Key Takeaways
- Circuit breakers are classified by voltage level (low, medium, high), arc-quenching medium (air, vacuum, SF6, oil), application (residential, commercial, industrial), and trip characteristics (Type A, B, C, D).
- MCBs (6-125A) suit residential applications, while MCCBs (100-2500A) serve commercial/industrial needs, and ACBs (800-6300A) protect heavy industrial systems.
- Specialized breakers like RCCB/RCD prevent electric shock through leakage detection, AFCI stops arc faults, and MPCB protects motors specifically.
- Selection criteria include rated current, breaking capacity, voltage class, environmental conditions, and compliance with IEC/ANSI/NEC standards.
- VIOX Electric manufactures comprehensive circuit breaker solutions with advanced arc-quenching technology and remote monitoring capabilities for optimal electrical safety.
Circuit breakers serve as the cornerstone of modern electrical safety systems, automatically interrupting current flow when faults occur to prevent equipment damage, fires, and electric shock hazards. Understanding the various types of circuit breakers and their specific applications is critical for electrical engineers, facility managers, and procurement professionals in selecting appropriate protection devices for residential, commercial, and industrial installations.

Understanding Circuit Breaker Classification Systems
Circuit breakers can be classified through multiple frameworks, each serving distinct engineering and application requirements. The four primary classification systems are:
Classification by Voltage Level
Low Voltage Circuit Breakers (Up to 1000V AC / 1500V DC)
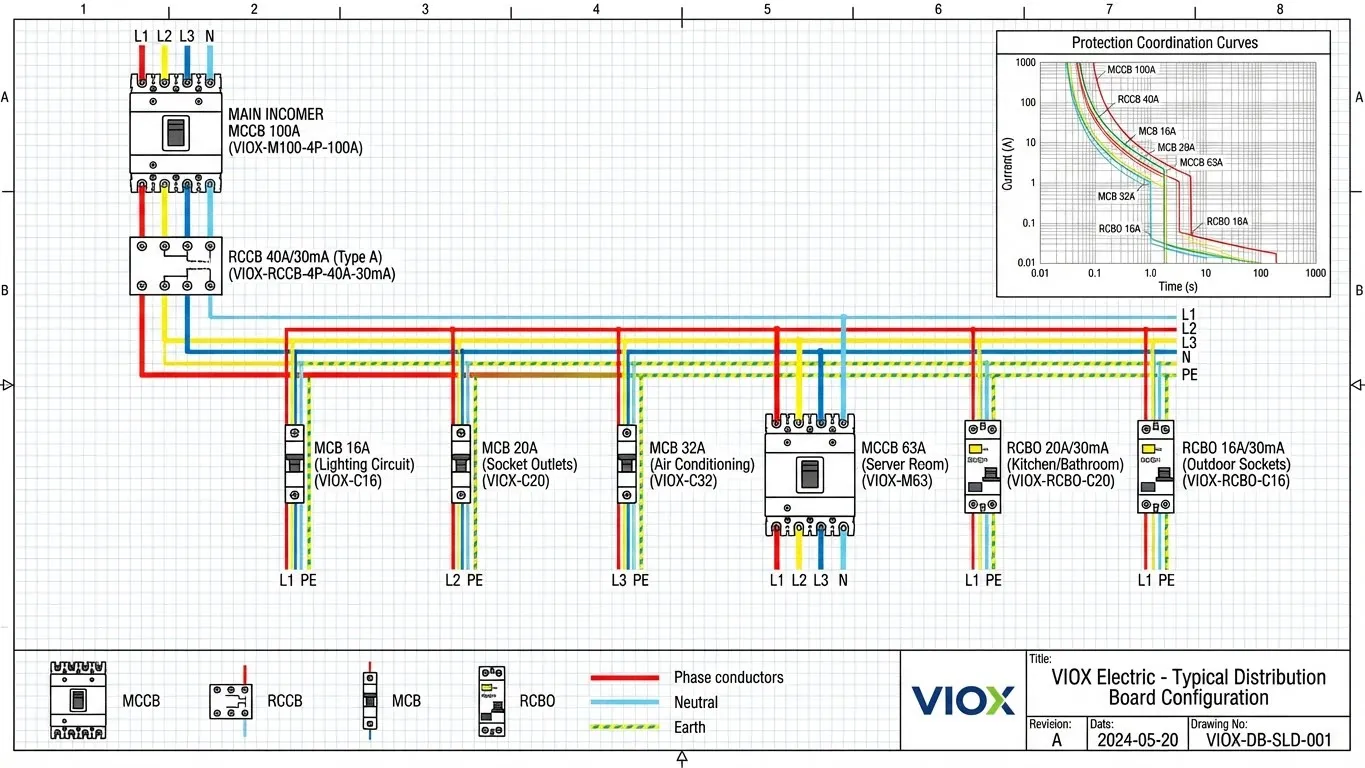
Low voltage breakers dominate residential, commercial, and light industrial applications. This category includes MCBs, MCCBs, and ACBs, designed for systems operating below 1 kV AC. VIOX Electric’s low voltage portfolio covers ratings from 6A to 6300A, providing comprehensive protection for distribution networks, motor control centers, and building electrical systems.
Medium Voltage Circuit Breakers (1kV to 72.5kV)
Medium voltage breakers protect utility distribution systems, industrial substations, and large commercial facilities. Vacuum Circuit Breakers (VCB) and SF6 Circuit Breakers excel in this voltage class, offering superior arc interruption performance. VIOX VCBs utilize advanced vacuum interrupter technology for maintenance-free operation in demanding industrial environments.
