A bolt-on circuit breaker is a type of electrical safety device that physically bolts or clamps directly onto the bus bars inside an electrical panel, providing a more secure and permanent connection than plug-in alternatives. Unlike standard plug-in breakers that simply snap into place, bolt-on breakers use mechanical fasteners to ensure maximum electrical contact and stability, making them essential for high-amperage applications and critical electrical systems.
Key Benefit: Bolt-on circuit breakers provide superior electrical connection integrity and are specifically required by electrical codes for circuits over 30 amps in most residential and commercial applications.
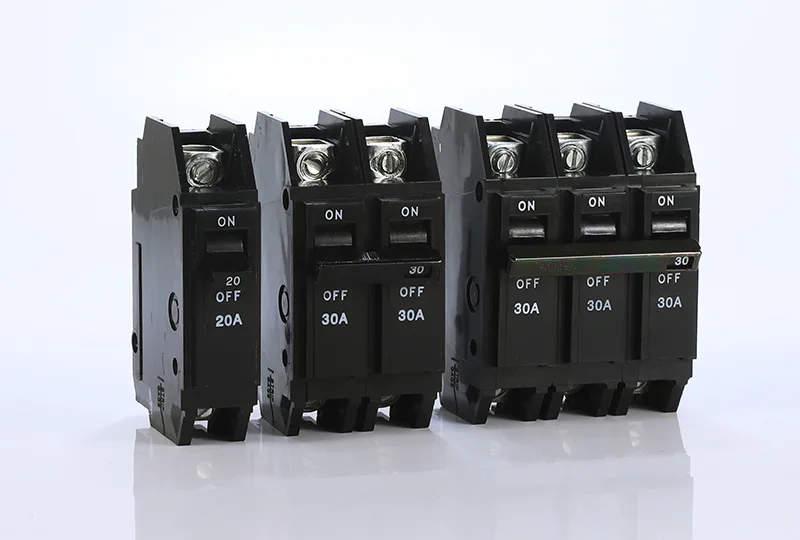

What Makes a Bolt-On Circuit Breaker Different?
Bolt-on circuit breakers distinguish themselves through their mechanical attachment method at enhanced electrical performance. Here’s how they compare to other circuit breaker types:
| Tampok | Bolt-On Breaker | Plug-In Breaker | Screw-In Breaker |
|---|---|---|---|
| Paraan ng Koneksyon | Bolted/clamped to bus bar | Clips onto bus bar | Threaded connection |
| Typical Amperage | 30-400+ amps | 15-30 amps | 15-30 amps (obsolete) |
| Connection Security | Pinakamataas | Katamtaman | Mababa |
| Pagiging Kumplikado ng Pag-install | Professional required | DIY possible | DIY possible |
| Mga Kinakailangan sa Code | Required for 30+ amp circuits | Standard for 15-30 amp | No longer code compliant |
| Paglaban sa Panginginig ng boses | Magaling | Mabuti | mahirap |
| Gastos | Mas mataas | Ibaba | Lowest |
Key Definitions You Need to Know
Bus Bar: The main copper or aluminum conductor inside an electrical panel that distributes power to individual circuit breakers.
Amperage Rating: The maximum electrical current a circuit breaker can safely handle before tripping to protect the circuit.
Mechanical Connection: A physical fastening method using bolts, clamps, or screws rather than simple plug-in contact points.
Load Center: Another term for electrical panel or breaker box where circuit breakers are installed.
When Do You Need a Bolt-On Circuit Breaker?
Required Applications (Code Mandated)
You must use bolt-on circuit breakers for:
- Electric dryer circuits (typically 30 amps)
- Electric range/cooktop circuits (40-50 amps)
- Central air conditioning units (30-60+ amps)
- Mga electric water heater (30-40 amps)
- EV charging stations (40-100+ amps)
- Sub-panel feeders (varies by load requirements)
Inirerekomendang Aplikasyon
Bolt-on breakers are preferred for:
- Workshop/garage circuits with high-power tools
- Welding equipment circuits
- Mga sistema ng komersyal na ilaw
- Mga circuit ng kontrol ng motor
- Any circuit experiencing frequent vibration
⚠️ Babala sa Kaligtasan: Never attempt to install or replace circuit breakers yourself. This work requires a licensed electrician and proper permits in most jurisdictions.
