When electrical systems malfunction, the consequences can be catastrophic—fires, equipment damage, and even loss of life. Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCBs) serve as the first line of defense, automatically detecting and interrupting dangerous electrical conditions before they cause irreversible damage. Understanding how MCBs prevent damage during electrical overloads or short circuits is essential for anyone working with electrical systems or seeking to protect their property and equipment.
Modern electrical protection has evolved significantly from simple fuses to sophisticated circuit breakers that offer superior safety, reliability, and convenience. MCBs represent the gold standard in residential and light commercial electrical protection, combining advanced thermal and magnetic detection mechanisms with user-friendly operation and maintenance.
Learn how Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCBs) prevent damage during electrical overloads or short circuits, ensuring safety and reliability in electrical systems.
Що таке мініатюрні автоматичні вимикачі (MCB)?
Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCBs) are automatic electrical switches designed to protect electrical circuits from damage caused by overcurrent conditions. Unlike traditional fuses that require replacement after operation, MCBs can be reset and reused multiple times, making them both economical and environmentally friendly.
MCBs operate as sophisticated safety devices that continuously monitor electrical current flow through circuits. When current exceeds safe operating limits—whether from overloads or short circuits—the MCB automatically interrupts power flow to prevent equipment damage, fires, and electrical hazards.
Key Components of MCBs
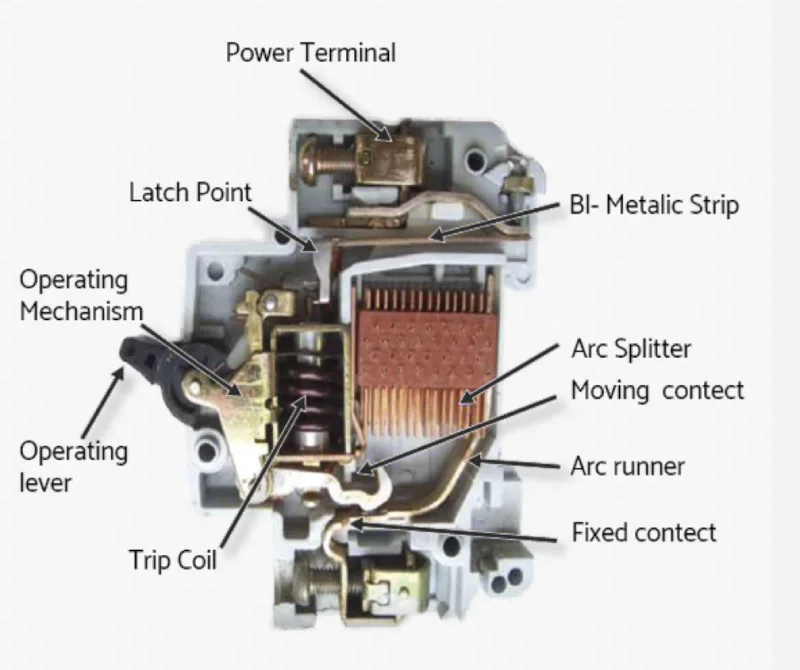
The internal structure of an MCB contains several critical components working in harmony to provide comprehensive electrical protection:
- Bimetallic strip: Provides thermal protection against overloads
- Electromagnetic coil: Offers magnetic protection against short circuits
- Arc chute: Safely extinguishes electrical arcs during contact separation
- Operating mechanism: Controls contact opening and closing
- Trip lever: Triggers circuit interruption when faults occur
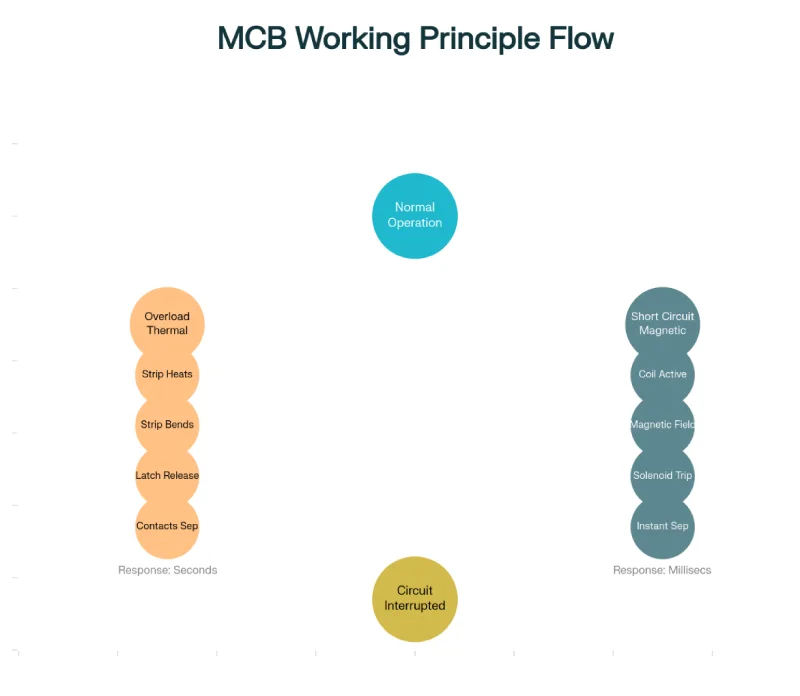
How MCBs Work: The Dual Protection Mechanism
MCBs employ a sophisticated dual protection mechanism that combines thermal and magnetic detection to safeguard electrical circuits against different types of faults. This comprehensive approach ensures reliable protection across a wide range of electrical conditions.
