente de disparo nominal
✓ Verificação de aperto: Verifique o torque de todas as conexões
Considerações ambientais
Combine a classificação do invólucro com o ambiente:
- Salas de plantas com controle climático: IP30 suficiente
- Semi-externo/armazém: IP43 ou IP54 mínimo
- Plantas costeiras/químicas: Aço inoxidável com IP65, revestimento resistente à corrosão
Instalação Qualificada
As instalações trifásicas exigem competência além do trabalho monofásico. Contrate eletricistas licenciados familiarizados com:
- IEC 61439-3 requisitos
- Códigos elétricos locais (BS 7671 no Reino Unido, AS/NZS 3000 na Austrália/NZ)
- Sistemas de aterramento adequados (configurações TN-S, TN-C-S)
Ficha de Especificações Típica de 2025
De uma perspectiva regulatória, esses conjuntos se enquadram no âmbito de IEC 61439-3:2024. Esta norma cobre especificamente Quadros de Distribuição destinados a serem Operados por pessoas comuns (DBO). Ela determina que, embora a engenharia interna seja sofisticada, a interface do usuário deve ser segura para que não especialistas acessem para tarefas básicas, como redefinir um disjuntor. A norma limita os circuitos de saída a 125A e o conjunto total a 250A com uma tensão nominal de até 300V AC para terra, garantindo que esses quadros sejam perfeitamente dimensionados para a zona intermediária entre os quadros de distribuição principais e os subcircuitos finais.
A distribuição de energia elétrica está evoluindo, impulsionada pela descarbonização, digitalização e geração descentralizada.
- Barras de distribuição: Cobre estanhado (padrão). O alumínio está desaparecendo para a distribuição final devido aos riscos de oxidação.
A Revolução do Prosumidor
A IEC 61439-3:2024 Anexo BB aborda a energia bidirecional. Os quadros modernos lidam com:
- Fornecimento da rede E geração solar/bateria local
- Comutação em tempo real entre fontes
- Anti-islanding protection
- Integração com sistemas de gerenciamento de energia (EMS)
O Ecossistema VIOX
Isto não é tecnologia do futuro. É a especificação atual para edifícios comerciais com instalações renováveis.
Crescente Demanda em Mercados Emergentes
Projetos do mercado de aparelhagem de baixa tensão da Índia CAGR de 7-8% até 2030. Condutores:
- Expansão imobiliária: Novos empreendimentos comerciais e residenciais
- Mandatos de eficiência energética: Requisitos governamentais para distribuição eficiente
- Implantação de redes inteligentes: Modernização da rede impulsionando atualizações de hardware
- Projetos modulares: Restrições de espaço em edifícios urbanos
- Aquisição de comércio eletrônico: O fornecimento online está acelerando a entrega
Conclusão: Especifique para a Realidade, Não Apenas para a Teoria
Especificação Típica de 2025
As ofertas atuais do mercado apresentam:
Classificações:
- Corrente do conjunto: 250A (máximo IEC 61439-3)
- Saídas: 12-36 circuitos
- Material da barra de distribuição: Cobre eletrolítico estanhado
- Invólucro: Aço galvanizado, revestido a pó (cores RAL)
Proteção:
- Classificações de IP: IP30 (padrão), IP43/IP54 (à prova de intempéries), IP65 (severo)
- Classificação IK: IK08 mínimo para industrial
Certificações:
- IEC 61439-1/-3 com ensaio de tipo
- Marcação CE (Europa)
- Certificação BIS (Índia)
- Conformidade com RoHS/REACH
Recursos preparados para Smart:
- Espaço para medidores de energia
- Montagem do módulo de comunicação
- Disposições de integração de IoT
8. VIOX Electric: Excelência em Engenharia em Soluções de Distribuição
A VIOX Electric oferece quadros de distribuição de metal TP&N com o apoio de vinte anos de experiência em fabricação. Nossos quadros não são itens de consumo — são sistemas de engenharia.
Ecossistema Abrangente de Produtos
Os quadros VIOX integram-se perfeitamente com a nossa MCB série:
VOB3-63 MCB:
- Classificações: 1-63A, capacidade de interrupção de 4,5/6kA
- Padrão: certificado IEC 60898-1
- Aplicação: Residencial e comercial leve
VOB4-63 MCB:
- Classificações: 1-63A, capacidade de interrupção de 6/10kA
- Normas: Conformidade dupla com IEC 60898-1 e 60947-2
- Aplicação: Circuitos comerciais e industriais exigentes
VOB4-125 e VOB5-125 MCB:
- Classificações: 80-125A
- Aplicação: Alimentadores pesados, circuitos de motor, entradas principais
Garantia de qualidade
Cada quadro VIOX passa por:
- ISO 9001:2015 gestão da qualidade (consistência da produção)
- IEC 61439-1/-3 ensaio de tipo e verificação de rotina
- Teste de elevação de temperatura na corrente nominal (validação térmica)
- Teste de curto-circuito para corrente de falta prospectiva nominal
- Marcação CE e UL para implantação global
Vantagens Diretas da Fábrica
Como fabricante verticalmente integrado:
Preços: Economia de 15-30% em comparação com os canais de distribuição. A fábrica direta elimina a margem de lucro do intermediário sem comprometer a qualidade.
Personalização: Classificações de barramento personalizadas, acabamentos de invólucro, marca para parceiros OEM. MOQ flexível para requisitos específicos do projeto.
Suporte técnico: Consulta pré-venda, assistência no cálculo de carga, suporte de comissionamento, solução de problemas pós-instalação. Nossa equipe é composta por engenheiros, não por scripts.
Prazos de entrega: Os produtos padrão são enviados em 2 a 3 semanas. Produção acelerada disponível para projetos urgentes.
O “o quê” dos Quadros de Distribuição de Metal TP&N é direto: hubs de energia trifásicos que gerenciam cargas de 230V e 415V simultaneamente.
O “porquê” determina o sucesso. Você especifica TP&N porque:
- Edifícios modernos exigem isso: Carregadores de EV, bombas de calor, HVAC — a capacidade monofásica é insuficiente
- O balanceamento de fase é importante: A distribuição adequada da carga reduz as perdas e evita o estresse do equipamento
- As normas definem a segurança: A conformidade com a IEC 61439-3 não é opcional
- Os invólucros de metal contêm falhas: O isolamento contra incêndio e a proteção contra impacto são apólices de seguro
- A qualidade da instalação determina a longevidade: O torque calibrado e o teste adequado evitam falhas na tarde de sexta-feira
Não deixe que seu próximo projeto falhe devido à distribuição com especificações insuficientes. Construa certo. Construa balanceado. Construa com a engenharia adequada.
Ao especificar os quadros TP&N, priorize:
- Conformidade com IEC 61439-3:2024 (verifique os relatórios de ensaio de tipo)
- Cálculo de carga adequado e balanceamento de fase
- Classificações de IP apropriadas para o ambiente
- Instalação calibrada por eletricistas qualificados
- Componentes certificados pela fábrica com documentação adequada
Na VIOX Electric, entendemos que por trás de cada especificação de quadro de distribuição há um compromisso com a segurança das instalações e a confiabilidade operacional. Nossa equipe de engenharia fornece suporte para cálculo de carga, documentação de conformidade e configurações personalizadas adaptadas aos requisitos do seu projeto.
Pronto para especificar seu próximo quadro de distribuição de metal TP&N?
Contacto VIOX Elétrico para fichas técnicas detalhadas, certificações de conformidade e preços diretos da fábrica. Nossos engenheiros elétricos apoiam seu projeto desde o projeto inicial até o comissionamento.


