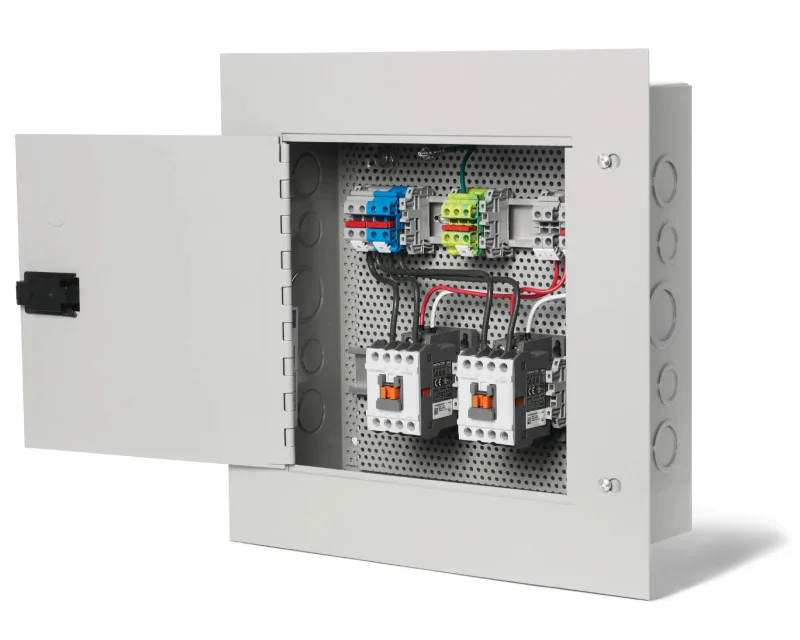
A alacsony feszültségű panel egy olyan elektromos elosztótábla, amely az elektromos áramot kezeli és osztja el, jellemzően 1000 volt AC vagy 1500 volt DC alatti feszültségen. Ezek a panelek központi vezérlőpontként szolgálnak, amelyek biztonságosan elosztják az áramot a fő áramforrásokból a különböző áramkörökhöz, terhelésekhez és berendezésekhez lakó-, kereskedelmi és ipari létesítményekben.
A kisfeszültségű panelek alapvető biztonsági alkatrészek, amelyek megszakítókon, biztosítékokon és felügyeleti eszközökön keresztül védik az elektromos rendszereket, miközben szervezett áramelosztást biztosítanak a világításhoz, a konnektorokhoz, a HVAC-rendszerekhez és más elektromos berendezésekhez.
Miben különböznek az alacsony feszültségű panelek a nagyfeszültségű panelektől?
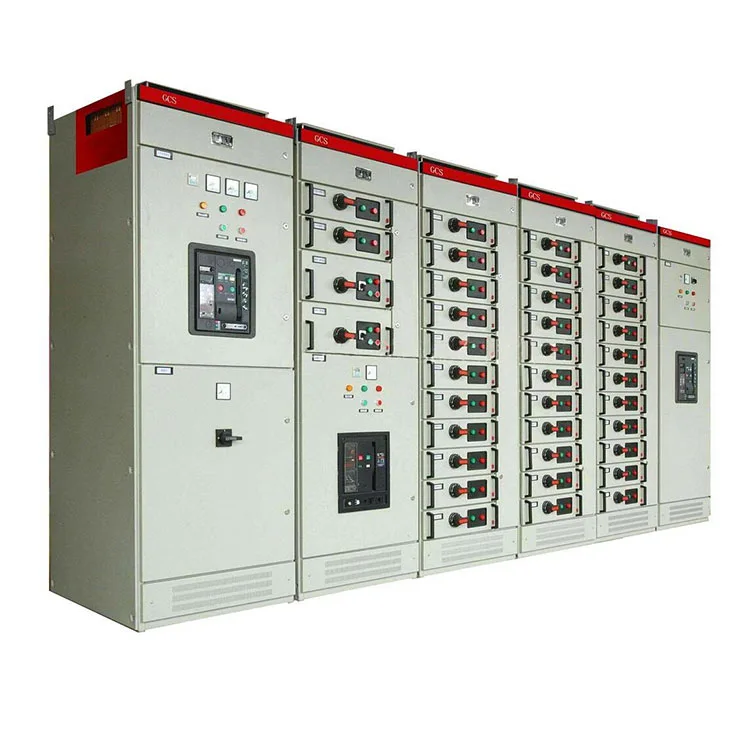

A kisfeszültségű és nagyfeszültségű panelek közötti különbség megértése kulcsfontosságú az elektromos biztonság és a megfelelő rendszertervezés szempontjából.
