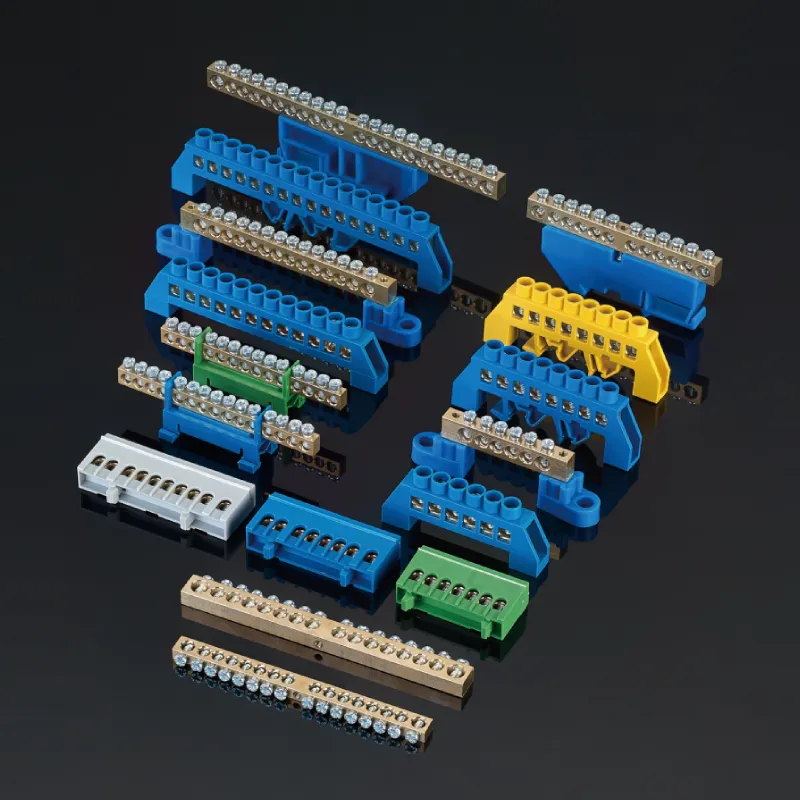
Understanding the Basics: What is a Terminal Block?
Terminal blocks are modular, insulated blocks that secure two or more wires together, serving as junction points in electrical systems. At their core, terminal blocks simplify complex wiring by providing organized connection points that are easier to manage, troubleshoot, and modify compared to direct wire-to-wire connections.
Most terminal blocks consist of three primary components:
- Insulating Body: Typically made of high-strength, heat-resistant materials like thermoplastics or thermosetting resins that prevent short circuits
- Current-Carrying Element: The conductive metal part (brass in this case) that creates an electrical path between connected wires
- Clamping Mechanism: Usually screws, clamps, or springs that securely hold wires against the conductive element
What Are Brass Terminal Blocks?
Brass terminal blocks are electrical connectors made primarily from brass, a copper-zinc alloy known for its excellent conductivity, durability, and corrosion resistance. They consist of a block or strip with multiple terminals for wire insertion and connection, designed to facilitate the secure joining and distribution of electrical circuits.
The defining feature of a brass terminal block is that the primary current-carrying conductive element within the block is made of brass. While the housing is typically plastic, the crucial metal components that the wires connect to—including strips, clamps, or screw terminals—are manufactured from brass alloy.
Key Features and Benefits of Brass Terminal Blocks
Superior Electrical Conductivity
One of the primary advantages of brass terminal blocks is their exceptional conductivity. Brass, an alloy of copper and zinc, offers excellent electrical conductivity, allowing for efficient transfer of current between connected conductors. While pure copper is slightly more conductive, brass provides excellent performance with minimal power loss and reduced risk of overheating, particularly in high-current applications.
Exceptional Corrosion Resistance
Brass terminal blocks exhibit remarkable resistance to corrosion and tarnishing. The zinc content in brass helps protect the copper from oxidation, ensuring reliable, long-lasting electrical connections even in moderately humid or challenging environments. This natural corrosion resistance makes brass terminal blocks suitable for various indoor and outdoor applications where exposure to moisture and other corrosive elements might occur.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Brass is a robust and durable material, capable of withstanding the demands of industrial environments. Terminal blocks made from brass offer high mechanical strength, enabling them to endure vibrations, shocks, and temperature fluctuations. Brass is harder and more durable than pure copper, meaning brass screw terminals can withstand repeated tightening and loosening without easily stripping or deforming, ensuring a secure physical connection for the wires.
