Dalam dunia distribusi daya listrik, isolator busbar memainkan peran penting namun sering diabaikan dalam memastikan keamanan, efisiensi, dan keandalan. Baik Anda seorang insinyur listrik, kontraktor, atau manajer fasilitas, memahami isolator busbar sangat penting untuk mempertahankan sistem kelistrikan yang optimal. Panduan komprehensif ini membahas semua yang perlu Anda ketahui tentang komponen vital ini.
Apa Itu Isolator Busbar?
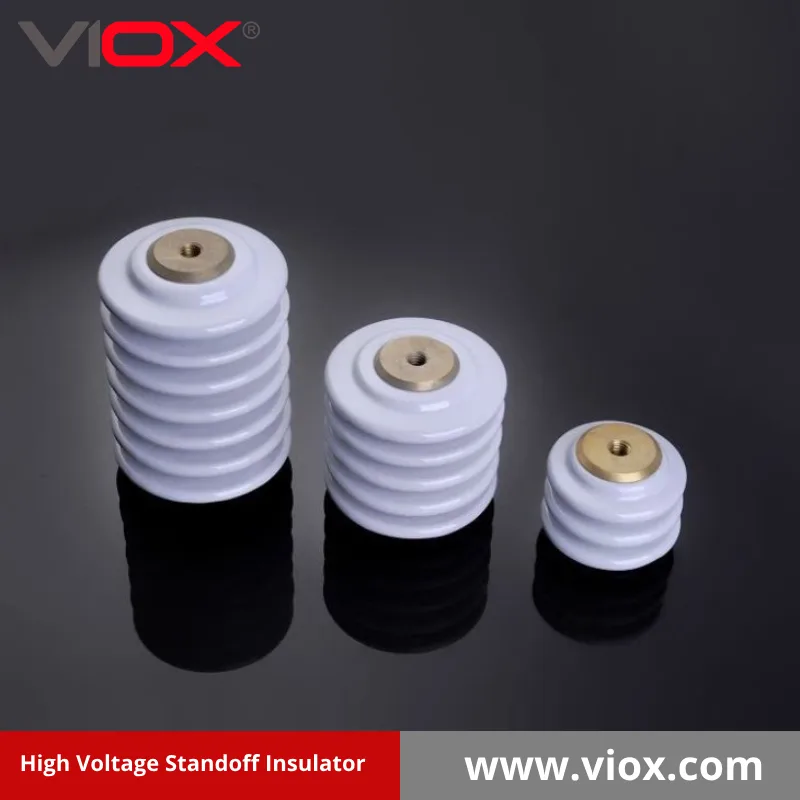
Isolator busbar adalah komponen khusus yang dirancang untuk mengisolasi busbar secara elektrik (konduktor logam yang digunakan untuk distribusi daya) dari sekelilingnya sambil memberikan dukungan mekanis. Busbar adalah strip atau batang konduktif yang terbuat dari bahan seperti tembaga atau aluminium yang mengalirkan listrik di switchgear, papan panel, dan selungkup busway. Tanpa isolasi yang tepat, konduktor arus tinggi ini akan menimbulkan risiko keselamatan yang serius, termasuk sengatan listrik, korsleting, dan kegagalan sistem yang dahsyat.
Biasanya, isolator busbar berbentuk seperti silinder atau kerucut dan dapat mencakup fitur seperti flensa atau braket pemasangan untuk dipasang pada struktur pendukung. Desainnya bervariasi berdasarkan aplikasi spesifik, persyaratan voltase, dan kondisi lingkungan.
Fungsi Penting dari Isolator Busbar
Isolator busbar memiliki beberapa tujuan penting dalam sistem distribusi listrik:
1. Isolasi Listrik
Isolator busbar mencegah aliran arus yang tidak diinginkan antara busbar dan struktur yang diarde, sehingga meminimalkan risiko korsleting dan kebakaran listrik. Isolasi ini sangat penting untuk keamanan listrik dalam sistem distribusi daya. Fungsi utama isolator busbar adalah untuk mengisolasi busbar dari struktur pendukungnya, sehingga mencegah arus mengalir di sepanjang jalur yang tidak diinginkan. Hal ini sangat penting dalam aplikasi tegangan tinggi di mana risiko lengkung dan korsleting tinggi.
