I. Introduction
A. Definition of a junction box
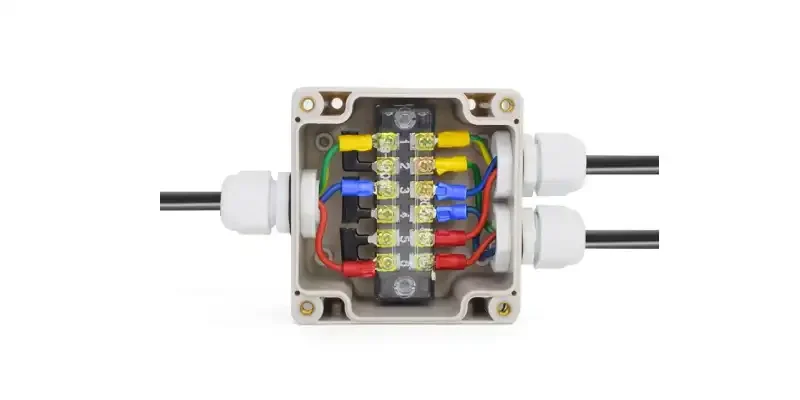
A junction box is an enclosure designed to house electrical connections, providing a safe and organized way to connect multiple wires and circuits. These boxes can be made from various materials, including metal and plastic, and are crucial in both residential and commercial electrical systems. They serve as connection points for wires, ensuring that electrical splices are protected from damage and environmental factors such as moisture and physical impacts.

B. Importance in electrical systems
Junction boxes are essential for preserving the safety and effectiveness of electrical systems because they shield wiring from outside threats, avoid unintentional contact with live wires, and reduce the possibility of electrical fires or short circuits. By offering a safe environment for electrical connections, junction boxes make it simpler to maintain and make changes to electrical systems without putting wires at risk of harm.
The significance of junction boxes can be summarized as follows:
- Protection: They shield electrical connections from weather elements and physical damage, reducing the risk of electrical hazards.
- Organization: Junction boxes help organize wiring pathways, making it easier to manage complex electrical systems.
- Accessibility: They provide accessible points for repairs or upgrades, allowing electricians to work safely on the wiring without needing to access hidden or hard-to-reach areas.
II. Types of Junction Boxes
Junction boxes are divided into groups according to their particular uses, designs, and materials. Selecting the right junction box for different electrical installations requires an understanding of these types.
A. Metallic junction boxes
Typically, steel or aluminum are used to make metallic junction boxes. They provide exceptional durability and are perfect for scenarios like industrial settings or outdoor applications where robustness is essential. These boxes are appropriate for locations that could sustain physical damage or fire threats since they can tolerate high temperatures and severe impacts.

B. Non-metallic junction boxes
Because of their corrosion resistance, non-metallic junction boxes—which are frequently made of PVC plastic—are a popular option for residential applications, such as inside walls or ceilings, and are lightweight and reasonably priced. They are primarily intended for indoor use, where they are exposed to harsh environmental conditions to a limited extent.
C. Weatherproof junction boxes
Specifically made to shield electrical connections from weather-related factors like rain, dust, and high temperatures, waterproof junction boxes are crucial for preventing moisture intrusion and associated risks and guaranteeing that wiring stays dry and safe in outdoor environments, like outdoor outlets or lighting.
D. Explosion-proof junction boxes
In order to prevent external atmospheres from igniting, explosion-proof junction boxes are designed to trap any explosive gasses or vapors that may arise within their enclosure. These boxes are essential in dangerous settings with combustible compounds, including chemical industries or oil refineries. By preserving the integrity of electrical connections in potentially explosive environments, they guarantee safety.
III. Components of a Junction Box
Junction boxes are made up of a number of crucial parts that cooperate to guarantee the effective and safe handling of electrical connections. It is essential to comprehend these elements in order to perform installation and maintenance correctly.
A. Box enclosure
The main component of a junction box is the box enclosure, which is used to house and protect electrical connections. Usually constructed of materials like plastic or metal, the enclosure avoids accidental contact with live wires and protects the internal components from physical damage, dust, and moisture.