Thermal Protection for Overloads
Thermal protection handles gradual overcurrent conditions that develop over time, typically caused by equipment overloading or excessive demand on circuits. The process works as follows:
- Current monitoring: The bimetallic strip continuously monitors current flow through the circuit
- Heat generation: When current exceeds rated capacity, resistive heating occurs in the strip
- Thermal expansion: The bimetallic strip heats up and begins to bend due to differential expansion
- Mechanical release: Strip deflection releases the mechanical latch mechanism
- Contact separation: Moving contacts separate from fixed contacts, interrupting current flow
The thermal protection mechanism typically responds within 1-60 seconds depending on the severity of the overload. This time delay prevents nuisance tripping from temporary current surges while ensuring protection against sustained overloads.
Magnetic Protection for Short Circuits
Magnetic protection provides instantaneous response to short circuit conditions where current can increase to dangerous levels within milliseconds. The electromagnetic protection system operates through:
- Rapid detection: The electromagnetic coil detects sudden current increases
- Magnetic field generation: High current creates a strong magnetic field in the coil
- Solenoid activation: The magnetic field energizes a solenoid or plunger mechanism
- Instant tripping: The plunger strikes the trip lever, immediately releasing contacts
- Arc extinction: The arc chute safely extinguishes any electrical arc formed during contact separation
Magnetic protection responds in less than 10 milliseconds for high-magnitude short circuits, providing virtually instantaneous protection.
MCB vs. Fuse: Why MCBs Offer Superior Protection
While both MCBs and fuses provide electrical protection, MCBs offer significant advantages that make them the preferred choice for modern electrical installations. Understanding these differences helps explain why MCBs have largely replaced fuses in contemporary applications.
MCB vs Fuse Comparison
| Особливість | MCB | Запобіжник. |
|---|---|---|
| Reusability | Reset & reuse | Single-use |
| Час відгуку | 20ms response | 2ms response |
| Protection Type | Overload + SC | Overload only |
| Operating Method | Manual/auto | Auto only |
| Вартість | Вища вартість | Lower cost |
| Обслуговування | Low maintain | Needs replace |
| Безпека | Safe handling | Shock risk |
| Поточний рейтинг | Up to 100A | Wide range |
| Пропускна здатність | 15kA limit | High capacity |
| Заявка | Domestic/light | Dom to heavy |
Key Advantages of MCBs Over Fuses
Reusability and Cost Effectiveness: MCBs can be reset and reused indefinitely, while fuses require replacement after each operation. This reusability significantly reduces long-term maintenance costs and ensures continued protection without service interruption.
Підвищена безпека: MCBs eliminate the shock hazard associated with fuse replacement. The reset operation can be performed safely without touching live electrical parts, unlike fuse replacement which may expose users to dangerous voltages.
Clear Fault Indication: When an MCB trips, its position clearly indicates the fault condition. This visual indication helps troubleshoot electrical problems quickly, while blown fuses may not provide obvious visual confirmation of failure.
Selective Protection: MCBs offer more precise current ratings and can be selected for specific applications. This selectivity allows for better coordination between protection devices and reduces unnecessary power outages.
