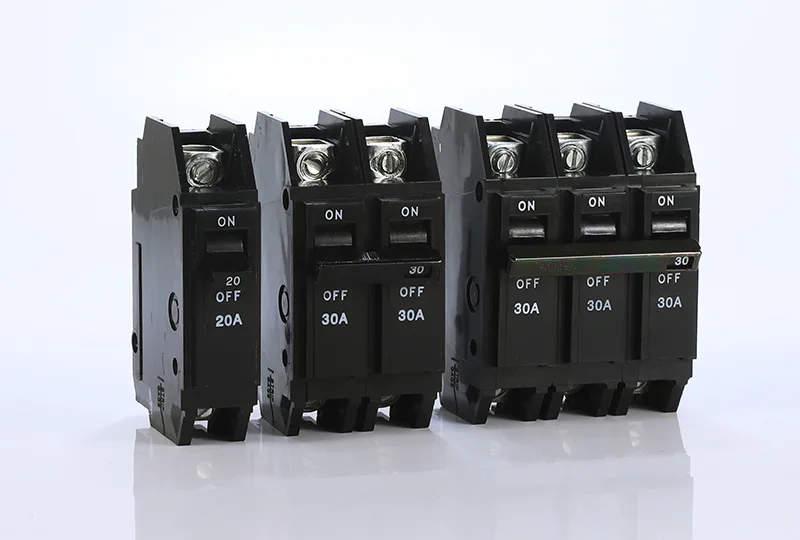
Một Cầu dao bắt vít (bolt-on circuit breaker) là một loại thiết bị an toàn điện được bắt vít hoặc kẹp trực tiếp vào các thanh cái bên trong tủ điện, cung cấp kết nối an toàn và cố định hơn so với các loại cầu dao cắm thông thường. Không giống như các cầu dao cắm tiêu chuẩn chỉ cần gắn vào vị trí, cầu dao bắt vít sử dụng các bộ phận siết cơ học để đảm bảo tiếp xúc điện và độ ổn định tối đa, khiến chúng trở nên cần thiết cho các ứng dụng có cường độ dòng điện cao và các hệ thống điện quan trọng.
Lợi ích chính: Cầu dao bắt vít cung cấp tính toàn vẹn kết nối điện vượt trội và được yêu cầu cụ thể theo các quy tắc điện cho các mạch trên 30 ampe trong hầu hết các ứng dụng dân dụng và thương mại.
Điều gì làm cho cầu dao bắt vít khác biệt?
Cầu dao bắt vít tự phân biệt thông qua phương pháp gắn cơ học và hiệu suất điện nâng cao. Dưới đây là so sánh với các ngắt mạch loại khác:
| Năng | Cầu dao bắt vít | Cầu dao cắm | Cầu dao vặn |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phương pháp kết nối | Bắt vít/kẹp vào thanh cái | Kẹp vào thanh cái | Kết nối ren |
| Cường độ dòng điện điển hình | 30-400+ ampe | 15-30 ampe | 15-30 ampe (lỗi thời) |
| Tính bảo mật kết nối | Cao nhất | Vừa phải | Thấp |
| Độ phức tạp của cài đặt | Yêu cầu chuyên gia | Có thể tự làm (DIY) | Có thể tự làm (DIY) |
| Yêu cầu về mã | Bắt buộc cho mạch 30+ ampe | Tiêu chuẩn cho 15-30 ampe | Không còn tuân thủ quy tắc |
| Khả năng chống rung | Xuất sắc | Tốt | Nghèo |
| Chi phí | Cao hơn | Thấp hơn | Thấp nhất |
Các định nghĩa chính bạn cần biết
Thanh cái (Bus Bar): Dây dẫn đồng hoặc nhôm chính bên trong tủ điện, phân phối điện cho các cầu dao riêng lẻ.
Định mức ampe: Dòng điện tối đa mà cầu dao có thể xử lý an toàn trước khi ngắt để bảo vệ mạch.
Kết nối cơ học: Một phương pháp siết chặt vật lý sử dụng bu lông, kẹp hoặc vít thay vì các điểm tiếp xúc cắm đơn giản.
