La chiamata di servizio è arrivata alle 14:00 di un martedì. Ispezione di routine dei pannelli solari. Non si prevedeva nulla di insolito.
Ma quando il tecnico ha aperto la scatola di giunzione, ha trovato qualcosa che gli ha fatto venire un nodo allo stomaco: i contatti dell'interruttore automatico CC si erano saldati insieme, fusi in una massa solida di rame. L'interruttore automatico avrebbe dovuto proteggere il sistema. Invece, era diventato un cortocircuito permanente.
Ecco cosa è terrificante: l'interruttore automatico non è mai scattato durante il guasto. L'arco che si è formato quando i contatti hanno cercato di separarsi ha generato abbastanza calore, oltre 6.000 °C, da fondere il rame prima che l'interruttore potesse interrompere la corrente. Il sistema ha continuato a funzionare, alimentando attraverso quella che era essenzialmente una massa di metallo fuso, fino a quando qualcuno non lo ha spento fisicamente.
Perché è successo? Qualcuno ha installato un interruttore automatico con specifiche CA in un sistema CC. Stessa tensione nominale. Stessa corrente nominale. Applicazione completamente errata.
Quell'errore è costato 40.000 € in attrezzature danneggiate e una settimana di inattività.
La differenza tra gli interruttori automatici CC e CA non è solo una curiosità tecnica, è la differenza tra protezione e disastro.
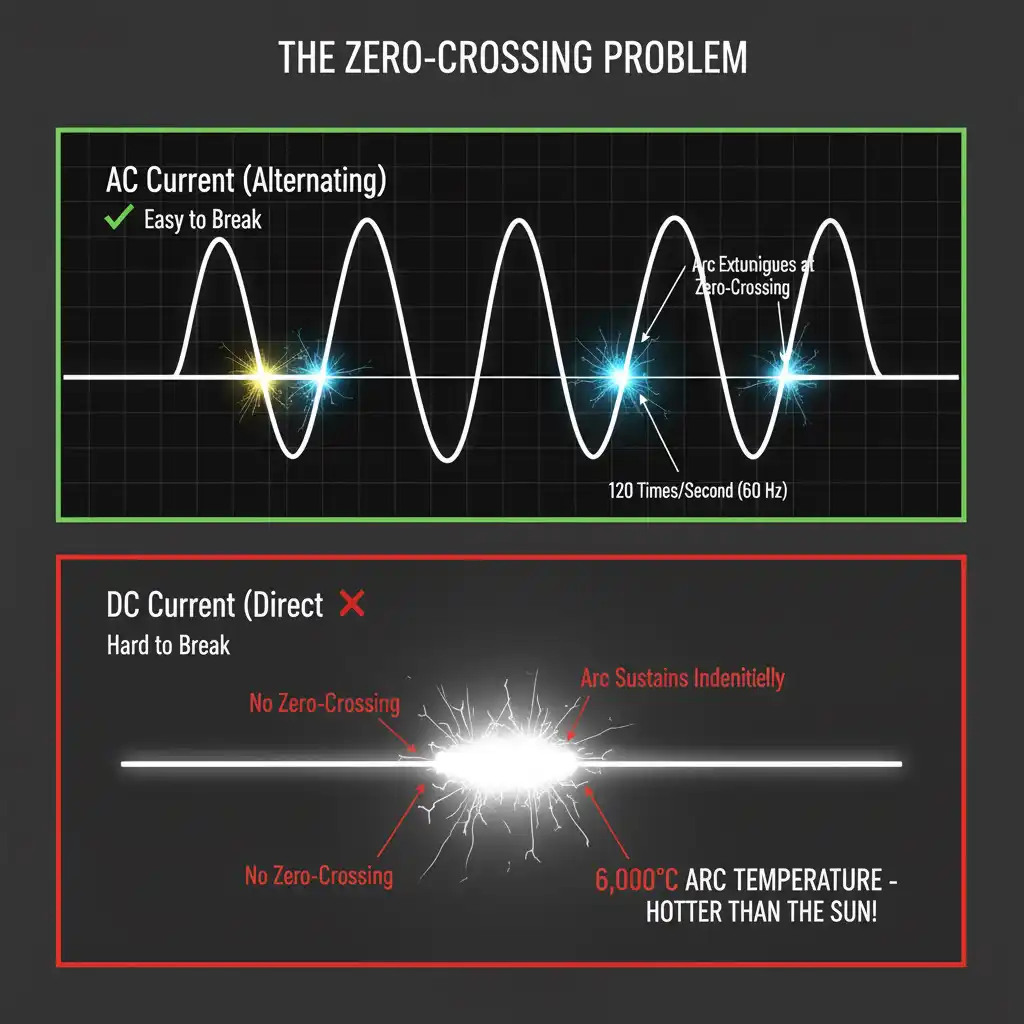
Perché la corrente continua è più difficile da interrompere: il problema dell'attraversamento dello zero
Pensa a come l'acqua scorre attraverso un tubo rispetto a come pulsa attraverso un'idropulitrice. Questa è la differenza tra corrente continua e corrente alternata.
