Caraterísticas do sensor indutivo
Os sensores indutivos são excelentes na deteção de objectos metálicos sem contacto físico, utilizando um campo eletromagnético gerado por uma bobina interna. Estes dispositivos podem detetar metais ferrosos a distâncias até 80 milímetros, com gamas reduzidas para materiais não ferrosos como o latão e o alumínio.
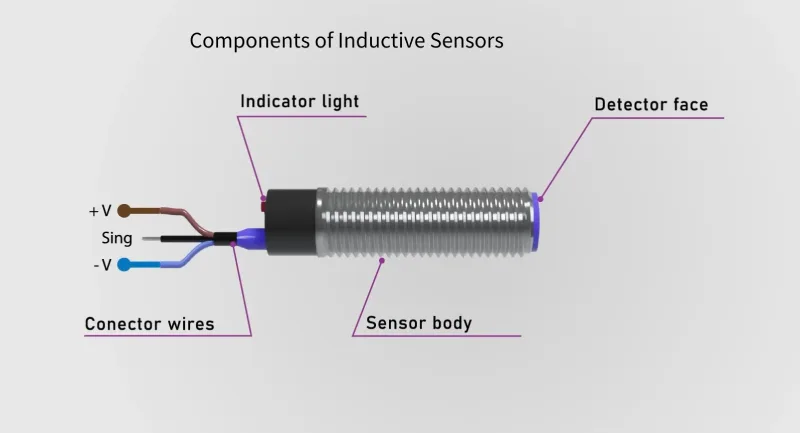
Os principais componentes incluem:
- Face do sensor, corpo, luz indicadora e fios de ligação
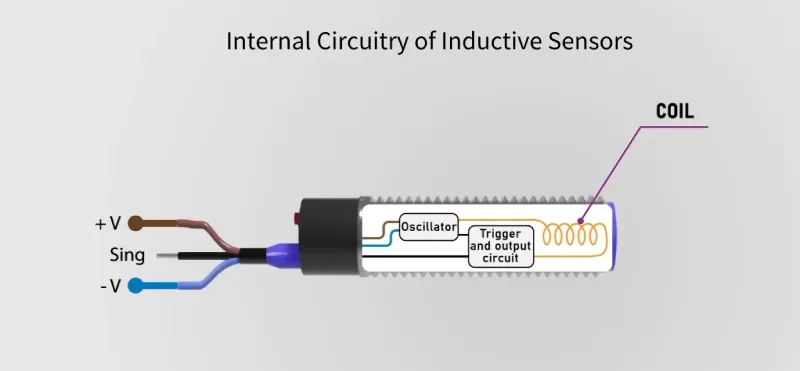
- Circuito interno com bobina, oscilador, circuito de disparo e circuito de saída
O funcionamento do sensor baseia-se no princípio da indução electromagnética, em que um objeto metálico que entre no campo do sensor provoca correntes de Foucault, alterando o estado de oscilação. Esta alteração é então detectada e convertida num sinal de saída.
Nomeadamente, os sensores indutivos são altamente robustos, resistentes a choques, vibrações e poeiras, o que os torna adequados para ambientes industriais adversos. A sua elevada frequência de comutação permite a deteção rápida de peças móveis, mesmo a velocidades de rotação elevadas.