High Voltage Circuit Breakers (Above 72.5kV)
High voltage breakers safeguard transmission lines, large power plants, and utility substations. SF6 circuit breakers and Gas-Insulated Switchgear (GIS) predominate in this category, handling fault currents exceeding 50kA. These systems demand specialized engineering expertise and rigorous testing protocols per IEEE C37 standards.
Classification by Arc-Quenching Medium
The arc-extinction mechanism fundamentally determines breaker performance, reliability, and maintenance requirements:
| Arc Medium | Voltage Range | Key Advantages | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Air | Up to 15kV | Cost-effective, visible operation | Low voltage industrial panels |
| Vacuum | 3.3kV – 40.5kV | Maintenance-free, long life | Medium voltage distribution |
| SF6 Gas | 12kV – 800kV | Superior dielectric strength | High voltage substations |
| Oil | Up to 220kV | Proven technology (legacy) | Older transmission systems |
Classification by Application and Protection Function
Overcurrent Protection Breakers
Standard MCBs and MCCBs provide thermal-magnetic overcurrent protection, utilizing bimetallic strips for overload detection and electromagnetic coils for short-circuit response. VIOX thermal-magnetic breakers offer adjustable trip curves (Type B, C, D) to match specific load characteristics.
Ground Fault Protection Breakers
RCCBs, RCDs, and GFCIs detect residual current imbalances indicating ground faults, typically tripping at 30mA (personnel protection) or 300mA (fire prevention). These devices prevent electric shock by disconnecting circuits within 30 milliseconds of fault detection.
Arc Fault Protection Breakers
AFCIs employ sophisticated electronics to identify dangerous arcing conditions in damaged wiring, preventing electrical fires. Mandatory in residential bedrooms per NEC 210.12, AFCIs distinguish between harmless arcs (switch operation) and hazardous series/parallel arcing.
Motor Protection Breakers
MPCBs integrate thermal overload protection, magnetic short-circuit protection, and phase-loss detection specifically calibrated for motor starting currents and locked-rotor conditions. VIOX MPCBs feature adjustable thermal settings from 0.6x to 1x rated current.
Detailed Analysis of Major Circuit Breaker Types
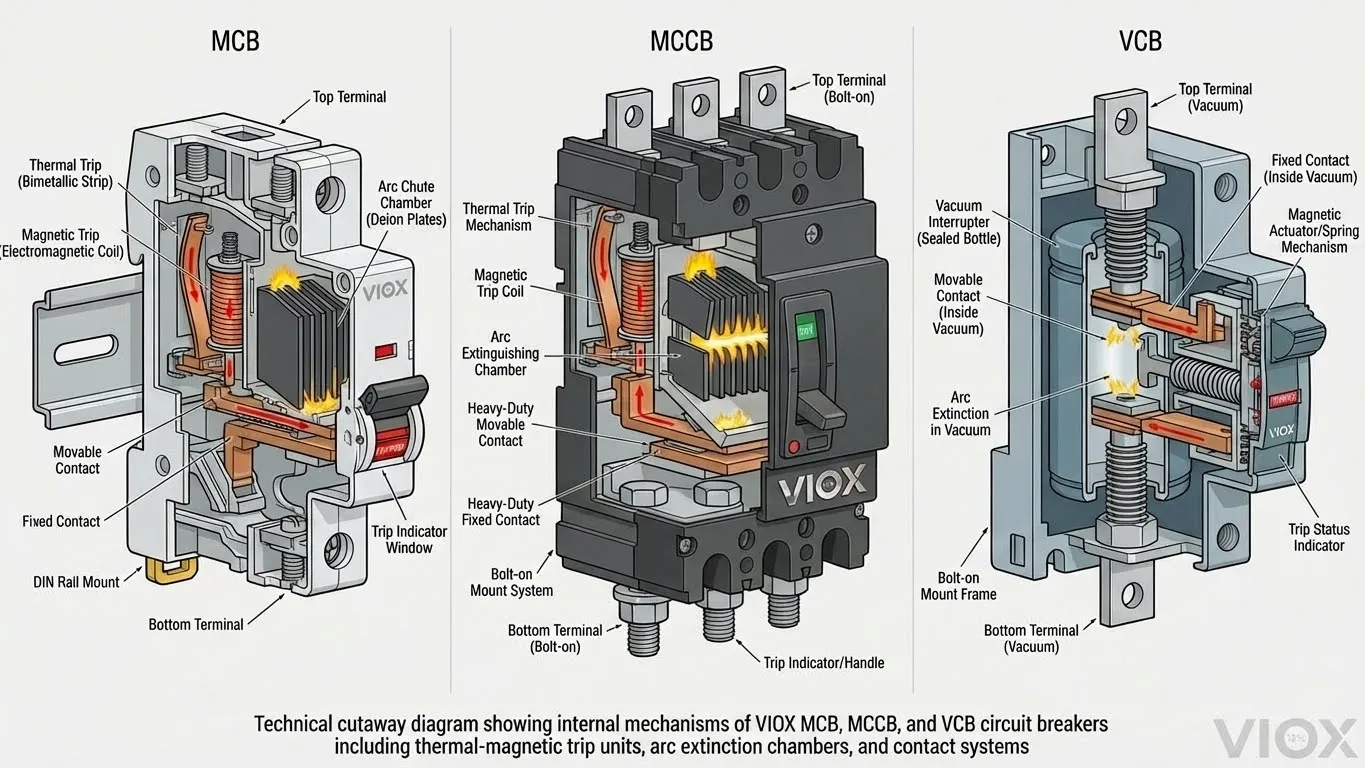
Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCB)
Technical Specifications
Miniature Circuit Breakers represent the most common protection device in residential and light commercial installations, with current ratings from 6A to 125A and breaking capacities up to 10kA (IEC 60898) or 18kA for industrial-grade units.
