Ang GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter) at AFCI (Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter) ay parehong mahalagang kagamitan sa kaligtasan ng kuryente, ngunit nagpoprotekta ang mga ito laban sa iba't ibang uri ng panganib sa kuryente. Pinipigilan ng mga GFCI ang electrical shock sa pamamagitan ng pagtukoy ng mga ground fault sa kasing baba ng 4-6 milliamps at pag-trip sa loob ng 1/40 ng isang segundo, habang pinipigilan ng mga AFCI ang mga sunog na dulot ng kuryente sa pamamagitan ng pagtukoy ng mga mapanganib na electrical arc gamit ang advanced na teknolohiya ng microprocessor. Ang mga modernong electrical code ay nangangailangan na ngayon ng parehong proteksyon sa magkakapatong na mga lugar, na ginagawang lalong mahalaga ang mga dual-function na GFCI/AFCI breaker para sa komprehensibong kaligtasan sa bahay.

Mga Pangunahing Takeaway
- Pinoprotektahan ng mga GFCI device ang mga tao mula sa electrical shock sa pamamagitan ng pagtukoy ng mga ground fault (pagtagas ng kuryente), habang Pinoprotektahan ng mga AFCI device ang ari-arian mula sa mga sunog na dulot ng kuryente sa pamamagitan ng pagtukoy ng mga mapanganib na kondisyon ng arcing
- Mga dual-function breaker Ang pagsasama ng proteksyon ng GFCI at AFCI ay ang pinaka-epektibong solusyon sa gastos para sa mga lugar na nangangailangan ng parehong proteksyon sa ilalim ng mga kinakailangan ng NEC 2023
- Ang mga GFCI ay mandatory sa mga basang lokasyon (banyo, kusina, labas, garahe) ayon sa NEC 210.8, habang Ang mga AFCI ay kinakailangan sa mga living space (silid-tulugan, sala, family room) ayon sa NEC 210.12
- Buwanang pagsubok ng parehong GFCI at AFCI device ay kritikal—ang mga device na pumalya sa pagsubok o higit sa 10-15 taong gulang ay dapat palitan kaagad
- Istorbo balakid sa mga AFCI device ay bumaba nang malaki sa mga mas bagong modelo ng kumbinasyon, ngunit ang hindi tugmang electronics at mga isyu sa paglalagay ng kable ay nananatiling karaniwang sanhi
- Ayon sa U. S. Consumer Product Safety Commission, Maaaring pigilan ng mga AFCI ang higit sa 50% ng mga sunog na dulot ng kuryente sa bahay, na nagdudulot ng humigit-kumulang $1.3 bilyon sa pinsala sa ari-arian taun-taon
Ano ang GFCI at AFCI Circuit Breakers?
Kahulugan ng GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter).
Ang GFCI ay isang electrical safety device na idinisenyo upang protektahan ang mga tao mula sa electrical shock na dulot ng mga ground fault. Patuloy nitong sinusubaybayan ang daloy ng kuryente na dumadaloy sa mainit at neutral na mga wire, kaagad na pinapatay ang kuryente kapag nakita nito ang kahit na maliliit na pagkakaiba na nagpapahiwatig na ang daloy ay dumadaloy sa lupa sa pamamagitan ng hindi sinasadyang daanan—gaya ng sa pamamagitan ng katawan ng isang tao.
Ang mga GFCI ay nakapagliligtas ng mga buhay mula nang ipakilala ang mga ito noong 1970s. Gumagana ang teknolohiya sa pamamagitan ng paghahambing ng kasalukuyang nasa hot wire sa kasalukuyang nasa neutral wire. Sa normal na mga kondisyon, dapat itong maging pantay. Kapag hinawakan ng isang tao ang isang may sira na appliance o tool, dumadaloy ang kuryente sa kanilang katawan patungo sa lupa, na lumilikha ng isang imbalance na agad na natutukoy ng GFCI. Ang nakapagliligtas-buhay na oras ng pagtugon na ito na 1/40 ng isang segundo (25-30 milliseconds) ay sapat na mabilis upang maiwasan ang nakamamatay na electrocution sa karamihan ng mga sitwasyon.
Kahulugan ng AFCI (Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter).
Ang AFCI ay isang electrical safety device na idinisenyo upang maiwasan ang mga sunog na dulot ng kuryente sa pamamagitan ng pagtukoy ng mga mapanganib na electrical arc sa mga sistema ng paglalagay ng kable. Gumagamit ito ng advanced na electronics at microprocessors upang makilala sa pagitan ng normal na electrical arc (tulad ng kapag tinanggal mo ang isang appliance o binuksan ang isang switch) at potensyal na mapanganib na mga arc na maaaring magdulot ng sunog, awtomatikong pinapatay ang kuryente kapag natukoy ang mga mapanganib na kondisyon.
Nangyayari ang electrical arcing kapag ang kuryente ay tumalon sa isang puwang sa nasira, lumala, o hindi wastong naka-install na mga kable. Ang mga arc na ito ay maaaring umabot sa mga temperatura na higit sa 10,000°F—sapat na init upang mag-apoy ng mga nakapaligid na materyales tulad ng wood framing at insulation. Ayon sa U. S. Fire Administration, ang mga pagkabigo o malfunction ng kuryente ay ang pangalawang nangungunang sanhi ng mga sunog sa bahay, na nagkakahalaga ng tinatayang 24,000 sunog taun-taon. Tinutugunan ng mga AFCI ang kritikal na agwat sa kaligtasan na ito sa pamamagitan ng pagbibigay ng proteksyon na tradisyonal mga circuit breaker hindi kayang ibigay.

Mga Pangunahing Pagkakaiba sa Pagitan ng GFCI at AFCI
Narito ang isang komprehensibong talahanayan na nagpapakita ng mga pangunahing pagkakaiba sa pagitan ng GFCI at AFCI circuit breaker:
| Tampok | GFCI | AFCI |
|---|---|---|
| Pangunahing Proteksyon | Pag-iwas sa electric shock | Pag-iwas sa sunog sa kuryente |
| Nakakakita | Mga ground fault (4-6 milliamps) | Mapanganib na mga arko ng kuryente |
| Oras Ng Pagtugon | 1/40 ng isang segundo (25-30 ms) | Milliseconds |
| Teknolohiya | Pag-detect ng pagkakaiba sa kasalukuyang | Pag-detect ng arc na nakabatay sa microprocessor |
| Mga Kinakailangang Lokasyon | Banyo, kusina, labas, garahe, crawl space, basement | Silid-tulugan, living area, family room, dining room, hallway |
| Seksyon ng NEC Code | Artikulo 210.8 | Artikulo 210.12 |
| Gastos sa Pag-install | $15-45 bawat outlet/breaker | $45-75 bawat breaker |
| Halaga ng Dual Function | N/A | $50-85 bawat breaker |
| habang-buhay | 10-15 taon | 10-20 taon |
| Dalas ng Pagsubok | Buwanan (kinakailangan) | Buwanan (kinakailangan) |
| False Trip Rate | Mababa | Katamtaman (makabuluhang pinabuti sa mga mas bagong modelo) |
| Unang Kinakailangan ng NEC | 1971 (mga partikular na lokasyon) | 1999 (mga silid-tulugan lamang) |
| Antas ng Proteksyon | Kaligtasan ng tauhan | Proteksyon ng ari-arian |
Kailan at Saan Gagamitin ang GFCI vs AFCI
Mga Kinakailangang Lokasyon ng GFCI (NEC 210.8)
⚠️ KINAKAILANGAN SA KALIGTASAN: Ang mga GFCI ay sapilitan sa mga lokasyong ito ayon sa National Electrical Code:
Residential (Mga Yunit ng Tirahan):
- Banyo – Lahat ng 125-volt, 15- at 20-ampere na receptacle
- Kitchens – Lahat ng receptacle na nagsisilbi sa mga countertop surface at nasa loob ng 6 na talampakan ng mga lababo
- Sa labas ng bahay – Lahat ng receptacle na naa-access mula sa grade level
- Mga garahe at accessory building – Lahat ng receptacle (maliban sa mga nakalaang appliance sa mga hindi naa-access na lokasyon)
- Mga crawl space – Lahat ng 125-volt, 15- at 20-ampere na receptacle
- Mga hindi tapos na basement – Lahat ng receptacle (na may mga pagbubukod para sa mga nakalaang appliance)
- Mga lugar ng labahan – Mga receptacle sa loob ng 6 na talampakan ng mga lababo
- Mga silid ng utility – Mga receptacle sa loob ng 6 na talampakan ng mga lababo
- Mga wet bar – Lahat ng receptacle sa loob ng 6 na talampakan ng lababo
- Mga boathouse – Lahat ng receptacle
Mga Update sa NEC 2023:
Pinalawak ng 2023 NEC ang mga kinakailangan sa GFCI nang malaki, na ngayon ay nag-uutos ng proteksyon para sa lahat ng 125-volt hanggang 250-volt na receptacle sa maraming lokasyon, kabilang ang mga dishwasher, disposal, at iba pang nakapirming appliance sa mga kusina at katulad na lugar.