Alacsony feszültségű és nagyfeszültségű panelek összehasonlítása
| Jellemző | Alacsony feszültségű panelek | Nagyfeszültségű panelek |
|---|---|---|
| Feszültségtartomány | 1000 V AC / 1500 V DC alatt | 1000 V AC / 1500 V DC felett |
| Tipikus alkalmazások | Lakó-, kiskereskedelmi és vezérlőrendszerek | Ipari üzemek, közmű alállomások |
| Biztonsági követelmények | Szabványos elektromos biztonsági gyakorlatok | Speciális nagyfeszültségű biztonsági protokollok |
| Telepítés bonyolultsága | Közepes – képzett villanyszerelők | Magasan képzett szakemberekre van szükség |
| Költségek | Alacsonyabb kezdeti és karbantartási költségek | Magasabb kezdeti és karbantartási költségek |
| Helyigény | Kompakt, falra szerelhető vagy álló | Nagyobb alapterület, speciális helyiségek |
| Ívvillanás kockázata | Alacsonyabb energiaszint | Magasabb energiaszint, speciális egyéni védőfelszerelés szükséges |
Az alacsony feszültségű panelek főbb alkotóelemei
A kisfeszültségű panelek számos kritikus alkatrészt tartalmaznak, amelyek együttműködve biztosítják a biztonságos és megbízható energiaelosztást:
Alapvető panelalkatrészek
1. Főkapcsoló vagy fő leválasztó
– A teljes panel áramellátását szabályozza
– Vészleállítási lehetőséget biztosít
– A panel teljes áramerősségének megfelelő méretezés
2. Fióktelep Megszakítók
– Védje az egyes áramköröket a következőktől: túláram
– Különböző áramerősséggel kapható értékelések (15A, 20A, 30A stb.)
– Automatikus lekapcsolás áramkör túlterhelés esetén
3. Buszbárok
– Réz- vagy alumíniumvezetők, amelyek elosztják az energiát
– A fő busz a szervizbejárattól kapja az áramot.
– Az elágazó buszok elosztják az energiát az egyes áramkörök között
4. Semleges és földelő rudak
– Biztosítsa az elektromos áram visszatérési útját
– Elengedhetetlen a biztonság és az áramkör megfelelő működése szempontjából
– Megfelelően kell rögzíteni az NEC előírásainak megfelelően
5. Panelburkolat
– Védi a belső alkatrészeket a környezeti tényezőktől
– Biztonsági gátat képez az elektromos érintkezés ellen
– Különböző NEMA minősítésekkel kapható, különböző környezetekhez
🔧 Szakértői tipp: Mindig ellenőrizze, hogy a kisfeszültségű panel megfelel-e a vonatkozó előírásoknak. NEMA telepítési környezetének megfelelő besorolást. A beltéri panelek jellemzően NEMA 1-et használnak, míg a kültéri telepítésekhez NEMA 3R vagy magasabb besorolás szükséges.
Alacsony feszültségű panelek típusai és osztályozása
Az alacsony feszültségű panelek különféle konfigurációkban kaphatók, amelyeket speciális alkalmazásokhoz és telepítési követelményekhez terveztek.
Paneltípusok alkalmazás szerint
| Panel típusa | Feszültségtartomány | Tipikus használat | Fő jellemzők |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lakóépületek terhelési központjai | 120/240V egyfázisú | Otthonok, kis lakások | 20-40 áramkör, dugaszolható megszakítók |
| Kereskedelmi panelek | 120/208V vagy 277/480V háromfázisú | Irodaépületek, kiskereskedelem | 30-84 áramkörök, csavarozható megszakítók |
| Ipari vezérlőpanelek | 24–600 V egyenáram/váltóáram | Gyártás, automatizálás | Egyedi konfigurációk, monitoring rendszerek |
| Motorvezérlő központok (MCC) | 208V-600V háromfázisú | Ipari motorok | Frekvenciaváltók, indítók |
| Elosztópanelek | 120V-600V | Nagy létesítmények | Nagy áramerősség, több betápláló |
Panel osztályozás konstrukció szerint
Felületre szerelt panelek
– Falfelületekre szerelve
– Könnyebb hozzáférés karbantartás céljából
– Gyakori a kereskedelmi alkalmazásokban
Süllyesztett panelek
– Falüregekbe szerelve
– Letisztultabb megjelenés, helytakarékos
– Népszerű lakossági telepítésekben
Szabadon álló panelek
– Padlóra szerelt egységek
– Nagyobb kapacitású alkalmazások
– Ipari és nagykereskedelmi felhasználás
Alkalmazások és felhasználási esetek kisfeszültségű panelekhez
Az alacsony feszültségű panelek sokféle alkalmazást szolgálnak ki a lakossági, kereskedelmi és ipari szektorban.