Types of MCBs and Their Applications
Different MCB types provide optimized protection for various electrical applications. Understanding these MCB characteristics helps ensure proper selection for specific circuit requirements.
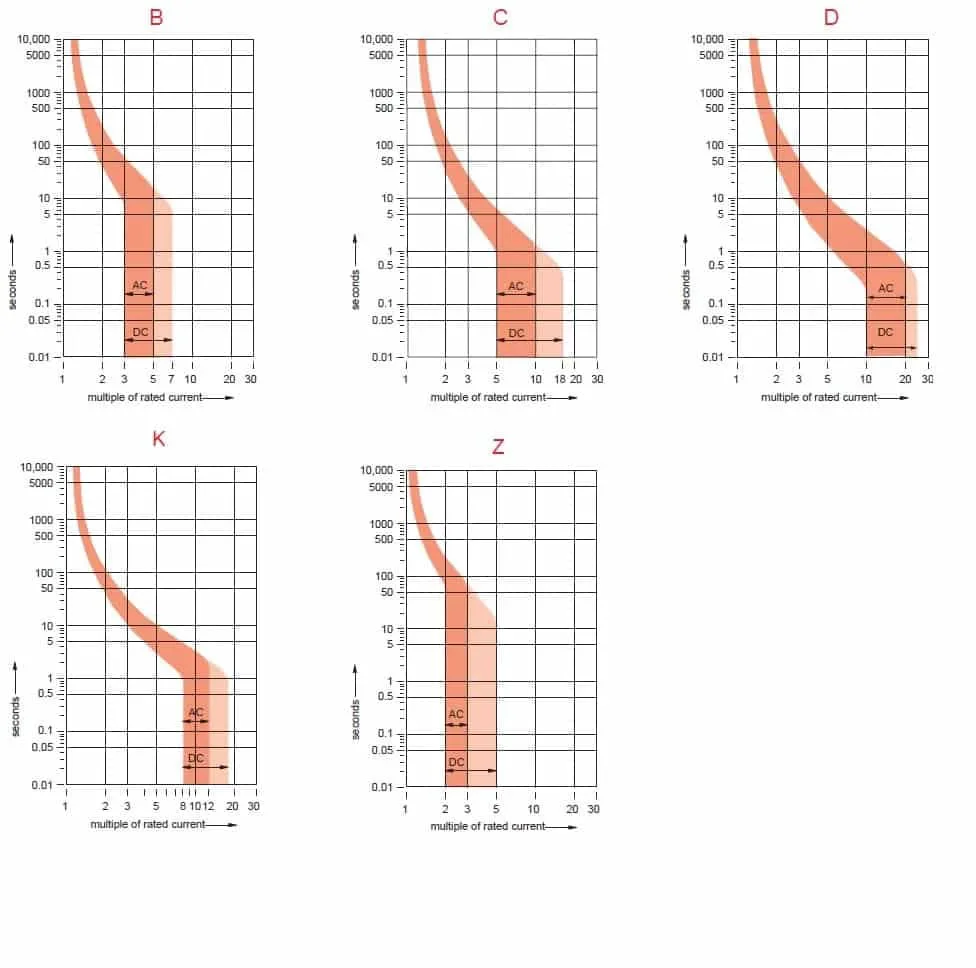
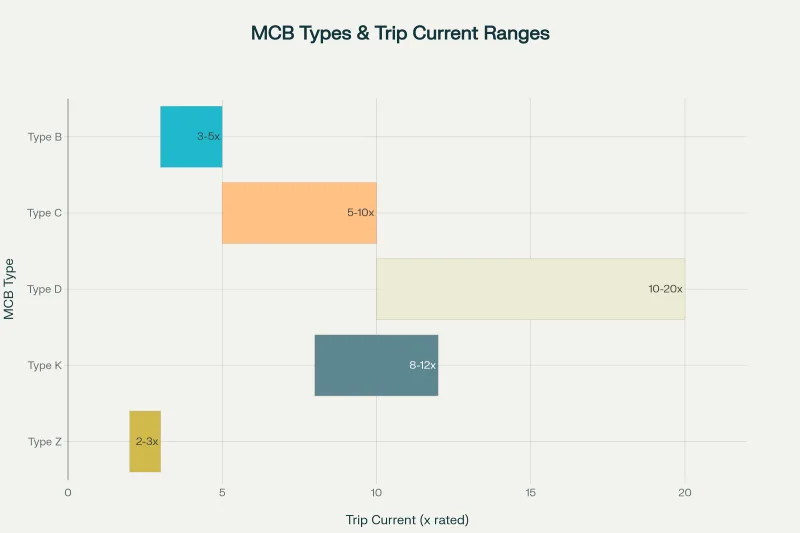
MCB Trip Curve Classifications
автоматичні вимикачі типу B (3-5x rated current): Designed for residential and light commercial applications. These breakers provide sensitive protection suitable for lighting circuits, small appliances, and electronic equipment where high inrush currents are not expected.