2. Dukungan Mekanis
Mereka dengan aman menahan busbar di tempatnya, menahan tekanan mekanis dari getaran, ekspansi termal, dan beban berat untuk menjaga integritas dan keselarasan struktural. Fungsi dukungan ini sangat penting untuk stabilitas seluruh sistem kelistrikan. Seperti yang dicatat dalam diskusi teknik, "Isolator busbar membantu menahan konduktor pada tempatnya dan mencegah pergerakan yang berlebihan," yang sangat penting untuk menjaga integritas sistem selama operasi normal dan terutama selama kondisi gangguan.
3. Perlindungan Lingkungan
Isolator busbar melindungi konduktor dari faktor lingkungan yang dapat mengganggu kinerjanya. Mereka melindungi busbar dari kelembaban, debu, radiasi UV, dan paparan bahan kimia, mencegah korosi dan degradasi dari waktu ke waktu. Perlindungan lingkungan ini memperpanjang masa operasional seluruh sistem kelistrikan, terutama di instalasi luar ruangan atau lingkungan industri yang keras.
4. Pengurangan Kebisingan
Dengan meredam getaran elektromagnetik, isolator membantu mengurangi dengungan dan dengungan yang terdengar pada peralatan listrik, yang berkontribusi pada pengoperasian sistem listrik yang lebih tenang. Pengurangan kebisingan ini bukan hanya tentang kenyamanan - ini menunjukkan bahwa energi terkandung dengan baik di dalam sistem daripada hilang melalui getaran, yang dapat menyebabkan kegagalan komponen dini.
Jenis-jenis Isolator Busbar
Memahami berbagai jenis isolator busbar dapat membantu Anda memilih opsi yang paling tepat untuk aplikasi spesifik Anda:
Berdasarkan Fungsi
1. Insulator Pendukung
Isolator pendukung dirancang untuk menahan busbar pada tempatnya dan menyediakan isolasi listrik. Mereka biasanya digunakan dalam switchgear dan sistem distribusi. Isolator ini memastikan busbar tetap stabil di bawah tekanan mekanis sekaligus mencegah kebocoran listrik, menjadikannya penting untuk operasi yang aman. Isolator pendukung adalah jenis yang paling umum, yang dirancang untuk memberikan dukungan mekanis untuk busbar dengan tetap menjaga isolasi listrik. Mereka biasanya digunakan dalam rakitan switchgear dan rakitan roda gigi kontrol, di mana mereka mempertahankan posisi busbar sambil memastikan mereka tetap terisolasi secara elektrik dari selungkup dan komponen lainnya.
2. Isolator Kebuntuan
Isolator penyekat biasanya berbentuk silinder atau kerucut dan memastikan jarak yang konsisten antara busbar dan permukaan pemasangan untuk memberikan isolasi udara yang tepat dan mencegah kontak yang tidak disengaja. Isolator ini menjaga jarak tetap antara elemen konduktif dan permukaan yang diarde, sehingga memungkinkan jarak bebas listrik yang tepat. Desainnya memprioritaskan isolasi listrik dan kekuatan mekanis, menjadikannya ideal untuk aplikasi di mana busbar harus dipasang dengan aman sambil mempertahankan jarak bebas listrik yang tepat dari struktur pendukung.
3. Isolator Suspensi
Insulator suspensi menggantung secara vertikal, menopang busbar tegangan tinggi sambil mempertahankan isolasi listrik. Mereka sangat penting dalam sistem overhead. Isolator ini mengurangi beban mekanis dan memberikan fleksibilitas, sehingga ideal untuk transmisi jarak jauh. Isolator suspensi digunakan untuk mendukung saluran transmisi overhead, memastikan bahwa saluran tetap tinggi dan terisolasi dari tanah atau struktur lainnya. Mereka memainkan peran penting dalam menjaga integritas transmisi daya jarak jauh.
4. Isolator Regangan
Insulator regangan dirancang untuk menangani tegangan mekanis, mendukung busbar di lingkungan dengan tekanan tinggi seperti sudut dan kurva dalam sistem daya. Kemampuan uniknya untuk menahan tegangan memastikan integritas struktural dalam pengaturan yang berat. Dirancang untuk menangani tekanan mekanis yang tinggi, isolator ini digunakan dalam situasi yang melibatkan bentang panjang saluran transmisi atau pada titik-titik di mana arah saluran berubah secara signifikan. Kemampuannya untuk menahan tegangan memastikan stabilitas sistem secara keseluruhan, terutama dalam aplikasi yang tunduk pada kekuatan fisik atau tekanan lingkungan.
5. Isolator Bushing
Isolator bushing memungkinkan konduktor melewati penghalang yang diarde, seperti tangki transformator atau selubung pemutus sirkuit, dengan tetap mempertahankan isolasi yang efektif. Mereka sangat penting untuk mencegah gangguan listrik dan memastikan operasi yang aman dalam sistem tertutup.
