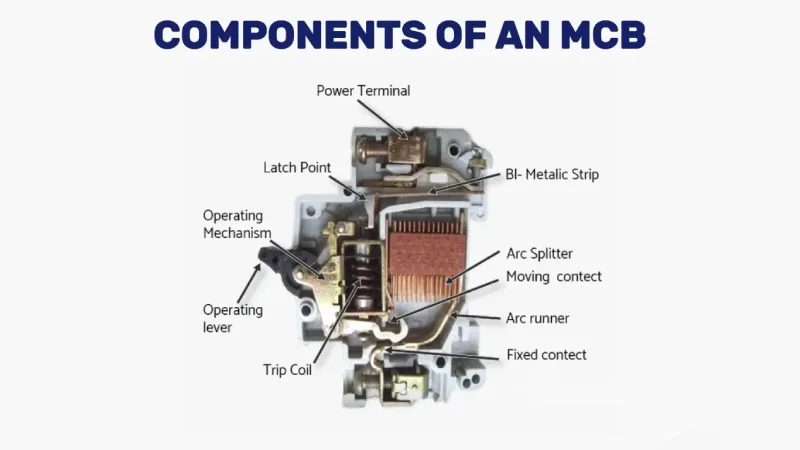
A Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB) is an automatically operated electrical safety device designed to protect electrical circuits from damage caused by excess current from overloads or short circuits. Unlike traditional fuses that must be replaced after activation, MCBs can be reset and reused, making them the preferred choice for modern residential, commercial, and industrial electrical installations.
Understanding MCBs is crucial for electrical safety, code compliance, and making informed decisions about your electrical system’s protection. This comprehensive guide covers everything you need to know about MCBs, from basic operation to professional selection criteria.
What Makes an MCB Different from Other Circuit Protection Devices?
MCB vs. Sikring vs. RCD: Key Differences
| Funksjon | MCB | Sikring | RCD/GFCI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beskyttelsestype | Overcurrent (overload + short circuit) | Overcurrent only | Earth leakage/ground fault |
| Tilbakestillingsmetode | Manual switch reset | Replace fuse wire/cartridge | Manual reset button |
| Responstid | Instantaneous for short circuits | Varies by fuse type | 25-40 milliseconds |
| Gjenbrukbarhet | Unlimited resets | Single use only | Unlimited resets |
| Installasjon | Snap-in to panel | Screw-in or cartridge | Wired in series |
| Kostnader | Higher initial, lower long-term | Lower initial, higher replacement | Highest initial cost |
| Nøyaktighet | Precise trip characteristics | Less precise | Highly sensitive |
Why MCBs Are Superior for Modern Applications
Enhanced Safety Features:
- Precise trip characteristics prevent nuisance tripping
- Visual indication of tripped state
- Arc quenching technology for safe interruption
- Temperature-independent operation
Economic Advantages:
- No replacement costs after activation
- Reduced downtime through quick tilbakestill
- Lavere krav til vedlikehold
- Extended lifespan (20+ years typical)
Eksperttips: While MCBs cost more initially than fuses, they typically pay for themselves within 2-3 activations through eliminated replacement costs and reduced downtime.
How Do Miniature Circuit Breakers Work?
Driftsprinsipp
MCBs operate on two primary protection mechanisms:
- Thermal Protection (Overload)
- Bimetallic strip heats up during sustained overcurrent
- Strip bends and releases trip mechanism
- Provides inverse time characteristics (higher current = faster trip)
- Magnetic Protection (Short Circuit)
- Electromagnetic coil creates magnetic field during high fault current
- Magnetic force instantly releases trip mechanism
- Provides instantaneous protection for short circuits
Trip Characteristics Explained
| Nåværende nivå | Trip Time | Beskyttelsesmetode |
|---|---|---|
| 100-113% of rating | No trip (tolerance) | Ingen |
| 113-145% of rating | 1+ hours | Thermal |
| 145-300% of rating | 1-60 minutes | Thermal |
| 300%+ of rating | Øyeblikkelig | Magnetic |
Sikkerhetsadvarsel: Never attempt to modify or bypass MCB trip characteristics. This can result in fire hazards, equipment damage, and code violations.