B. Cover plate
The cover plate, which is a protective lid for the junction box, secures the enclosure and keeps the internal wiring out of reach. It is a crucial safety component because it reduces the possibility of unintentional contact with electrical connections. Cover plates can be screw-on or snap-fit, and they may have features that prevent moisture or dust infiltration.
C. Knockouts
Knockouts are pre-scored junction box apertures that make it simple to insert cables. In order to facilitate connections between various circuits, these apertures can be eliminated to make room for electrical conduits or wires to enter the box. Because knockouts offer installation flexibility, electricians can modify the box to meet particular wire requirements.
D. Mounting brackets
Depending on the junction box’s design and the installation requirements, mounting brackets—hardware parts that fasten the box to walls, ceilings, or other surfaces—can be fixed or adjustable, ensuring that the box stays stable and positioned correctly during installation and use.
E. Grounding screws
Metal screws called “grounding screws” are found within the junction box and serve as a point of connection for grounding wires. By properly channeling surplus power into the earth, proper grounding lowers the likelihood of fire dangers and helps prevent electrical shock, making it essential for electrical safety. Grounding screws guarantee that the junction box’s metal parts stay at earth potential.
IV. Applications of Junction Boxes
Junction boxes are adaptable parts that are utilized in a variety of contexts to guarantee secure and well-organized electrical connections. Residential, commercial, industrial, and outdoor settings are the general categories into which their applications can be divided.
A. Residential use
Junction boxes are crucial for connecting electrical wires in residential settings; they are frequently placed in places like walls, attics, and basements to make connections for outlets, switches, and fixtures. By containing multiple wire connections, junction boxes help keep an electrical system neat and orderly, lowering the risk of hazards like electrical fires or short circuits. Their use also makes maintenance and troubleshooting easier, making them indispensable in home wiring systems.
B. Commercial applications
In commercial settings, where they oversee intricate electrical networks in public buildings, retail establishments, and office buildings, junction boxes are essential. They give electrical connections a single location, making maintenance and adjustments simpler. Junction boxes are used in commercial settings to assist maintain an orderly and effective electrical infrastructure, which is essential for handling large electrical demands and enabling prompt problem-solving.
C. Industrial environments
Designed to withstand harsh conditions like dust, moisture, and extreme temperatures, industrial junction boxes are essential for connecting heavy-duty machinery and equipment in industrial settings. Their sturdy construction ensures dependable power distribution while enhancing safety by protecting against environmental hazards. Their ability to manage complex electrical systems is crucial in industries where operational downtime can result in significant productivity losses.
D. Outdoor installations
The purpose of outdoor junction boxes is to shield electrical connections from environmental factors like rain, dust, and temperature changes. These weatherproof boxes are crucial for applications like landscape lighting, outdoor outlets, and outdoor lighting fixtures because they keep wiring dry and secure, avoiding potential risks from moisture or debris intrusion. Additionally, outdoor junction boxes frequently have locking mechanisms and sturdy materials to deter vandalism and guarantee long-term dependability.
V. Selecting the Right Junction Box
Choosing the appropriate junction box is crucial for ensuring safety, compliance, and functionality in electrical installations. Here are key considerations when selecting a junction box:
A. Considering the Environment
The environment where the junction box will be installed significantly influences the choice of material and design. For example:
- Indoor environments may allow for non-metallic boxes, which are lightweight and corrosion-resistant.
- Outdoor applications require weatherproof boxes to protect against moisture and UV exposure.
- Industrial settings may necessitate metallic or explosion-proof boxes to withstand harsh conditions and prevent hazards.
B. Size and Capacity Requirements
Proper sizing is essential to accommodate the number and size of conductors, as well as any devices or fittings within the box. The National Electrical Code (NEC) provides guidelines for determining the minimum volume required based on:
- The number of conductors.
- The size of conductors (e.g., 18 AWG to 4 AWG or larger).
- Additional allowances for devices like switches or receptacles.
Failure to select an appropriately sized box can lead to overheating, damage to insulation, or increased risk of electrical fires.
C. Material Selection
The choice of material affects durability, safety, and compliance:
- Metallic junction boxes (e.g., steel or aluminum) offer robustness and are suitable for environments with high physical demands.