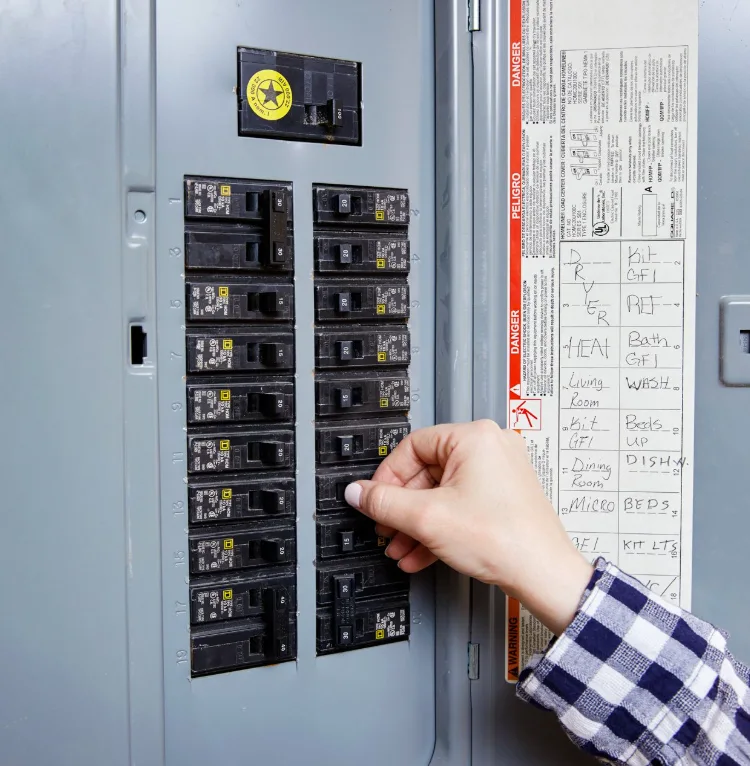
Trung tâm tải (Load Center): Một thuật ngữ khác cho tủ điện hoặc hộp cầu dao nơi lắp đặt các cầu dao.
Khi nào bạn cần cầu dao bắt vít?
Các ứng dụng bắt buộc (theo quy định của quy tắc)
Bạn phải sử dụng cầu dao bắt vít cho:
- Mạch máy sấy điện (thường là 30 ampe)
- Mạch bếp/bếp điện (40-50 ampe)
- Các dàn lạnh trung tâm (30-60+ ampe)
- Máy nước nóng điện (30-40 ampe)
- Trạm sạc xe điện (EV) (40-100+ ampe)
- Đường dây cấp điện cho tủ điện phụ (thay đổi theo yêu cầu tải)
Ứng dụng được đề xuất
Cầu dao bắt vít được ưu tiên cho:
- Mạch xưởng/gara với các công cụ công suất cao
- Mạch thiết bị hàn
- Hệ thống chiếu sáng thương mại
- Mạch điều khiển động cơ
- Bất kỳ mạch nào bị rung động thường xuyên
Dr. Trước An Toàn Cảnh Báo: Không bao giờ cố gắng tự lắp đặt hoặc thay thế cầu dao. Công việc này đòi hỏi một thợ điện được cấp phép và các giấy phép thích hợp ở hầu hết các khu vực pháp lý.
Các loại cầu dao bắt vít
1. Cầu dao bắt vít tiêu chuẩn
- Ứng dụng: Mạch dân dụng thông thường 30-60 ampe
- Cài đặt: Cấu hình một hoặc hai cực
- Phạm vi chi phí: 25-75 đô la cho mỗi cầu dao
2. Cầu dao bắt vít cường độ dòng điện cao
- Ứng dụng: Sử dụng trong công nghiệp và thương mại 70-400+ ampe
- Cài đặt: Yêu cầu các tủ điện chuyên dụng và lắp đặt chuyên nghiệp
- Phạm vi chi phí: $100-500+ trên mỗi bộ ngắt mạch
Bộ ngắt mạch GFCI kiểu bắt vít
- Ứng dụng: Bảo vệ chống chạm đất cho các mạch điện có cường độ dòng điện cao
- Cài đặt: Spa, thiết bị ngoài trời, bếp thương mại
- Phạm vi chi phí: $75-200 trên mỗi bộ ngắt mạch
Bộ ngắt mạch AFCI kiểu bắt vít
- Ứng dụng: Bảo vệ chống hồ quang điện cho các mạch phòng ngủ trên 30 ampe
- Cài đặt: Các yêu cầu xây dựng nhà ở mới hơn
- Phạm vi chi phí: $100-250 trên mỗi bộ ngắt mạch
Cách thức hoạt động của bộ ngắt mạch kiểu bắt vít
Quy trình kết nối
- Cách ly nguồn điện: Nguồn điện chính được tắt hoàn toàn
- Chuẩn bị thanh Bus: Các điểm kết nối được làm sạch và kiểm tra
- Định vị bộ ngắt mạch: Bộ ngắt mạch được căn chỉnh với các điểm kết nối thanh bus
- Siết chặt cơ học: Bu lông hoặc kẹp được siết chặt theo thông số kỹ thuật của nhà sản xuất
- Kiểm tra mô-men xoắn: Các kết nối được siết lực theo yêu cầu của quy chuẩn (thường là 250-350 inch-pound)
- Kiểm tra: Tính liên tục điện và hoạt động đúng được xác minh
Tại sao thiết kế bắt vít lại quan trọng
Tăng cường áp lực tiếp xúc: Siết chặt cơ học cung cấp áp lực tiếp xúc ổn định, không bị lỏng theo thời gian.