Mga Kinakailangang Lokasyon ng AFCI (NEC 210.12)
🔥 KINAKAILANGAN SA PAG-Iwas sa Sunog: Ang mga AFCI ay sapilitan sa mga lokasyong ito:
Residential (Mga Yunit ng Tirahan):
- Mga silid-tulugan – Lahat ng 120-volt, 15- at 20-ampere na branch circuit
- Mga sala – Lahat ng circuit na nagbibigay ng mga outlet o device
- Mga family room – Lahat ng circuit na nagbibigay ng mga outlet o device
- Mga dining room – Lahat ng circuit na nagbibigay ng mga outlet o device
- Mga hallway – Lahat ng circuit na nagbibigay ng mga outlet o device
- Mga closet – Lahat ng circuit na nagbibigay ng mga outlet o device
- Mga sunroom – Lahat ng circuit na nagbibigay ng mga outlet o device
- Mga recreation room – Lahat ng circuit na nagbibigay ng mga outlet o device
- Mga aklatan at silid-aralan – Lahat ng circuit na nagbibigay ng mga outlet o device
Pagpapalawak ng NEC 2023:
Ang 2023 code cycle ay higit pang pinalawak ang mga kinakailangan sa AFCI upang isama ang mga silid-tulugan sa mga istasyon ng bumbero, istasyon ng pulisya, istasyon ng ambulansya, at mga katulad na pasilidad, na kinikilala ang kritikal na kahalagahan ng pag-iwas sa sunog sa mga mahahalagang gusali ng serbisyo.
Mga Lokasyon na Nangangailangan ng PAREHONG Proteksyon ng GFCI at AFCI
💡 MGA DUAL PROTECTION ZONE: Ang ilang circuit ay nangangailangan ng parehong uri ng proteksyon:
- Mga receptacle sa kusina (GFCI para sa shock + AFCI para sa pag-iwas sa sunog)
- Mga lugar ng labahan (GFCI para sa mga basang lugar + AFCI para sa proteksyon sa espasyo ng tirahan)
- Mga espasyo ng tirahan sa basement (GFCI para sa mga mamasa-masang lugar + AFCI para sa mga tinitirhang lugar)
- Mga saksakan sa garahe sa mga circuit ng silid-tulugan (kapag ang mga circuit ay nagmumula sa mga silid-tulugan)
TIP MULA SA EKSPERTO: Para sa mga lugar na nangangailangan ng parehong proteksyon, gumamit ng mga dual-function na GFCI/AFCI circuit breaker sa halip na pagsamahin ang magkahiwalay na device. Ang mga dual-function na breaker ay nagkakahalaga lamang ng ₱500-₱800 na mas mahal kaysa sa mga AFCI-only breaker ngunit inaalis ang pagiging kumplikado at mga potensyal na isyu sa compatibility ng paggamit ng AFCI breaker na may mga GFCI receptacle.
Paano Gumagana ang GFCI at AFCI: Technical Breakdown
Mekanismo ng Operasyon ng GFCI
Gumagana ang mga GFCI sa pamamagitan ng patuloy na paghahambing ng kasalukuyang dumadaloy sa mainit (linya) na kawad sa kasalukuyang bumabalik sa pamamagitan ng neutral na kawad. Sa ilalim ng normal na mga kondisyon, ang mga agos na ito ay dapat na halos magkapareho. Kapag nagkaroon ng ground fault:
- Pagtuklas ng Hindi Balanseng Kuryente – Dumadaloy ang kuryente sa isang hindi sinasadyang daanan (tulad ng sa pamamagitan ng isang taong humahawak sa isang sirang appliance)
- Differential Sensing – Natutukoy ng sensing transformer ng GFCI ang hindi pagkakapantay-pantay na ito (kasing liit ng 4-6 milliamps)
- Rapid Response – Ang device ay nagti-trip sa loob ng 1/40th ng isang segundo (25-30 milliseconds)
- Pagkagambala ng kuryente – Agad na pinuputol ang kuryente upang maiwasan ang electrical shock
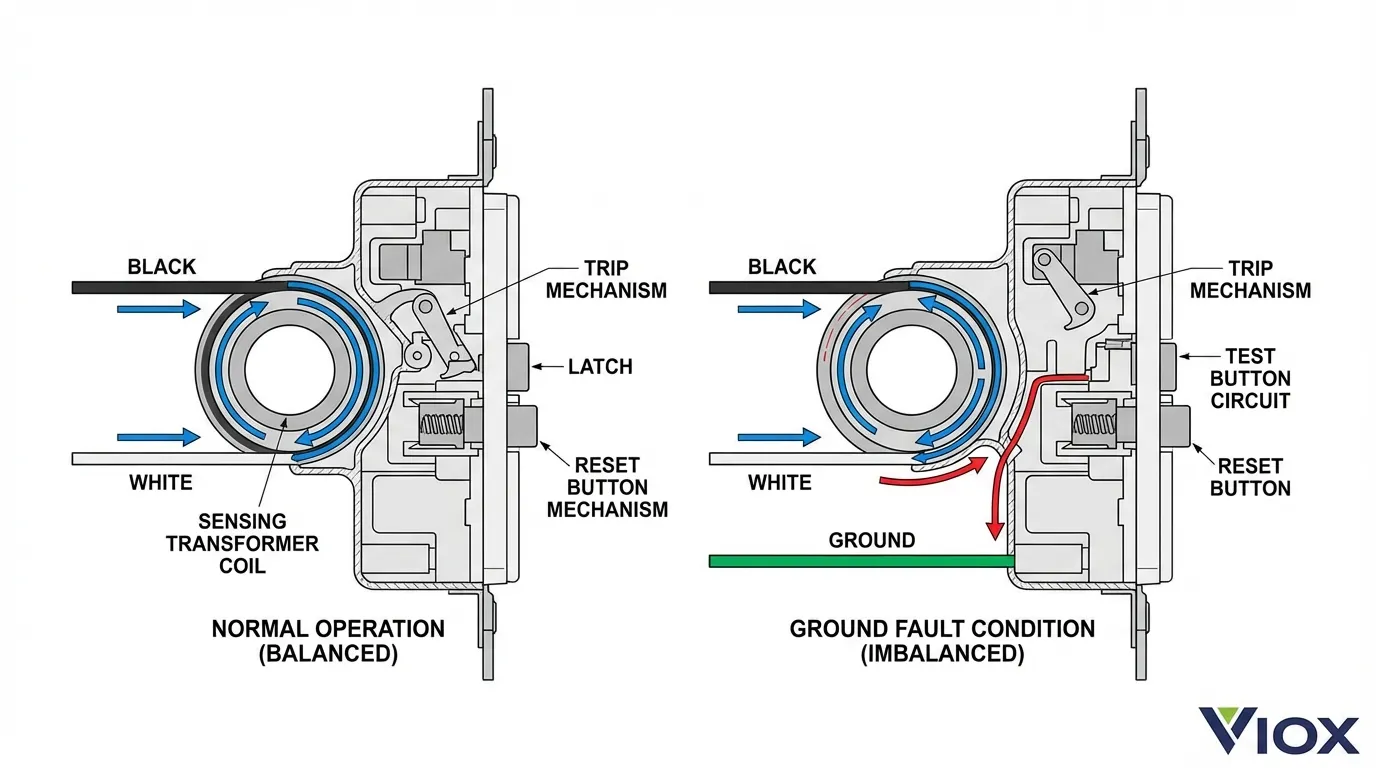
Teknikal na Pagtutukoy:
- Trip threshold: 4-6 mA ±1 mA
- Trip time: 25-30 milliseconds sa rated current
- Operating voltage: Karaniwan ay 120V o 240V
- Reset mechanism: Kinakailangan ang manual push-button reset
Ang 4-6 milliamp threshold ay maingat na kinakalibrate. Ipinapakita ng mga pag-aaral na ang mga kuryente na higit sa 10 mA ay maaaring magdulot ng mga pag-urong ng kalamnan na pumipigil sa isang tao na bitawan ang electrical source (tinatawag na “let-go threshold”), habang ang mga kuryente na higit sa 30 mA ay maaaring magdulot ng respiratory paralysis. Ang 4-6 mA threshold ng GFCI ay nagbibigay ng isang kritikal na safety margin.
