Bentuk Penuh MCB dalam Kelistrikan

Bentuk penuh MCB adalah “Pemutus Sirkuit Miniatur“ – sebuah perangkat keselamatan listrik penting yang secara otomatis memutuskan sirkuit listrik ketika arus lebih, korsleting, atau kondisi gangguan terdeteksi. Bentuk penuh MCB mewakili salah satu perangkat pelindung terpenting dalam instalasi listrik modern.
Jawaban Cepat: MCB adalah singkatan dari Miniature Circuit Breaker, yang melindungi sirkuit listrik dari kerusakan dengan secara otomatis memutus daya selama kondisi listrik berbahaya.
Memahami bentuk penuh MCB dan aplikasinya sangat penting untuk keselamatan listrik, kepatuhan kode, dan perlindungan sirkuit yang tepat dalam aplikasi perumahan, komersial, dan industri.
Bentuk Penuh MCB Dijelaskan: Apa Kepanjangan dari MCB?
Bentuk penuh MCB – Miniature Circuit Breaker – memberi tahu Anda dengan tepat apa yang dilakukan perangkat ini:
- Miniature: Ukuran ringkas dibandingkan dengan pemutus sirkuit yang lebih besar
- Sirkuit: Melindungi sirkuit dan jalur listrik
- Breaker: Memutus atau menginterupsi aliran listrik selama gangguan
Variasi Bentuk Penuh MCB Umum Lainnya
| Singkatan | Formulir Lengkap | Konteks |
|---|---|---|
| MCB | Pemutus Sirkuit Miniatur | Istilah listrik standar |
| MCB | Motor Circuit Breaker | Aplikasi perlindungan motor |
| MCB | Magnetic Circuit Breaker | Menekankan mekanisme trip magnetik |
Apa itu MCB dalam Sistem Kelistrikan?
Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB) adalah perangkat switching listrik yang dioperasikan secara otomatis yang dirancang untuk melindungi sirkuit listrik dari kerusakan yang disebabkan oleh kondisi arus lebih, termasuk korsleting dan situasi kelebihan beban. Tidak seperti sekering tradisional yang memerlukan penggantian setelah beroperasi, MCB dapat direset dan digunakan kembali berkali-kali.
Fungsi Utama: MCB mendeteksi kondisi listrik abnormal dan segera memutuskan sirkuit untuk mencegah kerusakan peralatan, kebakaran listrik, dan potensi bahaya sengatan listrik.
MCB vs Perangkat Perlindungan Sirkuit Lainnya: Perbandingan Lengkap
| Fitur | MCB (Pemutus Sirkuit Mini) | MCCB (Molded Case Circuit Breaker) | Fuse | RCD/GFCI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peringkat Saat Ini | 0,5A hingga 125A | 100A hingga 2500A | 1A hingga 800A | 25A hingga 100A |
| Peringkat Tegangan | Hingga 400V AC | Hingga 1000V AC | Beragam | Hingga 500V AC |
| Kapasitas Putus | 6kA hingga 25kA | 25kA hingga 200kA | 10kA hingga 200kA | 6kA hingga 25kA |
| Waktu Respons | 0,02 hingga 0,05 detik | 0,02 hingga 0,1 detik | 0,001 hingga 1 detik | 0,025 hingga 0,04 detik |
| Dapat digunakan kembali | Ya (reset setelah trip) | Ya (reset setelah trip) | Tidak (ganti setelah putus) | Ya (reset setelah trip) |