Ease of Installation and Maintenance
Brass terminal blocks are designed for easy installation and maintenance. They feature screw or clamp-type connections, allowing for quick and secure attachment of wires or cables. Additionally, brass terminal blocks are typically available in various sizes and configurations to accommodate different wire gauges and connection requirements.
Cost-Effectiveness and Machinability
Brass is relatively easy to machine into the complex shapes required for terminal components. This ease of manufacturing, combined with its performance characteristics, makes brass a cost-effective solution for high-volume production of reliable electrical terminal blocks. Brass terminal blocks offer an excellent balance of performance and affordability compared to other materials.
Material Composition and Specifications
Brass Alloy Composition
Brass terminal blocks utilize various grades of brass, each offering specific advantages:
- Brass C36000 (Free-Cutting Brass): Offers excellent machinability and conductivity
- Brass CZ121/CW614N: Provides corrosion resistance and is widely used in electrical components
- H59 Brass Alloy: Consists of copper and zinc phases, offering a balance of properties
- H70, H80, and H90 Alloys: Higher copper content versions with increased conductivity and stress corrosion resistance
Research indicates that with increasing copper content, brass strength decreases while conductivity and stress corrosion resistance increase. This allows manufacturers to select the optimal alloy composition based on specific application requirements.
Plating Options and Their Benefits
Brass terminal blocks are available with various surface treatments to enhance performance characteristics:
- Tin plating: Enhances electrical conductivity and prevents oxidation
- Nickel plating: Increases wear resistance and provides oxidation protection
- Silver plating: Reduces contact resistance in high-voltage applications
- Zinc plating: Offers additional corrosion protection
These plating options allow for customization based on environmental conditions and specific performance requirements.
Types of Brass Terminal Blocks
Several types of brass terminal blocks exist to suit different applications:
1. Single-Level Pass-Through Terminal Blocks
These are used for straightforward wire-to-wire connections, often referred to as single-feed terminal blocks. They are the simplest type, featuring one input contact and one output contact with an internal connection between them.
2. Multi-Level Terminal Blocks
Dual-level terminal blocks have an additional level of connection terminals stacked above the first one. This arrangement is commonly employed to save space while maintaining functionality. Similarly, three-level terminal blocks have an extra level at the top, offering even more connection options in a compact space.
3. Barrier Strips with Brass Connectors
Barrier strips have screws on either side of a raised barrier, providing isolation between terminals. The conductive strip and screws are typically made of brass, offering both electrical efficiency and physical separation of connections.
4. Specialized Terminal Blocks
Some terminal blocks are designed for specific functions:
- Ground Circuit Terminals: Used to ground components or systems and are typically interchangeable with standard terminal blocks
- Neutral Link Terminal Blocks: Commonly used in electrical panels and switchboards, providing dedicated connection points for neutral conductors
- Fuse Holder Terminal Blocks: Integrate fuse holders for overload protection, combining connection functionality with circuit protection
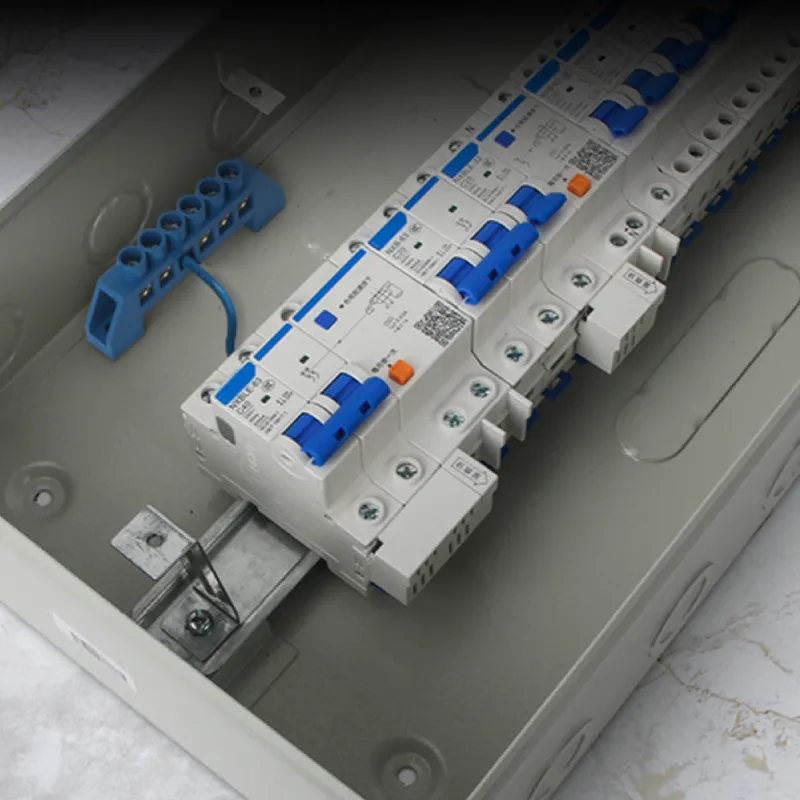
5. DIN Rail Mount Blocks
While the blocks themselves clip onto standard DIN rails, the internal conductive clamps and current bars are frequently made of brass for performance and reliability. These are common in industrial control panels and switchboards.