автоматичні вимикачі типу C (5-10x rated current): Ideal for motor circuits and general industrial applications. The moderate trip threshold accommodates normal motor starting currents while maintaining protection against sustained overloads and short circuits.
автоматичні вимикачі типу D (10-20x rated current): Engineered for heavy industrial machinery and welding equipment. These breakers withstand high inrush currents associated with large motors, transformers, and welding machines without nuisance tripping.
Type K MCBs (8-12x rated current): Specifically designed for motor protection applications. These specialized breakers provide optimized protection characteristics for motor starting and running conditions.
Type Z MCBs (2-3x rated current): Ultra-sensitive protection for electronic circuits and semiconductor equipment. The low trip threshold provides maximum protection for sensitive equipment vulnerable to small overcurrents.
MCB Installation and Maintenance Best Practices
Правильно MCB installation and maintenance ensures reliable operation and extends service life. Following established procedures protects both equipment and personnel while maintaining optimal electrical system performance.
Посібник з монтажу
Proper sizing: Select MCBs with current ratings matching circuit requirements. Undersized breakers cause nuisance tripping, while oversized breakers may not provide adequate protection.
Екологічні міркування: Install MCBs in clean, dry locations within specified temperature ranges. Avoid areas with excessive moisture, dust, or corrosive atmospheres that could impair operation.
Mounting and connections: Secure MCBs properly to DIN rails and ensure tight electrical connections. Loose connections create resistance heating that can cause premature failure or fire hazards.
Вимоги до технічного обслуговування
Regular inspection: Conduct annual visual inspections for signs of overheating, corrosion, or mechanical damage. Look for discoloration, burnt contacts, or unusual wear patterns that indicate problems.
Functional testing: Test MCB operation periodically by manually operating the switch mechanism. This exercise helps maintain proper mechanical function and identifies potential issues before they become critical.
Cleaning and lubrication: Remove dust and debris that can accumulate on MCB surfaces. Clean contacts and moving parts help ensure reliable operation and prevent corrosion-related failures.
Record keeping: Maintain detailed records of all maintenance activities, including inspection dates, test results, and any corrective actions taken. This documentation helps track performance trends and plan future maintenance activities.
Benefits and Applications of MCB Protection
MCBs provide comprehensive electrical protection across diverse applications, from residential homes to industrial facilities. Their versatility and reliability make them indispensable components of modern electrical systems.
Житлові програми
Home electrical panels: MCBs protect individual circuits throughout residential properties. They safeguard lighting, outlet, and appliance circuits from overloads and short circuits while providing convenient reset capability for homeowners.
Kitchen and bathroom protection: GFCI-equipped MCBs provide enhanced protection in wet locations. These specialized breakers combine overcurrent protection with ground fault detection for maximum safety in high-risk areas.
Whole-house surge protection: MCBs work with surge protective devices to create comprehensive electrical protection systems. This coordination protects both the electrical system and connected equipment from power quality issues.