La corrente alternata cambia direzione 50 o 60 volte al secondo. In un sistema a 60 Hz, la corrente attraversa lo zero di tensione 120 volte al secondo, due volte per ciclo. Quando i contatti di un interruttore automatico si separano e si forma un arco, quell'arco si estingue naturalmente al successivo attraversamento dello zero. L'interruttore automatico deve solo impedire all'arco di riaccendersi. Sta lavorando con la fisica della corrente alternata.
La corrente continua scorre in una direzione continua con tensione costante. Non ci sono attraversamenti dello zero. Mai.
Quando i contatti si separano in un circuito CC, l'arco si forma e semplicemente... rimane lì. Non si preoccupa del tentativo del tuo interruttore di interromperlo. Quell'arco continuerà fino a quando qualcosa non lo interrompe fisicamente, lo raffredda o lo allunga oltre la sostenibilità.
I numeri lo rendono brutalmente chiaro: un tipico arco CA si estingue entro 8 millisecondi (1/120 di secondo) grazie agli attraversamenti dello zero naturali. Un arco CC? Può sostenersi indefinitamente a temperature superiori a 6.000 °C, più calde della superficie del sole e ben al di sopra del punto di fusione del rame di 1.085 °C.
Questo è quello che chiamo “Il problema dell'attraversamento dello zero”.” Gli interruttori CA possono fare affidamento sulla fisica per aiutarli. Gli interruttori CC devono combattere la fisica in ogni fase del percorso.
L'impatto pratico: gli interruttori CC necessitano di meccanismi aggressivi di estinzione dell'arco. Bobine di soffiaggio magnetiche che letteralmente fanno esplodere l'arco. Geometrie di contatto speciali che allungano l'arco fino a quando non si raffredda e si rompe. Canali di scarico dell'arco riempiti con piastre isolanti che dividono l'arco in segmenti più piccoli e più facili da estinguere. Alcuni interruttori CC avanzati utilizzano persino camere a vuoto o gas esafluoruro di zolfo per spegnere gli archi più velocemente.
Tutta questa complessità esiste per risolvere un problema: la corrente continua è ostinata. Si rifiuta di lasciarsi andare.