Applications of Brass Terminal Blocks
Brass terminal blocks find applications across numerous industries and settings:
1. Industrial Control Panels and Cabinets
Brass terminal blocks are widely used in industrial control panels to connect and distribute power to various electrical components and devices. They provide a secure and organized means of connecting control wires, power cables, and signal wires, facilitating efficient operation and maintenance of control panels.
2. Power Distribution Systems
In power distribution units (PDUs) and junction boxes, brass terminal blocks serve as the interface between main power sources and downstream circuits. These terminal blocks ensure reliable and safe power distribution, allowing for easy connection and disconnection of electrical loads.
3. Building Wiring and Electrical Installations
In building wiring systems, brass terminal blocks are utilized to connect electrical wires and cables, enabling the distribution of power throughout the structure. They are commonly employed in junction boxes, distribution boards, and electrical enclosures, ensuring proper organization and efficient electrical connectivity.
4. HVAC Systems
For heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems, brass terminal blocks provide reliable connection points for control circuits and power distribution. Their durability makes them ideal for systems that may experience temperature variations and vibrations.
5. Lighting Systems
For the installation and upkeep of lighting fixtures and control systems, brass terminal blocks are essential. They provide a reliable connection between power supply lines, control wires, and lighting elements, facilitating the seamless operation of lighting systems in residential, commercial, and industrial settings.
6. Automotive and Transportation
Brass terminal blocks are widely used in railway and transportation systems for electrical connections in signaling, lighting, and control applications. Their durability and reliability ensure safe and uninterrupted operations in demanding environments subject to vibration and temperature changes.
7. Renewable Energy Systems
In solar panel installations and wind power systems, brass terminal blocks provide essential connection points that must withstand outdoor conditions while maintaining electrical integrity. Their corrosion resistance and conductivity make them particularly suitable for renewable energy applications.
8. Consumer Electronics and Telecommunications
Brass terminal blocks are used at power entry points for consumer electronics and in telecommunications equipment where reliable connections are critical for performance.
