ဆားကစ်ဘရိတ်ကာများတွင် အပူချိန်မြင့်တက်ခြင်းကို နားလည်ခြင်း- အဘယ်ကြောင့် အရေးကြီးသနည်း
ဆားကစ်ဘရိတ်ကာတိုင်းသည် ပုံမှန်လည်ပတ်နေစဉ်အတွင်း အပူကိုထုတ်ပေးသည်။ လျှပ်စစ်စီးကြောင်းသည် အတွင်းပိုင်းအစိတ်အပိုင်းများ—အဆက်အသွယ်များ၊ ဘိုင်မက်တယ်လ်အစင်းများနှင့် ဂိတ်များ—မှတဆင့် စီးဆင်းသောအခါ ခုခံမှုသည် အပူစွမ်းအင်ကို ဖန်တီးပေးသည်။ အပူချိန်အနည်းငယ်မြင့်တက်ခြင်းသည် ရှောင်လွှဲ၍မရသော်လည်း အပူချိန်အလွန်အကျွံမြင့်တက်ခြင်းသည် လျှပ်ကာကို ယိုယွင်းစေခြင်း၊ အဆက်အသွယ်များ စုတ်ပြဲမှုကို အရှိန်မြှင့်စေခြင်း၊ အနှောင့်အယှက်ဖြစ်စေသော ခရီးစဉ်များဖြစ်ပေါ်စေခြင်းနှင့် နောက်ဆုံးတွင် ဆိုးရွားသောပျက်ကွက်မှုများ ဖြစ်ပေါ်စေနိုင်သည်။.
လျှပ်စစ်အင်ဂျင်နီယာများနှင့် panel တည်ဆောက်သူများအတွက် သတ်မှတ်ခြင်း MCBs နှင့် MCCBs, အပူချိန်မြင့်တက်မှုကန့်သတ်ချက်များကို နားလည်ခြင်းသည် လိုက်နာမှုနှင့်သက်ဆိုင်သည်သာမက ရေရှည်တည်တံ့ခိုင်မြဲမှုနှင့် ဘေးကင်းမှုကိုပါ သေချာစေခြင်းဖြစ်သည်။ IEC 60947-2 (MCCB များအတွက်) နှင့် UL 489 (မြောက်အမေရိကစံနှုန်း) နှစ်ခုစလုံးသည် VIOX ကဲ့သို့သော ထုတ်လုပ်သူများက တင်းကျပ်သော အမျိုးအစားစမ်းသပ်ခြင်းဖြင့် ဖြည့်ဆည်းပေးရမည့် တိကျသောအပူစွမ်းဆောင်ရည်လိုအပ်ချက်များကို တည်ထောင်ထားသည်။.

အပူချိန်မြင့်တက်မှုနှင့် အကြွင်းမဲ့အပူချိန်- အရေးကြီးသော ခြားနားချက်