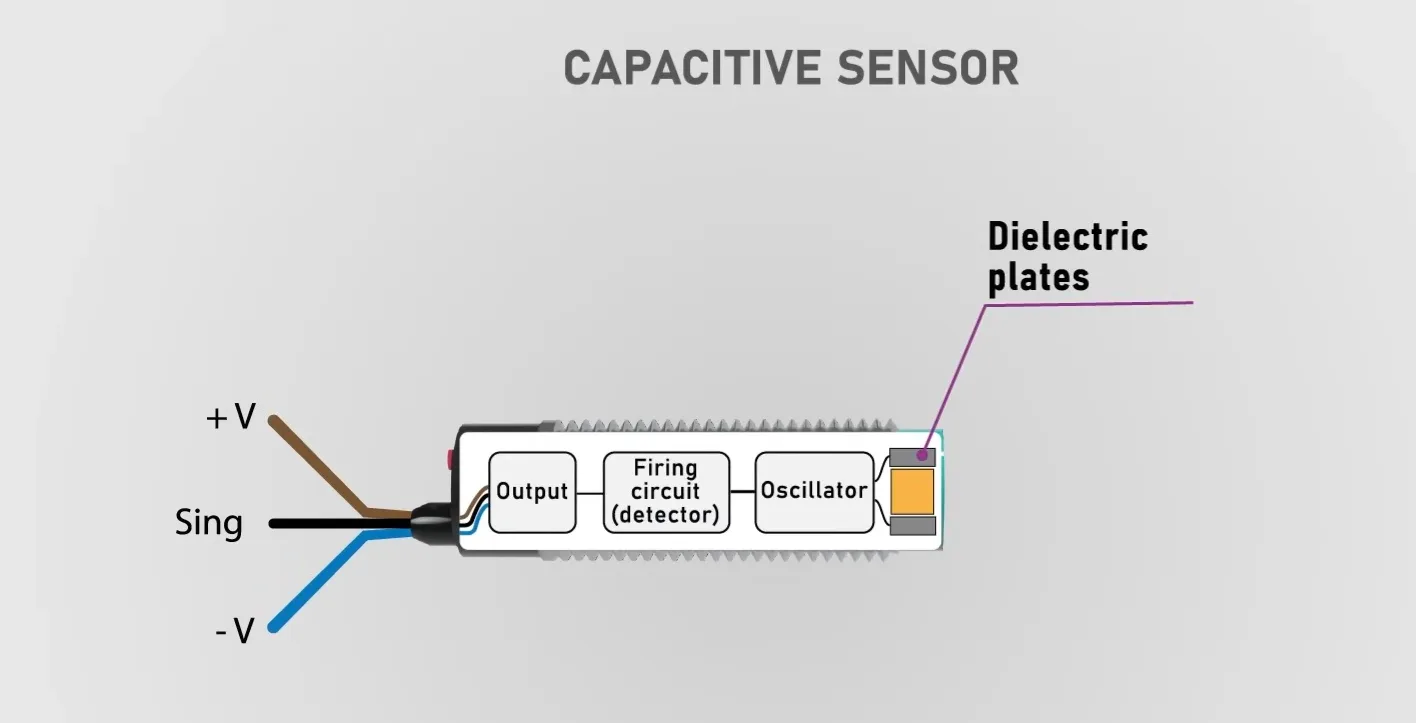
Caraterísticas do sensor capacitivo
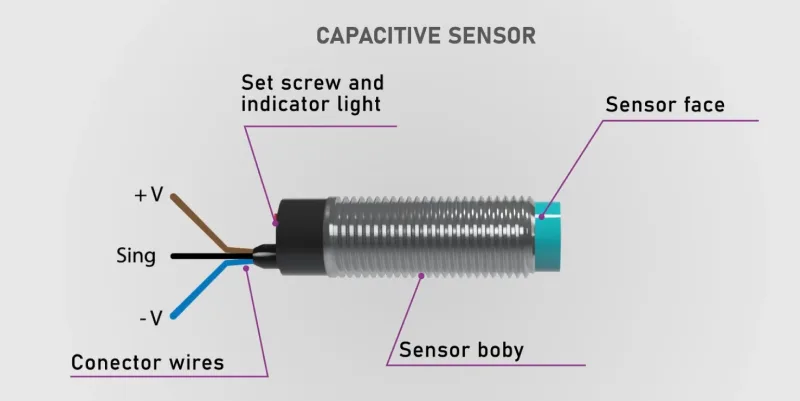
Os sensores capacitivos funcionam com base no princípio da deteção de alterações nos campos electrostáticos, o que lhes permite detetar uma gama diversificada de materiais, incluindo metais, plásticos, líquidos, vidro e madeira. Estes dispositivos versáteis consistem em placas dieléctricas que emitem um campo eletrostático, juntamente com um oscilador, um circuito de disparo e um circuito de saída.