Installation Best Practices and Maintenance
Proper Installation Techniques
When installing brass terminal blocks, several best practices should be followed:
- Wire Preparation: Ensure proper wire stripping to expose an appropriate length of conductor—too little prevents contact, too much exposes excess conductor
- Wire Insertion: Make sure all wire strands are inserted into the terminal without stray strands protruding
- Torque Settings: Tighten terminal screws to manufacturer-specified torque values—over-tightening can damage the brass threads or wire, while under-tightening leads to poor connection and potential overheating
- Spacing: Maintain proper spacing between terminal blocks to prevent overheating
- Terminal Selection: Use appropriate ring or fork terminals for more secure connections when needed
Maintenance and Inspection Guidelines
Regular maintenance helps ensure the continued reliable operation of brass terminal blocks:
- Periodically inspect connections for signs of corrosion or oxidation
- Check terminal screws for proper tightness, as vibration can cause loosening over time
- Look for discoloration, which may indicate overheating or excessive current
- Clean connections if necessary, removing any dust or contaminants
- Verify that insulation remains intact and undamaged
Choosing the Right Brass Terminal Block
When selecting a brass terminal block for your application, consider:
1. Current and Voltage Requirements
Brass terminal blocks are available in various current ratings, typically ranging from 5A to 500A, with custom designs available for high-current applications. When selecting terminal blocks:
- Determine the maximum current that will flow through the connection
- Add a safety margin of at least 25%
- Consider ambient temperature, as higher temperatures reduce current capacity
- Account for duty cycle in intermittent applications
- Verify compatibility with circuit protection devices
2. Environmental Factors
The installation environment significantly influences terminal block selection:
- For humid environments, consider tin or nickel-plated options
- In corrosive atmospheres, select terminal blocks with appropriate protective coatings
- For outdoor installations, ensure IP-rated enclosures protect the terminal blocks
- In high-temperature applications, verify temperature ratings of both metal and insulation components
- For high-vibration environments, consider terminal blocks with additional securing features
3. Wire Size and Configuration
- Determine the number of connection points required
- Consider the gauge of wires being connected
- Calculate the space available for installation
- Allow for future expansion when possible
- Ensure terminals can accommodate the required wire size
4. Compliance with Standards
Quality brass terminal blocks comply with various international standards, ensuring safety and reliability:
- IEC 60947-7-1: Standard for low-voltage switchgear and control gear terminal blocks
- BS 951: Standard for earthing and bonding applications
- ASTM B16: Material specification for brass rod and bar
- RoHS and REACH compliance: Ensuring environmental safety and lead-free composition
Comparison with Alternative Materials
Brass vs. Copper Terminal Blocks
While copper offers slightly better conductivity, brass provides numerous advantages:
- Better balance of conductivity, strength, and cost
- Superior corrosion resistance
- Higher mechanical strength and durability
- More cost-effective for mass production
- Better resistance to repeated mechanical stress
Brass vs. Aluminum Terminal Blocks
Compared to aluminum terminal blocks, brass offers:
- Superior conductivity
- Better corrosion resistance
- Greater mechanical strength
- More reliable long-term performance
- Lower contact resistance
Brass vs. Steel Terminal Blocks
In comparison to steel options, brass terminal blocks provide:
- Much higher electrical conductivity
- Better resistance to corrosion without protective coatings
- Easier machining and manufacturing
- No magnetic properties (important in some applications)
- Better performance in moisture-prone environments
Conclusion: The Enduring Value of Brass Terminal Blocks
Brass terminal blocks remain essential components in modern electrical systems, offering a perfect balance of conductivity, durability, versatility, and cost-effectiveness. Their widespread use across industries—from electrical power distribution to renewable energy systems and from automotive applications to building infrastructure—testifies to their reliable performance and adaptability.
For professionals involved in electrical installations, understanding the features, benefits, and applications of brass terminal blocks is essential for creating safe, efficient, and durable electrical connections. Whether for simple residential applications or complex industrial systems, brass terminal blocks provide the reliable connectivity foundation upon which our electrical infrastructure depends.
By selecting the appropriate brass terminal block for your specific application and following proper installation practices, you can ensure long-lasting, trouble-free electrical connections that deliver the performance and safety your systems require.
FAQs About Brass Terminal Blocks
What is the maximum current capacity of brass terminal blocks?
The current-carrying capacity of brass terminal blocks depends on their size and material composition. Standard blocks can handle from 5A to 500A, with custom designs available for high-current applications.
Why are brass terminal blocks preferred over other materials?
Brass terminal blocks are preferred for their high electrical conductivity, superior corrosion resistance, exceptional mechanical strength, and cost-effectiveness, making them ideal for various challenging environments.
Are brass terminal blocks suitable for outdoor applications?
Yes, brass terminal blocks are suitable for outdoor applications, especially when properly plated with protective finishes like tin or nickel. Their inherent corrosion resistance makes them a good choice for outdoor installations, though they should be housed in appropriate weatherproof enclosures for optimal performance.
How do I identify the quality of a brass terminal block?
Quality brass terminal blocks typically feature precision manufacturing, uniform plating, clean threading, and proper certification to relevant standards. Higher copper content generally indicates better electrical performance, while proper plating suggests better corrosion resistance.