Berdasarkan Bahan
1. Isolator Porselen
Isolator porselen telah menjadi pilihan tepercaya selama beberapa dekade karena sifat insulasi dan kekuatan mekaniknya yang sangat baik. Porselen sering digunakan dalam aplikasi luar ruangan di mana umur panjang dan keandalan sangat penting. Mereka dikenal karena daya tahan dan ketahanan suhu tinggi. Porselen menawarkan daya tahan tinggi dan tahan cuaca, membuatnya ideal untuk aplikasi luar ruangan. Bahan tradisional ini telah dipercaya selama beberapa dekade karena sifat listriknya yang sangat baik dan stabilitas jangka panjang, meskipun cenderung lebih rapuh daripada alternatif modern.
2. Isolator Keramik
Isolator busbar keramik dikenal karena ketahanannya yang tinggi dan stabilitas termal. Mereka cocok untuk digunakan di lingkungan bersuhu tinggi dan mampu menahan tekanan listrik yang terkait dengan sistem tegangan tinggi.
3. Insulator Komposit Polimer
Isolator polimer komposit ringan dan serbaguna, sehingga cocok untuk berbagai aplikasi modern. Ini ideal untuk proyek yang membutuhkan efisiensi anggaran tanpa mengorbankan kualitas. Mereka menawarkan sifat listrik yang sangat baik dan ideal untuk instalasi di mana berat menjadi perhatian. Isolator polimer memiliki keunggulan karena ringan, tahan terhadap faktor lingkungan, dan mudah dipasang. Isolator ini biasanya digunakan dalam aplikasi luar ruangan di mana paparan kelembaban, radiasi UV, dan elemen lainnya menjadi perhatian.
4. Insulator Kaca
Isolator kaca memberikan visibilitas yang jelas pada busbar dan secara estetika menyenangkan. Mereka menawarkan insulasi moderat dan paling cocok untuk instalasi yang terlihat di mana penampilan penting.
5. Insulator Epoksi dan BMC
Resin epoksi memberikan insulasi listrik terbaik, kekuatan mekanis, dan dapat menahan elemen lingkungan seperti kelembaban dan panas. Epoksi sering digunakan untuk melapisi atau membungkus busbar, memberikan insulasi yang kuat terhadap arus listrik dan faktor lingkungan.
Bulk Molding Compound (BMC) adalah material komposit yang terbuat dari resin termoseting yang diperkuat dengan serat kaca, yang menawarkan karakteristik listrik dan mekanik yang luar biasa. Bahan-bahan ini sangat berharga dalam aplikasi khusus berkinerja tinggi di mana bahan tradisional mungkin tidak memenuhi persyaratan.
Spesifikasi Tegangan: Isolator Tegangan Rendah vs Tegangan Tinggi
Isolator Busbar Tegangan Rendah (660V-4500V)
Busbar tegangan rendah isolator biasanya beroperasi pada kisaran 660V hingga 4500V. Mereka biasanya dibuat dari bahan seperti BMC (Bulk Molding Compound) atau SMC (Sheet Molding Compound), yang menawarkan ketahanan listrik yang sangat baik dan toleransi panas hingga 140 ° C.
Isolator ini sering kali memiliki sisipan kuningan atau baja berlapis seng dan dapat menahan kekuatan tarik hingga 1500 LBS. Mereka umumnya lebih kecil dan lebih sederhana dalam desain dibandingkan dengan rekan-rekan tegangan tinggi mereka, yang mencerminkan aplikasi mereka di lingkungan listrik yang tidak terlalu menuntut.
Isolator Busbar Tegangan Tinggi (Melebihi 100kV)
Isolator tegangan tinggi dirancang untuk sistem yang melebihi 100kV. Komponen ini dibuat dari bahan yang lebih kuat seperti keramik, kaca, atau komposit canggih untuk menangani tekanan listrik yang ekstrem dan faktor lingkungan.
Mereka dirancang dengan beberapa cakram atau gudang untuk meningkatkan luas permukaan dan mencegah lengkung listrik, pertimbangan penting dalam aplikasi tegangan tinggi di mana ionisasi udara dan kebocoran permukaan merupakan masalah yang signifikan.