Types of Bolt-On Circuit Breakers
1. Standard Bolt-On Breakers
- Application: General 30-60 amp residential circuits
- Pag-install: Single or double-pole configurations
- Cost Range: $25-75 per breaker
2. High-Amperage Bolt-On Breakers
- Application: 70-400+ amp industrial and commercial uses
- Pag-install: Requires specialized panels and professional installation
- Cost Range: $100-500+ per breaker
3. GFCI Bolt-On Breakers
- Application: Ground fault protection for high-amperage circuits
- Pag-install: Spas, outdoor equipment, commercial kitchens
- Cost Range: $75-200 per breaker
4. AFCI Bolt-On Breakers
- Application: Arc fault protection for bedroom circuits over 30 amps
- Pag-install: Newer residential construction requirements
- Cost Range: $100-250 per breaker
How Bolt-On Circuit Breakers Work
Connection Process
- Power Isolation: Main electrical supply is completely shut off
- Bus Bar Preparation: Connection points are cleaned and inspected
- Breaker Positioning: Breaker is aligned with bus bar connection points
- Mechanical Fastening: Bolts or clamps are tightened to manufacturer specifications
- Pag-verify ng Torque: Connections are torqued to code requirements (typically 250-350 inch-pounds)
- Pagsubok: Electrical continuity and proper operation are verified
Why the Bolt-On Design Matters
Enhanced Contact Pressure: Mechanical fastening provides consistent contact pressure that won’t loosen over time.
Paglaban sa Panginginig ng boses: Critical in industrial environments or areas with mechanical equipment.
Thermal Stability: Better heat dissipation prevents connection degradation under high loads.
Pagsunod sa Code: Nagkikita NEC (National Electrical Code) requirements for high-amperage applications.
Circuit Breaker Selection Guide
Step 1: Determine Required Amperage
- Calculate the total load of devices on the circuit
- Apply appropriate safety factors (typically 125% of continuous loads)
- Reference manufacturer specifications for connected equipment
Step 2: Check Panel Compatibility
- Verify your electrical panel accepts bolt-on breakers
- Confirm available bus bar space and configuration
- Check manufacturer compatibility (Square D, Siemens, GE, etc.)
Step 3: Consider Special Requirements
- Proteksyon ng GFCI para sa mga basang lugar
- AFCI protection for residential bedroom circuits
- Special ratings for motor loads or inductive equipment
Step 4: Professional Installation Planning
- Obtain required electrical permits
- Schedule licensed electrician for installation
- Plan for potential panel upgrades if needed
Installation Requirements & Safety
🔧 Tip ng Eksperto: Bolt-on breaker installation requires torquing connections to specific values. Under-torquing creates fire hazards; over-torquing can damage equipment.
Code Requirements (NEC Compliance)
- Mga Detalye ng Torque: Must meet manufacturer requirements (typically documented on breaker label)
- Wire Sizing: Circuit wiring must match breaker amperage rating
- Grounding: Proper equipment grounding required for all installations
- Pag-label: All circuits must be clearly labeled in the panel directory
Professional Installation Process
- Permit Acquisition: Most jurisdictions require permits for breaker additions/replacements
- Power Shutdown: Main electrical supply disconnection and verification
- Safety Procedures: Lockout/tagout procedures and personal protective equipment
- Pag-install: Proper mounting, connection, and torquing procedures
- Pagsubok: Electrical testing and functionality verification
- Inspeksyon: Local electrical inspector approval before energizing

Common Problems & Troubleshooting
Connection Issues
Problema: Loose bolt-on connections causing arcing or overheating
Solusyon: Professional re-torquing to manufacturer specifications
Mga Problema sa Pagkakatugma
Problema: Wrong breaker type for panel brand
Solusyon: Use only manufacturer-approved breakers for your specific panel
Overloading
Problema: Breaker trips frequently under normal loads
Solusyon: Load calculation review and potential circuit splitting
Age-Related Failures
Problema: Older bolt-on breakers failing to trip properly
Solusyon: Professional testing and replacement as needed
Global Usage: Which Countries Use Bolt-On Circuit Breakers?
Bolt-on circuit breaker adoption varies significantly worldwide based on electrical codes, safety standards, and infrastructure development. Understanding international usage patterns helps explain availability, compatibility, and regulatory requirements.