- Non-metallic boxes (e.g., PVC) are ideal for indoor use where moisture is minimal.
- Ensure materials are resistant to environmental factors such as moisture, UV light, and corrosion, especially in outdoor or industrial applications.
D. Compliance with Electrical Codes
Adherence to local electrical codes is mandatory when selecting a junction box. The NEC outlines specific requirements regarding:
- Minimum box sizes based on conductor types and numbers.
- Installation practices that ensure accessibility for maintenance.
- Grounding requirements to prevent static electricity buildup in hazardous locations.
Selecting a junction box that complies with these codes not only enhances safety but also ensures that installations pass inspections.
VI. Installation Process
Installing a junction box involves several critical steps to ensure safety and compliance with electrical standards. Here’s a detailed guide to the installation process:
A. Planning and Preparation
- Safety Precautions: Before starting, turn off the power at the main breaker panel for the circuit you will be working on. Use a voltmeter or non-contact tester to confirm that the power is off.
- Gather Tools and Materials: Collect all necessary tools and materials, including:
- Code-approved junction box (metal or plastic)
- Cable clamps (for metal boxes)
- Wire nuts
- Screws or nails for mounting
- Electrical tape
- Wire strippers and screwdrivers
- Choose the Location: Select an accessible location for the junction box that complies with local electrical codes. Ensure it is mounted securely to a stud or joist, with its face flush to the wall surface.
B. Mounting the Box
- Attach to Structure: Secure the junction box to a stud or joist using screws through pre-existing holes in the box, ensuring that it is stable and flush with the wall surface.
- Install Clamps: For metal boxes, remove knockouts using a screwdriver or hammer, then install cable clamps for each entry point. For plastic boxes, utilize internal clamps provided within the box.
C. Wiring Connections
- Prepare Wires: Strip approximately 3/4 inch of insulation from each wire using wire strippers. Ensure each conductor extends about 6 inches into the box.
- Connect Ground Wires: Join bare copper or green insulated ground wires first by twisting them together and securing them with a wire nut. If using a metal box, connect a pigtail ground wire to the ground screw inside the box.
- Join Hot and Neutral Wires: Connect black (hot) wires together and white (neutral) wires together using wire nuts for secure connections.
- Secure Cables: Tighten cable clamps to hold wires securely in place without over-tightening, which could damage the cables.
D. Sealing and Finishing
- Cover the Junction Box: After all connections are made, attach the cover plate securely to protect the internal wiring from dust and moisture.
- Final Check: Ensure all connections are tight and that no wires are exposed outside of the junction box.
- Restore Power: Turn on the power at the circuit breaker and test the connections to ensure everything is functioning properly.
VII. Safety Considerations
- Grounding
- Metal boxes: Ground using a screw or approved method
- Non-metallic boxes: Use approved grounding clip
- Ensure continuous, unbroken grounding conductor
- Overcurrent Protection
- Connect to appropriately rated circuit breakers or fuses
- Monitor for signs of overloading (warm boxes, flickering lights)
- Accessibility
- Install in easily accessible locations
- Maintain minimum working space (30″ wide x 36″ deep)
- Fire Safety
- Use non-combustible materials suitable for the environment
- Implement fireproofing for critical circuits
- Securely fasten junction box covers
X. Environmental Impact and Sustainability
In the electrical sector, junction boxes’ effects on the environment and their contribution to sustainability are becoming more and more significant factors. This section examines junction box energy conservation, recycling methods, and environmentally friendly materials.
A. Eco-friendly materials
Recycled Plastics: Since some junction boxes, like the i12 GreenLine, are composed of at least 90% post-consumer recyclate (PCR), which includes LDPE and PP, this shift not only saves raw materials but also drastically lowers the environmental impact by about 40% when compared to conventional plastics.
Durability and Performance: Eco-friendly junction boxes minimize dependency on new fossil-based plastics while maintaining high performance and safety standards, proving that sustainability and functionality can coexist.
NEW ABS VS. RECYCLED ABS IN WATERPROOF JUNCTION BOXES
B. Recycling old junction boxes
Recycling old junction boxes is an effective way to minimize waste and promote sustainability:
Material Recovery: Valuable components like metals (like copper) and polymers can be recovered and repurposed in manufacturing processes from junction boxes from retired electrical systems, including solar panels. This practice lessens the demand for virgin resources while also decreasing landfill garbage.