Mekanismo ng Operasyon ng AFCI
Gumagamit ang mga AFCI ng mga sopistikadong electronic circuit at microprocessor upang suriin ang mga electrical waveform at tuklasin ang mga mapanganib na arcing condition:
- Patuloy na Pagsubaybay – Sinusubaybayan ng mga advanced na microprocessor ang mga electrical signature sa real-time
- Arc Signature Analysis – Tinutukoy ng device ang pagkakaiba sa pagitan ng mga normal na arc (pagpapatakbo ng appliance, mga contact ng switch) at mga mapanganib na arc (sirang wiring, maluwag na koneksyon)
- Hazard Detection – Kapag natukoy ang mapanganib na arcing, ang AFCI ay nagti-trip sa loob ng milliseconds
- Pagkagambala ng Circuit – Pinuputol ang kuryente upang maiwasan ang mga sunog na dulot ng kuryente
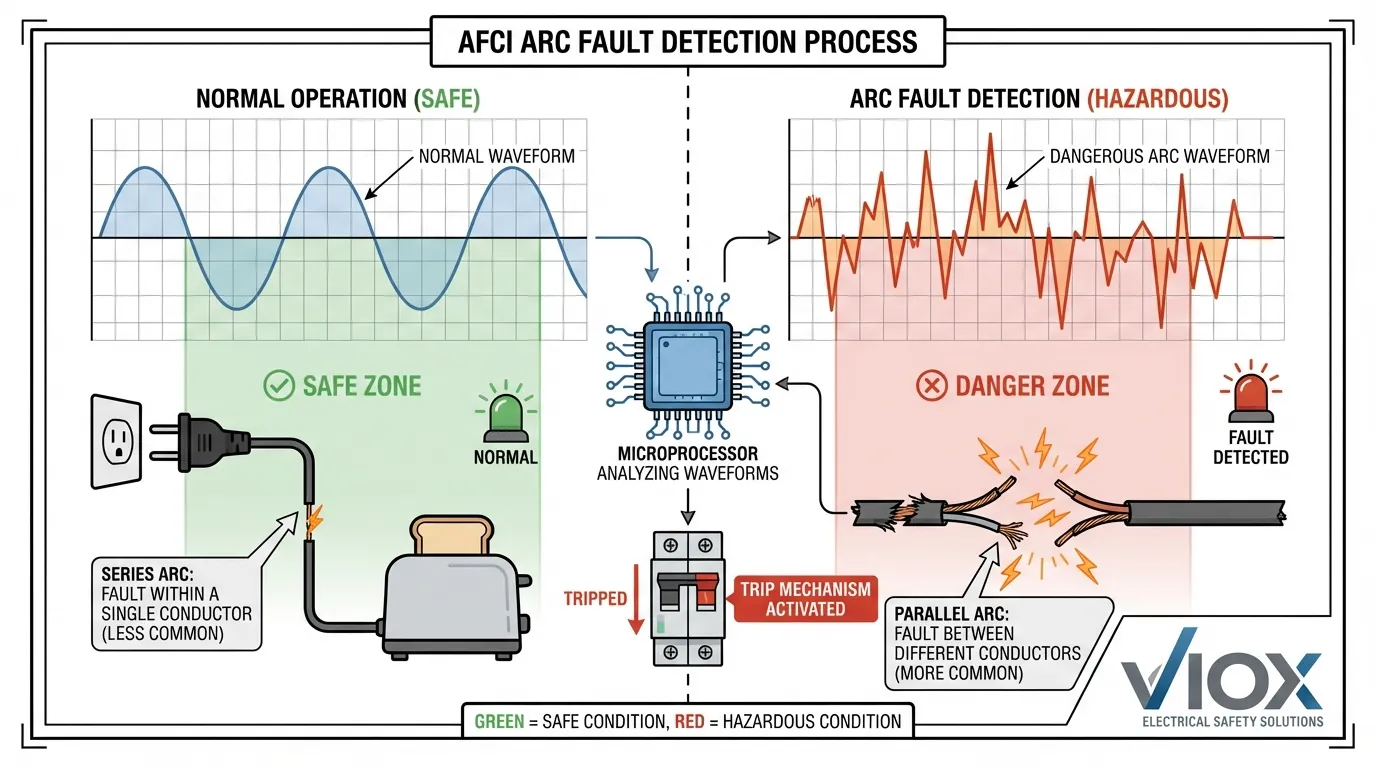
🔧 TEKNIKAL NA TALA: Kayang tuklasin ng mga modernong combination AFCI:
- Series arcs – Arcing sa kahabaan ng isang solong wire (hal., sirang insulation)
- Parallel arcs – Arcing sa pagitan ng hot at neutral o hot at ground wires
- Ground arcs – Arcing sa pagitan ng hot wire at ground
- Combination arcs – Maramihang uri ng arc na nangyayari nang sabay-sabay
Sinasala ng teknolohiya ang mga normal na operational arc habang tinutukoy ang mga mapanganib na pattern ng arcing. Kabilang dito ang pagsusuri sa tagal ng arc, dalas, kasalukuyang signature, at mga pattern ng pag-uulit upang mabawasan ang nuisance tripping habang pinapanatili ang kaligtasan.
Mga uri ng GFCI at AFCI Device
Mga Uri ng Device ng GFCI
| Uri | Application | Lokasyon ng Pag-install | Gastos Na Hanay | Mga kalamangan |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outlet ng GFCI | Indibidwal na proteksyon sa labasan | Pinapalitan ang karaniwang saksakan | $15-30 | Pinoprotektahan ang mga downstream outlet, madaling subukan |
| GFCI Circuit Breaker | Buong proteksyon ng circuit | Pangunahing panel ng kuryente | $45-75 | Proteksyon sa buong circuit, tamper-resistant |
| Portable na GFCI | Pansamantalang proteksyon | Naka-plug sa kasalukuyang outlet | $25-50 | Portable, hindi kinakailangan ang pag-install |
| GFCI Extension Cord | Panlabas/pansamantalang paggamit | Pinagsama sa kurdon | $30-60 | Maginhawa para sa mga panlabas na tool |
Mga Uri ng Device ng AFCI
| Uri | Arc Fault Detection | Application | Code Pagsunod | Mga tala |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Branch/Feeder AFCI | Mga seryeng arko lamang | Mas lumang teknolohiya | Hindi sumusunod sa NEC para sa mga bagong pag-install | Unti-unting inalis pagkatapos ng 2008 |
| Kumbinasyon ng AFCI | Mga serye at parallel na arko | Kasalukuyang pamantayan | Kinakailangan para sa mga bagong pag-install | Pamantayan ng industriya mula noong 2008 |
| Outlet Branch Circuit AFCI | Mga serye at parallel na arko | Proteksyon sa antas ng labasan | Alternatibo sa circuit breaker | Ginagamit sa mga sitwasyon ng remodeling |
| Dual-Function AFCI/GFCI | Lahat ng uri ng arc + ground faults | Mga lugar na nangangailangan ng parehong proteksyon | Sumusunod para sa parehong NEC 210.8 & 210.12 | Pinaka-cost-effective na solusyon |
Mahalagang Pagkakaiba: Ang terminong “combination” sa isang AFCI breaker ay tumutukoy sa kakayahan nitong tuklasin ang parehong series at parallel arc faults—HINDI ito nangangahulugan na kasama sa breaker ang proteksyon ng GFCI. Tanging ang mga breaker na partikular na may label na “Dual Function” o “AFCI/GFCI” ang nagbibigay ng parehong uri ng proteksyon.