Perbedaan Utama dalam Desain dan Bahan
Sementara isolator tegangan rendah biasanya lebih kecil dan lebih sederhana dalam desain, isolator tegangan tinggi dibuat untuk daya tahan dalam kondisi cuaca yang keras, dengan ketahanan yang lebih baik terhadap kerusakan akibat sinar UV dan kelembaban. Pedoman desain tipikal adalah memiliki insulasi kaku tegangan 1mm per kV di antara konduktor, yang dapat dicapai dengan menambahkan isolator kaku yang tebal (1-6mm).
Aplikasi tegangan tinggi sering kali memerlukan pertimbangan khusus untuk distribusi medan listrik, dengan penelitian terbaru yang berfokus pada analisis medan listrik celah udara yang dipasang di busbar-insulator berdasarkan pemodelan parametrik tiga dimensi.
Metode Isolasi untuk Busbar
Ada beberapa pendekatan untuk mengisolasi busbar, masing-masing dengan kelebihannya sendiri:
1. Insulasi Udara (AIS)
Sistem berinsulasi udara menggunakan busbar berlapis listrik yang memerangkap udara isolasi menggunakan busbar pendukung atau penyangga busbar. Ini adalah salah satu metode isolasi yang paling tradisional.
2. Berinsulasi Padat (SIS)
Dalam sistem Berinsulasi Padat, busbar dilapisi dengan bahan isolasi termoseting atau termoplastik untuk memberikan perlindungan yang lebih kuat.
3. Insulasi Penyusutan Panas
Busbar penyusutan panas memiliki lapisan insulasi sementara dari poliolefin, BPTM, BBIT, dll. Busbar ini tahan pelacakan dan dapat berfungsi pada suhu tinggi, sekitar -55 ° C hingga 200 ° C. Mereka memiliki peringkat mudah terbakar UL 94 V0 dan kompatibel dengan aplikasi tegangan tinggi, mulai dari 600V hingga 35kV.
4. Lapisan Epoksi
Lapisan epoksi bersifat kimiawi dan tahan panas. Lapisan ini tersedia dengan peringkat UL 130°C. Selain itu, pelapis ini memiliki peringkat isolasi yang tinggi sekitar 800 volt per mil dengan minimum 10 mil. Lapisan serbuk epoksi dapat meningkatkan kekuatan tarik permukaan hingga 7500 psi.
5. Pelapisan Bubuk
Lapisan serbuk menawarkan kekuatan dan daya tahan dielektrik yang tinggi pada busbar. Anda dapat mengontrol ketebalan lapisan dalam kisaran 6 hingga 120 mil. Dalam teknik unggun terfluidisasi, serbuk mengapung di unggun terfluidisasi, dan konduktor busbar diturunkan. Proses ini menciptakan lapisan yang halus, kontinu, dan tahan lama.
6. Cetakan Injeksi dan Ekstrusi
Untuk produksi dalam jumlah besar, insulasi cetakan injeksi adalah pilihan yang paling hemat biaya dan hemat waktu. Prosesnya melibatkan pemanasan bahan insulasi, menyuntikkan lelehan ke dalam cetakan negatif, memberikan waktu pendinginan, dan kemudian melepas batang insulasi.
Teknik ekstrusi juga dapat digunakan untuk mengisolasi busbar dengan melelehkan butiran plastik atau karet menjadi campuran yang homogen, misalnya, butiran PVC dan TPE, dan kemudian mengaplikasikan bahan insulasi ke batang. Insulasi busbar yang dapat memadamkan sendiri dan tahan migrasi dengan peringkat mudah terbakar UL 94 V0 dapat dicapai melalui teknik ini.
Aplikasi Isolator Busbar
Isolator busbar digunakan dalam berbagai aplikasi di berbagai industri:
1. Switchgear Kelistrikan dan Perlengkapan Kontrol
Isolator busbar digunakan secara luas dalam instalasi switchgear, di mana mereka secara fisik memisahkan dan mendukung komponen konduktif untuk menghindari korsleting dan memastikan keselamatan operasional. Demikian pula, dalam rakitan roda gigi kontrol, mereka berkontribusi pada manajemen arus listrik yang tepat, meningkatkan keandalan sistem.
2. Sistem Distribusi Daya
Lemari distribusi daya dan panel listrik mengandalkan isolator busbar untuk mengatur dan mengisolasi bagian konduktif, meminimalkan risiko kontak yang tidak disengaja atau kegagalan sistem. Lemari ini merupakan bagian penting dari infrastruktur distribusi daya dalam instalasi komersial, industri, dan skala utilitas.
Di pembangkit listrik dan gardu induk, isolator busbar memainkan peran penting dalam memastikan distribusi daya listrik yang aman dan efisien.