| Jenis Perlindungan | Arus Lebih & Korsleting | Arus Lebih & Korsleting | Arus Lebih & Korsleting | Gangguan Tanah & Arus Sisa |
| Biaya | Rendah hingga Sedang | Sedang hingga Tinggi | Sangat Rendah | Sedang |
| Perawatan | Minimal | Inspeksi rutin diperlukan | Hanya penggantian | Pengujian rutin diperlukan |
| Aplikasi | Perumahan & Komersial Ringan | Industri & Komersial Berat | Semua aplikasi | Hanya perlindungan keselamatan |
Jenis-jenis MCB dan Aplikasinya
Klasifikasi Berdasarkan Karakteristik Arus
Type B MCBs (3-5 times rated current)
- Aplikasi: Penerangan perumahan dan sirkuit daya umum
- Rentang Trip: 3In hingga 5In (di mana In = arus terukur)
- Contoh Penggunaan: Penerangan LED, kipas langit-langit, outlet umum
- Perlindungan: Aplikasi arus masuk sedang
Type C MCBs (5-10 times rated current)
- Aplikasi: Aplikasi komersial dan industri ringan
- Rentang Trip: 5In hingga 10In
- Contoh Penggunaan: Motor, transformator, lampu neon
- Perlindungan: Toleransi arus masuk lebih tinggi
Type D MCBs (10-20 times rated current)
- Aplikasi: Motor industri dan peralatan arus masuk tinggi
- Rentang Trip: 10In hingga 20In
- Contoh Penggunaan: Motor besar, peralatan las, mesin X-ray
- Perlindungan: Aplikasi arus masuk sangat tinggi
Klasifikasi Berdasarkan Jumlah Kutub
| Jenis MCB | Deskripsi | Aplikasi | Peringkat Tegangan |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kutub Tunggal (1P) | Memutus satu konduktor aktif | Sirkuit AC fase tunggal | 240V AC |
| Dua Kutub (2P) | Memutus fasa dan netral | Satu fasa dengan proteksi netral | 240V AC |
| Tiga Kutub (3P) | Memutus tiga konduktor fasa | Sirkuit AC tiga fasa | 415V AC |
| Empat Tiang (4P) | Memutus tiga fasa + netral | Tiga fase dengan netral | 415V AC |
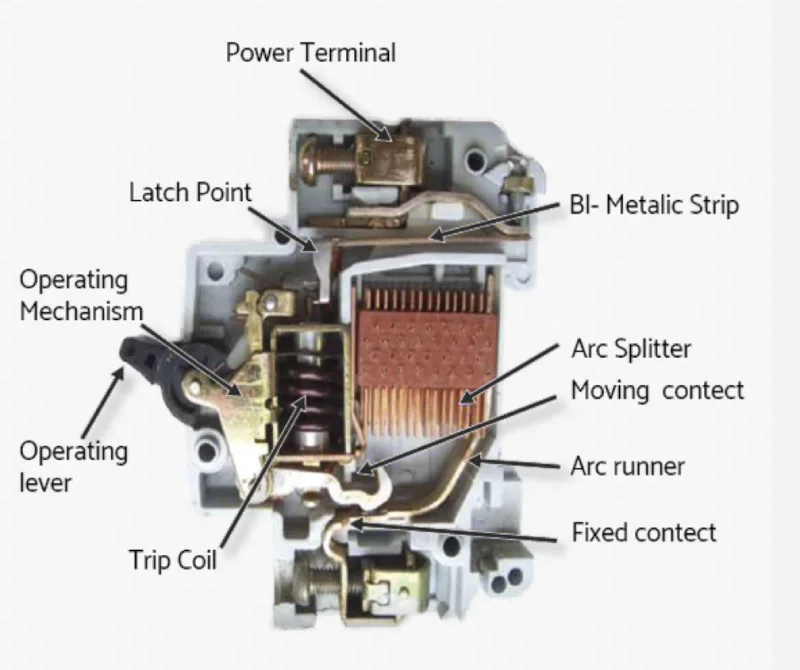
Cara Kerja MCB: Operasi Teknis
Mekanisme Operasi
1. Perlindungan Termal (Beban Berlebih)
- Bimetallic strip heats up during sustained overcurrent
- Strip membengkok dan memicu mekanisme trip
- Waktu respons: 1 detik hingga beberapa menit tergantung pada tingkat beban lebih
2. Perlindungan Magnetik (Hubung Pendek)
- Kumparan elektromagnetik menghasilkan medan magnet saat arus tinggi
- Gaya magnet menarik mekanisme trip secara instan
- Waktu respons: 0,02 hingga 0,05 detik
3. Pemadaman Busur Api
- Busur api terbentuk saat kontak terpisah di bawah beban
- Sistem peluncur busur api memadamkan busur api dengan aman
- Gas SF6 atau ruang hampa pada model canggih
Warning Peringatan Keamanan
Selalu pastikan daya benar-benar terputus sebelum mengerjakan instalasi MCB. Hanya teknisi listrik yang memenuhi syarat yang boleh memasang atau mengganti MCB untuk memastikan kepatuhan terhadap kode kelistrikan dan standar keselamatan.