သတ်မှတ်ထားသော ကန့်သတ်ချက်များထဲသို့ မ၀င်ရောက်မီ၊ အကြားခြားနားချက်ကို နားလည်ရန် အရေးကြီးပါသည်။ အပူချိန်မြင့်တက်မှု (ΔT) နှင့် အကြွင်းမဲ့အပူချိန်:
- အပူချိန်မြင့်တက်မှု (ΔT): ဆဲလ်စီးယပ် သို့မဟုတ် ဖာရင်ဟိုက်ဒီဂရီဖြင့် တိုင်းတာသော ပတ်ဝန်းကျင်အခြေအနေအထက် အပူချိန်မြင့်တက်မှု
- အကြွင်းမဲ့အပူချိန်: ပတ်ဝန်းကျင်အပူချိန်နှင့် အပူချိန်မြင့်တက်မှုကို ပေါင်းစပ်ထားသော အစိတ်အပိုင်းတစ်ခု၏ အမှန်တကယ်တိုင်းတာထားသော အပူချိန်
စံနှုန်းအများစုသည် 40°C (104°F) ၏ စံကိုက်ညှိအပူချိန်ကို ယူဆကာ အပူချိန်မြင့်တက်မှုကန့်သတ်ချက်များကို သတ်မှတ်ထားသည်။ ဆိုလိုသည်မှာ-
အကြွင်းမဲ့အပူချိန် = ပတ်ဝန်းကျင်အပူချိန် + အပူချိန်မြင့်တက်မှု
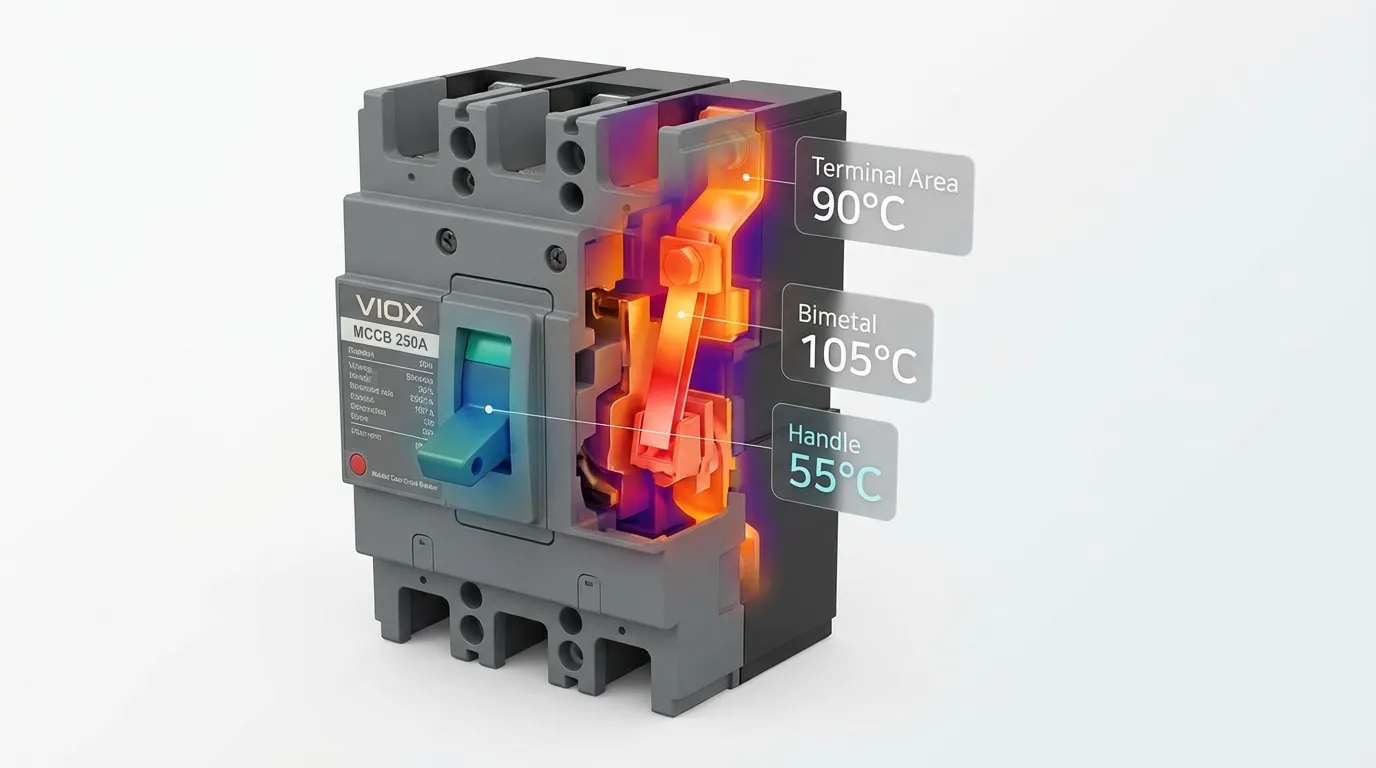
ဥပမာအားဖြင့်၊ 50°C မြင့်တက်မှုကန့်သတ်ချက်ရှိသော ဂိတ်တစ်ခုသည် 40°C ပတ်ဝန်းကျင်တွင် လည်ပတ်ပါက 90°C ၏ အကြွင်းမဲ့အပူချိန်သို့ ရောက်ရှိမည်ဖြစ်ပြီး၊ ၎င်းသည် လျှပ်ကူးပစ္စည်း လျှပ်ကာအမျိုးအစားများစွာအတွက် အမြင့်ဆုံးလုံခြုံသော လည်ပတ်မှုအမှတ်ဖြစ်သည်။.
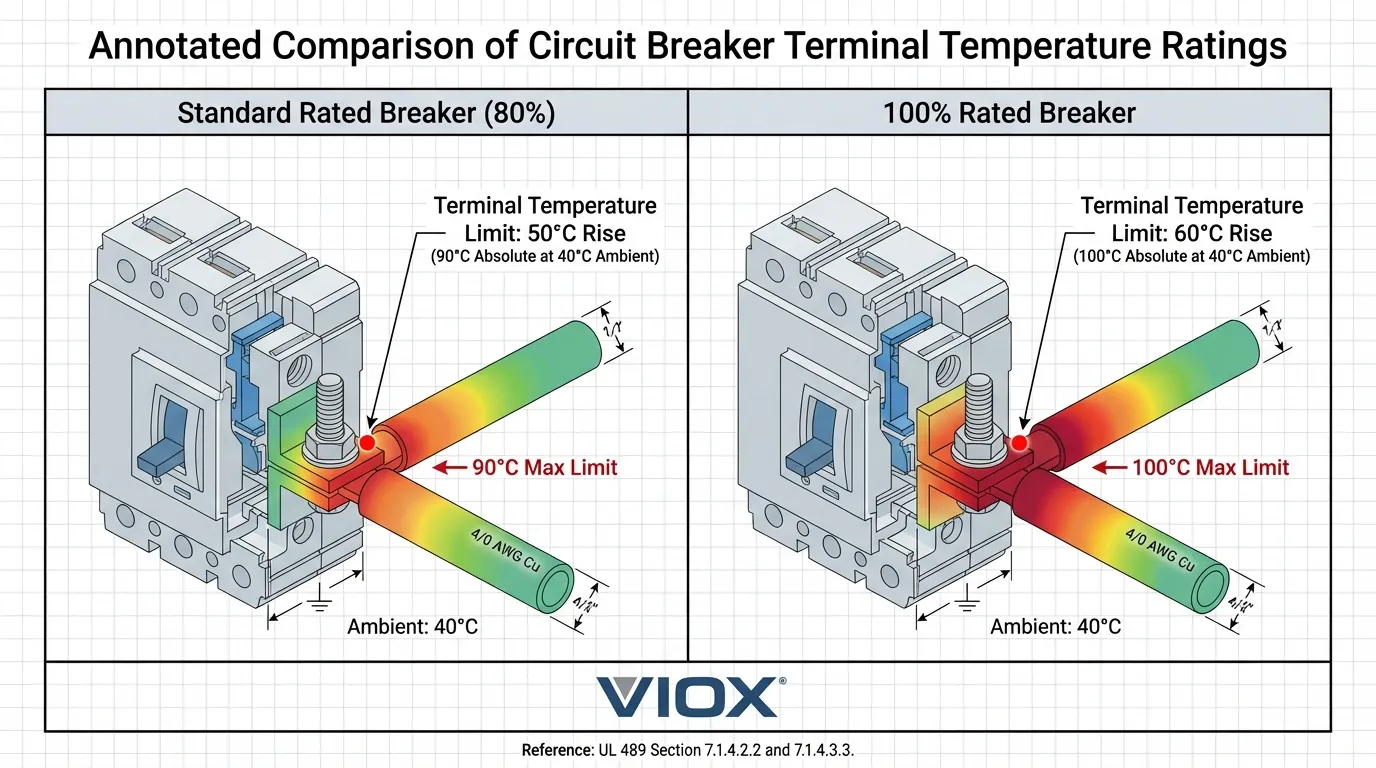
UL 489 အပူချိန်မြင့်တက်မှု လိုအပ်ချက်များ
UL 489 သည် မြောက်အမေရိက တပ်ဆင်မှုများတွင် အသုံးပြုသည့် ပုံသွင်းထားသော အိတ်ဆားကစ်ဘရိတ်ကာများအတွက် ပြည့်စုံသော အပူစမ်းသပ်မှု လိုအပ်ချက်များကို တည်ထောင်ထားသည်။ စံနှုန်းသည် စံနှုန်းသတ်မှတ်ထားသော (80% စဉ်ဆက်မပြတ်) နှင့် 100% သတ်မှတ်ထားသော ဘရိတ်ကာများအကြား ခွဲခြားထားသည်။.