Operating Principle
MCBs employ a thermal-magnetic trip mechanism combining:
- Thermal protection: Bimetallic strip deflection during sustained overload (typically 1.13x to 1.45x rated current)
- Magnetic protection: Electromagnetic coil actuation during short circuits (3x to 50x rated current depending on type)
Trip Characteristics and Selection
| Type | Trip Range | Typical Applications | VIOX Model Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type B | 3-5 x In | Residential lighting, general outlets | VIOX-B Series MCB |
| Type C | 5-10 x In | Commercial loads, small motors | VIOX-C Series MCB |
| Type D | 10-20 x In | Transformers, welding equipment | VIOX-D Series MCB |
| Type K/Z | 8-14 x In | Specialized industrial applications | VIOX-K Series MCB |
Application Guidelines
MCBs excel in branch circuit protection where:
- Normal operating current remains below 100A
- Available fault current stays under 10kA
- Space constraints demand compact protection (18mm modular width)
- Frequent reset operations are anticipated
- Cost optimization is prioritized
For residential installations, VIOX recommends Type B MCBs for lighting circuits and Type C for socket outlets and small appliance circuits. Commercial installations typically utilize Type C MCBs with 10kA breaking capacity as minimum specification.
Molded Case Circuit Breakers (MCCB)
Engineering Specifications
MCCBs bridge the gap between miniature circuit breakers and air circuit breakers, offering current ratings from 100A to 2500A with breaking capacities reaching 200kA. VIOX MCCBs feature adjustable thermal-magnetic or electronic trip units, providing flexible protection coordination.
Construction Features
The molded case construction provides:
- Arc chutes for rapid arc extinction using deion grids
- Robust housing resistant to mechanical stress and environmental factors
- Modular accessories (shunt trips, undervoltage releases, auxiliary contacts)
- Drawout or fixed mounting configurations
- Terminal options (lug, ring, bus bar connection)
Electronic Trip Units
Advanced VIOX MCCBs incorporate microprocessor-based trip units offering:
- Long-time delay (overload): 0.4x to 1x In with 1-200s delay
- Short-time delay (fault): 1.5x to 10x In with 0.05-0.5s delay
- Instantaneous (short-circuit): 2x to 15x In with <0.01s response
- Ground fault protection: Adjustable sensitivity 0.2-1x In, 0.1-1s delay
Selection Criteria Table
| Parameter | Residential/Light Commercial | Heavy Commercial | Industrial |
|---|---|---|---|
| Current Rating | 100-250A | 250-800A | 400-2500A |
| Breaking Capacity | 25-50kA | 50-100kA | 85-200kA |
| Trip Unit | Thermal-Magnetic | Electronic (optional) | Electronic (required) |
| Coordination | Basic | Selective | Fully coordinated |
| VIOX Series | VIOX-M100 Series | VIOX-M400 Series | VIOX-M1600 Series |
Real-World Applications
- Commercial Buildings: Main distribution panels, elevator feeders, HVAC equipment protection
- Industrial Facilities: Motor control centers, welding equipment, PLC/automation systems
- Data Centers: UPS distribution, critical power feeders requiring high reliability
- Marine Applications: Ship power distribution, thruster motors, generator protection
VIOX MCCBs meet IEC 60947-2, UL 489, and marine certifications (DNV, ABS, LR) for versatile deployment across global markets.

Air Circuit Breakers (ACB)
High-Current Protection Systems
Air Circuit Breakers serve as the workhorse protection device for industrial main distribution and large commercial facilities, handling current ratings from 800A to 6300A with breaking capacities up to 150kA.
Arc Interruption Technology
VIOX ACBs employ sophisticated arc extinction using:
- Deion Arc Chutes: Segmented metal plates that divide and cool the arc
- Magnetic Blowout Coils: Electromagnetic forces driving the arc into chutes
- Pressurized Air Flow: Enhanced cooling and ionization reduction
- Arc Runners: Extended paths increasing arc voltage and energy dissipation
Control and Protection Features
Modern VIOX ACBs integrate:
- Microprocessor-based protection relays with LCD displays
- Programmable trip curves (I²t, definite time, inverse time)
- Power quality monitoring (harmonics, power factor, demand)
- Communication protocols (Modbus RTU, Profibus, Ethernet/IP)
- Remote operation capability via shunt close/trip coils
- Zone selective interlocking (ZSI) for fault isolation
Typical Applications and Specifications
| Application | Current Rating | Breaking Capacity | VIOX Model | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main Incomer | 1600-6300A | 65-150kA | VIOX-ACB-6300 | Drawout, electronic trip, metering |
| Bus Coupler | 1600-4000A | 85-100kA | VIOX-ACB-4000 | Automatic transfer, paralleling |
| Generator Protection | 800-3200A | 50-85kA | VIOX-ACB-G Series | Reverse power, frequency protection |
| Motor Feeder | 800-2000A | 50-85kA | VIOX-ACB-M Series | Motor starting curves, stall detection |
Installation Environments
ACBs require professional installation in controlled environments:
- Switchgear rooms with adequate ventilation
- Temperature range: -5°C to +40°C (standard), -25°C to +55°C (special)
- Humidity: Up to 95% non-condensing
- Altitude: Up to 2000m (derating required above)
- Pollution degree: 3 per IEC 60664-1
Residual Current Circuit Breakers (RCCB/RCD)
Life-Safety Protection Devices
RCCBs detect potentially lethal ground fault currents that standard overcurrent devices cannot sense, tripping when residual current (difference between line and neutral) exceeds preset thresholds.