Cosa rende diversi (e più costosi) gli interruttori CC
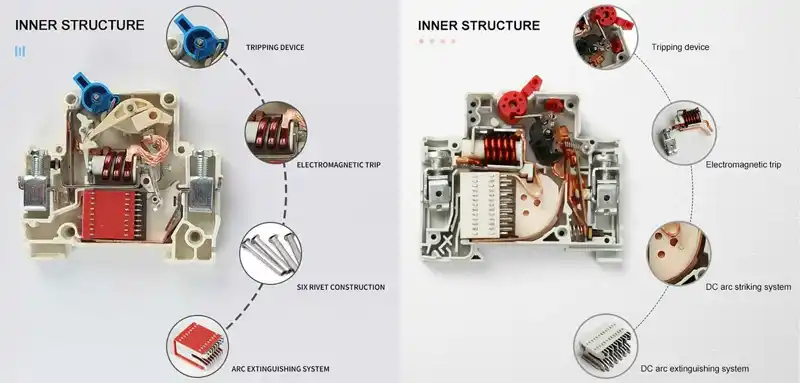
Interno di un MCB CA VS MCB CC
Entra in un negozio di forniture elettriche e confronta i prezzi. Un interruttore automatico CA standard da 20 A, 120 V: 15 €. Un interruttore automatico CC da 20 A, 125 V: 80-120 €.
Stessa corrente nominale, tensione simile, ma l'interruttore CC costa 5-8 volte di più.
Gli ingegneri amano lamentarsi di questa differenza di prezzo. “È solo un interruttore!” dicono. Ma ecco cosa c'è dentro quel “solo un interruttore”:
In un interruttore CA:
- Due contatti principali (linea e carico)
- Meccanismo di scatto termico-magnetico di base
- Semplice canale di scarico dell'arco con alcune piastre metalliche
- Costruzione a un polo
In un interruttore CC:
- Tre o più contatti principali disposti in serie
- Meccanismo di scatto termico-magnetico potenziato con maggiore forza magnetica
- Complesso canale di scarico dell'arco con dozzine di piastre in acciaio
- Bobine di soffiaggio magnetiche che consumano spazio extra
- Materiali di contatto speciali (leghe argento-tungsteno invece di argento-nichel)
- Ingegneria precisa del traferro (troppo piccolo e l'arco non si allunga; troppo grande e l'interruttore non si adatta agli involucri standard)
Quel premio di prezzo non è margine di profitto, è fisica. Ogni componente in un interruttore CC deve lavorare di più per superare il problema dell'attraversamento dello zero.
Ed ecco il punto cruciale: Non puoi sostituire l'uno con l'altro, anche se le tensioni e le correnti nominali corrispondono. Un interruttore CA in un sistema CC non interromperà i guasti ad alta energia. L'arco si sosterrà, i contatti si salderanno e il tuo “dispositivo di protezione” diventerà un conduttore incontrollato.
Ho visto questa modalità di guasto distruggere 50.000 € di attrezzature solari quando un installatore ha cercato di risparmiare 60 € sugli interruttori.
L'effetto di saldatura ad arco, quando i contatti dell'interruttore si fondono insieme, è spaventosamente comune negli interruttori CA applicati in modo errato sui sistemi CC. Una volta che i contatti si saldano, l'interruttore è permanentemente chiuso. Nessuna operazione manuale li separerà. Ti ritrovi con un circuito sempre attivo che non ha alcuna protezione.
Il limite di 600 Volt: perché le specifiche CC sono ingannevoli
Ecco una domanda che fa inciampare anche gli ingegneri esperti: perché i sistemi CC residenziali sono limitati a 600 V, mentre i sistemi CA funzionano comunemente a 240 V o anche 480 V negli edifici commerciali?
La risposta rivela qualcosa di controintuitivo sulle specifiche elettriche.
Le tensioni nominali non sono equivalenti tra i sistemi CA e CC. Un circuito CC a 600 V in realtà immagazzina e può scaricare più energia di un circuito CA a 480 V con la stessa corrente nominale. Ecco perché:
La tensione CA è tipicamente specificata come RMS (Root Mean Square), effettivamente un valore medio. Un sistema CA a 480 V in realtà raggiunge un picco di 679 V (480 V × √2) durante ogni ciclo, ma solo per un istante prima di tornare verso lo zero. L'interruttore deve solo sopportare quel picco momentaneamente.