Types of MCBs and Their Applications
MCB Types by Trip Characteristics
Type B MCBs (3-5 times rated current)
- Best for: Residential circuits, lighting, general outlets
- Rekkevidde: 3-5 × In (rated current)
- Bruksområder: Boliger, kontorer, lett næringsbygg
- Kodeoverholdelse: Meets NEC Article 240 requirements
Type C MCBs (5-10 times rated current)
- Best for: Motor circuits, transformers, fluorescent lighting
- Rekkevidde: 5-10 × In
- Bruksområder: HVAC equipment, industrial machinery
- Special feature: Handles motor starting currents
Type D MCBs (10-20 times rated current)
- Best for: Heavy industrial equipment, welding machines
- Rekkevidde: 10-20 × In
- Bruksområder: Large motors, transformers, industrial processes
- Requirement: Typically requires engineering evaluation
MCB Ratings and Current Capacities
| Current Rating (A) | Typiske bruksområder | Ledningsstørrelse (AWG) | Paneltype |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6-10A | Belysningskretser | 14-12 | Boliger |
| 15-20A | General outlets, small appliances | 12-10 | Residential/Commercial |
| 25-30A | Large appliances, HVAC | 10-8 | Residential/Commercial |
| 40-63A | Sub-panels, large equipment | 8-4 | Kommersiell/industriell |
| 80-100A | Main feeders, large loads | 4-2/0 | Industriell |
MCB Selection Criteria: How to Choose the Right MCB
Steg-for-steg utvelgelsesprosess
Trinn 1: Bestem lastkrav
- Calculate total circuit load (watts ÷ voltage = amperage)
- Add 25% safety margin for continuous loads
- Vurder fremtidige utvidelsesbehov
- Check maximum wire ampacity
Step 2: Select Appropriate Type
- Type B: Most residential and light commercial applications
- Type C: Motor loads and inductive equipment
- Type D: Heavy industrial applications only
Step 3: Verify Code Compliance
- Ensure rating matches wire ampacity (NEC Table 310.15(B)(16))
- Confirm AFCI/GFCI requirements for specific locations
- Check local amendments and requirements
Step 4: Consider Special Features
- Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter (AFCI) capability
- Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) protection
- Smart/connected capabilities for monitoring
Kriterier for profesjonelle utvalg
Sikkerhetshensyn:
- Never oversize MCB rating beyond wire capacity
- Consider ambient temperature derating
- Evaluate available fault current at installation point
- Ensure proper coordination with upstream protection
Kvalitetsindikatorer:
- UL 489 listing for North America
- IEC 60898 compliance for international standards
- Produsent reputation and warranty terms
- Breaking capacity adequate for installation
Eksperttips: Always consult local electrical codes and consider hiring a licensed electrician for MCB selection in commercial or complex residential applications.
MCB Installation and Maintenance Guidelines
Krav til installasjon
Pre-Installation Checklist:
- [ ] Verify power is OFF and locked out
- [ ] Confirm MCB compatibility with panel manufacturer
- [ ] Check adequate clearances per NEC 110.26
- [ ] Ensure proper grounding and bonding
- [ ] Verify wire connections are tight and secure
Installasjonstrinn:
- Turn off main power at service panel
- Remove panel cover following safety procedures
- Insert MCB into appropriate slot (snap-in design)
- Connect circuit wire to MCB terminal (hot wire only)
- Verify secure connection with gentle tug test
- Label circuit clearly and permanently
- Test operation before energizing circuit
Vedlikehold og testing
Monthly Visual Inspection:
- Check for signs of overheating (discoloration, burning smell)
- Verify all labels are legible and accurate
- Look for loose connections or corrosion
- Ensure panel access is clear and unobstructed
Annual Testing Procedure:
- Turn off circuit at MCB
- Test operation by pressing test button (if equipped)
- Manually trip and reset MCB
- Check for smooth operation and positive engagement
- Verify circuit function after reset
Sikkerhetsadvarsel: If an MCB trips repeatedly, do not continue resetting it. This indicates a serious electrical problem requiring immediate professional attention.
