Introduction
At VIOX Electric, we continuously strive to provide insightful information that helps our clientele make informed decisions about their electrical systems. Today, we delve into an essential topic for both residential and industrial applications: the distinction between single-phase and three-phase power systems. Understanding these two fundamental types of electrical power is crucial for optimizing performance, efficiency, and reliability in various settings.
Understanding Single-Phase Power
Overview and Principles
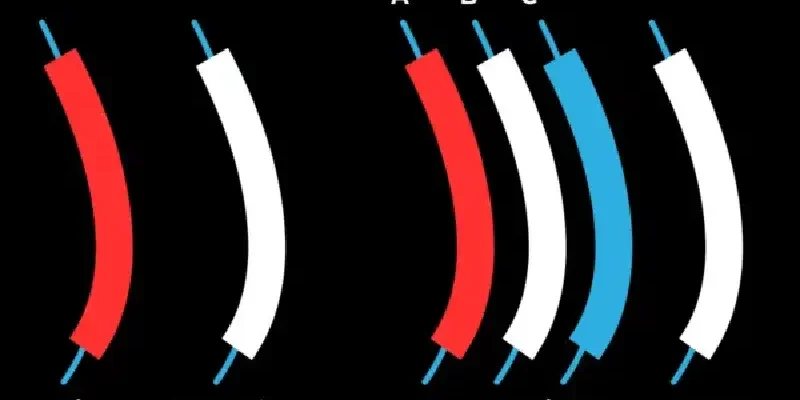
Single-phase power is a common form of alternating current (AC) utilized predominantly in residential settings. In essence, single-phase power involves a single loop or circuit of electrical current. This setup is sufficient for powering household electronics, lighting, and small appliances. Despite the appearance of two hot wires (black and red) alongside a neutral wire in typical household wiring, single-phase power operates through one continuous loop.
Operation Details
Single-phase power is generated by an AC generator that creates a single circuit of alternating current. This circuit forms a closed loop, commencing from the generator, traversing through a transformer, and ultimately powering residential electrical systems. The generation process involves the push-pull mechanism of AC current, ensuring a consistent flow of electricity.
Applications and Use Cases
Single-phase power is ideal for residential environments. It efficiently powers lights, refrigerators, washing machines, and smaller air conditioning units. Its simplicity and cost-effectiveness make it the preferred choice for homes and small commercial establishments with moderate power demands.
Exploring Three-Phase Power
Advanced Dynamics
Three-phase power, a more robust and efficient form of electrical distribution, is essential in industrial and large-scale commercial settings. It involves three interlinked circuits or loops, each 120 degrees out of phase with the others, resulting in a continuous and reliable power supply.
Mechanics and Generation
In three-phase systems, the AC generator operates with three separate windings, each offset by 120 degrees. This arrangement ensures that the power supply never drops to zero, providing a constant and balanced flow of electricity. This is critical for heavy machinery, large motors, and expansive HVAC systems, which require uninterrupted power to function efficiently.
Significance and Applications
The consistency and strength of three-phase power make it indispensable for industrial applications. It powers high-capacity equipment, large motors, and infrastructure in manufacturing plants, hospitals, and commercial buildings. The seamless power delivery supports the heavy electrical loads and critical systems required in these environments.
Comparative Analysis
Efficiency and Reliability
Three-phase power systems offer superior efficiency and reliability compared to single-phase systems. The balanced power distribution minimizes voltage drops and provides a stable electrical supply, crucial for high-load environments. In contrast, single-phase power, while adequate for residential use, does not offer the same level of efficiency for larger applications.
Cost and Installation Considerations
While three-phase systems are more complex and costly to install, their benefits in commercial and industrial settings far outweigh the initial investment. The continuous power supply reduces wear on equipment and enhances operational efficiency. Single-phase systems are simpler and more cost-effective for residential installations, providing adequate power for domestic needs.
Application Suitability
Single-phase power is ideal for residences and small businesses with lower power requirements. It supports everyday electrical needs without unnecessary complexity. Three-phase power, however, is essential for environments with substantial and consistent power demands, ensuring operational stability and efficiency in large-scale applications.
Practical Examples and Use Cases
Residential Applications of Single-Phase Power
Typical uses of single-phase power include household lighting, small kitchen appliances, and home HVAC systems. The straightforward and reliable nature of single-phase power meets the demands of daily living with ease.
Commercial and Industrial Uses of Three-Phase Power
Three-phase power is paramount in commercial buildings, factories, and large institutions. It drives high-performance HVAC systems, industrial compressors, large refrigeration units, and other critical infrastructure. The continuous power flow is necessary for maintaining operational efficiency and reducing downtime in these settings.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between single-phase and three-phase power systems is vital for selecting the appropriate electrical infrastructure. At Viox Electric, we are committed to delivering expertise and support to ensure our clients’ electrical systems are optimized for their specific needs. Whether it’s a residential setup or an industrial installation, knowing the intricacies of your power supply can significantly impact performance and efficiency.
For further insights or assistance with your electrical systems, connect with Viox Electric. Our team of experts is here to guide you through the complexities of power distribution, ensuring you make informed decisions tailored to your requirements.
Contact us today to learn more about optimizing your electrical systems with Viox Electric.