Primary Bolt-On Circuit Breaker Markets
| Country/Region | Usage Level | Primary Standards | Mga Pangunahing Aplikasyon |
|---|---|---|---|
| Estados Unidos | Malawak | NEC (NFPA 70) | 30+ amp residential/commercial |
| Canada | Malawak | CEC (CSA C22.1) | High-amperage applications |
| United Kingdom | Katamtaman | BS 7671 (18th Edition) | Industrial/commercial |
| Australia | Katamtaman | AS/NZS 3000 | Commercial installations |
| Alemanya | Limitado | VDE standards | Mga aplikasyon sa industriya |
| Japan | Limitado | JIS standards | Specific industrial uses |
| India | Growing | IS 732 | Commercial/industrial expansion |
| Brazil | Katamtaman | NBR standards | Industrial/commercial |
North American Dominance
United States and Canada represent the largest markets for bolt-on circuit breakers due to:
- Stringent Code Requirements: NEC and CEC mandate bolt-on breakers for circuits over 30 amps
- High-Power Appliance Standards: 240V electric dryers, ranges, and HVAC systems are standard
- Residential Infrastructure: Purpose-built electrical panels designed for bolt-on integration
- Market Maturity: Established supply chains and installer expertise
European Variations
United Kingdom and European Union show moderate adoption with regional differences:
- Industrial Focus: Primarily used in commercial and industrial applications
- Different Standards: IEC standards influence design and connection methods
- Alternative Technologies: Greater reliance on DIN rail mounting systems
- Voltage Differences: 230V/400V systems require different breaker designs
🌍 International Insight: European markets often use DIN rail-mounted circuit breakers for applications where North America uses bolt-on breakers.
Asia-Pacific Market Trends
Australia and New Zealand demonstrate growing adoption:
- Mga Komersyal na Aplikasyon: Increasing use in commercial and industrial settings
- Code Evolution: Standards moving toward requiring mechanical connections for high-amperage circuits
- Infrastructure Development: New construction incorporating bolt-on breaker panels
Japan and South Korea show limited but specialized usage:
- Industrial Application: Primarily in manufacturing and heavy industry
- Unique Standards: JIS and KS standards create different design requirements
- Compact Alternatives: Preference for space-saving panel designs
Mga Umuusbong na Merkado
India, Brazil, and Middle East represent growing markets:
- Infrastructure Expansion: Rapid commercial and industrial development
- Code Modernization: Adoption of international safety standards
- Technology Transfer: Influence from multinational electrical companies
- Economic Development: Increased demand for reliable electrical systems
Regional Code Requirements Comparison
| Rehiyon | High-Amp Requirement | Typical Threshold | Enforcement Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hilagang Amerika | Mandatory bolt-on | 30+ amps | Strict |
| UK/EU | Inirerekomenda | 32+ amps | Katamtaman |
| Australia/NZ | Increasingly required | 25+ amps | Growing |
| Asia | Varies by country | 30-50+ amps | Variable |
| Mga Umuusbong na Merkado | Developing standards | 40+ amps | Improving |
International Compatibility Considerations
Standard Differences:
- Connection Methods: Bolt patterns and mounting requirements vary
- Mga Rating ng Boltahe: Different nominal voltages require specific designs
- Arc Fault/Ground Fault: Protection requirements vary significantly by region
- Mga Rating sa Kapaligiran: Climate and installation conditions influence specifications
Manufacturing Considerations:
- Global Brands: Schneider Electric, ABB, Siemens adapt products for regional markets
- Local Production: Regional manufacturers focus on domestic code compliance
- Import/Export: Certification requirements affect international trade
Why Regional Differences Exist
Historical Infrastructure:
- Existing Systems: Established electrical infrastructure influences breaker types
- Renovation vs. New Construction: Different approaches to electrical upgrades
- Pang-ekonomiyang Salik: Cost considerations affect adoption rates
Regulatory Environment:
- Safety Philosophy: Different approaches to electrical safety and risk management
- Code Development: National electrical codes evolve at different rates
- Enforcement Mechanisms: Variation in inspection and compliance requirements
Market Factors:
- Installer Training: Availability of qualified electricians affects adoption
- Supply Chain: Local availability of compatible panels and breakers
- Economic Development: Industrial growth drives demand for reliable electrical systems
⚡ Global Trend: International adoption of bolt-on circuit breakers is increasing as countries modernize electrical codes and prioritize system reliability.