3. Aplikasi Industri
Dalam pengaturan industri, isolator busbar adalah komponen penting dalam pusat kendali motor, sistem penggerak frekuensi variabel, dan unit distribusi daya. Mereka memastikan operasi yang aman dari sistem kelistrikan arus tinggi sambil memberikan dukungan mekanis yang diperlukan dalam lingkungan industri yang menuntut.
Panel kontrol mendapat manfaat dari busbar berinsulasi dengan benar yang memungkinkan desain yang ringkas dengan tetap mempertahankan standar keamanan listrik. Hal ini sangat penting terutama di fasilitas yang memiliki keterbatasan ruang yang harus diseimbangkan dengan persyaratan kinerja listrik.
4. Sistem Energi Terbarukan
Isolator busbar memiliki berbagai aplikasi di seluruh industri, termasuk sistem energi terbarukan seperti pembangkit listrik tenaga surya dan instalasi tenaga angin. Ketika sistem energi terbarukan menjadi lebih umum, isolator busbar memainkan peran yang semakin penting dalam inverter surya, konverter tenaga angin, dan sistem penyimpanan energi. Aplikasi ini sering kali melibatkan berbagai profil beban dan kondisi lingkungan yang membutuhkan kinerja insulasi yang andal.
5. Infrastruktur Transportasi
Dalam sistem kereta api dan stasiun pengisian kendaraan listrik, isolator busbar membantu menjaga distribusi daya yang aman dan andal.
6. Pagar Listrik dan Penggunaan Khusus
Dalam sistem pagar listrik, isolator busbar memainkan peran penting dengan memisahkan komponen baja secara elektrik - seperti dudukan kotak kejut - dari kotak kejut. Pemisahan ini sangat penting untuk menjaga integritas sirkuit listrik dan memastikan bahwa sistem pagar beroperasi secara efisien tanpa kehilangan energi yang tidak disengaja atau bahaya keselamatan.
Aplikasi khusus lainnya termasuk sistem elektrifikasi kereta api, distribusi daya pusat data, dan sistem kelistrikan kelautan, masing-masing dengan persyaratan unik untuk kinerja insulasi dan stabilitas mekanis.
Praktik Terbaik Pemasangan untuk Isolator Busbar
Pertimbangan Keamanan Selama Pemasangan
Saat memasang isolator busbar, keamanan dan presisi adalah yang terpenting. Mulailah dengan mematikan sistem dan melakukan pemeriksaan menyeluruh terhadap semua komponen. Gunakan alat pelindung diri selama proses pemasangan untuk meminimalkan risiko cedera.
Pastikan torsi yang tepat saat mengencangkan baut dan sambungan, karena pengencangan yang kurang atau berlebihan dapat mengganggu integritas pemasangan. Pastikan resistensi pengardean kurang dari 0,1Ω untuk seluruh rakitan sebelum menjalankan sistem.
Teknik Pemasangan yang Tepat
Bersihkan area pemasangan dan posisikan isolator sesuai dengan spesifikasi produsen, pastikan keselarasan yang tepat dengan busbar. Kencangkan isolator dengan aman menggunakan perangkat keras yang sesuai, biasanya sekrup pendek untuk pemasangan ke braket dinding.
Untuk pemasangan vertikal, gunakan braket dan penyangga khusus untuk menjamin kestabilan. Selalu patuhi kode dan standar kelistrikan setempat selama proses pemasangan untuk memastikan kepatuhan dan keamanan.
Memastikan Jarak Bebas dan Spasi yang Memadai
Pertahankan jarak bebas minimum antara busbar dan struktur di sekitarnya untuk memungkinkan pembuangan panas dan mencegah masalah kelistrikan. Hal ini sangat penting dalam aplikasi arus tinggi di mana manajemen termal menjadi perhatian penting.
Pada pemasangan di bawah tanah, gunakan penyangga yang kokoh dan jaga jarak tertentu dari dinding dan langit-langit. Untuk aplikasi di luar ruangan, pertimbangkan isolator dengan lapisan pelindung atau bahan yang tahan terhadap faktor lingkungan seperti radiasi UV, kelembapan, dan fluktuasi suhu.
Pemeliharaan dan Umur Panjang Isolator Busbar
Protokol Inspeksi Reguler
Perawatan isolator busbar yang tepat sangat penting untuk memastikan umur panjang dan kinerja yang optimal. Inspeksi dan pembersihan rutin sangat penting, dengan interval yang disarankan tiga hingga enam bulan, atau lebih sering di lingkungan yang keras.