La tensione CC è costante. Un sistema CC a 600 V mantiene 600 V continuamente, senza picchi, senza valli, senza attraversamenti dello zero per aiutare con l'interruzione. L'interruttore affronta la massima sollecitazione in ogni momento.
Questo è “Il limite di 600 Volt”: il limite del National Electrical Code per le installazioni CC residenziali. Sopra i 600 V CC, sei in territorio commerciale/industriale con requisiti più severi per il percorso dei cavi, l'etichettatura e il personale qualificato. Nel frattempo, i sistemi CA possono raggiungere i 480 V negli edifici commerciali senza attivare le stesse restrizioni.
Rendiamo questo concreto con il confronto della potenza:
| Tipo di sistema | Tensione | Attuale | Energia |
|---|---|---|---|
| CA residenziale | 240 V RMS | 100A | 24.000 W |
| CC solare (residenziale) | 600V | 100A | 60.000 W |
| CA commerciale | 480 V RMS | 100A | 48.000 W |
Stessa corrente nominale (100 A), ma livelli di potenza estremamente diversi. Questo è il motivo per cui le specifiche della capacità di interruzione dell'interruttore CC sembrano così estreme. Un interruttore CC a 600 V potrebbe aver bisogno di una capacità di interruzione di 25.000 A dove un interruttore CA a 240 V ha bisogno solo di 10.000 A per la stessa applicazione.
⚡ Suggerimento professionale: Quando si dimensionano gli interruttori CC per i sistemi solari, tenere sempre conto della tensione a circuito aperto (Voc) corretta per la temperatura. Un sistema di batterie nominale a 48 V potrebbe vedere 58 V a piena carica. Una stringa solare con una potenza nominale di 500 V potrebbe produrre 580 V in una fredda mattina invernale quando l'efficienza del pannello raggiunge il picco. Arrotonda generosamente le tensioni nominali: costa qualche euro in più ma previene guasti catastrofici.
Come selezionare l'interruttore automatico giusto: metodo in 5 passaggi
Permettetemi di illustrarvi l'approccio sistematico che previene i 40.000 errori di cui ho parlato prima.
Fase 1: Identificare il tipo di corrente
Sistemi CC:
- Pannelli solari fotovoltaici (sempre uscita CC)
- Sistemi di accumulo a batteria (le batterie sono CC per natura)
- Stazioni di ricarica per veicoli elettrici (il lato batteria è CC)
- Azionamenti per motori CC industriali
- Apparecchiature di telecomunicazione
- Elettrificazione ferroviaria (spesso CC)
Sistemi CA:
- Alimentazione di rete dalle utenze (residenziale/commerciale)
- Controllo motore per motori a induzione CA
- Sistemi HVAC
- Distribuzione elettrica generale degli edifici
- La maggior parte degli elettrodomestici e dell'illuminazione
Sistemi misti (richiedono entrambi i tipi):
- Sistemi solari + batteria con connessione alla rete
- Ricarica EV (ingresso CA, CC al veicolo)
- Gruppi di continuità (UPS)
- Azionamenti a frequenza variabile (ingresso CA, bus CC, uscita CA)
Per i sistemi misti, avrete bisogno di interruttori automatici appropriati su ciascun lato. La connessione solare-batteria necessita di interruttori automatici CC. La connessione alla rete necessita di interruttori automatici CA. Non incrociateli mai.
Fase 2: Calcolare i requisiti di tensione massima
Per i sistemi CC:
Calcolare la tensione a circuito aperto con correzione della temperatura. I pannelli solari aumentano la tensione quando fa freddo, a volte del 25% o più.