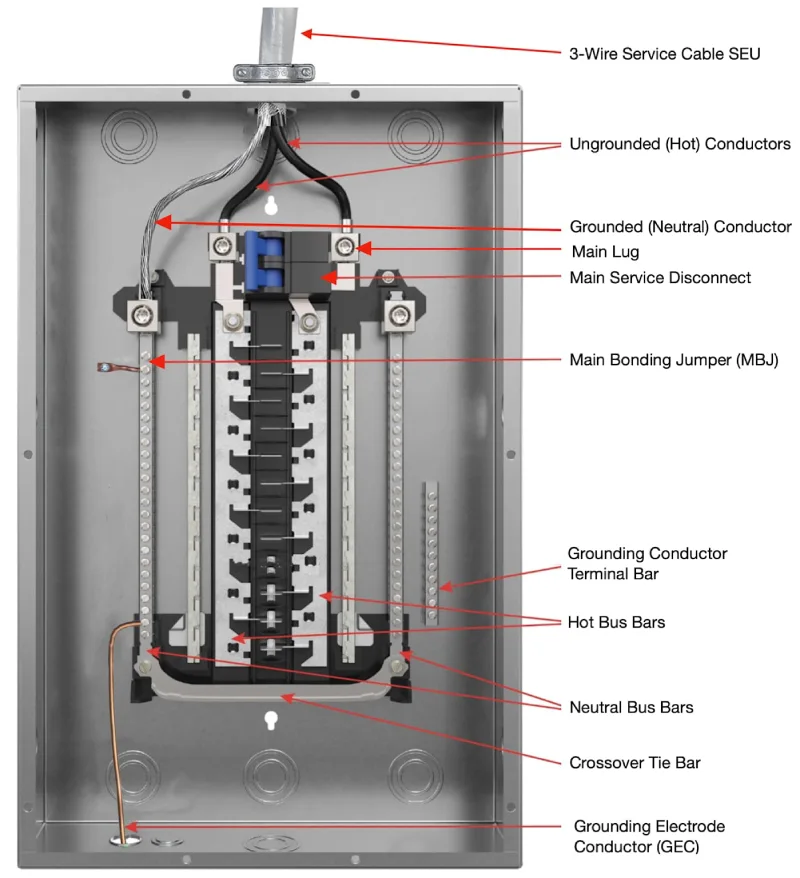
Комерційне та промислове застосування
Motor protection: MCBs provide reliable protection for motors, pumps, and other rotating machinery. Proper MCB selection ensures motors receive appropriate protection while avoiding unnecessary shutdowns.
Control panel protection: MCBs protect control circuits and instrumentation in industrial control panels. Their compact size and reliable operation make them ideal for space-constrained applications.
Emergency systems: MCBs provide critical protection for emergency lighting, fire alarm systems, and other life safety equipment. Their reliability ensures these systems remain operational when needed most.
Advanced MCB Technologies and Future Developments
Modern MCB technology continues evolving to meet changing electrical protection needs. Understanding these advances helps engineers and technicians select the most appropriate protection solutions.
Smart MCB Features
Electronic trip units: Advanced MCBs incorporate electronic sensing and control systems for precise protection. These systems offer adjustable trip characteristics and enhanced diagnostic capabilities.
Комунікаційні можливості: Smart MCBs can communicate status information to building management systems. This connectivity enables remote monitoring and predictive maintenance strategies.
Виявлення дугових замикань: Some MCBs include arc fault circuit interrupter (AFCI) technology. This feature detects dangerous electrical arcs that could cause fires and automatically interrupts the circuit.
Energy Efficiency Considerations
Reduced power losses: Modern MCBs minimize resistive losses during normal operation. Lower losses reduce energy consumption and heat generation in electrical panels.
Improved materials: Advanced contact materials and arc extinction techniques enhance MCB performance and longevity. These improvements reduce maintenance requirements and extend service life.
Conclusion and Best Practices
MCBs prevent damage during electrical overloads or short circuits through sophisticated dual protection mechanisms that have revolutionized electrical safety. Their combination of thermal and magnetic detection provides comprehensive protection against diverse electrical faults while offering superior convenience and reliability compared to traditional fuses.
Key Takeaways for Electrical Safety
- Choose appropriate MCB types based on specific application requirements and load characteristics
- Ensure proper installation following manufacturer guidelines and electrical codes
- Implement regular maintenance programs to maintain optimal performance and reliability
- Consider advanced features like GFCI and AFCI protection for enhanced safety
- Plan for future needs when designing electrical systems and selecting protection devices
Understanding how MCBs work and implementing proper selection, installation, and maintenance practices ensures reliable electrical protection for years to come. As electrical systems become increasingly complex and critical to daily operations, the role of MCBs in preventing damage and ensuring safety becomes ever more important.
For those working with electrical systems, whether as professionals or property owners, investing in quality MCB protection and following established best practices provides peace of mind and protects valuable equipment and property from electrical hazards.
Пов'язане
5 головних причин, чому ваш автоматичний вимикач постійно спрацьовує, та як їх виправити
Автоматичні вимикачі проти мініатюрних автоматичних вимикачів: повний порівняльний посібник