Operating Principle
VIOX RCCBs utilize differential current transformers monitoring phase and neutral conductors:
- Under normal conditions: ΣI(in) = ΣI(out), net flux = 0
- Ground fault: Leakage current creates flux imbalance
- Secondary coil induces voltage proportional to leakage
- Trip mechanism actuates when threshold exceeded (typically 30ms)
Sensitivity Classifications
| Type | Sensitivity | Response Time | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10mA | Ultra-sensitive | <10ms | Medical locations, swimming pools |
| 30mA | Standard | <30ms | Personnel protection (residential/commercial) |
| 100mA | Equipment | <130ms | Fire prevention, commercial/industrial |
| 300mA | Fire protection | <150ms | Large installations, fire risk areas |
AC vs. A vs. B Type Selection
- Type AC: Responds to AC residual sinusoidal current (basic residential)
- Type A: Detects AC + pulsating DC (washing machines, variable drives)
- Type B: Comprehensive including smooth DC, high-frequency (solar inverters, EV chargers, medical equipment)
VIOX Type B RCCBs meet stringent requirements for modern electronic loads, preventing nuisance tripping while maintaining protection integrity.
Critical Applications
- Bathrooms, kitchens, outdoor outlets (30mA mandatory per NEC 210.8)
- Construction sites and temporary installations (30mA required)
- Healthcare facilities (10mA for patient care areas per IEC 60364-7-710)
- Swimming pools and fountains (10mA or 30mA depending on zone)
- Commercial kitchens and food preparation areas (30mA recommended)
Residual Current Breaker with Overcurrent (RCBO)
Combined Protection Solution
RCBOs integrate MCB overcurrent protection with RCCB ground fault detection in a single device, offering space-efficient comprehensive protection. VIOX RCBOs combine Type C trip characteristics with 30mA Type A residual current sensing.
Technical Advantages
- Compact installation: Single module width (18mm) vs. MCB+RCCB combination
- Individual circuit isolation: Fault on one circuit doesn’t affect others
- Simplified troubleshooting: Combined indication for fault type
- Enhanced discrimination: Both overcurrent and residual current selectivity
Application Comparison
| Installation Type | MCB + RCCB | RCBO | VIOX Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| New residential | Group protection | Individual circuits | RCBO for critical loads |
| Renovation | Existing MCB board | Replace selected MCBs | RCBO for wet areas |
| Commercial | Feeder protection | Branch protection | Mixed approach |
| Cost consideration | Lower per circuit | Higher per circuit | Depends on fault isolation needs |
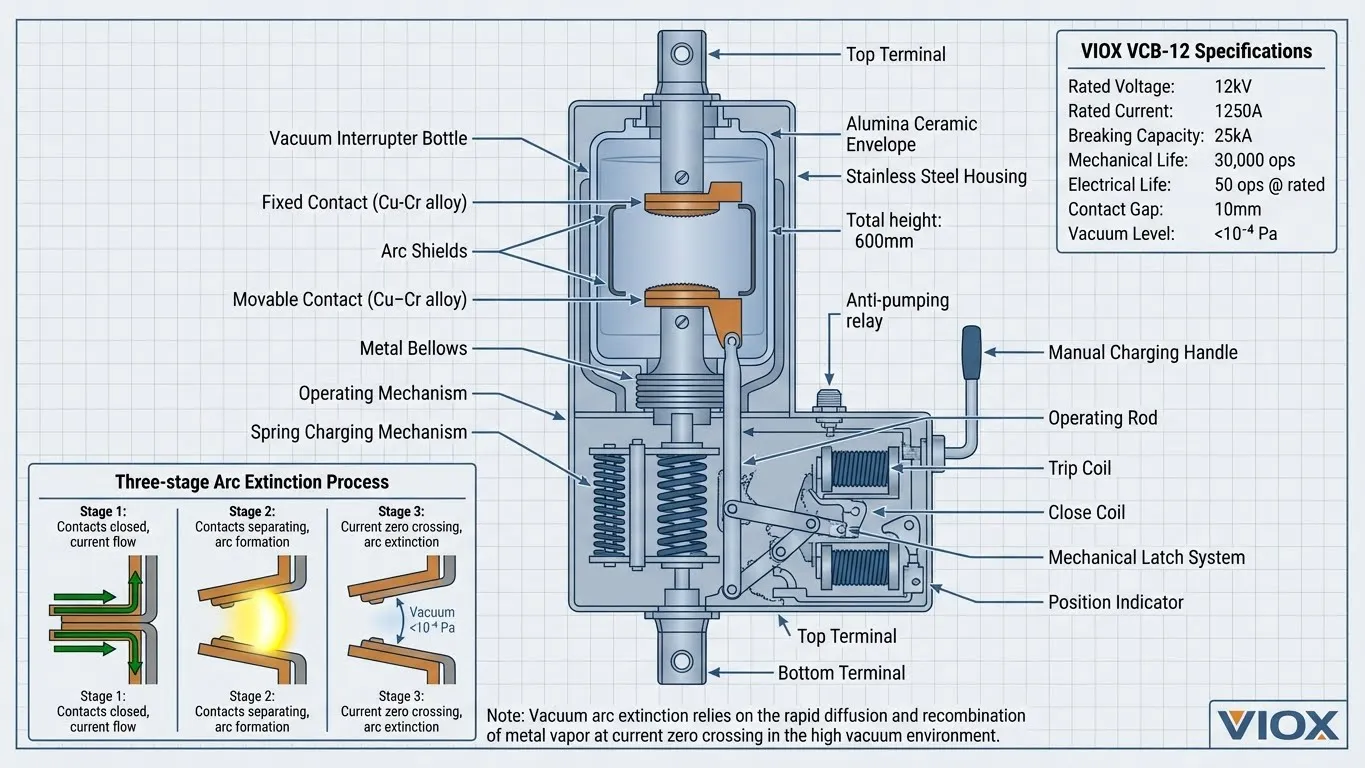
Vacuum Circuit Breakers (VCB)
Medium Voltage Excellence
Vacuum Circuit Breakers dominate medium voltage applications (3.3kV to 40.5kV), utilizing vacuum as the arc-quenching medium within sealed interrupter chambers. VIOX VCBs feature extended contact life exceeding 30,000 operations with minimal maintenance requirements.