Componentes do sensor capacitivo
Circuito interno do sensor capacitivo
Quando um objeto entra na zona de deteção do sensor, altera a capacitância, fazendo com que o oscilador seja ativado na frequência e amplitude máximas. A distância de deteção pode ser ajustada com um parafuso de ajuste, tornando os sensores capacitivos adaptáveis a várias aplicações, como a deteção do nível de líquidos em recipientes não metálicos.
Caraterísticas principais: Capacidade de detetar objectos através de paredes não metálicas
Limitações: Suscetível à interferência da humidade e de vapores densos
Aplicações: Utilização generalizada na deteção de nível e deteção de curto alcance de materiais transparentes
Durabilidade: Longa duração de vida devido à ausência de desgaste mecânico.
Configurações de sensores e aplicações
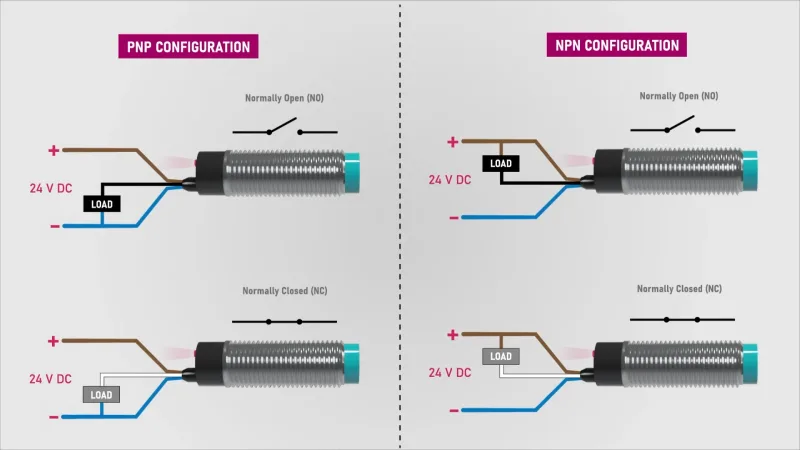
Tanto os sensores indutivos como os capacitivos oferecem várias configurações para se adequarem a diferentes aplicações industriais. Estes sensores podem ser blindados ou não blindados, sendo que os sensores blindados permitem uma montagem embutida e os sensores não blindados proporcionam uma área de deteção maior. Estão disponíveis em configurações normalmente abertas ou normalmente fechadas, bem como em tipos de saída NPN ou PNP para compatibilidade com diferentes sistemas de controlo.
Os sensores indutivos são particularmente úteis em aplicações de deteção de metais, como a deteção de tampas de contentores em linhas de produção, enquanto os sensores capacitivos são excelentes em tarefas de deteção de nível, como a monitorização de níveis de líquidos em garrafas de plástico. A escolha entre estes tipos de sensores depende do material específico a ser detectado, das condições ambientais e da gama de deteção necessária para a aplicação.
https://viox.com/4-wire-proximity-sensor-wiring-diagram/
https://viox.com/npn-vs-pnp-proximity-sensors/
Comparação entre indutivo e capacitivo
| Recurso | Sensores indutivos | Sensores capacitivos |
|---|---|---|
| Gama de deteção | Relativamente baixo, até 80 mm | Variável, pode ser detectado através de paredes não metálicas |
| Materiais detectáveis | Principalmente objectos metálicos | Vasta gama, incluindo metais, plásticos, líquidos, vidro, madeira |
| Resistência ambiental | Resistente a choques, vibrações e poeiras | Alterável por humidade e vapores densos |
| Frequência de comutação | Elevado, adequado para aplicações de alta velocidade | Não especificado, mas geralmente inferior ao indutivo |
| Desgaste | Sem partes móveis, resistente ao desgaste | Ausência de desgaste mecânico, longa vida útil |
| Aplicações específicas | Deteção de metais, contagem de peças a alta velocidade | Deteção de nível, deteção de material transparente |
| Deteção através da parede | Não é possível | Pode detetar objectos através de barreiras não metálicas |
Os sensores indutivos são excelentes em cenários de deteção de metais, oferecendo elevada precisão e fiabilidade em ambientes industriais adversos. A sua capacidade de resistir a choques, vibrações e poeiras torna-os ideais para aplicações em linhas de fabrico onde é necessário detetar objectos metálicos a alta velocidade.