Khả năng chống rung: Rất quan trọng trong môi trường công nghiệp hoặc khu vực có thiết bị cơ khí.
Độ ổn định nhiệt: Tản nhiệt tốt hơn ngăn ngừa sự suy giảm kết nối dưới tải cao.
Tuân thủ quy tắc: Gặp gỡ NEC (Quy chuẩn Điện Quốc gia) các yêu cầu đối với các ứng dụng cường độ dòng điện cao.
Hướng dẫn chọn bộ ngắt mạch
Bước 1: Xác định cường độ dòng điện yêu cầu
- Tính tổng tải của các thiết bị trên mạch
- Áp dụng các hệ số an toàn thích hợp (thường là 125% tải liên tục)
- Tham khảo thông số kỹ thuật của nhà sản xuất cho thiết bị được kết nối
Bước 2: Kiểm tra khả năng tương thích của tủ điện
- Xác minh tủ điện của bạn có chấp nhận bộ ngắt mạch kiểu bắt vít hay không
- Xác nhận không gian và cấu hình thanh bus có sẵn
- Kiểm tra khả năng tương thích của nhà sản xuất (Square D, Siemens, GE, v.v.)
Bước 3: Xem xét các yêu cầu đặc biệt
- Bảo vệ GFCI cho những nơi ẩm ướt
- Bảo vệ AFCI cho các mạch phòng ngủ dân dụng
- Xếp hạng đặc biệt cho tải động cơ hoặc thiết bị cảm ứng
Bước 4: Lập kế hoạch lắp đặt chuyên nghiệp
- Lấy giấy phép điện cần thiết
- Lên lịch thợ điện có giấy phép để lắp đặt
- Lập kế hoạch nâng cấp tủ điện tiềm năng nếu cần
Yêu cầu lắp đặt & An toàn
🔧 Mẹo của chuyên gia: Việc lắp đặt bộ ngắt mạch kiểu bắt vít yêu cầu siết chặt các kết nối đến các giá trị cụ thể. Siết lực không đủ tạo ra nguy cơ hỏa hoạn; siết lực quá mức có thể làm hỏng thiết bị.