Cost Comparison Analysis
| Uri ng Circuit | Plug-In Breaker Cost | Bolt-On Breaker Cost | Installation Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 30 Amp Dryer | Not code compliant | $35-60 | $150-250 labor |
| 40 Amp Range | Not code compliant | $45-75 | $150-250 labor |
| 50 Amp A/C | Not code compliant | $55-90 | $200-300 labor |
| 60 Amp Sub-panel | Hindi available | $75-125 | $250-400 labor |
💡 Tip ng Eksperto: While bolt-on breakers cost more upfront, they provide superior long-term reliability and are required by code for high-amperage applications.

Mga Madalas Itanong
Can I replace a plug-in breaker with a bolt-on breaker?
You can only install bolt-on breakers in panels specifically designed for them. Most residential panels have dedicated spaces for bolt-on breakers, typically for high-amperage circuits like dryers and ranges.
How do I know if my panel accepts bolt-on breakers?
Check your electrical panel’s specifications label or consult with a licensed electrician. Most modern residential panels have both plug-in spaces (15-30 amps) and bolt-on spaces (30+ amps).
What’s the difference between single-pole and double-pole bolt-on breakers?
Single-pole bolt-on breakers protect 120V circuits, while double-pole versions protect 240V circuits. Most high-amperage appliances (dryers, ranges, A/C units) require double-pole bolt-on breakers.
Can bolt-on breakers be installed in any orientation?
Bolt-on breakers must be installed in the specific orientation designed for your panel. The mechanical connections are engineered for precise alignment with the bus bars.
How often should bolt-on breakers be inspected?
Professional inspection every 3-5 years is recommended, with more frequent inspection in industrial environments or areas with high vibration.
Are bolt-on breakers more reliable than plug-in breakers?
Yes, for their intended applications. The mechanical connection provides superior contact integrity and vibration resistance, making them more reliable for high-amperage and critical applications.
Can I upgrade from plug-in to bolt-on breakers for better performance?
This requires panel compatibility verification and professional installation. While bolt-on breakers offer superior performance, they’re primarily designed for high-amperage applications where codes require them.
What tools are needed for bolt-on breaker installation?
Professional installation requires torque wrenches, electrical testing equipment, and specialized tools. This is not a DIY project due to safety and code requirements.
Mga Tip ng Dalubhasa para sa Pinakamainam na Pagganap
Selection Tips
- Always match breaker brand to panel brand for optimal compatibility and warranty coverage
- Isaalang-alang ang mga pangangailangan sa pagpapalawak sa hinaharap when planning high-amperage circuits
- Invest in GFCI or AFCI bolt-on breakers where code required for enhanced safety
Mga Rekomendasyon sa Pagpapanatili
- Taunang visual na inspeksyon of connections for signs of overheating or corrosion
- Professional torque verification every 5 years in residential applications
- Immediate professional evaluation if you notice burning smells or panel warmth
Pinakamahuhusay na Kasanayan sa Pag-install
- Always use manufacturer-specified torque values to prevent connection problems
- Verify proper wire sizing for the full amperage rating of the bolt-on breaker
- Ensure adequate panel ventilation for high-amperage applications
Kailan Tawagan ang isang Propesyonal
Kailangan ng Agarang Tulong na Propesyonal:
- Any electrical work involving high-amperage circuits
- Burning smells or signs of overheating in your electrical panel
- Frequent tripping of bolt-on breakers under normal loads
- Any modifications to existing electrical panel configurations
Planning Professional Consultation:
- Upgrading electrical service or adding high-amperage circuits
- Installing EV charging stations or other major appliances
- Evaluating older electrical systems for safety and code compliance
⚠️ Kritikal na Paalala sa Kaligtasan: Working with electrical panels and high-amperage circuits presents serious risks of electrical shock, burns, and fire. Always hire licensed electricians for installation, maintenance, and repairs.
Konklusyon
Bolt-on circuit breakers are essential components for high-amperage electrical circuits, providing superior connection integrity and code compliance for applications over 30 amps. While they require professional installation and cost more than plug-in alternatives, their mechanical connection design offers unmatched reliability and safety for critical electrical systems.
Mga Pangunahing Takeaway:
- Bolt-on breakers are required by code for circuits over 30 amps
- They provide superior electrical connection through mechanical fastening
- Professional installation is mandatory for safety and code compliance
- They’re essential for modern high-power appliances and EV charging systems
For any bolt-on circuit breaker installation or evaluation, consult with a licensed electrician who can ensure proper selection, installation, and code compliance for your specific application.