Technical Superiority
Arc Interruption in Vacuum
- Vacuum pressure: <10⁻⁴ Pa (near-perfect insulation)
- Contact separation: 5-20mm (voltage dependent)
- Arc duration: <1 cycle at current zero
- Dielectric recovery: Instantaneous upon arc extinction
Construction Components
- Vacuum Interrupter: Sealed ceramic or glass envelope containing contacts
- Operating Mechanism: Spring-charged or motor-operated actuator
- Control Cubicle: Microprocessor protection relay and HMI
- Current Transformers: Precision metering and protection
- Insulation System: Epoxy or air-insulated bus bars
Performance Specifications
| Parameter | Indoor VCB | Outdoor VCB | VIOX Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage Class | 7.2kV – 40.5kV | 12kV – 40.5kV | IEC 62271-100 |
| Current Rating | 630A – 4000A | 630A – 3150A | Continuous duty |
| Breaking Current | 20kA – 50kA | 20kA – 40kA | 3-second rating |
| Mechanical Life | 30,000 ops | 20,000 ops | Type tested |
| Electrical Life | 50 ops at rated | 50 ops at rated | Full short-circuit |
Industrial Applications
- Manufacturing plants: Motor feeders, transformer protection, bus sectionalizers
- Mining operations: Variable frequency drives, longwall systems, dragline excavators
- Utility distribution: Pad-mounted switchgear, substations, ring main units
- Renewable energy: Wind farm collection, solar inverter combining, battery storage
- Marine vessels: Medium voltage distribution, propulsion drives, bow thrusters
VIOX VCBs incorporate intelligent electronic devices (IEDs) with IEC 61850 communication for seamless integration into SCADA systems, enabling predictive maintenance and operational analytics.
SF6 Circuit Breakers
High Voltage Protection
Sulfur Hexafluoride (SF6) circuit breakers utilize the superior dielectric and arc-quenching properties of SF6 gas for medium-to-high voltage applications (12kV to 800kV). Despite environmental concerns regarding SF6’s global warming potential (GWP = 23,500), these breakers remain prevalent in transmission systems due to unmatched performance.
Arc Interruption Mechanism
SF6 gas provides:
- Exceptional dielectric strength: 2-3 times air at atmospheric pressure
- Electronegative properties: Rapid arc electron capture
- Thermal conductivity: Efficient heat dissipation
- Chemical stability: Non-toxic, non-flammable (under normal conditions)
Design Variations
Puffer Type: Compressed gas blast from piston movement
Self-Blast Type: Arc energy generates pressure differential
Rotating Arc Type: Magnetic field rotates arc for extended cooling
Application Domains
- Transmission substations: 132kV to 765kV circuit protection
- Gas-insulated switchgear (GIS): Compact substation solutions
- Generator circuit breakers: High continuous current, low voltage
- Industrial substations: 15kV to 36kV distribution systems
Environmental Considerations
VIOX actively researches SF6 alternatives including:
- Fluoronitrile mixtures (3M Novec 4710, GWP <1)
- Synthetic air/CO₂ mixtures
- Vacuum technology extension to higher voltages
- Solid-state breakers for future installations
Motor Protection Circuit Breakers (MPCB)
Specialized Motor Protection
MPCBs integrate thermal overload protection, magnetic short-circuit protection, and manual motor control in a compact device designed specifically for motor circuits. VIOX MPCBs feature adjustable thermal settings accommodating motor service factors and ambient temperature variations.
Protection Functions
Thermal Overload Protection
- Adjustable range: 0.6x to 1.0x rated current
- Class 10 trip: 2-10 seconds at 7.2x setting (motor starting)
- Ambient compensation: Temperature-stable calibration
- Phase loss sensitivity: Detects single-phasing conditions
Magnetic Short-Circuit Protection
- Fixed magnetic trip: Typically 13x rated current ±20%
- Breaking capacity: 50kA to 100kA per IEC 60947-4-1
- Coordination with contactors: Type 2 coordination standard
Application Sizing
| Motor Power | Starter Type | MPCB Rating | VIOX Model | Coordination |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.37-4kW | DOL | 0.6-6.3A | VIOX-MP10 | Contactor Type 2 |
| 5.5-15kW | DOL/Star-Delta | 8-25A | VIOX-MP25 | Contactor Type 2 |
| 18.5-45kW | Star-Delta/Soft Start | 32-63A | VIOX-MP63 | Contactor Type 2 |
| 55-110kW | Soft Start/VFD | 80-160A | VIOX-MP160 | Fuse backup |
Installation Benefits
- Space savings: 45mm width vs. separate overload relay + MCB
- Simplified wiring: Integrated control switch eliminates auxiliary contacts
- Cost reduction: Single device vs. multiple components
- Enhanced safety: Lockout/tagout capability, visible contact position
- Global approvals: IEC, UL, CSA, CE marked for worldwide use
Real-World Case Study
A VIOX customer in automotive manufacturing replaced 847 conventional motor starters with VIOX-MP Series MPCBs, achieving:
- 32% reduction in panel space
- 41% decrease in installation time
- 28% lower total cost of ownership
- Zero nuisance trips during 18-month operation
Circuit Breaker Selection Guide
Decision Framework
Selecting appropriate circuit breakers requires systematic evaluation of electrical parameters, environmental conditions, and operational requirements:
Step 1: Determine System Parameters
- Nominal voltage: 230V, 400V, 690V (LV); 3.3kV, 11kV, 33kV (MV)
- Available fault current: Prospective short-circuit current (PSCC) at installation point
- Normal operating current: Continuous current including future load growth
- Load characteristics: Inductive, resistive, capacitive, motor starting
Step 2: Calculate Required Ratings
- Rated current (In): ≥ 1.25 × maximum continuous load current
- Breaking capacity (Icu/Ics): ≥ Available fault current with safety margin
- Short-time withstand: For selectivity coordination with downstream devices
Quick Reference: Wire Gauge vs. Breaker Rating (Copper Conductors)
Matching the breaker to the wire size is critical to prevent fire hazards. The breaker protects the wire, not just the device. Undersized wiring with oversized breakers creates dangerous conditions where conductors overheat before the breaker trips, potentially igniting building materials.