Kriteria Pemilihan MCB: Panduan Ahli
Pilihan Peringkat Saat Ini
Langkah 1: Hitung Arus Beban
Arus Beban = Total Daya (W) ÷ Tegangan (V)
Langkah 2: Terapkan Faktor Penurunan Peringkat
- Penurunan suhu lingkungan: 0.8-1.0
- Faktor pengelompokan: 0.8-0.95
- Penurunan kabel: Sesuai dengan pabrikan kabel
Langkah 3: Pilih Rating MCB
- Rating MCB harus ≥ 125% dari arus beban yang dihitung
- Tidak boleh melebihi kapasitas hantar arus kabel
- Pertimbangkan ekspansi beban di masa mendatang (biasanya 20-30%)
Pemilihan Kapasitas Pemutusan
| Jenis Instalasi | Kapasitas Pemutusan Minimum |
|---|---|
| Perumahan | 6kA |
| Komersial | 10kA |
| Industri | 25kA |
| Industri Berat | 50kA+ |
Expert
Selalu verifikasi arus hubung singkat prospektif pada titik pemasangan menggunakan perhitungan atau pengukuran tingkat gangguan. Kapasitas pemutusan MCB harus melebihi arus gangguan maksimum setidaknya dengan margin keselamatan 25%.
Panduan Pemasangan dan Pengkabelan
Praktik Pengkabelan Standar
Koneksi MCB Satu Kutub:
- Hubungkan kabel fasa masuk ke terminal input MCB
- Hubungkan kabel fasa keluar ke terminal output MCB
- Kabel netral melewati MCB (terhubung langsung di papan distribusi)
- Kabel ground terhubung langsung ke bar ground
Koneksi MCB Tiga Kutub:
- Hubungkan ketiga kabel fasa ke terminal input MCB masing-masing
- Hubungkan kabel fasa beban ke terminal output MCB
- Pertahankan urutan fasa yang benar (R-Y-B)
- Gunakan ukuran kabel yang sesuai untuk setiap fasa
⚠️ Persyaratan Kepatuhan Kode
Standar IEC 60898:
- MCB harus sesuai dengan IEC 60898-1 untuk aplikasi AC
- Pengujian hubung singkat dan beban lebih wajib
- Batas kenaikan suhu dan persyaratan isolasi
Persyaratan Kode Kelistrikan Nasional (NEC) :
- Pasal 240: Persyaratan Proteksi Arus Lebih
- Bagian 240.4: Perlindungan konduktor
- Bagian 240.6: Rating ampere standar
Standar Instalasi:
- Jarak bebas minimum: 50mm di semua sisi
- Rating suhu lingkungan: -25°C hingga +70°C
- Rating perlindungan minimum IP20 untuk penggunaan di dalam ruangan
Masalah Umum dan Pemecahan Masalah
Masalah MCB Sering Trip
Masalah:
MCB trip segera setelah direset
Penyebab:
Hubung singkat pada kabel hilir
Solusi:
- Lepaskan semua beban dari sirkuit
- Uji resistansi isolasi menggunakan megger
- Identifikasi dan perbaiki lokasi hubung singkat
- Ganti kabel yang rusak jika perlu
Masalah:
MCB trip setelah beberapa waktu di bawah beban
Penyebab:
Kondisi beban lebih atau koneksi longgar
Solusi:
- Hitung beban aktual vs rating MCB
- Periksa semua koneksi terminal untuk kekencangan
- Verifikasi kecukupan ukuran kabel untuk beban
- Distribusikan ulang beban atau tingkatkan rating MCB jika diperlukan
Masalah:
MCB tidak trip selama kondisi gangguan
Penyebab:
Kegagalan MCB atau rating yang tidak tepat
Solusi:
- Uji MCB menggunakan peralatan pengujian yang sesuai
- Ganti MCB jika rusak
- Verifikasi kapasitas pemutusan memadai untuk instalasi
🔧 Rekomendasi Profesional
Pengujian MCB harus dilakukan setiap tahun di instalasi komersial dan setiap 3 tahun di aplikasi perumahan menggunakan peralatan pengujian yang dikalibrasi. Setiap MCB yang gagal trip dalam karakteristik waktu-arus yang ditentukan harus segera diganti.