Yêu cầu quy chuẩn (Tuân thủ NEC)
- Thông số mô-men xoắn: Phải đáp ứng các yêu cầu của nhà sản xuất (thường được ghi trên nhãn bộ ngắt mạch)
- Kích thước dây: Dây điện mạch phải phù hợp với định mức ampe của bộ ngắt mạch
- Tiếp đất: Yêu cầu nối đất thiết bị thích hợp cho tất cả các cài đặt
- Ghi nhãn: Tất cả các mạch phải được dán nhãn rõ ràng trong thư mục tủ điện
Quy trình lắp đặt chuyên nghiệp
- Xin giấy phép: Hầu hết các khu vực pháp lý yêu cầu giấy phép cho việc bổ sung/thay thế bộ ngắt mạch
- Tắt nguồn: Ngắt kết nối và xác minh nguồn điện chính
- Quy trình an toàn: Quy trình khóa/treo biển báo và thiết bị bảo vệ cá nhân
- Cài đặt: Quy trình lắp, kết nối và siết lực thích hợp
- Kiểm tra: Kiểm tra điện và xác minh chức năng
- Điều tra: Phê duyệt của thanh tra điện địa phương trước khi cấp điện
Các vấn đề thường gặp & Khắc phục sự cố
Vấn đề kết nối
Vấn đề: Các kết nối bắt vít lỏng lẻo gây ra hồ quang hoặc quá nhiệt
Giải pháp: Siết lại chuyên nghiệp theo thông số kỹ thuật của nhà sản xuất
Các vấn đề về khả năng tương thích
Vấn đề: Loại cầu dao sai cho thương hiệu tủ điện
Giải pháp: Chỉ sử dụng cầu dao được nhà sản xuất phê duyệt cho tủ điện cụ thể của bạn
Quá tải
Vấn đề: Cầu dao nhảy thường xuyên khi tải bình thường
Giải pháp: Xem xét tính toán tải và phân chia mạch tiềm năng
Lỗi liên quan đến tuổi tác
Vấn đề: Cầu dao bắt vít cũ không nhảy đúng cách
Giải pháp: Kiểm tra và thay thế chuyên nghiệp khi cần thiết
Sử dụng trên toàn cầu: Những quốc gia nào sử dụng cầu dao bắt vít?
Việc áp dụng cầu dao bắt vít khác nhau đáng kể trên toàn thế giới dựa trên các quy tắc điện, tiêu chuẩn an toàn và phát triển cơ sở hạ tầng. Hiểu các mô hình sử dụng quốc tế giúp giải thích tính khả dụng, khả năng tương thích và các yêu cầu pháp lý.
Thị trường cầu dao bắt vít chính
| Quốc gia/Khu vực | Mức độ sử dụng | Tiêu chuẩn chính | Ứng dụng chính |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hoa Kỳ | Rộng rãi | NEC (NFPA 70) | 30+ amp dân dụng/thương mại |
| Canada | Rộng rãi | CEC (CSA C22.1) | Các ứng dụng dòng điện cao |
| Vương Quốc Anh | Vừa phải | BS 7671 (Ấn bản thứ 18) | Công nghiệp/thương mại |
| Úc | Vừa phải | AS/NZS 3000 | Cơ sở thương mại |
| Đức | Giới hạn | Tiêu chuẩn VDE | Ứng dụng công nghiệp |
| Nhật Bản | Giới hạn | Tiêu chuẩn JIS | Sử dụng công nghiệp cụ thể |
| Ấn Độ | Đang phát triển | IS 732 | Mở rộng thương mại/công nghiệp |
| Brazil | Vừa phải | Tiêu chuẩn NBR | Công nghiệp/thương mại |
Sự thống trị của Bắc Mỹ
Hoa Kỳ và Canada đại diện cho các thị trường lớn nhất cho cầu dao bắt vít do:
- Yêu cầu mã nghiêm ngặt: NEC và CEC yêu cầu cầu dao bắt vít cho các mạch trên 30 ampe
- Tiêu chuẩn thiết bị điện công suất cao: Máy sấy điện 240V, bếp và hệ thống HVAC là tiêu chuẩn
- Cơ sở hạ tầng dân cư: Tủ điện được xây dựng có mục đích được thiết kế để tích hợp bắt vít
- Sự trưởng thành của thị trường: Chuỗi cung ứng và chuyên môn của người lắp đặt đã được thiết lập
Các biến thể của Châu Âu
Vương quốc Anh và Liên minh Châu Âu cho thấy mức độ chấp nhận vừa phải với sự khác biệt theo khu vực:
- Tập trung vào công nghiệp: Chủ yếu được sử dụng trong các ứng dụng thương mại và công nghiệp
- Tiêu chuẩn khác nhau: Tiêu chuẩn IEC ảnh hưởng đến thiết kế và phương pháp kết nối
- Công nghệ thay thế: Sự phụ thuộc lớn hơn vào hệ thống lắp ray DIN
- Sự khác biệt về điện áp: Hệ thống 230V/400V yêu cầu các thiết kế cầu dao khác nhau
🌍 Thông tin chi tiết quốc tế: Thị trường châu Âu thường sử dụng cầu dao gắn trên ray DIN cho các ứng dụng mà Bắc Mỹ sử dụng cầu dao bắt vít.