Reuse Potential: Many junction boxes can be renovated and reused if they are still in good condition. Ensuring that all unused apertures are sealed enables for their safe reinstallation, contributing to resource conservation.
C. Energy conservation aspects
- Efficient Wiring Management: Properly installed junction boxes facilitate efficient wiring configurations, reducing energy losses associated with poor connections or overloading circuits. This efficiency can lead to lower energy consumption in electrical systems.
- Support for Renewable Energy: Junction boxes are integral components in solar energy systems, connecting solar panels to inverters and other electrical components. By enabling the integration of renewable energy sources, they contribute to overall energy conservation efforts.
XI. Regulatory Standards and Compliance
Ensuring compliance with regulatory standards is critical for the safe installation and operation of junction boxes. This section discusses key requirements from the National Electrical Code (NEC), UL designations, and international standards.
A. National Electrical Code (NEC) Requirements
The NEC sets forth specific guidelines for junction box installation to minimize electrical hazards. Key provisions include:
- Material Specifications: Junction boxes must be constructed from non-combustible materials, such as metal or suitable plastic, depending on their intended environment (NEC Section 314.28). For example, boxes used in damp locations must be rated accordingly.
- Volume and Size Requirements: The NEC outlines minimum volume sizes based on the number and size of conductors within the box (NEC Section 314.16). For instance, a box containing three to six conductors requires a minimum volume of 18 cubic inches.
- Grounding Requirements: Junction boxes must be grounded to provide a safe path for fault current, preventing electrical shock hazards (NEC Section 250.110). Grounding methods vary based on whether the box is metallic or non-metallic.
- Accessibility: Boxes must be installed in accessible locations for maintenance and inspection, ensuring that they are not concealed behind walls or ceilings (NEC Section 314.29).
B. UL Listings and Certifications
Underwriters Laboratories (UL) provides safety certifications for junction boxes, ensuring they meet specific performance standards. Key points include:
- Safety Assurance: UL-listed products have undergone rigorous testing to verify their safety and reliability in various applications.
- Compliance with Standards: UL certifications ensure that junction boxes comply with relevant safety standards, including those for fire resistance, moisture protection, and electrical performance.
- Market Acceptance: Many local building codes require UL-listed products for compliance, making it essential for electricians and contractors to choose certified junction boxes.
C. International Standards
In addition to NEC regulations and UL certifications, international standards also govern junction box specifications:
- IEC Standards: The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) provides guidelines for electrical installations that may include junction box specifications, particularly concerning safety and environmental conditions.
- ISO Certifications: The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) sets quality management standards that can apply to manufacturers of electrical components, including junction boxes.
Compliance with these international standards ensures that junction boxes are suitable for global applications and meet diverse regulatory requirements.
XIII. Manufacturers of Junction Boxes
- NEMA Enclosure
- Location: USA
- Website: nemaenclosures.com
- Polycase
- Location: USA
- Website: polycase.com
- Turck, Inc
- Location: USA
- Website: turck.com
- VIOX Electric Co., Ltd
- Location: China
- Website: viox.com
- KAISER Group
- Location: Germany
- Website: kaiser-elektro.de
- Hammond Manufacturing
- Location: Canada
- Website: hammondmfg.com
- Marechal Electric
- Location: France
- Website: marechal.com
- Spina Group
- Location: Italy
- Website: spinagroup.com
- Takachi
- Location: Japan
- Website: takachi.com
XIV. Conclusion
Junction boxes, which offer secure and well-organized connections for wiring in a variety of settings, are crucial parts of electrical systems. These devices are essential for preserving electrical efficiency and safety in both household and commercial settings. For both homeowners and electricians, it is essential to comprehend their types, components, and appropriate installation techniques. Junction boxes continue to evolve, with eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient designs becoming more common as technology develops and sustainability gains importance. We can guarantee that junction boxes continue to act as dependable protectors of our electrical infrastructure, fostering functionality and safety in our increasingly electrified environment, by abiding by best practices and regulatory regulations.