Spesifikasi dan Standar MCB
Tabel Spesifikasi Teknis
| Parameter | Rentang Nilai | Referensi Standar |
|---|---|---|
| Nilai Saat Ini | 0,5A hingga 125A | IEC 60898-1 |
| Tegangan Pengenal | 230V hingga 400V AC | IEC 60898-1 |
| Frekuensi | 50Hz hingga 60Hz | IEC 60898-1 |
| Kapasitas Putus | 6kA hingga 25kA | IEC 60898-1 |
| Kehidupan Listrik | 10.000 operasi | IEC 60898-1 |
| Kehidupan Mekanis | 20.000 operasi | IEC 60898-1 |
| Kisaran Suhu | -25°C hingga +70°C | IEC 60898-1 |
| Tegangan Isolasi | 500V AC selama 1 menit | IEC 60898-1 |
Penandaan dan Identifikasi
Penandaan Wajib:
- Nama produsen atau merek dagang
- Penunjukan jenis dan nomor model
- Arus dan tegangan terukur
- Kapasitas putus
- Karakteristik trip (B, C, atau D)
- Kepatuhan standar (IEC 60898)
Pertimbangan Keselamatan dan Praktik Terbaik
Keamanan Instalasi
Sebelum Pemasangan:
- Verifikasi isolasi daya menggunakan penguji tegangan yang disetujui
- Periksa kompatibilitas MCB dengan peralatan yang ada
- Pastikan kapasitas pemutusan yang memadai untuk instalasi
- Verifikasi rating suhu lingkungan
Selama Instalasi:
- Gunakan alat pelindung diri (APD) yang sesuai
- Ikuti prosedur penguncian/penandaan
- Pertahankan torsi yang tepat pada koneksi terminal
- Verifikasi ukuran dan routing kabel yang benar
Setelah Instalasi:
- Uji operasi MCB menggunakan peralatan pengujian yang sesuai
- Verifikasi pelabelan dan identifikasi sirkuit yang benar
- Dokumentasikan detail instalasi dan hasil pengujian
- Berikan instruksi pengoperasian kepada pengguna akhir
Note Catatan Keamanan Kritis
MCB memberikan perlindungan terhadap kondisi arus lebih tetapi tidak melindungi terhadap sengatan listrik atau gangguan tanah. Pasang RCD (Residual Current Devices) untuk perlindungan keselamatan listrik yang komprehensif.
Analisis Biaya dan Faktor Pemilihan
Perbandingan Biaya Awal
| Jenis MCB | Kisaran Harga (USD) | Kesesuaian Aplikasi | Biaya Siklus Hidup |
|---|---|---|---|
| MCB Standar | $5 – $25 | Perumahan/komersial dasar | Rendah |
| Kapasitas Pemutusan Tinggi | $15 – $50 | Aplikasi industri | Sedang |
| MCB Elektronik | $50 – $200 | Aplikasi presisi | Awal tinggi, perawatan rendah |
| MCB Pintar | $100 – $500 | Sistem IoT dan pemantauan | Awal tinggi, mengurangi waktu henti |
💰 Tips Optimalisasi Biaya
- Pilih kapasitas pemutusan yang sesuai (jangan terlalu tinggi)
- Pertimbangkan pembelian massal untuk beberapa instalasi
- Pertimbangkan keandalan jangka panjang dan biaya perawatan
- Evaluasi manfaat MCB pintar untuk aplikasi kritis
Tren dan Teknologi Masa Depan
Teknologi MCB Pintar
- Konektivitas IoT untuk pemantauan jarak jauh
- Kemampuan pemeliharaan prediktif
- Pengukuran dan pelaporan energi
- Integrasi aplikasi seluler untuk status waktu nyata
Fitur Perlindungan Tingkat Lanjut
- Deteksi dan interupsi gangguan busur
- Integrasi perlindungan gangguan tanah
- Protokol komunikasi (Modbus, BACnet)
- Kemampuan pencatatan dan analisis data
Panduan Referensi Cepat
Daftar Periksa Pemilihan Rating MCB
- [ ] Hitung arus beban maksimum
- [ ] Terapkan faktor penurunan rating yang sesuai
- [ ] Pilih rating MCB ≥ 125% dari arus beban
- [ ] Verifikasi kapasitas kabel melebihi rating MCB
- [ ] Konfirmasi kapasitas pemutusan untuk instalasi
- [ ] Periksa karakteristik tipe (B, C, atau D)
- [ ] Verifikasi rating tegangan dan frekuensi
- [ ] Pertimbangkan ekspansi beban di masa depan
Prosedur Darurat
- MCB Tidak Mau Reset: Periksa adanya korsleting, hilangkan semua beban, periksa perkabelan
- Sering Tersandung: Verifikasi perhitungan beban, periksa koneksi, uji isolasi
- Tidak Ada Daya Setelah Reset: Periksa koneksi hilir, verifikasi operasi MCB
- Bau Terbakar: Segera putuskan daya, periksa kerusakan, ganti jika perlu
Pertanyaan yang Sering Diajukan Tentang Kepanjangan MCB
Apa kepanjangan MCB dalam kelistrikan?
Kepanjangan MCB adalah Miniature Circuit Breaker. Ini adalah sakelar listrik otomatis yang dirancang untuk melindungi sirkuit listrik dari kerusakan yang disebabkan oleh kondisi arus lebih termasuk korsleting dan beban berlebih.
Apa arti MCB dalam teknik elektro?