| Wire Size (AWG) | Wire Size (mm²) | Max Breaker Rating (Amps) | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| 14 AWG | 2.5 mm² | 15A | Lighting circuits, general outlets |
| 12 AWG | 4.0 mm² | 20A | Kitchen outlets, bathroom circuits, laundry |
| 10 AWG | 6.0 mm² | 30A | Water heaters, A/C units, electric dryers |
| 8 AWG | 10.0 mm² | 40A | Electric ranges, large air conditioners |
| 6 AWG | 16.0 mm² | 50-60A | EV chargers, subpanels, heavy appliances |
| 4 AWG | 25.0 mm² | 70-80A | Main feeders, large commercial equipment |
| 2 AWG | 35.0 mm² | 95A | Service entrance conductors, industrial machinery |
Important Notes:
- Values shown are for standard 75°C (167°F) rated copper wire with 60/75°C insulation per NEC Table 310.15(B)(16)
- Always verify with local electrical codes (NEC, IEC, BS 7671) as requirements vary by jurisdiction
- Aluminum wire requires one wire size larger than copper for the same amperage
- For detailed wire sizing information across different standards, see our comprehensive cable size conversion guide
- Standard breaker sizes follow preferred ratings: 15A, 20A, 25A, 30A, 35A, 40A, 45A, 50A, 60A, etc.
- Specific high-amperage applications like 50-amp circuits require careful wire selection and installation practices
For comprehensive guidance on determining your electrical system’s requirements, consult our homeowner’s guide to circuit breaker sizing and load calculation.
Step 3: Environmental Assessment
- Operating temperature: -25°C to +70°C (derating may apply)
- Altitude: Above 2000m requires derating per IEC 60947
- Pollution degree: PD1 (clean), PD2 (normal), PD3 (industrial), PD4 (extreme)
- Vibration/shock: Marine, mobile, seismic considerations
Step 4: Regulatory Compliance
- Building codes: NEC (USA), IEC 60364 (International), BS 7671 (UK)
- Industry standards: IEEE C37 (power systems), UL 489 (molded case)
- Special requirements: Hazardous locations (Class I/II/III), marine (DNV, ABS)
Understanding circuit breaker altitude derating requirements is essential for installations above 2000 meters, where reduced air density affects arc-quenching performance and cooling capacity.
Installation and Maintenance Safety
Installation Requirements
Proper circuit breaker installation is critical for safety and performance. Following professional installation practices prevents 90% of breaker-related failures and ensures code compliance.
1. Qualified Personnel Requirements
All circuit breaker installation, replacement, and maintenance must be performed by licensed electricians per local regulations. In the United States, this typically requires:
- State-issued electrical contractor license
- Journeyman or master electrician certification
- Familiarity with NEC, local amendments, and AHJ requirements
- Proper PPE (Personal Protective Equipment) including arc-rated clothing for energized work
For DIY homeowners considering breaker work, review our guide on how to replace a circuit breaker to understand when professional help is mandatory versus when basic replacement is permissible.
2. De-energization and Lockout/Tagout
OSHA 29 CFR 1910.147 requires:
- Complete de-energization of circuits before work
- Lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures with personal locks
- Voltage verification using calibrated test equipment
- Never work on energized circuits unless qualified for energized work per NFPA 70E
- Multiple person LOTO requires group lockout boxes
3. Terminal Connection Best Practices
Pro Tip: The Importance of Terminal Torque
One of the most common causes of circuit breaker failure isn’t the internal mechanism—it’s loose connections. Field investigations reveal that approximately 30% of breaker-related electrical fires trace back to improperly torqued terminals.
Under-torquing consequences:
- High-resistance connections generate excessive heat (I²R losses)
- Arcing occurs between conductor and terminal, creating carbon deposits
- Progressive heating degrades insulation, eventually melting breaker casing
- Hot connections accelerate metal oxidation, further increasing resistance
- Potential ignition of surrounding combustible materials
Over-torquing risks:
- Sheared terminal screws requiring complete breaker replacement
- Cracked breaker housing compromising insulation integrity
- Damaged conductor strands reducing effective cross-sectional area
- Stripped threads preventing proper future maintenance
VIOX Recommendation:
Always use a calibrated torque screwdriver or torque wrench ensuring connections meet the Newton-meter (Nm) specifications printed on the breaker label or datasheet. For most MCBs: 2.0-2.5 Nm; MCCBs: 4-10 Nm depending on terminal size; ACBs: 10-50 Nm for power terminals.