Formula: Voc(freddo) = Voc(STC) × [1 + (Tcoeff × ΔT)]
Esempio: Array solare nominale a 48V
- Voc(STC) = 60V @ 25°C
- Coefficiente di temperatura = -0,3%/°C
- Temperatura ambiente più fredda = -10°C
- ΔT = 25°C – (-10°C) = 35°C
- Voc(freddo) = 60V × [1 + (-0,003 × 35)] = 60V × 1,105 = 66,3V
Il vostro interruttore automatico deve essere dimensionato per almeno 66,3 V, non 60 V, non 48 V nominali. Arrotondare al valore nominale standard: interruttore automatico da 80 V CC minimo.
Per i sistemi CA:
Utilizzare la tensione di targa. I valori nominali standard sono fissi: 120 V, 240 V, 277 V, 480 V, 600 V CA. Corrispondere o superare la tensione del sistema.
Fase 3: Determinare la corrente nominale (con declassamento appropriato)
Interruttori automatici CC per solare/batteria:
Corrente nominale = Isc(max) × 1,25 (Requisito NEC 690.8)
Esempio: Array solare con corrente di cortocircuito (Isc) = 40A
- Corrente nominale dell'interruttore automatico richiesta = 40A × 1,25 = 50A minimo
- Dimensioni standard: 50A, 60A, 70A → Selezionare l'interruttore automatico da 50A
Interruttori automatici CA per carichi continui:
Corrente nominale = Corrente di carico × 1,25 (Requisito NEC 210.20)
Esempio: Carico HVAC continuo da 30A
- Corrente nominale dell'interruttore automatico richiesta = 30A × 1,25 = 37,5A
- Dimensioni standard: 30A, 35A, 40A → Selezionare l'interruttore automatico da 40A
Declassamento della temperatura: Se il vostro interruttore automatico funziona a una temperatura ambiente superiore a 40°C (comune nelle scatole di combinazione solare), applicare un declassamento aggiuntivo. Per ogni 10°C sopra i 40°C, declassare di circa il 15%.
Esempio: Interruttore automatico da 50A in scatola di combinazione a 60°C
- Eccesso di temperatura = 60°C – 40°C = 20°C
- Fattore di declassamento = 0,85 × 0,85 = 0,72
- Capacità effettiva = 50A × 0,72 = 36A
Se il vostro requisito di carico calcolato è di 40A, quell'interruttore automatico “50A” non sarà sufficiente. Avreste bisogno di un interruttore automatico da 60A per ottenere una capacità effettiva di 43,2A.
Fase 4: Verificare il potere di interruzione (la specifica più trascurata)
Il potere di interruzione (chiamato anche capacità di interruzione o corrente di cortocircuito nominale) è la corrente massima che l'interruttore automatico può interrompere in sicurezza senza esplodere, saldare i contatti o causare guasti a cascata.
È qui che i sistemi CC diventano spaventosi.
I sistemi a batteria possono fornire enormi correnti di cortocircuito perché le batterie hanno un'impedenza interna quasi nulla. Un “piccolo” banco di batterie al litio da 48 V, 100 Ah può erogare 5.000 A o più durante un cortocircuito diretto.
| Tipo di sistema | Tensione | Potere di interruzione tipico richiesto |
|---|---|---|
| 12V CC automobilistico | 12V | 5.000A @ 12V |
| 48V CC solare/batteria | 48V | 1.500-3.000A @ 48V |
| 125V CC industriale | 125V | 10.000-25.000A @ 125V |
| Array solare 600V CC | 600V | 14.000-65.000A @ 600V |
| CA residenziale | 120/240V | 10.000 AIC tipici |
| AC commerciale | 480V | 22.000-65.000 AIC |
Avete notato come le capacità di interruzione in CC siano simili o superiori a quelle in CA, anche se i sistemi CC gestiscono in genere tensioni inferiori? È la "Corrente Ostinata" al lavoro. I guasti in CC sono più difficili da interrompere, quindi gli interruttori automatici necessitano di una maggiore capacità di interruzione.