ဇယား ၁- UL 489 အပူချိန်မြင့်တက်မှု ကန့်သတ်ချက်များ အကျဉ်းချုပ်
| အစိတ်အပိုင်း/တည်နေရာ | စံနှုန်းသတ်မှတ်ထားသော ဘရိတ်ကာ (80%) | 100% သတ်မှတ်ထားသော ဘရိတ်ကာ | ကိုးကားချက်အပိုဒ် |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wiring Terminals များ | 50°C မြင့်တက်မှု (40°C ပတ်ဝန်းကျင်တွင် 90°C အကြွင်းမဲ့) | 60°C မြင့်တက်မှု (40°C ပတ်ဝန်းကျင်တွင် 100°C အကြွင်းမဲ့) | UL 489 §7.1.4.2.2 / §7.1.4.3.3 |
| သတ္တုလက်ကိုင်များ/ခလုတ်များ | 60°C အမြင့်ဆုံးအကြွင်းမဲ့ | 60°C အမြင့်ဆုံးအကြွင်းမဲ့ | UL 489 §7.1.4.1.6 |
| သတ္တုမဟုတ်သော လက်ကိုင်များ/ခလုတ်များ | 85°C အမြင့်ဆုံးအကြွင်းမဲ့ | 85°C အမြင့်ဆုံးအကြွင်းမဲ့ | UL 489 §7.1.4.1.6 |
| အတွင်းပိုင်းအဆက်အသွယ်များ | သီးခြားကန့်သတ်ချက်မရှိပါ (ခံနိုင်ရည်အတွက် စမ်းသပ်ထားသည်) | သီးခြားကန့်သတ်ချက်မရှိပါ (ခံနိုင်ရည်အတွက် စမ်းသပ်ထားသည်) | UL 489 §8.7 |
| အကာအရံမျက်နှာပြင် | ပစ္စည်းနှင့် တည်နေရာအလိုက် ကွဲပြားသည် | ပစ္စည်းနှင့် တည်နေရာအလိုက် ကွဲပြားသည် | UL 489 §7.1.4 |
အဓိက ထိုးထွင်းသိမြင်မှု: စံနှုန်းနှင့် 100% သတ်မှတ်ထားသော ဘရိတ်ကာများ (50°C နှင့် 60°C) အကြား ဂိတ်အပူချိန်မြင့်တက်မှုတွင် 10°C ခြားနားမှုသည် အဆင့်သတ်မှတ်ထားသော လျှပ်စီးကြောင်းအပြည့်ဖြင့် စဉ်ဆက်မပြတ်လည်ပတ်သည့်အခါ အပိုအပူဖိအားကို ထင်ဟပ်စေသည်။ ဒါကြောင့် 100% သတ်မှတ်ထားသော ဘရိတ်ကာများ အဆင့်မြှင့်ထားသော ဂိတ်ဒီဇိုင်းနှင့် အပူစွန့်ထုတ်မှု လိုအပ်သည်။.

IEC 60947-2 နှင့် IEC 60898-1 အပူချိန်လိုအပ်ချက်များ
နိုင်ငံတကာစံနှုန်းများသည် အပူစွမ်းဆောင်ရည်အတွက် အလားတူသော်လည်း အနည်းငယ်ကွဲပြားသော ချဉ်းကပ်မှုကို ခံယူသည်-
ဇယား ၂- IEC 60947-2 နှင့် IEC 60898-1 အပူချိန်လိုအပ်ချက်များ နှိုင်းယှဉ်ခြင်း
| ဇာတိ | IEC 60947-2 (MCCB များ – စက်မှု) | IEC 60898-1 (MCB များ – လူနေအိမ်) | အဓိက ခြားနားချက် |
|---|---|---|---|
| ကိုးကားချက် ပတ်ဝန်းကျင် | 40°C (အချို့အသုံးချမှုများအတွက် 30°C ဖြစ်နိုင်သည်) | 30°C စံကိုးကားချက် | စက်မှုနှင့် လူနေအိမ် ကိုက်ညှိခြင်း |
| ဂိတ်အပူချိန်မြင့်တက်မှု | ဂိတ်အမျိုးအစားပေါ်မူတည်၍ 50-70°C | ဝက်အူဂိတ်များအတွက် 60°C | ပစ္စည်းအလိုက် သီးခြားကန့်သတ်ချက်များ |
| လည်ပတ်မှုလက်ကိုင် | 55°C မြင့်တက်မှု (သတ္တု)၊ 70°C မြင့်တက်မှု (လျှပ်ကာ) | အလားတူလိုအပ်ချက်များ | အသုံးပြုသူ အဆက်အသွယ် ဘေးကင်းရေး |
| အကာအရံမျက်နှာပြင် | ပစ္စည်းပေါ်မူတည်၍ 60-80°C မြင့်တက်မှု | 60°C မြင့်တက်မှု ပုံမှန် | ညစ်ညမ်းမှုဒီဂရီအလိုက် ကွဲပြားသည် |
| အပူခရီးစဉ် ကိုက်ညှိခြင်း | အဆင့်သတ်မှတ်ထားသော လျှပ်စီးကြောင်းတွင် 40°C ပတ်ဝန်းကျင် | သတ်မှတ်ထားသော current တွင်၊ 30°C ပတ်ဝန်းကျင်အပူချိန် | သက်ရောက်မှုရှိသည်။ derating factors များ |
အရေးကြီးမှတ်ချက်: IEC 60947-2 သည် အောက်ပါတို့နှင့် သက်ဆိုင်သည်။ ပုံသွင်းထားသော case circuit breakers (MCCBs) fault level မြင့်မားပြီး ပတ်ဝန်းကျင်အခြေအနေ ပိုမိုလိုအပ်သော စက်မှုလုပ်ငန်းသုံး application များအတွက် ဒီဇိုင်းထုတ်ထားပြီး IEC 60898-1 သည် လူနေအိမ်နှင့် ကုန်သွယ်လုပ်ငန်းသုံး အသေးစား circuit breaker များကို အုပ်ချုပ်သည်။.