Pemeriksaan visual harus memeriksa tanda-tanda kerusakan, perubahan warna, atau korosi. Setelah pemasangan, lakukan uji resistensi isolasi untuk memverifikasi integritas sistem, dengan target nilai resistensi minimal 20MΩ per bagian.
Masalah Umum dan Pemecahan Masalah
Pemantauan suhu sangat penting, karena kinerja isolator menurun secara signifikan dengan meningkatnya suhu. Kenaikan 10°C dapat mengurangi resistansi isolasi sebesar 32,9%. Untuk memperpanjang masa pakai, gunakan termometer inframerah untuk memantau suhu, terutama pada sistem arus tinggi.
Penelitian terbaru telah mengidentifikasi gangguan pelepasan pada switchgear berinsulasi gas tegangan tinggi sebagai area yang perlu diperhatikan, menekankan pentingnya pemilihan dan pemeliharaan isolator yang tepat untuk mencegah kegagalan tersebut.
Memperpanjang Masa Pakai Melalui Perawatan yang Tepat
Pembersihan harus dilakukan dengan menggunakan metode dan pelarut yang disetujui untuk menghilangkan debu dan serpihan tanpa merusak isolator atau komponen di sekitarnya. Simpan catatan perawatan yang terperinci dan berikan pelatihan rutin bagi personel untuk memastikan penanganan yang tepat dan prosedur tanggap darurat.
Praktik-praktik ini berkontribusi pada umur panjang dan keandalan sistem dengan mengurangi keausan pada busbar dan komponen lainnya, yang pada akhirnya menurunkan biaya perawatan dan meminimalkan kegagalan yang tidak terduga.
Manfaat Menggunakan Busbar Berinsulasi
Menggabungkan insulasi yang tepat untuk busbar menawarkan banyak keuntungan:
1. Keamanan yang Ditingkatkan
Peran utama isolator adalah mengisolasi elemen listrik dan busbar. Oleh karena itu, Anda dapat menghindari kecelakaan yang tidak diinginkan seperti sengatan listrik dan korsleting. Busbar berinsulasi menawarkan keandalan dengan mengurangi kemungkinan terjadinya flashover dan korsleting yang menyebabkan kerusakan pada peralatan dan menyebabkan pemadaman yang mahal.
2. Peningkatan Efisiensi Sistem
Desainer dapat meningkatkan desain dan efisiensi busbar dengan memperkenalkan isolasi. Misalnya, batang berinsulasi dapat mengurangi radius belokan dan meminimalkan jejak sirkuit. Ini juga dapat menghilangkan masalah jarak bebas dan rambat. Dengan demikian, busbar berinsulasi dapat menawarkan lebih banyak watt dan muat di ruang yang lebih sempit.
3. Perlindungan Lingkungan
Busbar berinsulasi memberikan perlindungan konduktor di fasilitas industri dengan bahan jejak dalam jumlah besar seperti minyak, serbuk gergaji, kelembapan, dan bahan kaustik.
4. Sifat Tahan Api
Insulasi terbuat dari bahan tahan api dan bahan yang dapat memadamkan sendiri. Oleh karena itu, busbar berinsulasi tetap aman dalam bahaya kebakaran apa pun.
5. Umur Komponen yang Diperpanjang
Insulasi dapat melindungi busbar dari keausan dan korosi, sehingga memperpanjang umur operasional seluruh sistem.
Bagaimana Memilih Isolator Busbar yang Tepat untuk Aplikasi Anda
Faktor Utama yang Perlu Dipertimbangkan
Memilih isolator busbar yang tepat sangat penting untuk memastikan keamanan dan efisiensi sistem kelistrikan. Pertimbangkan peringkat tegangan terlebih dahulu - pilih isolator dengan tegangan pengenal yang tidak kurang dari tegangan pengenal sistem busbar untuk memastikan insulasi yang andal dan mencegah kerusakan.
Kondisi lingkungan juga memainkan peran utama. Faktor-faktor seperti fluktuasi suhu, kelembapan, dan paparan terhadap kontaminan akan memengaruhi pilihan Anda. Untuk lingkungan yang keras, komposit polimer menawarkan ketahanan yang sangat baik terhadap polusi dan kelembapan.
Mencocokkan Isolator dengan Persyaratan Khusus
Kekuatan mekanis harus dievaluasi berdasarkan kemampuan isolator untuk menahan beban statis dan dinamis, serta tekanan termal. Isolator porselen ideal untuk aplikasi yang membutuhkan kekuatan mekanik tinggi, sementara jenis polimer menawarkan keuntungan dalam aplikasi yang mengutamakan bobot dan ketahanan lingkungan.