⚡ Suggerimento professionale: Per i sistemi a batteria, utilizzare la specifica di corrente di scarica massima del produttore della batteria, non la corrente nominale. Una batteria con una corrente nominale di 100 A potrebbe erogare 500 A durante i guasti. La capacità di interruzione del vostro interruttore automatico deve superare tale corrente di guasto.
Fase 5: Verificare la conformità al codice (requisiti NEC)
Sistemi CC (NEC Articolo 690 per FV, Articolo 706 per accumulo di energia):
- Limiti di tensione: massimo 600 V CC in ambito residenziale (abitazioni unifamiliari e bifamiliari)
- Protezione del circuito richiesta per tutti i conduttori superiori a 30 V o 8 A
- Canalina metallica o cavo di tipo MC richiesto per i circuiti CC interni superiori a 30 V
- Etichettatura richiesta: “PHOTOVOLTAIC POWER SOURCE” o “SOLAR PV DC CIRCUIT” su tutti gli involucri CC
- Protezione contro i guasti a terra richiesta per i sistemi FV montati sul tetto
- Requisiti di spegnimento rapido (spegnimento a livello di modulo o a livello di array entro 30 secondi)
Sistemi CA (NEC Articolo 210 per circuiti derivati, Articolo 240 per protezione da sovracorrente):
- AFCI (Arc-Fault Circuit Interrupter) richiesto per la maggior parte dei circuiti a 120 V delle unità abitative
- GFCI (Ground-Fault Circuit Interrupter) richiesto per luoghi umidi, cucine, bagni, prese esterne
- Interruttori tandem (interruttori doppi in un unico spazio) consentiti solo dove il quadro è omologato per essi
- Gli interruttori automatici devono essere elencati (UL 489) per la protezione dei circuiti derivati
Standard UL materia:
- UL 489: Protezione completa del circuito derivato (massima valutazione, richiesta per circuiti autonomi)
- UL 1077: Protezione supplementare (solo per uso all'interno delle apparecchiature, non autonoma)
- UL 2579: Specifica per la protezione del circuito da arco voltaico CC FV
Non sostituire mai un protettore supplementare UL 1077 dove è richiesta la protezione del circuito derivato UL 489. Non sono equivalenti.
Dove appartiene ogni tipo (e dove non appartiene)
Applicazioni dell'interruttore automatico CC
Sistemi fotovoltaici solari – Qui è dove gli interruttori automatici CC sono assolutamente non negoziabili. Ogni stringa necessita di interruttori automatici con classificazione CC. Ogni scatola di combinazione. Ogni connessione dai pannelli al regolatore di carica, alla batteria, all'inverter (sul lato CC). Lo richiede il National Electrical Code. Lo esige la fisica.
Ho lavorato a un progetto in cui l'installatore ha utilizzato interruttori automatici CA $15 anziché interruttori automatici CC $80 per risparmiare denaro su un array solare da 50 kW. Sei mesi dopo, durante un guasto a terra, un interruttore automatico si è saldato e ha alimentato continuamente la corrente di guasto fino a quando l'isolamento del cavo CC non si è bruciato.
Costo totale della riparazione: $35.000. Il “risparmio” è costato 400 volte di più di quanto sarebbero costati gli interruttori automatici corretti.
Infrastruttura di ricarica per veicoli elettrici – Il lato CC (dal caricabatterie alla batteria del veicolo) richiede interruttori automatici CC omologati per la tensione della batteria. I caricabatterie rapidi CC di livello 3 funzionano a 400-800 V CC con correnti superiori a 200 A. Queste sono condizioni brutali. Il lato di alimentazione CA (d dalla rete al caricabatterie) utilizza interruttori automatici CA standard.
Sistemi di accumulo di energia a batteria – I banchi di batterie al litio sono CC per natura. Ogni connessione necessita di interruttori automatici CC omologati per la tensione del banco e, soprattutto, per l'enorme corrente di cortocircuito che le batterie possono erogare. Un banco di batterie residenziali da 48 V, 10 kWh può scaricare 5.000 A+ in un cortocircuito. Il vostro interruttore automatico deve gestire tale capacità di interruzione.