Os sensores capacitivos, por outro lado, oferecem uma maior versatilidade na deteção de materiais. A sua capacidade única de detetar níveis através de recipientes não metálicos torna-os particularmente úteis em aplicações de monitorização de nível de líquidos, como a deteção de níveis de enchimento em garrafas de plástico. No entanto, a sua sensibilidade a factores ambientais como a humidade e vapores densos requer uma consideração cuidadosa durante a implementação.
Ambos os tipos de sensores podem ser configurados como normalmente abertos ou normalmente fechados, e com saídas NPN ou PNP, permitindo flexibilidade na integração com vários sistemas de controlo. A escolha entre sensores indutivos e capacitivos depende, em última análise, dos requisitos específicos da aplicação, incluindo o tipo de material a ser detectado, o ambiente de funcionamento e o intervalo de deteção pretendido.
Impacto ambiental no desempenho do sensor
Os factores ambientais influenciam significativamente o desempenho dos sensores, especialmente no caso dos sensores indutivos e capacitivos utilizados na automação industrial. As flutuações de temperatura, os níveis de humidade e as interferências electromagnéticas podem afetar a precisão e a fiabilidade dos sensores. Para um desempenho ótimo, os sensores devem ser instalados em ambientes com níveis de luz entre 100 e 1000 LUX.
Os sensores indutivos são geralmente mais robustos contra factores ambientais, mantendo a precisão em condições adversas com pó, vibrações e variações de temperatura. Os sensores capacitivos, embora versáteis, são mais susceptíveis a alterações ambientais, especialmente humidade e vapores densos, que podem alterar as suas capacidades de deteção. Para atenuar estes efeitos, a calibração regular, a filtragem de dados e as técnicas de fusão de sensores são essenciais para manter a precisão em condições ambientais variáveis. Além disso, a escolha do tipo de sensor adequado para condições ambientais específicas é crucial para otimizar o desempenho e garantir uma deteção fiável em aplicações industriais.
Distinções visuais dos sensores
Os sensores indutivos e capacitivos, embora semelhantes nas suas capacidades de deteção sem contacto, têm caraterísticas visuais distintas que podem ajudar na sua identificação. Aqui estão as principais distinções visuais entre estes dois tipos de sensores:
- Material do invólucro: Os sensores indutivos apresentam normalmente invólucros metálicos, muitas vezes fabricados em aço inoxidável ou latão niquelado, para resistirem a ambientes industriais agressivos.
- Face de deteção: Os sensores capacitivos têm normalmente uma superfície de deteção maior e plana, enquanto os sensores indutivos podem ter uma área de deteção mais pequena e mais focada.
- Luzes indicadoras: Ambos os tipos incluem frequentemente indicadores LED, mas a sua colocação e cor podem diferir consoante o fabricante e o modelo.
- Tamanho e forma: Indutivos sensores são geralmente mais compacta e cilíndrica, enquanto que os sensores capacitivos podem vir em várias formas, incluindo retangular ou televisão projetos.
- Opções de montagem: Os sensores indutivos são frequentemente concebidos para montagem embutida em superfícies metálicas, enquanto os sensores capacitivos podem oferecer opções de montagem mais flexíveis devido à sua capacidade de detetar através de materiais não metálicos.
- Tipos de conectores: Os tipos de ligação eléctrica podem variar, com os sensores indutivos a apresentarem frequentemente conectores industriais normalizados e os sensores capacitivos a oferecerem potencialmente uma gama mais vasta de opções de ligação.