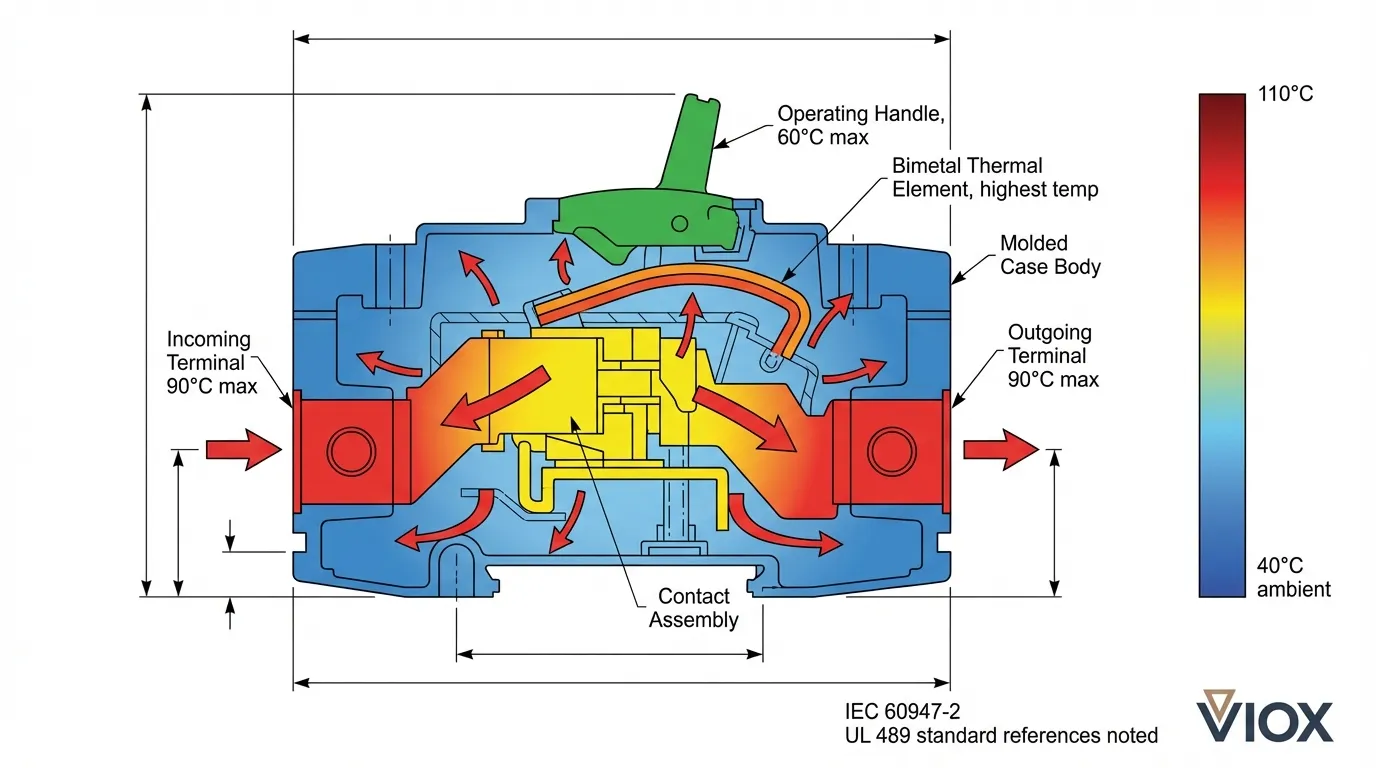
မတူညီသော ပတ်ဝန်းကျင်အခြေအနေများတွင် အမြင့်ဆုံး အပူချိန်များ
လက်တွေ့တပ်ဆင်မှုများသည် စံ 40°C ချိန်ညှိအပူချိန်တွင် လည်ပတ်ခဲပါသည်။ သင့်လျော်သောအသုံးပြုမှုအတွက် မတူညီသော ပတ်ဝန်းကျင်အခြေအနေများတွင် အမြင့်ဆုံးအပူချိန်ကန့်သတ်ချက်များကို နားလည်ရန် အရေးကြီးပါသည်။.
ဇယား ၃: မတူညီသော ပတ်ဝန်းကျင်အခြေအနေများတွင် အမြင့်ဆုံး အပူချိန်များ
| ပတ်ဝန်းကျင် အပူချိန် | Standard Rated Terminal (50°C မြင့်တက်) | 100% Rated Terminal (60°C မြင့်တက်) | Metallic Handle (60°C max) | Non-metallic Handle (85°C max) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25°C (77°F) | 75°C (167°F) | 85°C (185°F) | 60°C (140°F) | 85°C (185°F) |
| 30°C (86°F) | 80°C (176°F) | 90°C (194°F) | 60°C (140°F) | 85°C (185°F) |
| 40°C (104°F) | 90°C (194°F) | 100°C (212°F) | 60°C (140°F) | 85°C (185°F) |
| 50°C (122°F) | 100°C (212°F) ⚠️ | 110°C (230°F) ⚠️ | 60°C (140°F) | 85°C (185°F) |
| 60°C (140°F) | 110°C (230°F) ❌ | 120°C (248°F) ❌ | 60°C (140°F) | 85°C (185°F) |
⚠️ = derating သို့မဟုတ် အအေးခံခြင်းကို မြှင့်တင်ရန် လိုအပ်သည်။
❌ = ပုံမှန် conductor insulation ratings (90°C THHN/XHHW) ထက် ကျော်လွန်သည်။
အရေးကြီးတယ်။: ပတ်ဝန်းကျင်အပူချိန် မြင့်မားလာသောအခါ terminals များသည် စံ 75°C သို့မဟုတ် 90°C conductor insulation ၏ အပူချိန် rating ထက် ကျော်လွန်နိုင်သည်။ ဒါကြောင့် အပူချိန်အတွက် လျှပ်စစ် derating ပူပြင်းသောပတ်ဝန်းကျင်တွင် အရေးကြီးလာသည်။.