VIOX torque-controlled installation tools are available through our distributor network, featuring:
- Pre-set torque limiting clutches
- Audible/tactile feedback at correct torque
- Calibration certificates traceable to NIST standards
- Insulated handles rated 1000V for safety
Common Installation Mistakes to Avoid:
- Mixing conductor materials: Never connect aluminum and copper directly—use anti-oxidant compound and proper bi-metal lugs
- Inadequate wire stripping: Too much exposed conductor creates shock hazard; too little prevents solid connection
- Back-stabbing terminals: Always use screw terminals, not push-in connections, for circuits >15A
- Reversed polarity: Line (supply) must connect to fixed contacts; load to movable contacts
- Missing terminal covers: Required per NEC 110.27 for exposed live parts
- Improper wire bending radius: Maintain minimum 5× wire diameter bend radius to prevent insulation damage
4. Clearance Requirements
Maintain NEC 110.26 working space clearances:
- Minimum 3 feet (914mm) depth in front of panels
- 30 inches (762mm) width, or panel width if greater
- 6.5 feet (1.98m) headroom minimum
- No storage, piping, or obstructions in dedicated electrical space
- Adequate illumination (minimum 200 lux at working height)
5. Proper Grounding and Bonding
- Continuous equipment grounding conductor (EGC) connection
- Main bonding jumper only at service entrance
- Isolated neutral-ground bonding in subpanels
- Torque ground connections to 75% of phase conductor torque
- Use listed grounding bars and maintain proper wire color codes
Common Selection Mistakes to Avoid
- Undersizing Breaking Capacity: Fault current grows with system expansion; specify 20-30% margin
- Ignoring Ambient Temperature: Each 10°C above 40°C reduces capacity by ~10-15%
- Neglecting Coordination: Upstream and downstream devices must coordinate for selective tripping
- Wrong Trip Characteristic: Type B MCB on motor circuit causes nuisance tripping
- Inadequate IP Rating: IP20 indoor breaker fails in dusty/wet industrial environments
Proper breaker selectivity and coordination ensures that only the breaker closest to the fault trips, maintaining power to unaffected circuits and minimizing downtime in critical facilities.
Safety Standards and Compliance
International Standards
IEC Standards (International Electrotechnical Commission)
- IEC 60898-1: MCBs for household and similar installations
- IEC 60947-2: Low voltage switchgear – Circuit breakers
- IEC 62271-100: High voltage switchgear – Alternating current circuit breakers
- IEC 61008: RCCBs without integral overcurrent protection
- IEC 61009: RCBOs with integral overcurrent protection
ANSI/IEEE Standards (North America)
- IEEE C37.13: Low voltage AC power circuit breakers
- IEEE C37.04: Rating structure for AC high voltage circuit breakers
- ANSI C37.50: Test procedures for low voltage circuit breakers
- UL 489: Molded case circuit breakers
- UL 1077: Supplementary protectors
VIOX Certification Matrix
All VIOX circuit breakers undergo rigorous third-party testing and maintain certifications including:
- CE marking (European Union)
- UL/CSA listing (North America)
- CCC certification (China)
- ASTA/BSI approval (United Kingdom)
- Marine approvals (DNV-GL, ABS, LR, BV)
- ATEX/IECEx (explosive atmospheres)
Installation and Maintenance Safety
Installation Requirements
- Qualified Personnel: Licensed electricians per local regulations
- De-energization: Lockout/tagout procedures mandatory
- Torque Specifications: Terminal connections per manufacturer datasheet
- Clearances: Maintain IEC 61439 spacing requirements
- Grounding: Proper PE connection with continuous earth bonding
Maintenance Schedules
| Breaker Type | Inspection Frequency | Key Maintenance Tasks | Expected Lifespan |
|---|---|---|---|
| MCB | Annual visual | Contact inspection, test operation | 20-30 years |
| MCCB | 6-12 months | Contact wear check, trip test, torque verification | 15-25 years |
| ACB | Quarterly | Contact gap measurement, arc chute inspection, lubrication | 20-30 years |
| VCB | Annual | Vacuum integrity test, mechanism lubrication, CT accuracy | 25-35 years |
| SF6 CB | 6-12 months | Gas density monitor, contact travel, SF6 leak detection | 30-40 years |
VIOX provides comprehensive maintenance training, specialized tools, and genuine spare parts to ensure optimal circuit breaker performance throughout operational life.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is the main difference between MCB and MCCB?
MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker) handles lower current ratings (6-125A) with fixed trip settings, ideal for residential and light commercial applications. MCCB (Molded Case Circuit Breaker) covers higher ratings (100-2500A) with adjustable trip settings, suited for commercial and industrial installations. MCBs use thermal-magnetic mechanisms while MCCBs may incorporate electronic trip units. Breaking capacity differs significantly: MCBs typically 6-10kA vs. MCCBs 25-200kA.
Q2: When should I use RCCB vs. RCBO?
Use RCCB when protecting multiple circuits with a single ground fault device (group protection). Choose RCBO for individual circuit protection combining overcurrent and residual current sensing. RCBOs provide better fault discrimination—one circuit’s fault doesn’t disconnect others. For new installations, VIOX recommends RCBOs for critical loads (medical equipment, IT systems) and wet areas (bathrooms, kitchens), while RCCBs suit cost-effective group protection of standard socket circuits.
Q3: How do I calculate the required breaking capacity?
Breaking capacity (Icu or Icn) must exceed the maximum prospective short-circuit current (PSCC) at the installation point. Calculate PSCC using: PSCC = Voltage / Total Impedance (transformer + cable). For example: 400V system with 0.01Ω impedance = 40kA fault current; specify breaker with minimum 50kA breaking capacity. VIOX engineers recommend 20-30% safety margin for future system expansion and utility grid strengthening.
Q4: What are Type B, C, and D circuit breakers?
Trip types define magnetic instantaneous response:
- Type B: Trips at 3-5× rated current; use for residential lighting, long cable runs
- Type C: Trips at 5-10× rated current; commercial loads, small motors, transformers
- Type D: Trips at 10-20× rated current; heavy inductive loads, welding equipment, X-ray machines
Select based on inrush current characteristics. VIOX Type C MCBs handle most commercial applications; Type D suits specialized industrial equipment with high starting currents.