Dual-Function GFCI/AFCI Breakers: Ang Modernong Solusyon
Bakit Nagiging Popular ang mga Dual-Function Breaker
Habang lumalawak ang mga kinakailangan ng NEC, maraming circuit ngayon ang nangangailangan ng parehong proteksyon ng GFCI at AFCI. Nag-aalok ang mga dual-function breaker ng ilang kalamangan:
Kahusayan sa Gastos:
- Dual-function breaker: ₱2,500-₱4,500
- AFCI breaker + GFCI outlet: ₱3,000-₱5,000
- Mga Pagtitipid: ₱500-₱1,000 bawat circuit kasama ang pinababang oras ng pag-install
Pagtitipid sa Espasyo:
- Sumasakop ng isang slot ng breaker sa panel
- Inaalis ang pangangailangan para sa mga GFCI outlet sa maraming lokasyon
- Pinapasimple ang organisasyon ng panel
Mga Benepisyo sa Pagiging Maaasahan:
- Ang iisang punto ng proteksyon ay nagpapababa ng mga posibleng sira
- Mas madaling pag-troubleshoot kapag may mga trip
- Pare-parehong proteksyon sa buong circuit
Pagsunod sa Code:
- Nakakatugon sa parehong mga kinakailangan ng NEC 210.8 (GFCI) at 210.12 (AFCI)
- Tamang-tama para sa mga circuit ng kusina, mga lugar ng labahan, at mga basement living space
- Pinapasimple ang proseso ng inspeksyon at pag-apruba
Kailan Gagamit ng Dual-Function vs. Hiwalay na Device
Gumamit ng Dual-Function Breaker Kapag:
- Naglalagay ng mga bagong circuit sa mga kusina, labahan, o basement living area
- Nag-a-upgrade ng mga lumang panel upang matugunan ang kasalukuyang code
- Pinoprotektahan ang mga appliances tulad ng dishwasher, disposal, at washing machine
- Pinapasimple ang proteksyon sa mga lugar na may parehong mga kinakailangan
Gumamit ng Hiwalay na GFCI Outlet sa mga AFCI Circuit Kapag:
- Nagre-remodel ng mga kasalukuyang circuit (mas cost-effective)
- Kailangan ng point-of-use GFCI protection para sa mga tiyak na outlet
- Limitado ang espasyo sa panel at naka-install na ang AFCI breaker
- Nag-troubleshoot ng nuisance tripping (mas madaling ihiwalay ang mga isyu)
Mga Pagsasaalang-alang sa Pag-install at Kaligtasan
Mga Kinakailangan sa Propesyonal na Pag-install
⚠️ BABALA SA KALIGTASAN: Ang pag-install ng GFCI at AFCI ay dapat isagawa ng mga lisensyadong electrician. Ang pagtatrabaho sa mga electrical panel at circuit ay nagdadala ng malubhang panganib ng electrocution, sunog, at mga paglabag sa code. Ang hindi wastong pag-install ay maaaring lumikha ng mga panganib na mas malala pa kaysa sa walang proteksyon.
Bakit Mahalaga ang Propesyonal na Pag-install:
- Wastong paghihiwalay ng neutral wire (kritikal para sa operasyon ng AFCI)
- Tamang pagkalkula ng load upang maiwasan ang overloading
- Pagsunod sa mga lokal na electrical code at mga susog
- Wastong pagsubok at pagpapatunay ng operasyon
- Dokumentasyon para sa mga layunin ng insurance at resale
Mga Karaniwang Pagkakamali sa Pag-install na Dapat Iwasan
Mga Pagkakamali sa Pag-install ng AFCI:
- Shared neutral wires – Ang mga multi-wire circuit ay nangangailangan ng espesyal na paghawak
- Hindi wastong mga koneksyon ng neutral – Dapat gumamit ng dedicated neutral terminal
- Paghahalo ng luma at bagong mga wiring – Maaaring magdulot ng nuisance tripping
- Hindi tugmang mga device – Hindi lahat ng breaker ay kasya sa lahat ng panel
Mga Pagkakamali sa Pag-install ng GFCI:
- Binaliktad na mga koneksyon ng line/load – Pinipigilan ang wastong proteksyon
- Shared neutral sa mga non-GFCI circuit – Nagdudulot ng agarang tripping
- Bootleg grounds – Mapanganib na kasanayan na sumisira sa proteksyon ng GFCI
- Nawawalang mga weatherproof cover – Kinakailangan para sa mga panlabas na pag-install
Hakbang-hakbang na Proseso ng Pagsusuri ng GFCI
Buwanang Protokol ng Pagsubok:
- Visual na Inspeksyon – Suriin kung may pisikal na pinsala, pagkawalan ng kulay, o amoy ng sunog
- Pindutin ang TEST Button – Dapat agad na mag-trip ang device (tunog ng click, napuputol ang kuryente)
- Patunayan ang Pagkawala ng Kuryente – Gumamit ng voltage tester o isaksak ang ilaw upang kumpirmahin na walang kuryente
- Pindutin ang RESET Button – Dapat mag-reset ang device na may maririnig na click
- Patunayan ang Pagbabalik ng Kuryente – Kumpirmahin na bumalik ang kuryente sa mga outlet
- Idokumento ang mga Resulta – Panatilihin ang log ng pagsubok na may petsa at mga resulta
Mga Tagapagpahiwatig ng Pagkabigo:
- Hindi napa-trip ng TEST button ang device
- Hindi nananatiling naka-engage ang RESET button
- Bahagyang kuryente (gumagana ang ilang outlet, ang iba ay hindi)
- Nakikita pinsala o burn ng amoy
- Ang device ay higit sa 10-15 taong gulang
Hakbang-hakbang na Proseso ng Pagsusuri ng AFCI
Buwanang Protokol ng Pagsubok:
- Hanapin ang AFCI Breaker – Tukuyin ang breaker sa main panel (nakalagay ang label na “AFCI” o “Combination AFCI”)
- Pindutin ang TEST Button – Dapat mag-trip ang handle ng breaker sa gitnang posisyon
- Beripikahin ang Pagkawala ng Enerhiya sa Sirkito – Kumpirmahin na walang kuryente ang lahat ng saksakan sa sirkito
- I-reset ang Breaker – Itulak nang mariin ang handle sa posisyong OFF, pagkatapos ay sa posisyong ON
- Beripikahin ang Pagpapanumbalik – Tingnan kung bumalik ang kuryente sa lahat ng saksakan
- Subaybayan ang mga Nuisance Trip – Itala ang anumang hindi inaasahang trip para sa pag-troubleshoot
🔧 EXPERT TIP: Panatilihin ang log ng pagsubok para sa mga GFCI at AFCI device. Palitan ang anumang device na hindi nagtagumpay sa pagsubok nang maayos o higit sa 10-15 taong gulang. Maraming modernong device ang may kasamang self-test feature, ngunit ang manu-manong buwanang pagsubok ay nananatiling pamantayan para sa pagberipika ng kaligtasan.