Xu hướng thị trường Châu Á - Thái Bình Dương
Úc và New Zealand thể hiện sự chấp nhận ngày càng tăng:
- Ứng dụng thương mại: Sử dụng ngày càng tăng trong các cơ sở thương mại và công nghiệp
- Sự phát triển của mã: Các tiêu chuẩn đang hướng tới việc yêu cầu các kết nối cơ học cho các mạch điện có cường độ dòng điện cao
- Phát triển cơ sở hạ tầng: Xây dựng mới kết hợp các tấm cầu dao bắt vít
Nhật Bản và Hàn Quốc cho thấy mức sử dụng hạn chế nhưng chuyên biệt:
- Ứng dụng công nghiệp: Chủ yếu trong sản xuất và công nghiệp nặng
- Các Tiêu Chuẩn Độc Đáo: Tiêu chuẩn JIS và KS tạo ra các yêu cầu thiết kế khác nhau
- Các Giải Pháp Thay Thế Nhỏ Gọn: Ưu tiên cho các thiết kế bảng điều khiển tiết kiệm không gian
Thị trường mới nổi
Ấn Độ, Brazil và Trung Đông đại diện cho các thị trường đang phát triển:
- Mở Rộng Cơ Sở Hạ Tầng: Phát triển thương mại và công nghiệp nhanh chóng
- Hiện Đại Hóa Quy Chuẩn: Áp dụng các tiêu chuẩn an toàn quốc tế
- Chuyển Giao Công Nghệ: Ảnh hưởng từ các công ty điện đa quốc gia
- Phát Triển Kinh Tế: Nhu cầu ngày càng tăng đối với các hệ thống điện đáng tin cậy
So Sánh Yêu Cầu Quy Chuẩn Khu Vực
| Vùng đất | Yêu Cầu Dòng Điện Cao | Ngưỡng Điển Hình | Mức Độ Thực Thi |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bắc Mỹ | Bắt buộc bắt vít | 30+ ampe | Nghiêm ngặt |
| Vương quốc Anh/EU | Đề nghị | 32+ ampe | Vừa phải |
| Úc/New Zealand | Ngày càng được yêu cầu | 25+ ampe | Đang phát triển |
| Châu Á | Thay đổi theo quốc gia | 30-50+ ampe | Biến |
| Thị trường mới nổi | Tiêu chuẩn đang phát triển | 40+ ampe | Đang được cải thiện |
Cân Nhắc Khả Năng Tương Thích Quốc Tế
Sự Khác Biệt Tiêu Chuẩn:
- Phương Pháp Kết Nối: Các mẫu bu lông và yêu cầu lắp đặt khác nhau
- Xếp hạng điện áp: Các điện áp danh định khác nhau đòi hỏi các thiết kế cụ thể
- Lỗi Hồ Quang/Lỗi Chạm Đất: Các yêu cầu bảo vệ khác nhau đáng kể theo khu vực
- Xếp Hạng Môi Trường: Điều kiện khí hậu và lắp đặt ảnh hưởng đến thông số kỹ thuật
Cân Nhắc Sản Xuất:
- Các Thương Hiệu Toàn Cầu: Schneider Electric, ABB, Siemens điều chỉnh sản phẩm cho thị trường khu vực
- Sản Xuất Tại Chỗ: Các nhà sản xuất khu vực tập trung vào tuân thủ quy chuẩn trong nước
- Nhập Khẩu/Xuất Khẩu: Các yêu cầu chứng nhận ảnh hưởng đến thương mại quốc tế
Tại Sao Có Sự Khác Biệt Khu Vực
Cơ Sở Hạ Tầng Lịch Sử:
- Các Hệ Thống Hiện Tại: Cơ sở hạ tầng điện hiện có ảnh hưởng đến các loại bộ ngắt mạch
- Cải Tạo so với Xây Dựng Mới: Các phương pháp khác nhau để nâng cấp điện
- Các yếu tố kinh tế: Cân nhắc chi phí ảnh hưởng đến tỷ lệ chấp nhận
Môi Trường Pháp Lý:
- Triết Lý An Toàn: Các phương pháp khác nhau để quản lý rủi ro và an toàn điện
- Phát Triển Quy Chuẩn: Các quy chuẩn điện quốc gia phát triển với tốc độ khác nhau
- Cơ Chế Thực Thi: Sự khác biệt trong các yêu cầu kiểm tra và tuân thủ
Các Yếu Tố Thị Trường:
- Đào Tạo Người Lắp Đặt: Sự sẵn có của thợ điện có trình độ ảnh hưởng đến việc áp dụng
- Chuỗi cung ứng: Tính sẵn có tại địa phương của các bảng điện và cầu dao tương thích
- Phát Triển Kinh Tế: Tăng trưởng công nghiệp thúc đẩy nhu cầu về hệ thống điện đáng tin cậy
⚡ Xu hướng toàn cầu: Việc áp dụng quốc tế các cầu dao bắt vít đang tăng lên khi các quốc gia hiện đại hóa các quy tắc điện và ưu tiên độ tin cậy của hệ thống.