Troubleshooting Common MCB Problems
MCB Keeps Tripping
Mulige årsaker og løsninger:
| Problem | Sannsynlig årsak | Løsning |
|---|---|---|
| Immediate trip on reset | Kortslutning | Call electrician immediately |
| Trip after few minutes | Overload condition | Reduser belastningen på kretsen |
| Random tripping | Løse forbindelser | Tighten all connections |
| Trip during motor start | Wrong MCB type | Upgrade to Type C MCB |
MCB Won’t Reset
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Ensure MCB is fully OFF before attempting reset
- Check for visible damage to MCB housing
- Verify no loose wires in panel
- Test with known good MCB if available
- Replace MCB if mechanical failure suspected
Nuisance Tripping Solutions
Common Fixes:
- Fluorescent lighting: Use Type C MCB instead of Type B
- Motor circuits: Verify proper starting method and MCB type
- Electronic loads: Consider specialized MCBs for non-linear loads
- Multiple small loads: Check total circuit amperage calculation
Sikkerhet og samsvar med forskrifter
Krav i nasjonale elektriske forskrifter (NEC)
Key NEC Articles for MCBs:
- Artikkel 240: Overcurrent Protection requirements
- Article 210: Branch Circuit requirements
- Artikkel 408: Switchboard and Panelboard requirements
- Artikkel 110: General requirements for electrical installations
Critical Compliance Points:
- MCB rating must not exceed wire ampacity
- AFCI protection required in most residential areas
- GFCI protection required in wet/damp locations
- Proper labeling and identification mandatory
Beste sikkerhetspraksis
Do’s:
- Always use lockout/tagout procedures
- Test MCBs annually or after any electrical work
- Keep electrical panels clean and accessible
- Use only manufacturer-approved accessories
- Maintain adequate clearances around panels
Don’ts:
- Never use MCBs as switches for routine operation
- Don’t ignore repeated tripping conditions
- Never modify or tamper with MCB mechanisms
- Don’t use wrong MCB type for application
- Never install MCBs beyond their breaking capacity
Faglig anbefaling: For any electrical work beyond simple MCB replacement, consult a licensed electrician to ensure code compliance and safety.
Hurtigreferanseguide
MCB Selection Quick Chart
| Søknad | MCB-type | Typical Rating | Spesielle krav |
|---|---|---|---|
| Belysningskretser | Type B | 15-20A | AFCI in bedrooms/living areas |
| General outlets | Type B | 15-20A | GFCI in wet locations |
| Kjøkkenapparater | Type B | 20A | GFCI for countertop outlets |
| HVAC-utstyr | Type C | Per equipment | Sized per manufacturer specs |
| Motors (general) | Type C | 125% motor FLA | Consider motor starting method |
| Welding/industrial | Type D | Per load calc | Engineering evaluation required |
Emergency Contact Information
When to Call an Electrician:
- MCB trips immediately upon reset
- Burning smell or visible damage
- Multiple MCBs tripping simultaneously
- Installation of new circuits
- Paneloppgraderinger eller modifikasjoner
Ofte stilte spørsmål
What’s the difference between a circuit breaker and an MCB?
An MCB is a specific type of circuit breaker designed for lower current ratings (typically up to 100A) in residential and light commercial applications. All MCBs are circuit breakers, but not all circuit breakers are MCBs.
How long do MCBs typically last?
Quality MCBs typically last 20-30 years with proper maintenance. However, they should be tested annually and replaced if they show signs of wear, fail testing, or have been subjected to multiple fault conditions.
Can I replace a fuse with an MCB?
Yes, but it requires panel modification or replacement. MCBs and fuses have different mounting systems, so you typically need a new panel designed for MCBs. This work should be done by a licensed electrician.
Why does my MCB trip when I turn on certain appliances?
This usually indicates either an overloaded circuit or an appliance with high starting current (like motors). The solution may be upgrading to a Type C MCB, using a dedicated circuit, or having the appliance serviced.
Is it safe to reset a tripped MCB?
Yes, if it stays reset and doesn’t trip again immediately. However, if an MCB trips repeatedly, do not keep resetting it – this indicates a serious problem requiring professional attention.
What’s the difference between MCB types B, C, and D?
The difference is in their magnetic trip characteristics: Type B trips at 3-5 times rated current, Type C at 5-10 times, and Type D at 10-20 times. This determines how much temporary overcurrent they can handle before tripping.
Do MCBs protect against electric shock?
No, standard MCBs only protect against overcurrent. For shock protection, you need GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter) or RCD (Residual Current Device) protection, which can be combined with MCBs in some products.
How do I know what size MCB I need?
MCB size should match the circuit wire ampacity and load requirements. For a 15A circuit with 14 AWG wire, use a 15A MCB. Never use an MCB larger than the wire can safely handle.
Expert Consultation Available: For complex electrical projects, panel upgrades, or safety concerns, always consult with a licensed electrician who can ensure proper installation, code compliance, and optimal safety for your specific application.
Relatert
Komplett guide til symboler for sikringsbrytere
Hvordan vite om sikringsbryteren er dårlig
7 kritiske varseltegn på at luftsikringsbryteren din svikter