Thermal Testing လုပ်ထုံးလုပ်နည်းများနှင့် ချိန်ညှိခြင်း
UL 489 နှင့် IEC 60947-2 နှစ်ခုစလုံးသည် ထုတ်လုပ်သူများအား ကျယ်ပြန့်သော thermal testing ပြုလုပ်ရန် လိုအပ်သည်-
- Test Setup: Breakers များကို ၎င်းတို့၏ ရည်ရွယ်ထားသော configuration (ပိတ်ထားသော သို့မဟုတ် ဖွင့်ထားသော) တွင် တပ်ဆင်ပြီး သတ်မှတ်ထားသော current သို့ တင်ဆောင်ထားသည်။
- Stabilization Period: thermal equilibrium ရောက်သည်အထိ အနည်းဆုံး ၃ နာရီ ဆက်တိုက်လည်ပတ်ပါ။
- Measurement Points: Thermocouples များကို terminals၊ handles များနှင့် enclosure မျက်နှာပြင်များတွင် ထားရှိသည်။
- Ambient Control: 40°C ပတ်ဝန်းကျင် (UL 489) သို့မဟုတ် ထုတ်လုပ်သူ၏ ကြေငြာထားသော reference temperature (IEC) အရ စမ်းသပ်ခြင်းကို ပြုလုပ်သည်။
- အောင်/ရှုံး စံနှုန်းများ: တိုင်းတာသည့်နေရာအားလုံးသည် သတ်မှတ်ထားသော အပူချိန်မြင့်တက်မှု ကန့်သတ်ချက်များအောက်တွင် ရှိနေရမည်။
VIOX သည် အားလုံးတွင် thermal testing ပြုလုပ်သည်။ circuit breaker ဒီဇိုင်း ကျွန်ုပ်တို့၏ အသိအမှတ်ပြု ဓာတ်ခွဲခန်းများတွင် IEC နှင့် UL လိုအပ်ချက်များနှင့်အညီ လိုက်နာဆောင်ရွက်ကြောင်း သေချာစေပါသည်။ ဤ dual certification သည် ကျွန်ုပ်တို့၏ ထုတ်ကုန်များကို ကမ္ဘာ့ဈေးကွက်များတွင် ယုံကြည်မှုအပြည့်ဖြင့် ဝန်ဆောင်မှုပေးနိုင်စေပါသည်။.
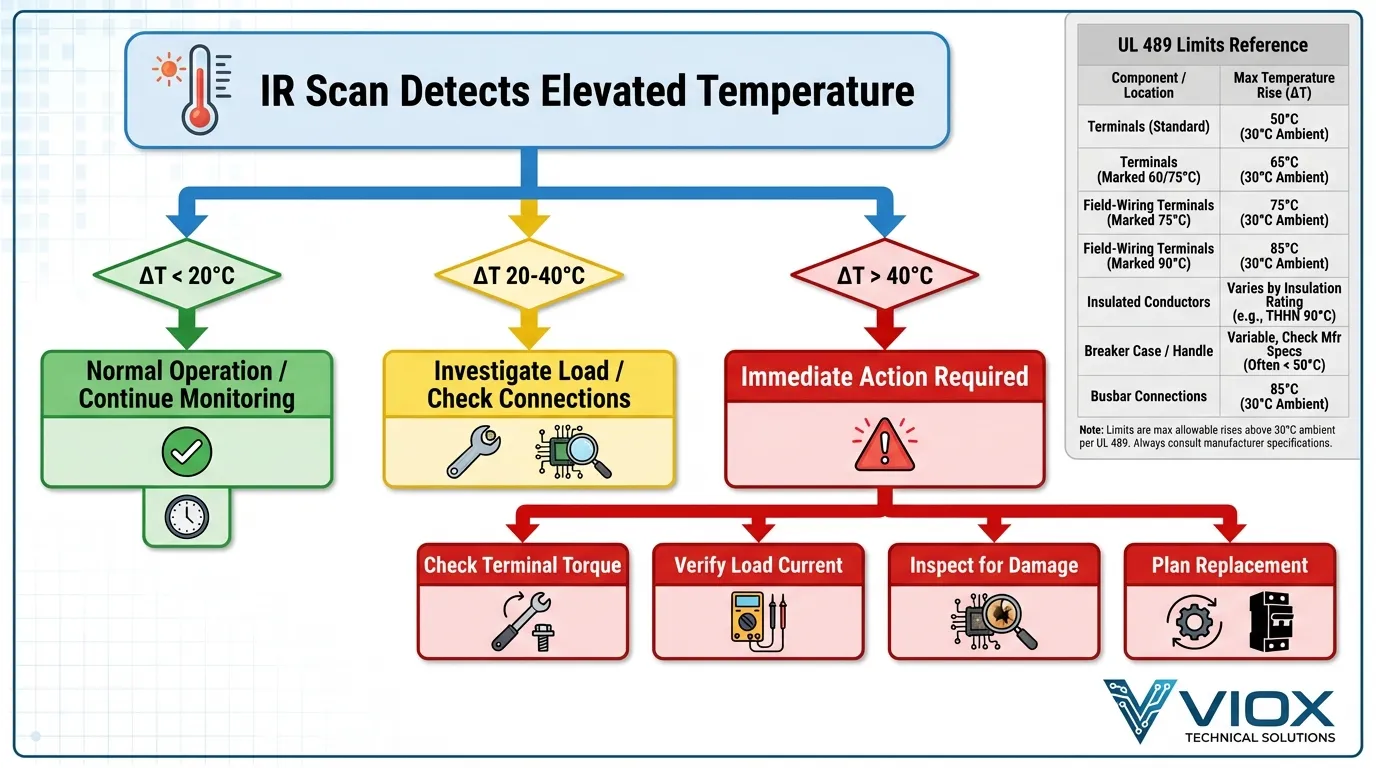
Infrared Thermography: လက်တွေ့ အပူချိန် စောင့်ကြည့်ခြင်း
Infrared (IR) thermography သည် circuit breaker အပူချိန်ကို ကျူးကျော်ဝင်ရောက်ခြင်းမရှိသော စောင့်ကြည့်ခြင်းအတွက် စက်မှုလုပ်ငန်းစံနှုန်း ဖြစ်လာခဲ့သည်။ သို့သော် သင့်လျော်သောအဓိပ္ပာယ်ဖွင့်ဆိုမှုသည် နည်းပညာနှင့် စံနှုန်းနှစ်ခုလုံးကို နားလည်ရန် လိုအပ်သည်။.