Phân tích so sánh chi phí
| Loại mạch | Chi phí cầu dao cắm | Chi phí cầu dao bắt vít | Sự khác biệt trong lắp đặt |
|---|---|---|---|
| Máy sấy 30 Amp | Không tuân thủ quy tắc | $35-60 | $150-250 nhân công |
| Bếp điện 40 Amp | Không tuân thủ quy tắc | $45-75 | $150-250 nhân công |
| Máy lạnh 50 Amp | Không tuân thủ quy tắc | $55-90 | $200-300 nhân công |
| Bảng điện phụ 60 Amp | Không có sẵn | $75-125 | $250-400 nhân công |
💡 Chuyên Gia Mẹo: Mặc dù cầu dao bắt vít có chi phí trả trước cao hơn, nhưng chúng mang lại độ tin cậy lâu dài vượt trội và được yêu cầu theo quy tắc cho các ứng dụng có cường độ dòng điện cao.
Những Câu Hỏi Thường
Tôi có thể thay thế cầu dao cắm bằng cầu dao bắt vít không?
Bạn chỉ có thể lắp đặt cầu dao bắt vít trong các bảng điện được thiết kế đặc biệt cho chúng. Hầu hết các bảng điện dân dụng đều có các vị trí dành riêng cho cầu dao bắt vít, thường là cho các mạch có cường độ dòng điện cao như máy sấy và bếp điện.
Làm cách nào để biết bảng điện của tôi có chấp nhận cầu dao bắt vít không?
Kiểm tra nhãn thông số kỹ thuật của bảng điện hoặc tham khảo ý kiến của thợ điện được cấp phép. Hầu hết các bảng điện dân dụng hiện đại đều có cả vị trí cắm (15-30 amps) và vị trí bắt vít (30+ amps).
Sự khác biệt giữa cầu dao bắt vít đơn cực và lưỡng cực là gì?
Cầu dao bắt vít đơn cực bảo vệ các mạch 120V, trong khi các phiên bản lưỡng cực bảo vệ các mạch 240V. Hầu hết các thiết bị có cường độ dòng điện cao (máy sấy, bếp điện, máy lạnh) đều yêu cầu cầu dao bắt vít lưỡng cực.
Cầu dao bắt vít có thể được lắp đặt theo bất kỳ hướng nào không?
Cầu dao bắt vít phải được lắp đặt theo hướng cụ thể được thiết kế cho bảng điện của bạn. Các kết nối cơ học được thiết kế để căn chỉnh chính xác với các thanh cái.
Cần kiểm tra cầu dao bắt vít bao lâu một lần?
Nên kiểm tra chuyên nghiệp 3-5 năm một lần, với tần suất kiểm tra thường xuyên hơn trong môi trường công nghiệp hoặc khu vực có độ rung cao.
Cầu dao bắt vít có đáng tin cậy hơn cầu dao cắm không?
Có, cho các ứng dụng dự kiến của chúng. Kết nối cơ học cung cấp tính toàn vẹn tiếp xúc và khả năng chống rung vượt trội, làm cho chúng đáng tin cậy hơn cho các ứng dụng có cường độ dòng điện cao và quan trọng.
Tôi có thể nâng cấp từ cầu dao cắm lên cầu dao bắt vít để có hiệu suất tốt hơn không?
Điều này đòi hỏi phải xác minh khả năng tương thích của bảng điện và lắp đặt chuyên nghiệp. Mặc dù cầu dao bắt vít mang lại hiệu suất vượt trội, nhưng chúng chủ yếu được thiết kế cho các ứng dụng có cường độ dòng điện cao, nơi các quy tắc yêu cầu chúng.