Pag-troubleshoot ng Mga Karaniwang Isyu sa GFCI at AFCI
Gabay sa Pag-troubleshoot ng GFCI
Problema: Hindi Magre-reset ang GFCI
Mga Posibleng Dahilan:
- Aktibong ground fault sa sirkito
- Sira na ang GFCI device
- Kahalumigmigan sa outlet box
- Sira na ang mga panloob na bahagi
Mga solusyon:
- Tanggalin sa saksakan ang lahat ng device mula sa GFCI at mga downstream outlet
- Subukang i-reset nang walang nakakabit na load
- Kung matagumpay, isaksak ang mga device isa-isa upang matukoy ang may sirang kagamitan
- Kung hindi matagumpay, tingnan kung may kahalumigmigan sa box at hayaang matuyo
- Palitan ang GFCI kung higit sa 10 taong gulang o kung nagpapatuloy ang problema
Problema: Madalas na Biyahe ng GFCI
Mga Posibleng Dahilan:
- May sirang appliance o tool na lumilikha ng ground fault
- Alumana sa mga kable o koneksyon
- Nasira na pagkakabukod ng mga kable
- Pinagsama-samang leakage current mula sa maraming device
- Normal na pagkasira sa pagtatapos ng buhay
Mga solusyon:
- Tukuyin ang pattern (partikular na appliance, may kaugnayan sa panahon, batay sa oras)
- Subukan ang mga appliance nang paisa-isa sa iba't ibang sirkito
- Siyasatin kung may kahalumigmigan sa mga panlabas na box o mga lugar na basa
- Tingnan ang edad ng GFCI (palitan kung 10+ taong gulang)
- Isaalang-alang ang pag-install ng mga dedikadong sirkito para sa mga high-leakage device
Gabay sa Pag-troubleshoot ng AFCI
Problema: Madalas na Biyahe ng AFCI (Nuisance Tripping)
Mga Posibleng Dahilan:
- Hindi tugmang mga elektronikong device (vacuum cleaner, treadmill, fluorescent light, lumang TV)
- Hindi wastong mga koneksyon ng neutral wire
- Pinaghalong luma at bagong mga wiring sa parehong sirkito
- Maluwag na mga koneksyon ng wire na lumilikha ng intermittent arcing
- May depektong AFCI breaker
Mga solusyon:
- Tukuyin ang trigger – Itala kung anong device/aktibidad ang sanhi ng mga trip
- Suriin ang compatibility ng device – Ang ilang lumang electronics ay lumilikha ng mga arc-like signature
- Siyasatin ang mga koneksyon ng wiring – Beripikahin na ang lahat ng koneksyon ay mahigpit at wasto
- Beripikahin ang neutral separation – Tiyakin na ang mga neutral wire ay hindi ibinabahagi sa ibang mga sirkito
- I-update ang AFCI breaker – Ang mga bagong modelo ay may pinahusay na filtering upang mabawasan ang mga false trip
- Isaalang-alang ang mga firmware update – Ang ilang smart breaker ay maaaring i-update upang mapabuti ang performance
Problema: Hindi Mare-reset ang AFCI Pagkatapos ng Biyahe
Mga Posibleng Dahilan:
- Aktibong arc fault condition pa rin
- Sira na ang wiring na nangangailangan ng pagkukumpuni
- May depektong AFCI breaker
- Hindi tugmang multi-wire circuit configuration
Mga solusyon:
- Siyasatin ang sirkito para sa nakikitang pinsala (sunog na mga outlet, sirang mga cord)
- Idiskonekta ang lahat ng device at subukang i-reset
- Kung matagumpay, ikonekta muli ang mga device isa-isa
- Tingnan kung may maluwag na koneksyon sa mga outlet at junction box
- Beripikahin ang wastong pag-install (dedikadong neutral, tamang wiring)
- Palitan ang breaker kung may depekto (subukan sa isang kilalang-maayos na breaker kung posible)
🔥 PAUNAWA SA KALIGTASAN SA SUNOG: Ayon sa pananaliksik ng Consumer Product Safety Commission, maaaring maiwasan ng mga AFCI ang higit sa 50% ng mga sunog na elektrikal sa mga tahanan. Bagama't nakakabigo ang nuisance tripping, huwag kailanman i-bypass o i-disable ang proteksyon ng AFCI. Sa halip, makipagtulungan sa isang kwalipikadong electrician upang matukoy at malutas ang pinagmulan habang pinapanatili ang mahalagang proteksyon sa sunog.
Pagsusuri ng Gastos at ROI
Paghahati-hati ng Gastos ng GFCI
| Uri ng Pag-install | Gastos ng Materyal | Gastos sa Paggawa | Kabuuang Puhunan | Taunang Halaga ng Kaligtasan |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nag-iisang Outlet ng GFCI | $15-30 | $75-125 | $90-155 | Hindi mabibili ng shock prevention |
| GFCI Circuit Breaker | $45-75 | $100-175 | $145-250 | Proteksyon ng buong circuit |
| Maraming Outlet (3-5) | $60-150 | $200-400 | $260-550 | Komprehensibong kaligtasan |
| Buong Bahay na Pag-upgrade ng GFCI | $300-600 | $800-1,500 | $1,100-2,100 | Pinakamataas na proteksyon ng tauhan |
AFCI Cost Breakdown
| Uri ng Pag-install | Gastos ng Materyal | Gastos sa Paggawa | Kabuuang Puhunan | Halaga ng Pag-iwas sa Sunog |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nag-iisang AFCI Breaker | $45-75 | $100-150 | $145-225 | $50,000+ proteksyon sa ari-arian |
| Mga Sirkito ng Silid-tulugan (3-4) | $180-300 | $300-500 | $480-800 | Kumpletong kaligtasan sa kwarto |
| Buong Bahay na AFCI | $500-1,200 | $800-1,500 | $1,300-2,700 | Pinakamataas na pag-iwas sa sunog |
| Mga Dual-Function Breaker | ₱50-85 bawat isa | ₱100-150 bawat isa | $150-235 bawat isa | Pinagsamang proteksyon sa shock at sunog |
Pagsusuri ng Return on Investment
Mga Benepisyo sa Seguro:
- Maraming kompanya ng seguro ang nag-aalok ng 5-10% diskuwento para sa komprehensibong proteksyon ng GFCI/AFCI
- Karaniwang taunang matitipid: $50-150 sa seguro ng may-ari ng bahay
- Panahon ng pagbawi ng puhunan: 3-5 taon para sa mga pagpapabuti sa buong bahay
Epekto sa Halaga ng Ari-arian:
- Ang mga modernong tampok sa kaligtasan ng kuryente ay nagpapataas ng halaga ng bahay
- Kinakailangan para sa pagsunod sa code sa karamihan ng mga hurisdiksyon
- Inaalis ang mga alalahanin ng mamimili sa panahon ng inspeksyon ng bahay
- Tinatayang pagtaas ng halaga: $1,000-3,000 para sa komprehensibong proteksyon
Pagpapagaan ng Panganib:
- Karaniwang gastos ng sunog na sanhi ng kuryente: $50,000-100,000
- Karaniwang gastos ng pinsala sa shock ng kuryente: $10,000-50,000 (gastos sa medikal)
- Ang proteksyon ng AFCI ay maaaring maiwasan ang 50% ng mga sunog na sanhi ng kuryente
- Ang proteksyon ng GFCI ay pumipigil sa tinatayang 70% ng mga pagkamatay dahil sa electrocution
💰 INSURANCE CONSIDERATION: Maraming kompanya ng seguro ang nag-aalok ng mga diskuwento para sa mga bahay na may komprehensibong proteksyon ng GFCI at AFCI, na madalas na bumabawi sa mga gastos sa pag-install sa loob ng 3-5 taon. Bukod pa rito, maaaring bawasan ng ilang insurer ang mga premium o magbigay ng mas mahusay na mga tuntunin ng saklaw para sa mga bahay na nakakatugon sa kasalukuyang pamantayan sa kaligtasan ng kuryente.
Mga Kinakailangan sa Pagsunod sa Code at Inspeksyon
Mga Kinakailangan sa National Electrical Code (NEC).
Kasalukuyang Pamantayan ng Code (NEC 2023):
Mga Kinakailangan sa GFCI (NEC 210.8):
- Pinalawak upang masakop ang 125-250V na mga receptacle sa maraming lokasyon
- Idinagdag ang mga kinakailangan para sa mga nakapirming appliances sa mga kusina
- Nilinaw ang mga sukat ng distansya mula sa mga lababo (pinakamaikling landas, hindi sa pamamagitan ng mga pintuan)
- Pinahusay na mga kinakailangan sa labas at garahe
Mga Kinakailangan sa AFCI (NEC 210.12):
- Pinalawak sa lahat ng 15A at 20A, 120V na mga branch circuit sa mga lugar ng tirahan
- Idinagdag ang mga silid-tulugan sa mga istasyon ng bumbero at mga katulad na pasilidad
- Nilinaw ang mga kinakailangan para sa mga extension at pagbabago ng circuit
- Pinahusay na proteksyon para sa lahat ng mga tirahan
Mga Kinakailangan sa Dual Protection:
- Ang mga receptacle sa kusina ay nangangailangan na ngayon ng parehong GFCI at AFCI
- Ang mga lugar ng labahan ay nangangailangan ng parehong proteksyon
- Ang mga basement living space ay nangangailangan ng pareho
- Ang mga dishwasher, disposal, at mga katulad na appliances ay nangangailangan ng pareho
Mga Pagkakaiba-iba ng Lokal na Code
Mahalagang mga Pagsasaalang-alang:
- Maaaring gamitin ng mga lokal na hurisdiksyon ang iba't ibang edisyon ng NEC (2017, 2020, 2023)
- Ang ilang mga lugar ay may mga susog na lumalampas sa mga kinakailangan ng NEC
- Ang mga baybayin at mga rehiyon na may mataas na halumigmig ay madalas na may mas mahigpit na mga kinakailangan sa GFCI
- Palaging i-verify ang mga lokal na kinakailangan bago simulan ang trabaho
Karaniwang Lokal na Susog:
- Mas maagang paggamit ng mga bagong kinakailangan sa kaligtasan
- Karagdagang mga lokasyon na nangangailangan ng proteksyon
- Mga partikular na kinakailangan sa listahan ng produkto
- Pinahusay na mga kinakailangan sa pagsubok at dokumentasyon
📋 TANDAAN SA PAGSUNOD: Ang mga lokal na electrical code ay maaaring may karagdagang o binagong mga kinakailangan na lampas sa NEC. Palaging i-verify ang mga lokal na kinakailangan sa code bago ang pag-install at kumuha ng mga tamang permit para sa gawaing elektrikal. Ang pagkabigong sumunod ay maaaring magresulta sa mga nabigong inspeksyon, mga isyu sa seguro, at mga panganib sa kaligtasan.