Q5: How often should circuit breakers be replaced?
Circuit breakers don’t require routine replacement if properly maintained. Replace when:
- Physical damage, burning, or overheating signs visible
- Failed to trip during fault (test annually per NFPA 70B)
- Exceeded rated short-circuit interruptions (logged by electronic trip units)
- 25-30 years operational age for mechanical breakers
- Obsolescence prevents obtaining spare parts
VIOX circuit breakers feature mechanical endurance exceeding 20,000 operations and electrical endurance of 50+ rated breaking operations. Implement condition-based maintenance using thermal imaging and contact resistance measurements.
Q6: Can I use AC circuit breakers for DC applications?
No—AC and DC breakers differ fundamentally. AC current naturally crosses zero 100-120 times per second, facilitating arc extinction. DC current maintains constant value, requiring specialized arc interruption. DC-rated breakers feature:
- Extended contact gaps (2-3× AC breaker)
- Stronger magnetic blowout coils
- Enhanced arc chutes
- Electronic monitoring for polarity
VIOX manufactures dedicated DC circuit breakers for solar PV systems (up to 1500V DC), battery storage, traction power, and industrial DC drives. Never substitute AC breakers in DC circuits—catastrophic failure may result.
Q7: What does ‘selectivity’ or ‘discrimination’ mean?
Selectivity ensures only the breaker closest to the fault trips, maintaining power to healthy circuits. Achieve selectivity through:
- Current discrimination: Upstream breaker rated higher than downstream fault current
- Time discrimination: Upstream breaker delays tripping allowing downstream operation
- Energy discrimination: I²t coordination between breakers
- Zone selective interlocking (ZSI): Communication between breakers for instantaneous selective tripping
VIOX provides selectivity tables and software tools for engineering coordination studies per IEC 60364-5-53. Properly coordinated systems minimize downtime and simplify troubleshooting.
Q8: Are circuit breakers environmentally sustainable?
Modern circuit breakers incorporate sustainable practices:
- Material selection: Recyclable metals (copper, aluminum, steel) comprise 70-85% of mass
- Longevity: 25-40 year lifespan reduces replacement frequency
- Energy efficiency: Minimize losses (<2W for MCBs, <50W for ACBs)
- SF6 alternatives: VIOX researches fluoronitrile mixtures and vacuum technology
- RoHS compliance: Lead-free, mercury-free, cadmium-free construction
VIOX maintains ISO 14001 environmental management certification and offers product take-back programs for responsible end-of-life recycling. Our vacuum circuit breakers eliminate SF6 greenhouse gas in medium voltage applications.
Q9: How do smart circuit breakers differ from traditional breakers?
Smart circuit breakers integrate IoT connectivity, providing:
- Real-time monitoring: Current, voltage, power, energy consumption
- Remote operation: Trip/close via mobile app or SCADA
- Predictive maintenance: Temperature trending, contact wear algorithms
- Power quality analysis: Harmonics, power factor, demand response
- Data logging: Historical records for analysis and reporting
VIOX Smart Breaker Series communicates via Modbus TCP, BACnet, or MQTT protocols, integrating with building management systems and energy monitoring platforms. These devices enable proactive maintenance, reducing unplanned downtime by 40-60% versus traditional breakers.
Q10: What causes circuit breakers to trip frequently?
Common causes and solutions:
| Cause | Symptoms | VIOX Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Genuine overload | Gradual heating, trips after minutes | Upsize breaker rating or reduce load |
| Loose connections | Random tripping, terminal discoloration | Torque terminals to specification |
| Nuisance tripping | Trips during motor starting | Change to Type D or use MCCB |
| Ground fault | Immediate trip, RCCB activation | Identify and repair insulation fault |
| Worn contacts | Increasing frequency over time | Replace breaker (contact resistance test) |
| Ambient temperature | Summer afternoon trips | Upgrade to higher rating or improve ventilation |
VIOX technical support provides root cause analysis and recommends appropriate corrective actions, preventing recurring nuisance trips while maintaining safety.
Why Choose VIOX Electric Circuit Breakers
As a leading B2B manufacturer of electrical equipment, VIOX Electric combines innovative engineering, rigorous quality control, and comprehensive support to deliver circuit protection solutions that exceed industry expectations.
Technical Excellence
- Advanced arc-quenching technology reducing arc energy by 30% vs. conventional designs
- Microprocessor-based trip units with 0.1% accuracy class
- Extended mechanical life through precision manufacturing (30,000+ operations)
- Comprehensive testing: 100% routine tests + statistically sampled type tests
Global Compliance
- Multi-standard certification (IEC, UL, CSA, CE, CCC, marine)
- Regional technical support in 40+ countries
- Customization capability for project-specific requirements
- Complete documentation packages for engineering approvals
Sustainability Commitment
- ISO 14001 environmental management
- RoHS and REACH compliant materials
- Product lifecycle extending 25-40 years
- End-of-life recycling programs
Customer Partnership
- Free application engineering support
- Selectivity studies and coordination analysis
- Training programs for installation and maintenance personnel
- Genuine spare parts availability with 24-48 hour delivery
For technical specifications, product catalogs, and application engineering support, contact VIOX Electric’s experienced team to ensure your electrical protection systems deliver optimal safety, reliability, and performance.
This comprehensive guide provides foundational knowledge for selecting appropriate circuit breaker types. For specific applications requiring detailed engineering analysis, consult qualified electrical engineers and reference applicable codes and standards. VIOX Electric provides complimentary application review services—contact our technical team for project-specific recommendations.