Dalam teknik elektro, MCB adalah singkatan dari Miniature Circuit Breaker – perangkat pelindung yang menggabungkan perlindungan arus lebih dengan kemampuan untuk direset dan digunakan kembali setelah beroperasi, tidak seperti sekering tradisional.
Apa perbedaan antara kepanjangan MCB dan pemutus sirkuit lainnya?
Sementara MCB adalah singkatan dari Miniature Circuit Breaker (untuk aplikasi yang lebih kecil), MCCB adalah singkatan dari Molded Case Circuit Breaker (untuk aplikasi industri yang lebih besar), dan ACB adalah singkatan dari Air Circuit Breaker (untuk aplikasi arus yang sangat tinggi).
Mengapa disebut Miniature Circuit Breaker?
“Miniature” dalam kepanjangan MCB mengacu pada ukurannya yang ringkas dibandingkan dengan pemutus sirkuit industri yang lebih besar, sehingga ideal untuk aplikasi perumahan dan komersial ringan di mana ruang terbatas.
Apa perbedaan antara MCB dan MCCB?
MCB dirancang untuk rating arus yang lebih rendah (hingga 125A) dan penggunaan perumahan/komersial ringan, sedangkan MCCB menangani arus yang lebih tinggi (100A hingga 2500A) untuk aplikasi industri. MCCB juga menawarkan pengaturan trip yang dapat disesuaikan dan kapasitas pemutusan yang lebih tinggi.
Bagaimana saya tahu jika MCB saya rusak?
Tanda-tanda kegagalan MCB meliputi: kegagalan untuk trip selama kelebihan beban, ketidakmampuan untuk mereset setelah trip, kerusakan fisik atau bekas terbakar, terminal yang longgar atau berkarat, dan operasi yang tidak konsisten. Pengujian profesional direkomendasikan untuk verifikasi.
Bisakah saya mengganti MCB dengan rating yang lebih tinggi?
Hanya jika perkabelan dan komponen hilir dapat menangani arus yang meningkat dengan aman. Kapasitas hantar arus kabel harus melebihi rating MCB yang baru, dan perhitungan beban yang tepat harus dilakukan.
Seberapa sering MCB harus diuji?
Instalasi perumahan: Setiap 3 tahun. Instalasi komersial: Setiap tahun. Instalasi industri: Setiap 6 bulan atau sesuai jadwal pemeliharaan. Aplikasi kritis mungkin memerlukan pengujian yang lebih sering.
Apa yang menyebabkan MCB sering trip?
Penyebab umum meliputi: kondisi kelebihan beban aktual, koneksi terminal yang longgar, kabel yang rusak, masuknya kelembapan, masalah suhu sekitar, dan keausan atau kegagalan MCB.
Do MCBs protect against electric shock?
Tidak, MCB standar hanya melindungi terhadap arus lebih dan korsleting. Untuk perlindungan sengatan listrik, pasang RCD (Residual Current Devices) atau unit RCBO kombinasi.
Kesimpulan: Memahami Kepanjangan dan Aplikasi MCB
Kepanjangan MCB – Miniature Circuit Breaker – mewakili salah satu perangkat keselamatan listrik paling penting dalam instalasi modern. Memahami arti MCB dan bagaimana perangkat ini berfungsi memastikan keselamatan listrik, kepatuhan terhadap kode, dan perlindungan sirkuit yang andal.
Poin Penting Tentang Kepanjangan MCB:
- MCB adalah singkatan dari Miniature Circuit Breaker – penting untuk perlindungan listrik
- Sebutan “miniature” mengacu pada ukuran yang ringkas untuk penggunaan perumahan/komersial
- Kepanjangan MCB mencakup perlindungan otomatis terhadap arus lebih dan korsleting
- Pemasangan profesional dan pengujian rutin memastikan kinerja MCB yang optimal
- Menggabungkan MCB dengan RCD memberikan perlindungan listrik yang komprehensif
Untuk instalasi listrik yang kompleks atau pertanyaan tentang aplikasi kepanjangan MCB, selalu konsultasikan dengan insinyur listrik yang berkualifikasi atau teknisi listrik bersertifikat untuk memastikan keselamatan dan kepatuhan terhadap kode.
Rekomendasi Ahli: Memahami kepanjangan MCB hanyalah permulaan – pemilihan, pemasangan, dan pemeliharaan Miniature Circuit Breaker yang tepat memerlukan pengetahuan mendetail tentang kode listrik, perhitungan beban, dan standar keselamatan untuk perlindungan sistem listrik yang optimal.
Terkait
Apa Itu Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB): Panduan Lengkap untuk Keselamatan dan Pemilihan