Ukuran dan jarak bebas merupakan pertimbangan penting - pastikan jarak bebas dan jarak rambat yang tepat untuk mencegah lengkung listrik dan menjaga integritas isolasi. Hal ini menjadi sangat penting dalam instalasi yang ringkas di mana keterbatasan ruang harus diseimbangkan dengan persyaratan keselamatan.
Perbandingan Jenis Isolator Busbar yang Berbeda
Tabel di bawah ini memberikan perbandingan komprehensif tentang jenis isolator busbar yang paling umum untuk membantu Anda memilih opsi yang tepat untuk kebutuhan spesifik Anda:
| Fitur | Isolator Porselen | Isolator Polimer/Komposit | Isolator Kaca | Isolator Keramik | Insulator Epoksi |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Komposisi Bahan | Tanah liat, kuarsa, feldspar | Karet silikon, EPDM, inti fiberglass | Kaca yang dikeraskan | Alumina, silikon karbida | Resin epoksi, fiberglass |
| Rentang Tegangan | 600V-765kV | 600V-1100kV | 600V-400kV | 600V-500kV | 600V-35kV |
| Kekuatan Mekanis | Tinggi | Sedang hingga Tinggi | Sedang | Sangat Tinggi | Sedang |
| Berat | Berat | Ringan | Sedang | Berat | Sedang |
| Aplikasi Utama | Gardu induk luar ruangan, sistem tegangan tinggi | Daerah rawan polusi, daerah pesisir | Sistem distribusi, instalasi yang terlihat | Lingkungan bersuhu tinggi | Switchgear dalam ruangan, sistem tertutup |
| Tahan Suhu | Sangat baik (hingga 1000°C) | Baik (hingga 250°C) | Baik (hingga 400°C) | Sangat baik (hingga 1500°C) | Baik (hingga 130°C) |
| Tahan UV | Luar biasa | Cukup hingga Baik (perlu tambahan) | Luar biasa | Luar biasa | Adil (perlu tambahan) |
| Ketahanan terhadap Polusi | Adil | Luar biasa | Bagus. | Bagus. | Bagus. |
| Tahan terhadap kelembapan | Bagus. | Luar biasa | Bagus. | Bagus. | Cukup hingga Baik |
| Resistensi Dampak | Buruk (rapuh) | Luar biasa | Buruk (rapuh) | Adil | Bagus. |
| Kemudahan Instalasi | Sulit (berat) | Mudah (ringan) | Sedang | Sulit (berat) | Mudah |
| Persyaratan Perawatan | Rendah | Sangat Rendah | Rendah | Rendah | Rendah |
| Biaya Relatif | Sedang | Biaya awal yang tinggi, biaya seumur hidup yang lebih rendah | Sedang hingga Tinggi | Tinggi | Rendah hingga Sedang |
| Kehidupan Pelayanan | 40+ tahun | 25-30 tahun | 40+ tahun | 40+ tahun | 20-25 tahun |
| Dampak Lingkungan | Rendah (dapat didaur ulang) | Sedang (tidak mudah didaur ulang) | Rendah (dapat didaur ulang) | Rendah (dapat didaur ulang) | Sedang (tidak mudah didaur ulang) |
Perbandingan ini menyoroti kekuatan dan keterbatasan masing-masing jenis isolator. Sebagai contoh, sementara isolator porselen menawarkan sifat listrik yang sangat baik dan umur yang panjang, isolator polimer memberikan kinerja polusi yang unggul dan lebih mudah dipasang karena bobotnya yang lebih ringan. Persyaratan aplikasi spesifik Anda harus memandu proses pemilihan Anda.
Pertimbangan Pemilihan Bahan
Bahan yang berbeda menawarkan tingkat isolasi, daya tahan, dan ketahanan yang berbeda-beda terhadap faktor lingkungan:
- Porselen: Insulasi yang sangat baik, cocok untuk aplikasi tegangan tinggi, tahan terhadap UV dan pelapukan
- Polimer: Insulasi yang baik dengan fleksibilitas dalam desain, rentan terhadap degradasi UV dari waktu ke waktu
- Kaca: Insulasi sedang, terbaik untuk instalasi yang terlihat, rentan terhadap kerusakan tetapi tahan terhadap paparan bahan kimia
Kepatuhan terhadap Sertifikasi dan Standar
Verifikasi bahwa isolator mematuhi standar industri yang relevan seperti IEC, ANSI, atau CE untuk memastikan keamanan dan keandalan. Sertifikasi ini memberikan jaminan bahwa komponen memenuhi kriteria kinerja dan keselamatan yang ditetapkan.