ဇယား ၄: IR Thermography အဓိပ္ပာယ်ဖွင့်ဆိုခြင်း လမ်းညွှန်
| အပူချိန်မြင့်တက်မှု (ΔT) | Thermal Signature | Recommended Action | Urgency Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| ပတ်ဝန်းကျင်ထက် 0-10°C မြင့်သည်။ | thermal ပုံရိပ်တွင် အစိမ်း/အပြာရောင် | ပုံမှန်လည်ပတ်မှု; baseline ကို မှတ်တမ်းတင်ပါ။ | Routine |
| ပတ်ဝန်းကျင်ထက် 10-20°C မြင့်သည်။ | thermal ပုံရိပ်တွင် အဝါရောင် | trend ကို စောင့်ကြည့်ပါ။ load သည် rating အတွင်းရှိမရှိ စစ်ဆေးပါ။ | Low Priority |
| ပတ်ဝန်းကျင်ထက် 20-30°C မြင့်သည်။ | thermal ပုံရိပ်တွင် လိမ္မော်ရောင် | ချိတ်ဆက်မှုများကို စုံစမ်းပါ။ terminal torque ကို စစ်ဆေးပါ။ conductor အရွယ်အစားကို စစ်ဆေးပါ။ | Medium Priority |
| ပတ်ဝန်းကျင်ထက် 30-40°C မြင့်သည်။ | thermal ပုံရိပ်တွင် အနီရောင် | ချက်ချင်းစစ်ဆေးရန် စီစဉ်ပါ။ ချိတ်ဆက်မှုများ လျော့ရဲခြင်း၊ သံချေးတက်ခြင်း သို့မဟုတ် ဝန်ပိုခြင်း ရှိမရှိ စစ်ဆေးပါ။ | High Priority |
| ပတ်ဝန်းကျင်ထက် >40°C ကျော် | အပူပုံရိပ်တွင် အနီရင့်/အဖြူရောင် | ချက်ချင်းဆောင်ရွက်ရန်လိုအပ်သည်; ဖြစ်နိုင်ချေရှိသော ဘေးအန္တရာယ်; အစားထိုးရန် စီစဉ်ပါ | ဝေဖန်ပိုင်းခြားပါ။ |
IR Scanning အတွက် အကောင်းဆုံးအလေ့အကျင့်များ:
- စကင်မစစ်ဆေးမီ အနည်းဆုံး ၃ နာရီကြာ တည်ငြိမ်သောလည်ပတ်မှုကို ခွင့်ပြုပါ
- တိကျသော ΔT တွက်ချက်မှုအတွက် ပတ်ဝန်းကျင်အပူချိန်ကို သီးခြားတိုင်းတာပါ
- အလားတူဝန်အောက်တွင်ရှိသော အလားတူ Breaker များကို နှိုင်းယှဉ်ပြီး ပုံမှန်မဟုတ်သော အရာများကို ရှာဖွေပါ
- ယိုယွင်းပျက်စီးမှုလမ်းကြောင်းများကို ဖော်ထုတ်ရန် အချိန်ကြာလာသည်နှင့်အမျှ တိုင်းတာမှုများကို မှတ်တမ်းတင်ပါ
- Emissivity ဆက်တင်များကို ထည့်သွင်းစဉ်းစားပါ (ပုံမှန်အားဖြင့် ဆေးသုတ်ထားသော မျက်နှာပြင်များအတွက် 0.95၊ အဝတ်မပါသော ကြေးနီအတွက် 0.3-0.5)
Hot Circuit Breaker များ၏ ချို့ယွင်းချက်များကို ရှာဖွေခြင်း
အပူပုံရိပ်ဖော်ခြင်း သို့မဟုတ် ရုပ်ပိုင်းဆိုင်ရာစစ်ဆေးခြင်းသည် မြင့်မားသောအပူချိန်များကို ဖော်ပြသောအခါ၊ စနစ်တကျ ချို့ယွင်းချက်ရှာဖွေခြင်းသည် မရှိမဖြစ်လိုအပ်ပါသည်။.
ဇယား ၅- ချို့ယွင်းချက်ရှာဖွေခြင်းလမ်းညွှန် - အပူချိန်နှင့် ပြဿနာရှာဖွေခြင်း
| လက္ခဏာ | ဖွယ်ရှိပီး | ရောဂါရှာဖွေရေးအဆင့်များ | ဖြေရှင်းနည်း |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hot terminals သာ | ချောင်နေသော ချိတ်ဆက်မှု၊ အရွယ်အစားမမှန်သော conductor၊ မြင့်မားသော ခုခံမှုအဆစ် | Torque သတ်မှတ်ချက်များကို စစ်ဆေးပါ။ သံချေးတက်ခြင်းအတွက် စစ်ဆေးပါ။ conductor ampacity ကို အတည်ပြုပါ | terminals များကို ပြန်လည်တင်းကျပ်ပါ။ အဆက်အသွယ်များကို သန့်ရှင်းပါ။ လိုအပ်ပါက conductor ကို အရွယ်အစားကြီးအောင်ပြုလုပ်ပါ |
| Hot breaker body | ဝန်ပိုအခြေအနေ၊ ယိုယွင်းပျက်စီးနေသော bimetal၊ အတွင်းပိုင်းအဆက်အသွယ်များ ဟောင်းနွမ်းခြင်း | အမှန်တကယ်ဝန်စီးကြောင်းကို တိုင်းတာပါ။ breaker အဆင့်သတ်မှတ်ချက်နှင့် နှိုင်းယှဉ်ပါ။ ခရီးစဉ်မျဉ်းကွေးကို စစ်ဆေးပါ | ဝန်ကိုလျှော့ချပါ။ သက်တမ်းကုန်ခါနီးပါက breaker ကို အစားထိုးပါ |
| Hot handle | အဆက်အသွယ်များ/bimetal မှ အတွင်းပိုင်းအပူလွှဲပြောင်းခြင်း (အချို့အတိုင်းအတာအထိ ပုံမှန်) | လက်ကိုင်အပူချိန်ကို အတည်ပြုပါ <60°C (metallic) or <85°C (non-metallic) | ကန့်သတ်ချက်အတွင်းရှိပါက အရေးယူဆောင်ရွက်ရန်မလိုပါ။ ကျော်လွန်ပါက breaker ကို အစားထိုးပါ |
| Panel တစ်ခုလုံး ပူနေခြင်း | လုံလောက်သောလေဝင်လေထွက်မရှိခြင်း၊ အလွန်အကျွံအုပ်စုဖွဲ့ခြင်း၊ မြင့်မားသောပတ်ဝန်းကျင် | အကာအရံလေဝင်လေထွက်ကို စစ်ဆေးပါ။ panel အတွင်းရှိ ပတ်ဝန်းကျင်ကို တိုင်းတာပါ။ ပြန်လည်သုံးသပ်ပါ derating factors များ | လေဝင်လေထွက်ကို မြှင့်တင်ပါ။ အအေးခံစနစ်ထည့်ပါ။ NEC/IEC အရ breakers များကို လျှော့ချပါ |