Cần những công cụ gì để lắp đặt cầu dao bắt vít?
Việc lắp đặt chuyên nghiệp yêu cầu cờ lê lực, thiết bị kiểm tra điện và các công cụ chuyên dụng. Đây không phải là một dự án DIY do các yêu cầu về an toàn và quy tắc.
Lời khuyên của chuyên gia cho hiệu suất tối ưu
Mẹo lựa chọn
- Luôn khớp thương hiệu cầu dao với thương hiệu bảng điện để có khả năng tương thích tối ưu và phạm vi bảo hành
- Xem xét nhu cầu mở rộng trong tương lai khi lập kế hoạch các mạch có cường độ dòng điện cao
- Đầu tư vào cầu dao bắt vít GFCI hoặc AFCI nơi quy tắc yêu cầu để tăng cường an toàn
Khuyến nghị bảo trì
- Kiểm tra trực quan hàng năm của các kết nối để tìm dấu hiệu quá nhiệt hoặc ăn mòn
- Xác minh mô-men xoắn chuyên nghiệp 5 năm một lần trong các ứng dụng dân dụng
- Đánh giá chuyên nghiệp ngay lập tức nếu bạn nhận thấy mùi khét hoặc bảng điện ấm
Cài Đặt Thực Hành Tốt Nhất
- Luôn sử dụng các giá trị mô-men xoắn do nhà sản xuất chỉ định để ngăn ngừa các vấn đề về kết nối
- Xác minh kích thước dây thích hợp cho định mức cường độ dòng điện đầy đủ của cầu dao bắt vít
- Đảm bảo thông gió đầy đủ cho bảng điện cho các ứng dụng có cường độ dòng điện cao
Khi để Gọi một người Chuyên nghiệp
Ngay Lập Tức, Sự Giúp Đỡ Chuyên Nghiệp Yêu Cầu:
- Bất kỳ công việc điện nào liên quan đến các mạch có cường độ dòng điện cao
- Mùi khét hoặc dấu hiệu quá nhiệt trong bảng điện của bạn
- Cầu dao bắt vít bị ngắt thường xuyên khi tải bình thường
- Bất kỳ sửa đổi nào đối với cấu hình bảng điện hiện có
Lập kế hoạch tư vấn chuyên nghiệp:
- Nâng cấp dịch vụ điện hoặc thêm các mạch có cường độ dòng điện cao
- Lắp đặt trạm sạc EV hoặc các thiết bị lớn khác
- Đánh giá các hệ thống điện cũ hơn về an toàn và tuân thủ quy tắc
⚠️ Lưu ý an toàn quan trọng: Làm việc với bảng điện và các mạch có cường độ dòng điện cao gây ra những rủi ro nghiêm trọng về điện giật, bỏng và hỏa hoạn. Luôn thuê thợ điện được cấp phép để lắp đặt, bảo trì và sửa chữa.
Kết luận
Cầu dao bắt vít là các thành phần thiết yếu cho các mạch điện có cường độ dòng điện cao, cung cấp tính toàn vẹn kết nối vượt trội và tuân thủ quy tắc cho các ứng dụng trên 30 amps. Mặc dù chúng yêu cầu lắp đặt chuyên nghiệp và tốn kém hơn so với các lựa chọn thay thế cắm, nhưng thiết kế kết nối cơ học của chúng mang lại độ tin cậy và an toàn vô song cho các hệ thống điện quan trọng.
Những điểm chính cần ghi nhớ:
- Cầu dao bắt vít được yêu cầu theo quy tắc cho các mạch trên 30 amps
- Chúng cung cấp kết nối điện vượt trội thông qua cơ cấu siết chặt cơ học
- Việc lắp đặt chuyên nghiệp là bắt buộc để đảm bảo an toàn và tuân thủ quy định
- Chúng rất cần thiết cho các thiết bị điện công suất cao hiện đại và hệ thống sạc xe điện
Đối với bất kỳ việc lắp đặt hoặc đánh giá cầu dao dạng bắt vít nào, hãy tham khảo ý kiến của thợ điện có giấy phép, người có thể đảm bảo lựa chọn, lắp đặt và tuân thủ quy định phù hợp cho ứng dụng cụ thể của bạn.