Mga Propesyonal na Rekomendasyon at Mga Tip sa Eksperto
Pamantayan sa Pagpili para sa Mga GFCI Device
🏆 REKOMENDASYON NG EKSPERTO: Pumili ng mga GFCI device batay sa mga salik na ito:
- Sertipikasyon na Nakalista sa UL – Tinitiyak na natutugunan ng device ang mga pamantayan sa kaligtasan (UL 943 para sa mga GFCI)
- Paglaban sa Panahon – Mga device na may WR-rating para sa mga panlabas na aplikasyon (kinakailangan ng NEC)
- Paglaban sa Pag-tamper – Mga outlet na may TR-rating para sa kaligtasan ng bata (kinakailangan sa karamihan ng mga tirahan)
- Mga LED Indicator – Visual na pagsubaybay sa status para sa madaling pag-verify
- Kakayahan sa Self-Test – Awtomatikong pagsubaybay na nagpapababa sa pasanin sa pagpapanatili
- Reputasyon ng Tagagawa – Pumili ng mga itinatag na brand na may napatunayang pagiging maaasahan
- Saklaw ng Warranty – Maghanap ng 5-10 taong warranty
Mga Inirerekomendang Tampok para sa mga Tiyak na Aplikasyon:
- Mga banyo: Lumalaban sa pag-tamper, self-test, LED indicator
- Mga kusina: Lumalaban sa panahon (malapit sa mga lababo), 20A rating, self-test
- Sa labas: Lumalaban sa panahon, mga in-use cover, na maaring i-lock
- Mga garahe: Lumalaban sa panahon, 20A rating, maraming outlet
Pamantayan sa Pagpili para sa Mga AFCI Device
🔥 PRAYORIDAD SA PAG-Iwas sa Sunog: Pumili ng mga AFCI device na isinasaalang-alang:
- Uri ng Kombinasyon – Kinakailangan para sa mga bagong pag-install (nakakakita ng mga series at parallel arc)
- Reputasyon ng Tagagawa – Pumili ng mga brand na may mababang nuisance trip rate
- Pagkakatugma ng Panel – I-verify na ang breaker ay akma sa iyong partikular na brand/modelo ng panel
- Opsyon na Dual-Function – Isaalang-alang para sa mga lugar na nangangailangan ng parehong GFCI at AFCI
- Mga Update sa Firmware – Ang ilang smart breaker ay nag-aalok ng mga update upang mapabuti ang pagganap
- Kasaysayan ng Maling Pag-trip – Magsaliksik ng mga review ng user para sa pagiging maaasahan
- Saklaw ng Warranty – Maghanap ng 10+ taong warranty
Mga Pagsasaalang-alang sa Brand:
- Ang mga pangunahing tagagawa ay makabuluhang napabuti ang teknolohiya ng AFCI mula noong 2008
- Ang mga mas bagong modelo ay may mas mababang rate ng nuisance trip
- Ang ilang brand ay nag-aalok ng mga diagnostic feature upang matukoy ang mga sanhi ng pag-trip
- Ang mga smart breaker ay maaaring magbigay ng remote monitoring at mga alerto
Mga Alituntunin sa Pagpapanatili at Pagpapalit
Kailan Palitan ang GFCI at AFCI Devices
Mga Tagapahiwatig ng Pagpapalit:
Agarang Kinakailangan na Pagpapalit:
- Nabigo ang device sa buwanang pagsubok
- Nakikitang pinsala, pagkasunog, o pagkulay
- Hindi nagre-reset ang device pagkatapos mag-trip
- Madalas na nuisance tripping nang walang matukoy na sanhi
- Tunaw o kinakalawang na mga terminal
- Ang device ay higit sa 15 taong gulang
Isaalang-alang ang Pagpapalit:
- Ang device ay 10-15 taong gulang (malapit na sa katapusan ng buhay)
- Paglipat sa bahay na may mas lumang mga device
- Pag-upgrade sa mga self-test na modelo
- Pagdaragdag ng dual-function na kakayahan
- Pagpapabuti ng pagganap ng nuisance trip
Mga Oportunidad sa Pag-upgrade:
- Palitan ang mga karaniwang breaker ng Proteksyon ng AFCI sa panahon ng mga pag-upgrade ng panel
- Magdagdag ng proteksyon ng GFCI sa mga mas lumang bahay sa panahon ng remodeling
- Mag-upgrade sa mga dual-function na breaker kapag kinakailangan ang parehong proteksyon
- Mag-install ng mga smart breaker para sa remote monitoring
Iskedyul ng Propesyonal na Pagpapanatili
| Gawain sa Pagpapanatili | Dalas | Ginawa Ni | Kahalagahan | Mga tala |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buwanang Pagsusuri | Buwanang | May-ari ng bahay | Kritikal | Pindutin ang button na TEST sa lahat ng device |
| Visual na Inspeksyon | quarterly | May-ari ng bahay | Mahalaga | Suriin kung may pinsala, pagkulay |
| Propesyonal na Inspeksyon | Taun-taon | Lisensyadong Electrician | Mahalaga | Komprehensibong pagsusuri ng sistema |
| Pagsusuri ng Pag-load | Bawat 5 taon | Lisensyadong Electrician | Inirerekomenda | I-verify na hindi overloaded ang mga circuit |
| Pagsusuri ng Panel | Sa bawat 10 taon | Lisensyadong Electrician | Mahalaga | Tasahin ang pangangailangan para sa mga pag-upgrade |
| Pagpapalit ng Device | 10-15 taon | Lisensyadong Electrician | Kritikal | Proactive na programa sa pagpapalit |
🔧 TIP SA PAGMEMENTENA: Gumawa ng simpleng log ng pagsubok gamit ang isang kalendaryo o smartphone app. Magtakda ng buwanang mga paalala upang subukan ang lahat ng GFCI at AFCI device. Idokumento ang petsa, lokasyon, at mga resulta. Ang log na ito ay maaaring maging mahalaga para sa mga layunin ng insurance at tumutulong upang matukoy ang mga device na maaaring pumalya.
Mga Advanced na Paksa: Mga Solusyon sa Nuisance Tripping
Pag-unawa sa AFCI Nuisance Tripping
Ang nuisance tripping—kapag nag-trip ang isang AFCI nang walang aktwal na panganib—ay ang pangunahing reklamo tungkol sa teknolohiya ng AFCI. Gayunpaman, may mga makabuluhang pagpapabuti na nagawa:
Makasaysayang Konteksto:
- Mga Unang AFCI (1999-2008): Mataas na rate ng nuisance trip
- Combination AFCI (2008-2014): Pinabuti ngunit may problema pa rin
- Modernong AFCI (2014-kasalukuyan): Makabuluhang nabawasan ang mga maling trip
- Smart AFCI (2020+): Mga update sa firmware at mga kakayahan sa diagnostic
Mga Karaniwang Sanhi ng Nuisance Trip:
- Hindi Tugmang mga Device (40% ng mga kaso)
- Mga vacuum cleaner na may universal motor
- Mga treadmill at kagamitan sa pag-eehersisyo
- Mga fluorescent light at mas lumang dimmer
- Ilang power tool at appliances
- Mga Isyu sa Verkada (35% ng mga kaso)
- Shared neutral wires sa pagitan ng mga circuit
- Maluwag na koneksyon na lumilikha ng pasulput-sulpot na contact
- Pinaghalong luma at bagong verkada
- Hindi wastong neutral-ground bonding
- Mga Error sa Pag-install (20% ng mga kaso)
- Hindi tamang mga koneksyon ng neutral wire
- Multi-wire circuit incompatibility
- Maling uri ng breaker para sa aplikasyon
- Mga isyu sa pagiging tugma ng panel
- Mga Depekto sa Device (5% ng mga kaso)
- Mga depekto sa paggawa
- Pagkasira dahil sa edad
- Mga isyu sa firmware sa mga lumang smart breaker
Sistematikong Paraan ng Pag-troubleshoot
Hakbang 1: Idokumento ang Pattern
- Kailan nangyayari ang tripping? (oras ng araw, panahon, mga partikular na aktibidad)
- Anong mga device ang ginagamit kapag nangyayari ang mga trip?