Lakossági alkalmazások
Elsődleges funkciók:
– Áram elosztása a közműszolgáltatótól az otthoni áramkörökig
– Védje a villámokat és a konnektorokat
– Főbb készülékek vezérlése (vízmelegítők, HVAC stb.)
– Biztosítson GFCI és AFCI a kód által előírt védelem
Gyakori lakossági panelméretek:
– 100 amperes szolgáltatás: Kisebb otthonok, alapvető elektromos igények kielégítése
– 200 amperes szolgáltatás: Standard modern otthonok
– 400 amperes szolgáltatás: Nagy otthonok kiterjedt elektromos rendszerekkel
Kereskedelmi alkalmazások
Irodaépületek:
– Áramelosztás az emeletekre és a bérlői terekre
– Világításvezérlő rendszerek
– HVAC berendezések teljesítménye
– Vészvilágítási áramkörök
Kiskereskedelmi létesítmények:
– Üzletvilágítás és kijelzőteljesítmény
– Értékesítési pont rendszer áramkörei
– Biztonsági rendszer tápellátása
– Hűtőberendezések áramkörei
Ipari alkalmazások
Gyártóüzemek:
– Motorvezérlés és energiaelosztás
– Folyamatirányító rendszer teljesítménye
– Biztonsági áramkörök
– Műszerezés és felügyeleti berendezések
Adatközpontok:
– Szerver rack áramelosztás
– UPS rendszerintegráció
– Környezetvédelmi szabályozási erő
– Hálózati berendezések áramkörei
⚠️ Biztonsági figyelmeztetés: Minden kisfeszültségű paneltelepítésnek meg kell felelnie a következő előírásoknak: Nemzeti Villamos Szabályzat (NEC) 408. cikkely és a helyi elektromos előírásokat. Kizárólag képzett, engedéllyel rendelkező villanyszerelők végezhetnek el kapcsolótáblák telepítését vagy módosítását.
Hogyan válasszuk ki a megfelelő kisfeszültségű panelt?
A megfelelő kisfeszültségű panel kiválasztásához számos kritikus tényezőt kell gondosan figyelembe venni.
Kiválasztási kritériumok ellenőrzőlistája
1. Elektromos terhelési követelmények
– Számítsa ki a teljes csatlakoztatott terhelést amperben
– Vegye figyelembe a jövőbeli bővítési igényeket (25-30% kapacitás hozzáadása)
– Feszültség- és fáziskövetelmények meghatározása
– Értékelje a rövidzárlati áramerősséget
2. Környezeti feltételek
– Beltéri vs. kültéri telepítés
– Hőmérséklet- és páratartalom-megfontolások
– Korrozív légkörre vonatkozó követelmények
– Szeizmikus és rezgési tényezők
3. Kódexmegfelelőségi követelmények
– NEC 408. cikk (Kapcsolótáblák és panelek)
– Helyi elektromos előírások módosításai
– UL 67 (kapcsolópanelek) tanúsítvány
– NEMA szabványoknak való megfelelés
4. Fizikai térbeli korlátok
– Elérhető telepítési hely
– Szükséges munkavégzési távolságok (NEC 110.26)
– Rögzítési konfigurációs beállítások
– Jövőbeli akadálymentesítési igények
Panelméretezési útmutató
| Alkalmazás | Ajánlott áramerősség | Tipikus áramkörszám |
|---|---|---|
| Kis rezidencia | 100-150A | 20-30 áramkör |
| Standard Otthon | 200A | 30-40 áramkör |
| Nagy otthon | 300-400A | 40-60 áramkör |
| Kiskereskedelmi | 225-400A | 30-50 áramkör |
| Nagy kereskedelmi | 600-1200A | 50-84 áramkörök |
🔧 Szakértői tipp: A 80% paneleket mindig a névleges kapacitásuk alapján méretezzük, hogy biztosítsuk a megfelelő hőelvezetést és az előírásoknak való megfelelést. Egy 200 amperes panel csatlakoztatott terhelése nem haladhatja meg a 160 ampert.