Pertimbangan Biaya vs Kinerja
Meskipun biaya awal selalu menjadi pertimbangan, kinerja jangka panjang dan persyaratan pemeliharaan isolator busbar harus dipertimbangkan dengan cermat. Isolator yang sedikit lebih mahal yang menawarkan daya tahan atau ketahanan lingkungan yang lebih baik mungkin terbukti lebih ekonomis selama masa pakai sistem.
Peran Isolator Busbar yang Terus Berkembang dalam Sistem Kelistrikan Modern
Isolator busbar tetap menjadi komponen penting dalam distribusi daya listrik, menyediakan fungsi penting isolasi listrik dan dukungan mekanis yang memastikan keamanan dan keandalan sistem. Karena sistem kelistrikan terus berkembang dengan kepadatan daya yang lebih tinggi, integrasi energi terbarukan, dan teknologi jaringan yang lebih cerdas, pentingnya komponen khusus ini semakin meningkat.
Pasar isolator busbar mengalami pertumbuhan yang stabil, didorong oleh meningkatnya permintaan akan sistem distribusi daya yang andal di berbagai industri. Baik dalam infrastruktur daya tradisional, aplikasi industri, atau teknologi yang muncul seperti kendaraan listrik dan sistem energi terbarukan, isolator busbar yang dipilih dan dipelihara dengan benar sangat penting untuk kinerja sistem kelistrikan.
Kesimpulan
Isolator busbar adalah komponen penting dalam sistem distribusi tenaga listrik, yang menyediakan isolasi listrik dan dukungan mekanis untuk busbar. Dengan memahami berbagai jenis, bahan, dan aplikasi isolator busbar, Anda dapat membuat keputusan yang tepat yang meningkatkan keamanan, keandalan, dan efisiensi instalasi listrik Anda.
Apakah Anda sedang merancang sistem kelistrikan baru atau meningkatkan sistem yang sudah ada, memilih isolator busbar yang tepat dapat membuat perbedaan yang signifikan dalam kinerja keseluruhan dan umur panjang infrastruktur distribusi daya Anda.
Tanya Jawab Tentang Isolator Busbar
Apa perbedaan antara busbar dan isolator busbar?
Busbar adalah konduktor logam yang digunakan untuk distribusi daya, sedangkan isolator busbar adalah komponen yang secara elektrik mengisolasi dan secara mekanis menopang busbar.
Bagaimana cara mengetahui apakah isolator busbar saya perlu diganti?
Tanda-tanda bahwa isolator mungkin perlu diganti termasuk retakan atau kerusakan yang terlihat, perubahan warna, tanda pelacakan, atau masalah operasional seperti sering tersandung atau kebisingan yang tidak biasa.
Dapatkah isolator busbar digunakan di luar ruangan?
Ya, beberapa jenis isolator busbar tertentu, terutama yang terbuat dari porselen atau polimer tahan UV, dirancang untuk penggunaan di luar ruangan dan dapat menahan paparan lingkungan.
Standar apa yang mengatur kualitas isolator busbar?
Standar utama termasuk IEC 60137, ANSI C29, dan berbagai sertifikasi regional yang memastikan isolator memenuhi persyaratan keselamatan dan kinerja.
Apakah ada opsi ramah lingkungan untuk isolator busbar?
Ya, banyak produsen sekarang menawarkan opsi isolator ramah lingkungan yang terbuat dari bahan yang berkelanjutan atau dirancang untuk dapat didaur ulang di akhir masa pakainya.
Berapa kisaran tegangan tipikal untuk isolator busbar tegangan rendah?
Isolator busbar tegangan rendah biasanya beroperasi dalam kisaran 660V hingga 4500V.
Bagaimana suhu memengaruhi kinerja isolator busbar?
Temperatur secara signifikan memengaruhi kinerja isolator. Peningkatan 10°C dapat mengurangi resistansi isolasi sekitar 32,9%, sehingga pemantauan suhu sangat penting dalam sistem arus tinggi.
Blog Terkait
Panduan Pemilihan Isolator Busbar
5 Kegagalan Isolator Busbar yang Umum Terjadi dan Cara Mencegahnya
Analisis Komprehensif Isolator Busbar Tegangan Rendah dalam Sistem Kelistrikan Modern