- Gaano kadalas nangyayari ang tripping?
- Ito ba ay bagong installation o umiiral na circuit?
Hakbang 2: Ihiwalay ang Sanhi
- Tanggalin sa saksakan ang lahat ng device mula sa circuit
- I-reset ang AFCI breaker
- Ikabit muli ang mga device isa-isa
- Tukuyin kung aling device ang nagti-trigger ng trip
Hakbang 3: I-verify ang Installation
- Suriin ang mga koneksyon ng neutral wire (dapat nakalaan sa circuit na iyon)
- I-verify na walang shared neutrals sa ibang mga circuit
- Suriin ang lahat ng mga koneksyon para sa higpit
- Kumpirmahin ang tamang pag-install ng breaker
Hakbang 4: Subukan ang mga Solusyon
- Subukan ang device sa ibang circuit (kinukumpirma ang isyu sa device vs. wiring)
- Mag-update sa mas bagong modelo ng AFCI breaker
- Paghiwalayin ang mga hindi tugmang device sa iba't ibang circuit
- Isaalang-alang ang mga nakalaang circuit para sa mga problemadong kagamitan
Hakbang 5: Propesyonal na Ebalwasyon
- Kung magpatuloy ang problema, kumuha ng lisensyadong electrician
- Maaaring kailanganin ang circuit rewiring o pag-upgrade ng panel
- Maaaring mangailangan ng mga nakalaang neutral runs
- Maaaring makinabang mula sa smart breaker na may diagnostics
Madalas Na Tinatanong Na Mga Katanungan
Maaari ba akong mag-install ng mga GFCI at AFCI device sa aking sarili?
Bagama't ang mga GFCI outlet ay madalas na kayang ikabit ng mga may karanasan sa DIY na may wastong pag-iingat sa kaligtasan, ang mga AFCI circuit breaker at anumang gawain sa mga electrical panel ay dapat lamang isagawa ng mga lisensyadong electrician. Ang hindi wastong pagkakabit ay maaaring lumikha ng malubhang panganib sa kaligtasan, paglabag sa code, at pagpapawalang-bisa sa saklaw ng insurance. Bukod pa rito, maraming hurisdiksyon ang nangangailangan ng mga permit at inspeksyon para sa mga pagkakabit ng circuit breaker. Ang panganib ng pagkakuryente, sunog, o paglikha ng mga panganib na mas malala pa kaysa sa orihinal na problema ay ginagawang ang propesyonal na pagkakabit ang tanging ligtas na pagpipilian para sa gawain sa panel.
Kailangan ko ba ang parehong proteksyon ng GFCI at AFCI sa parehong circuit?
Oo, maraming lugar ngayon ang nangangailangan ng parehong uri ng proteksyon sa ilalim ng NEC 2023. Ang mga kusina, labahan, at mga espasyo sa basement ay karaniwang mga halimbawa kung saan mandatory ang parehong proteksyon. Ang pinaka-epektibong solusyon ay ang paggamit ng dual-function na GFCI/AFCI circuit breakers, na nagbibigay ng parehong proteksyon sa isang device. Bilang alternatibo, maaari kang mag-install ng mga GFCI receptacle sa mga circuit na protektado ng mga AFCI breaker, bagaman ito ay karaniwang mas mahal at mas kumplikado. Huwag ipagpalagay na ang isang uri ng proteksyon ay sumasaklaw sa parehong panganib—pinoprotektahan ng mga GFCI ang mga tao mula sa kuryente, habang pinoprotektahan ng mga AFCI ang ari-arian mula sa sunog.
Bakit ba trip ang aking AFCI breaker kapag gumagamit ako ng ilang appliances?
Ang mga AFCI breaker ay maaaring makaranas ng nuisance tripping sa ilang mga device na lumilikha ng mga electrical signature na katulad ng mga mapanganib na arko. Kabilang sa mga karaniwang sanhi ang mga vacuum cleaner na may universal motor, treadmill, fluorescent lights, mga lumang dimmer switch, at ilang power tools. Hindi ito nangangahulugan na ang iyong AFCI ay may depekto—sinusubukan ka nitong protektahan. Ang mga mas bagong combination AFCI breaker (pagkatapos ng 2014) ay may malaking pagbuti sa filtering upang mabawasan ang mga false trip habang pinapanatili ang kaligtasan. Kasama sa mga solusyon ang: pag-update sa mas bagong modelo ng AFCI, pag-install ng problemadong device sa isang nakalaang circuit, o pagkonsulta sa isang electrician upang i-verify ang tamang pag-install at wiring.
Gaano kadalas ko dapat subukan ang mga GFCI at AFCI device?
Subukan ang parehong GFCI at AFCI device buwan-buwan gamit ang kanilang built-in na test button. Tinitiyak nito na gumagana ang mga ito nang maayos at poprotektahan ka kapag kinakailangan. Ang buwanang pagsubok ay inirerekomenda ng mga manufacturer, mga organisasyon sa kaligtasan ng kuryente, at ang National Electrical Code. Bukod pa rito, subukan ang mga device pagkatapos ng mga electrical storm, pagkatapos ng anumang gawaing elektrikal sa iyong bahay, at bago gamitin ang mga outdoor outlet sa pana-panahon. Panatilihin ang isang testing log na may mga petsa at resulta. Kung ang anumang device ay nabigong subukan nang maayos (hindi magti-trip kapag pinindot ang TEST, o hindi magre-reset), palitan ito kaagad anuman ang edad.
Ano ang pagkakaiba sa pagitan ng mga GFCI outlet at GFCI circuit breaker?
Ang mga GFCI outlet ay nagpoprotekta lamang sa partikular na outlet kung saan naka-install ang mga ito kasama ang anumang mga outlet sa downstream (nakakonekta sa mga LOAD terminal), habang ang mga GFCI circuit breaker ay nagpoprotekta sa buong circuit mula sa electrical panel. Ang mga circuit breaker ay nag-aalok ng mas malawak na proteksyon at tamper-resistant dahil nasa panel ang mga ito, ngunit mas mahal ang mga ito ($45-75 vs. $15-30 para sa mga outlet) at nangangailangan ng propesyonal na pag-install. Ang mga GFCI outlet ay perpekto para sa point-of-use na proteksyon sa mga madaling puntahan na lokasyon, habang ang mga GFCI breaker ay mas mahusay para sa pagprotekta sa maraming outlet, mga hindi madaling puntahan na lokasyon, o mga hardwired appliance. Para sa komprehensibong proteksyon, maraming electrician ang gumagamit ng kombinasyong paraan.
Maaari ba akong gumamit ng mga extension cord na may proteksyon ng GFCI at AFCI?
Ang mga extension cord na GFCI at mga portable na GFCI device ay available at napakaganda para sa pansamantalang paggamit sa labas, mga construction site, o pagdaragdag ng proteksyon sa mga lumang bahay. Gayunpaman, ang mga permanenteng instalasyon ay dapat gumamit ng maayos na nakakabit na mga GFCI outlet o circuit breaker sa halip na umasa sa mga extension cord. Ang proteksyon ng AFCI ay karaniwang nangyayari sa antas ng circuit breaker, hindi sa pamamagitan ng mga extension cord, dahil ang teknolohiya ay nangangailangan ng pagsubaybay sa buong circuit mula sa panel. Huwag kailanman gumamit ng mga extension cord bilang permanenteng solusyon sa mga kable, at tiyakin na ang anumang GFCI extension cord ay na-rate para sa kanilang nilalayon na paggamit (panloob kumpara sa panlabas, amperage rating).