Telepítési és biztonsági megfontolások
A kisfeszültségű panelek megfelelő telepítése kritikus fontosságú a biztonság, a szabványoknak való megfelelés és a megbízható működés szempontjából.
Telepítés előtti követelmények
1. Tervezés és engedélyek
– Szerezze be a szükséges elektromos engedélyeket
– Teljes terhelési számítások és paneltáblázatok
– Közműszolgáltatási követelmények ellenőrzése
– Tervezze meg a szükséges munkaterületeket
2. Helyszín előkészítése
– Biztosítsa a megfelelő szerkezeti alátámasztást
– Környezeti feltételek ellenőrzése
– Kábelvezetés és hozzáférés megtervezése
– Összehangolás más épületgépészeti rendszerekkel
Telepítési biztonsági követelmények
Munkavégzési engedélyre vonatkozó követelmények (NEC 110.26):
– Elülső: Minimum 90 cm szabad munkaterület
– Szélesség: Panel szélessége vagy minimum 30 hüvelyk, attól függően, hogy melyik nagyobb
– Magasság: 6,5 láb (kb. 2 méter) a padlótól vagy a platformtól
– Dedikált tér: A panel feletti terület a szerkezeti mennyezetig
Földelési és kötési követelmények:
– Fő összekötő áthidaló beszerelése
– Berendezés földelővezetékének csatlakozásai
– Semleges és földelt leválasztás (alpanelekhez)
– Földelőelektróda vezetőjének méretezése
⚠️ Fontos biztonsági figyelmeztetés: Soha ne kíséreljen meg kisfeszültségű paneleket telepíteni, módosítani vagy szervizelni megfelelő villanyszerelési képzés és engedély nélkül. Az elektromos munkák komoly áramütés, tűz és halál kockázatát hordozzák magukban.
Karbantartás és hibaelhárítás
A rendszeres karbantartás biztosítja a kisfeszültségű panelek biztonságos és megbízható működését, miközben meghosszabbítja a berendezések élettartamát.
Rutinszerű karbantartási ütemterv
Havi ellenőrzések:
– Szemrevételezéssel ellenőrizhető a túlmelegedés jelei
– Ellenőrizze a laza csatlakozásokat vagy sérült alkatrészeket
– Ellenőrizze a panelajtó záródását és a zár működését
– Dokumentálja a szokatlan körülményeket
Éves szakmai karbantartás:
– Csatlakozások termográfiai vizsgálata
– Minden csatlakozás nyomatékának ellenőrzése
– Szigetelési ellenállás vizsgálata
– Ívvillanás veszélyértékelésének frissítése
Gyakori problémák és megoldások
| Probléma | Lehetséges Okok | Professzionális megoldások |
|---|---|---|
| Gyakori áramkör-megszakító kioldások | Túlterhelt áramkörök, hibás berendezések | Terheléselemzés, áramkör újrakonfigurálása |
| Panel túlmelegedés | Laza csatlakozások, túlterhelés | Csatlakozás meghúzása, terheléselosztás |
| Feszültségingadozások | Közműproblémák, rossz kapcsolatok | Közműkoordináció, csatlakozási javítás |
| Korrózió/oxidáció | Környezeti expozíció | Alkatrészcsere, házfrissítés |
🔧 Szakértői tipp: Évente ütemezzen be termográfiai vizsgálatokat a forró pontok azonosítására, mielőtt azok biztonsági kockázatot jelentenének. A laza csatlakozások veszélyes ívkisülést okozhatnak.
Kódexmegfelelőség és szabványok
A kisfeszültségű paneleknek számos előírásnak és szabványnak kell megfelelniük a biztonság és a megfelelő működés biztosítása érdekében.
Kulcskód-követelmények
Nemzeti Villamos Szabályzat (NEC) cikkek:
– 408. cikk: Kapcsolótáblák és panelek
– 110. cikk: Elektromos berendezésekre vonatkozó követelmények
– 240. cikk: Túláramvédelem
– 250. cikk: Földelés és kötés
Iparági szabványok:
– UL 67: Standard elosztószekrények
– UL 891: Kapcsolótáblák szabvány
– NEMA PB 1: Panelek szabványai
– IEEE szabványok: Telepítési és tesztelési követelmények
Tanúsítási követelmények
Panel tanúsítványok:
– UL által jóváhagyott alkatrészek és szerelvények
– CSA tanúsítvány kanadai telepítésekhez
– NRTL (Országosan Elismert Vizsgálólaboratórium) jóváhagyás
– Illetékes helyi önkormányzat (AHJ) jóváhagyása
Gyakran Ismételt Kérdések
Mi a különbség a kapcsolótábla és a kapcsolótábla között?