| အတူတူပင် အိမ်နီးချင်းများထက် Breaker တစ်ခုသည် သိသိသာသာ ပိုပူနေခြင်း | အတွင်းပိုင်းချို့ယွင်းချက်၊ အဆက်အသွယ်ယိုယွင်းပျက်စီးခြင်း၊ ချိန်ညှိမှုပြောင်းလဲခြင်း | အလားတူဝန်အောက်တွင်ရှိသော အလားတူ Breaker များ၏ အပူချိန်များကို နှိုင်းယှဉ်ပါ | သံသယရှိသော breaker ကို အစားထိုးပါ။ အကြောင်းရင်းကို စုံစမ်းပါ |
ဘယ်အချိန်မှာ အစားထိုးရမလဲ: Breaker သည် သင့်လျော်သော ဝန်တင်အခြေအနေများအောက်တွင်ပင် ၎င်း၏ အပူချိန်မြင့်တက်မှု ကန့်သတ်ချက်များထက် အဆက်မပြတ်လည်ပတ်နေပါက အစားထိုးရန် မဖြစ်မနေလိုအပ်ပါသည်။ အပူလွန်ကဲသော breakers များကို ဆက်လက်လည်ပတ်ခြင်းသည် လျှပ်ကာပျက်ကွက်ခြင်း၊ မီးလောင်ခြင်း သို့မဟုတ် overcurrent ကာကွယ်မှု ဆုံးရှုံးခြင်းတို့ကို ဖြစ်စေနိုင်သည်။ အကြောင်းပိုမိုလေ့လာပါ မကောင်းတဲ့ circuit breakers တွေကို ဖော်ထုတ်ခြင်း.
Conductor Insulation Compatibility
အပူချိန်မြင့်တက်မှု ကန့်သတ်ချက်များ၏ အရေးကြီးသော်လည်း မကြာခဏ လျစ်လျူရှုထားသော ရှုထောင့်မှာ conductor insulation အဆင့်သတ်မှတ်ချက်များနှင့် ၎င်းတို့၏ ဆက်စပ်မှုဖြစ်သည်။ NEC နှင့် IEC စံနှုန်းများသည် conductor insulation အပူချိန်အဆင့်သတ်မှတ်ချက်များသည် terminal အပူချိန်နှင့် ကိုက်ညီရန် သို့မဟုတ် ကျော်လွန်ရန် လိုအပ်သည်။.
Common Conductor Insulation အမျိုးအစားများ:
- 60°C (140°F): TW, UF (ပိုမိုဟောင်းနွမ်းသော တပ်ဆင်မှုများ)
- 75°C (167°F): THW, THWN, RHW, USE
- 90°C (194°F): THHN, THWN-2, XHHW-2, RHH, RHW-2
50°C မြင့်တက်မှု (40°C ပတ်ဝန်းကျင်တွင် 90°C အကြွင်းမဲ့) ရှိသော စံနှုန်းသတ်မှတ်ထားသော breakers များအတွက်၊ 90°C insulation သည် လုံလောက်သော အနားသတ်ကို ပေးပါသည်။ သို့သော် 60°C insulation သည် မလုံလောက်ဘဲ စောစီးစွာ ပျက်ကွက်နိုင်သည်။.
အဓိကစည်းမျဉ်း: conductor insulation အပူချိန်အဆင့်သတ်မှတ်ချက်သည် မျှော်မှန်းထားသော ပတ်ဝန်းကျင်အခြေအနေများအောက်တွင် terminal အကြွင်းမဲ့အပူချိန်ထက် ≥ ရှိမရှိ အမြဲစစ်ဆေးပါ။ ၎င်းသည် ပူပြင်းသောပတ်ဝန်းကျင်များတွင် သို့မဟုတ် အသုံးပြုသည့်အခါ အထူးအရေးကြီးပါသည်။ 100% သတ်မှတ်ထားသော ဘရိတ်ကာများ.
IEC နှင့် UL စံနှုန်းများ- အဓိက ကွာခြားချက်များ
IEC 60947-2 နှင့် UL 489 တို့သည် အလားတူ ရည်မှန်းချက်များကို မျှဝေကြသော်လည်း အရေးကြီးသော ကွာခြားချက်များစွာသည် ထုတ်ကုန်ရွေးချယ်မှုကို ထိခိုက်စေသည်-
| ရှုထောင့် | IEC ၆၀၉၄၇-၂ | အဆိုပါ ၄၈၉ | ထိခိုက်မှု |
|---|---|---|---|
| ကိုးကားချက် ပတ်ဝန်းကျင် | 40°C (ကွဲပြားနိုင်သည်) | 40°C (သတ်မှတ်ထားသည်) | IEC သည် ထုတ်လုပ်သူမှ ကြေငြာထားသော ကိုးကားချက်ကို ခွင့်ပြုသည် |
| Terminal မြင့်တက်မှု ကန့်သတ်ချက်များ | ပစ္စည်းအပေါ်မူတည်သည် (50-70°C) | သတ်မှတ်ထားသည် (50°C စံ၊ 100% အတွက် 60°C) | IEC သည် terminal တည်ဆောက်မှုအပေါ်အခြေခံ၍ ပိုမိုပြောင်းလွယ်ပြင်လွယ်ရှိသည် |
| Enclosure စမ်းသပ်ခြင်း | ကိုယ်စားပြု အကာအရံတွင် စမ်းသပ်သည်။ | ဖြစ်နိုင်ခြေအနည်းဆုံး အကာအရံတွင် စမ်းသပ်သည်။ | UL သည် ပို၍ပင် တင်းကျပ်နိုင်သည်။ |
| Continuous Rating | 100% သည် မူလအားဖြင့် စဉ်ဆက်မပြတ်ဖြစ်သည်။ | 80% သည် 100% ဟုမှတ်သားမထားပါက စဉ်ဆက်မပြတ်ဖြစ်သည်။ | IEC breakers များသည် ယေဘုယျအားဖြင့် စဉ်ဆက်မပြတ်တာဝန်အတွက် ပိုမိုခိုင်ခံ့သည်။ |
| Derating Guidance | Manufacturer-provided curves | NEC provides application guidance | Different approaches to high-temperature environments |
For panel builders serving global markets, VIOX offers circuit breakers certified to both standards, ensuring compliance regardless of installation location. Our quality assurance processes verify thermal performance to the most stringent requirements.