Gumagana ba ang mga GFCI at AFCI device sa panahon ng pagkawala ng kuryente?
Hindi, kailangan ng mga device na ito ng kuryente upang gumana. Sa panahon ng mga outage, hindi sila makapagbibigay ng proteksyon, ngunit awtomatiko nilang ipagpapatuloy ang proteksyon kapag naibalik ang kuryente. Ito ay isang mahalagang pagsasaalang-alang sa kaligtasan—kung gumagamit ka ng generator sa panahon ng outage, tiyakin na kasama sa iyong generator system ang tamang proteksyon ng GFCI para sa kaligtasan ng mga tao. Ang mga portable generator ay dapat may built-in na proteksyon ng GFCI o gumamit ng mga extension cord na protektado ng GFCI. Kapag bumalik ang kuryente pagkatapos ng outage, subukan ang iyong mga GFCI at AFCI device upang matiyak na gumagana ang mga ito nang maayos, dahil ang mga power surge sa panahon ng pagpapanumbalik ay maaaring paminsan-minsan na makapinsala sa mga electronic component.
Gaano katagal ang mga GFCI at AFCI device?
Ang mga de-kalidad na GFCI device ay karaniwang tumatagal ng 10-15 taon na may tamang pagpapanatili, habang ang mga AFCI device ay maaaring tumagal ng 10-20 taon. Gayunpaman, ang haba ng buhay ay nag-iiba batay sa paggamit, mga kondisyon ng kapaligiran, at kalidad. Ang mga device sa malupit na kapaligiran (panlabas, mataas na halumigmig, madalas na paggamit) ay maaaring mas maagang masira. Palitan ang anumang device na pumalya sa pagsubok o nagpapakita ng mga senyales ng pagkasira anuman ang edad. Maraming modernong device ang may kasamang mga self-test feature na awtomatikong nagbeberipika ng functionality, ngunit ang manu-manong buwanang pagsubok ay nananatiling mahalaga. Ang proactive na pagpapalit sa 10-15 taon ay inirerekomenda kahit na ang mga device ay gumagana pa rin nang maayos sa pagsubok, dahil ang mga panloob na bahagi ay nasisira sa paglipas ng panahon.
Ano ang dual-function breaker at kailan ko ito dapat gamitin?
Ang dual-function breaker ay pinagsasama ang parehong proteksyon ng GFCI at AFCI sa isang solong circuit breaker, na nakakatugon sa parehong mga kinakailangan ng NEC 210.8 (GFCI) at 210.12 (AFCI). Ang mga breaker na ito ay nagkakahalaga ng $50-85, bahagyang mas mahal lamang kaysa sa mga AFCI-only breaker ($45-75), na ginagawa itong lubos na cost-effective para sa mga circuit na nangangailangan ng parehong proteksyon. Gumamit ng mga dual-function breaker para sa mga kitchen circuit, laundry area, basement living space, at anumang lokasyon kung saan kinakailangan ang parehong shock at fire protection. Nakakatipid ang mga ito ng espasyo sa panel, pinapasimple ang pag-install, binabawasan ang pagiging kumplikado ng pag-troubleshoot, at tinitiyak ang komprehensibong proteksyon. Nagiging pamantayang pagpipilian ang mga ito para sa mga bagong construction at malalaking renovation.
Maaari bang maging sanhi ng pag-trip ng mga AFCI breaker ang lumang mga kable?
Oo, ang lumang wiring ay isang karaniwang sanhi ng AFCI nuisance tripping. Ang nasirang insulation, maluwag na koneksyon, oxidized terminal, at nasirang conductor ay maaaring lumikha ng mga electrical signature na binibigyang-kahulugan ng mga AFCI bilang mga mapanganib na arko. Bagama't maaaring mukhang nuisance tripping ito, sa katunayan ay nakikita ng AFCI ang mga tunay na problema sa iyong wiring na maaaring magdulot ng sunog sa kalaunan. Kung ang mga AFCI breaker ay madalas na nagti-trip sa mga lumang circuit, ipasuri ang wiring sa isang lisensyadong electrician. Maaaring kailanganin mo ang circuit rewiring, paghihigpit ng koneksyon, o pagpapalit ng outlet. Huwag i-disable ang proteksyon ng AFCI—tugunan ang mga pinagbabatayang isyu sa wiring upang makakuha ng parehong kaligtasan at pagiging maaasahan.
Konklusyon: Paggawa ng Tamang Pagpili para sa Kaligtasan sa Elektrisidad
Ang proteksyon ng GFCI at AFCI ay parehong mahahalagang bahagi ng mga modernong sistema ng kaligtasan ng kuryente, bawat isa ay tumutugon sa magkakaiba ngunit pantay na kritikal na mga panganib. Pinipigilan ng mga GFCI ang mga potensyal na nakamamatay na electrical shock sa pamamagitan ng pagtukoy ng mga ground fault sa loob ng milliseconds, habang pinipigilan ng mga AFCI ang mga sunog sa kuryente sa pamamagitan ng pagtukoy ng mga mapanganib na arcing condition bago pa man magliyab ang mga nakapaligid na materyales. Sama-sama, ang mga teknolohiyang ito ay maaaring maiwasan ang libu-libong pagkamatay, pinsala, at bilyun-bilyong halaga ng pinsala sa ari-arian taun-taon.
Ang pag-unawa sa kanilang mga pagkakaiba, tamang aplikasyon, at mga kinakailangan sa pag-install ay tinitiyak na ang iyong electrical system ay nakakatugon sa kasalukuyang mga pamantayan sa kaligtasan at nagbibigay ng maximum na proteksyon para sa iyong pamilya at ari-arian. Ang ebolusyon ng mga electrical code ay sumasalamin sa mga dekada ng pananaliksik at real-world na data na nagpapakita ng nakapagliligtas-buhay na halaga ng mga device na ito.
Mga Pangunahing Istratehiya sa Pagpapatupad:
- Unahin ang Kaligtasan ng Buhay – Mag-install muna ng proteksyon ng GFCI sa lahat ng kinakailangang basang lokasyon
- Tugunan ang Pag-iwas sa Sunog – Magdagdag ng proteksyon ng AFCI sa lahat ng living space at silid-tulugan
- Gumamit ng mga Dual-Function Breaker – Pinaka cost-effective para sa mga lugar na nangangailangan ng parehong proteksyon
- Subukan Buwan-buwan – Tinitiyak ng regular na pagsubok na gumagana ang mga device kapag kinakailangan
- Palitan nang Proaktibo – Huwag maghintay ng pagkasira; palitan ang mga device sa loob ng 10-15 taon
- Idokumento ang Lahat – Panatilihin ang mga testing log at mga talaan ng pag-install
- Manatiling Kasalukuyan – I-update ang mga lumang bahay upang matugunan ang kasalukuyang mga pamantayan sa kaligtasan
🏠 PANGHULING REKOMENDASYON: Kumonsulta sa isang lisensyadong electrician upang suriin ang iyong kasalukuyang electrical system at bumuo ng isang komprehensibong plano para sa proteksyon ng GFCI at AFCI na nakakatugon sa mga lokal na code at nagbibigay ng maximum na kaligtasan para sa iyong mga partikular na pangangailangan. Ang pamumuhunan na ito sa kaligtasan ng kuryente ay nagpoprotekta sa mga buhay, pinipigilan ang pinsala sa ari-arian, maaaring magpababa ng mga gastos sa insurance, at nagpapataas ng halaga ng bahay.
Para sa mga kumplikadong gawaing elektrikal, renovation, o kapag may pagdududa tungkol sa mga kinakailangan ng code, palaging kumuha ng mga kwalipikadong propesyonal upang matiyak ang ligtas at sumusunod na mga pag-install na nagpoprotekta sa mga buhay at ari-arian sa loob ng mga dekada.
Mga Kaugnay na Mapagkukunan:
- Alamin ang tungkol sa mga uri at aplikasyon ng circuit breaker
- Unawain kung paano i-reset ang isang circuit breaker nang ligtas
- Galugarin mga rating ng circuit breaker para sa tamang pagpili
- Tuklasin Mga pagkakaiba ng RCBO vs AFDD para sa mga internasyonal na aplikasyon
- Repasuhin standard breaker sizes para sa iyong tahanan