A kapcsolótáblák jellemzően 1200 amper vagy annál kisebb áramerősségre vannak méretezve, és dugaszolható vagy csavarozható megszakítókat használnak. Az 1200 amper feletti névleges áramerősségű kapcsolótáblák egyedileg szerelt, rögzített kapcsolókat és megszakítókat használnak egyedi összeállításban.
Milyen gyakran kell ellenőrizni a kisfeszültségű kapcsolótáblákat?
A vizuális ellenőrzéseket havonta, az átfogó szakmai ellenőrzéseket pedig évente kell elvégezni. A nagy igénybevételű ipari paneleknél gyakrabban, félévente szükséges lehet a karbantartás.
Hozzáadhatok áramköröket egy meglévő kisfeszültségű panelhez?
Igen, ha a panel rendelkezik szabad hellyel és kapacitással. Ezt a munkát azonban engedéllyel rendelkező villanyszerelőnek kell elvégeznie, és jellemzően elektromos engedély és ellenőrzés szükséges hozzá.
Mi okozhatja egy alacsony feszültségű panel meghibásodását?
Gyakori okok közé tartoznak a hőképződést okozó laza csatlakozások, a túláram, a környezeti tényezők, mint például a nedvesség vagy a korrózió, valamint az alkatrészek életkorral összefüggő degradációja.
Honnan tudom, hogy ki kell cserélni a kisfeszültségű panelemet?
A jelek közé tartozik a gyakori megszakító-leoldás, a látható korrózió vagy sérülés, a 25-30 évnél idősebb panelek, a jelenlegi terhelésekhez nem elegendő kapacitás, vagy az aktuális biztonsági előírásoknak nem megfelelő panelek.
Mennyi egy alacsony feszültségű panel tipikus élettartama?
A jól karbantartott panelek általában 25-40 évig tartanak. Azonban a zord környezetben vagy nagy igénybevételnek kitett paneleket hamarabb ki kell cserélni.
Szükség van speciális szerszámokra a kisfeszültségű panelek karbantartásához?
Igen, a megfelelő karbantartáshoz infravörös hőmérők, nyomatékkulcsok, szigetelésvizsgálók és megfelelő személyi védőfelszerelések (PPE) szükségesek az elektromos munkákhoz.
Befolyásolhatja az időjárás a kisfeszültségű panelek teljesítményét?
Igen, a szélsőséges hőmérsékletek, a páratartalom és a nedvesség befolyásolhatja a panelek teljesítményét. A kültéri panelekhez megfelelő NEMA-besorolás szükséges, és további környezeti védelemre lehet szükség.
Gyorstalpaló útmutató
Panelválasztási ellenőrzőlista
- Számítsa ki a teljes elektromos terhelési igényt
- Feszültség- és fázisigény meghatározása
- Ellenőrizze a rendelkezésre álló telepítési helyet
- Ellenőrizze a környezeti feltételeket
- Kód megfelelőségi követelményeinek megerősítése
- Tervezze meg a jövőbeli bővítési igényeket
- Szerezze be a szükséges engedélyeket és jóváhagyásokat
Biztonsági emlékeztetők
- A panelen végzett munka előtt mindig kapcsolja ki az áramellátást
- Használjon megfelelő egyéni védőfelszerelést elektromos munkákhoz
- Tartsa be az előírt munkatávolságokat
- A munka megkezdése előtt tesztelje az áramköröket
- Kövesse a kizárási/kitáblázási eljárásokat
- Csak szakképzett villanyszerelőket engedjen meg a munkálatok elvégzésére
Vészhelyzeti eljárások
- Elektromos vészhelyzet: Azonnal kapcsolja ki a főkapcsolót
- Tűz: Csak C osztályú tűzoltó készüléket használjon
- Áramütés: Hívja a 911-et, ne érintse meg a sérültet, amíg áramtalanítás nincs.
- Ívvillanás: Evakuálják a területet, hívják a mentőszolgálatokat
Kapcsolódó
Mi okozza a napelemek kigyulladását? Teljes körű biztonsági útmutató