လက်တွေ့အသုံးချမှု လမ်းညွှန်ချက်များ
For Panel Builders:
- Always verify breaker temperature ratings match your application environment
- Account for enclosure heating effects—interior ambient can be 10-20°C above room temperature
- Use thermal imaging during commissioning to establish baseline temperatures
- Implement periodic IR scanning as part of preventive maintenance programs
- Document all temperature readings for trend analysis
Facility Manager များအတွက်:
- Schedule annual thermal surveys of critical electrical distribution equipment
- Train maintenance personnel to recognize abnormal thermal patterns
- Establish temperature thresholds that trigger investigation (typically ΔT > 20°C)
- Maintain records of IR scans to identify degradation trends
- Budget for proactive replacement of breakers showing thermal degradation
For Electrical Contractors:
- Verify terminal torque specifications during installation—loose connections are the #1 cause of hot terminals
- Use anti-oxidant compound on aluminum conductors to prevent high-resistance joints
- Allow adequate spacing between breakers in panels to promote heat dissipation
- Consider ambient temperature derating in hot environments
- Document installation conditions for future reference
FAQ: Circuit Breaker Temperature Rise
Q: What is the maximum safe temperature for a circuit breaker terminal?
A: For standard-rated breakers per UL 489, terminals should not exceed 90°C absolute temperature (50°C rise above 40°C ambient). For 100%-rated breakers, the limit is 100°C absolute (60°C rise). IEC 60947-2 has similar limits but may vary based on terminal material and construction. Always verify the specific breaker’s datasheet.
Q: How do I know if my circuit breaker is running too hot?
A: Use infrared thermography to measure the temperature rise above ambient. If ΔT exceeds 30°C, investigate immediately. Physical signs include discolored insulation near terminals, a burning smell, or buzzing/humming sounds. If the breaker handle is uncomfortably hot to touch (>60°C for metal, >85°C for plastic), it may be operating outside normal parameters.
Q: What’s the difference between temperature rise and absolute temperature?
A: Temperature rise (ΔT) is the increase above ambient temperature, while absolute temperature is the actual measured temperature. For example, a terminal at 85°C in a 40°C ambient has a 45°C temperature rise. Standards specify rise limits because ambient conditions vary, but absolute temperature determines insulation compatibility.
Q: Can I use a 60°C rated wire on a circuit breaker terminal?
A: Generally no, unless the breaker is specifically rated for 60°C terminations and operates in a controlled environment. Most modern breakers assume 75°C minimum conductor insulation. With a 50°C terminal rise at 40°C ambient, you’d reach 90°C absolute—well above 60°C insulation limits. Always match or exceed the terminal temperature rating.
Q: How long should I wait before taking IR readings on a breaker?
A: Allow minimum 3 hours of continuous operation at steady load for the breaker to reach thermal equilibrium. Thermal mass in the breaker and surrounding enclosure takes time to stabilize. For critical measurements, 4-6 hours is preferable. Taking readings too early will underestimate actual operating temperatures.
Q: What does UL 489 say about 100% rated breakers?
A: UL 489 Paragraph 7.1.4.3.3 allows 100%-rated breakers to have terminal temperature rise up to 60°C (vs. 50°C for standard breakers), resulting in 100°C absolute temperature at 40°C ambient. These breakers must be specifically marked “Suitable for Continuous Operation at 100% of Rating” and typically feature enhanced terminal designs and heat dissipation.
သော့ထုတ်ယူမှုများ
- Temperature rise limits are safety-critical: UL 489 and IEC 60947-2 establish maximum temperature rise values to prevent insulation failure, contact degradation, and fire hazards in circuit breakers.
- Standard vs. 100% rated breakers differ by 10°C: Standard breakers allow 50°C terminal rise (90°C absolute at 40°C ambient), while 100% rated breakers permit 60°C rise (100°C absolute)—a crucial difference for continuous-duty applications.
- Absolute temperature = Ambient + Rise: Always calculate absolute terminal temperature based on actual ambient conditions, not just the standard 40°C calibration temperature, especially in hot environments.
- Conductor insulation must match terminal temperature: Use 90°C rated conductors (THHN, XHHW-2) for modern breakers; 60°C insulation is inadequate for most applications and violates code requirements.
- IR thermography requires 3+ hours stabilization: Thermal imaging is only accurate after circuit breakers reach thermal equilibrium—premature readings underestimate actual operating temperatures.
- ΔT > 30°C demands immediate investigation: Temperature rise exceeding 30°C above ambient indicates loose connections, overloading, or internal degradation requiring prompt corrective action.
- IEC and UL standards align on fundamentals: While test procedures differ slightly, both IEC 60947-2 and UL 489 target similar terminal temperature limits, ensuring global safety standards.
- Preventive maintenance prevents failures: Regular thermal surveys, proper terminal torque, and trend analysis identify problems before they cause downtime or safety incidents—invest in IR equipment and training.
For reliable circuit protection that meets the most stringent thermal performance requirements, explore VIOX’s complete line of MCBs နှင့် MCCBs engineered to IEC and UL standards. Our technical team can assist with product selection, thermal analysis, and application-specific guidance to ensure your installations operate safely within temperature limits.