Telecomunicazioni – Le torri cellulari, i data center e le strutture di telecomunicazione funzionano con alimentazione CC (in genere 48 V) perché la CC è più affidabile e non presenta i problemi di fattore di potenza della CA. Tutta la protezione sul lato della distribuzione CC deve essere omologata per CC.
Applicazioni dell'interruttore automatico CA
Distribuzione di edifici residenziali e commerciali – Il quadro principale della vostra casa, tutti i circuiti derivati per prese e illuminazione, i circuiti degli elettrodomestici: sono tutti CA. L'alimentazione di rete è CA, quindi la distribuzione degli edifici è CA. Utilizzare interruttori automatici CA standard omologati per 120 V, 240 V o 277 V (per l'illuminazione commerciale).
Controllo motore CA – I motori a induzione, i compressori HVAC, i motori delle pompe: funzionano con alimentazione CA. L'avviatore del motore o il VFD ricevono ingresso CA, quindi utilizzare interruttori automatici CA per la protezione dell'alimentazione.
Uscita CA dell'inverter connesso alla rete – I sistemi solari con inverter grid-tie producono uscita CA sul lato rivolto alla rete. Tale connessione al vostro quadro principale utilizza interruttori automatici CA. L'array solare stesso è CC (interruttori automatici CC), ma una volta che l'inverter converte in CA, siete nel territorio degli interruttori automatici CA.
Dove servono ENTRAMBI
I sistemi solari ibridi con backup a batteria richiedono interruttori automatici CC sul lato dell'array FV, interruttori automatici CC sulle connessioni della batteria e interruttori automatici CA sui circuiti CA lato rete e lato carico. Un tipico sistema residenziale potrebbe avere:
- Interruttori automatici CC: 4-6 (stringhe FV + carica/scarica della batteria)
- Interruttori automatici CA: 2-3 (uscita CA dell'inverter + connessione alla rete + backup dei carichi critici)
Errori comuni (e come falliscono)
Errore #1: Valutazioni di tensione “abbastanza vicine”
Pensiero dell'ingegnere: “Il mio sistema nominale a 48 V raggiunge un picco di 58 V, quindi un interruttore automatico CC a 60 V dovrebbe funzionare.”
Realtà: Quel sistema a 48 V può raggiungere i 66 V in una mattinata fredda quando i pannelli solari funzionano alla massima efficienza. L'interruttore automatico a 60 V vede condizioni di sovratensione, le prestazioni di estinzione dell'arco si degradano e si sta spingendo l'interruttore automatico oltre il suo margine di sicurezza testato.
Soluzione: Utilizzare sempre la Voc corretta per la temperatura per i sistemi solari. Arrotondare alla successiva valutazione di tensione standard dell'interruttore automatico. Costa $10-20 in più. Ne vale la pena.
Errore #2: Utilizzo di interruttori automatici CA in sistemi CC
Questo è l'errore da $40.000 a cui continuo a fare riferimento. Un interruttore automatico CA semplicemente non può interrompere gli archi CC in modo affidabile. L'assenza di attraversamenti dello zero significa che l'arco si mantiene, i contatti si surriscaldano e si verifica la saldatura.
Soluzione: Non applicare mai in modo incrociato. I sistemi CC ottengono interruttori automatici CC. I sistemi CA ottengono interruttori automatici CA. In caso di dubbi, guardare l'etichetta dell'interruttore automatico. Indicherà esplicitamente le valutazioni “CC” o “CA”. Se elenca solo le valutazioni CA, non utilizzarlo su circuiti CC.
Errore #3: Ignorare la capacità di interruzione
Corrente nominale ≠ capacità di interruzione. Un interruttore automatico da 100 A potrebbe avere solo una capacità di interruzione di 5.000 A. Se il vostro banco di batterie può erogare 10.000 A durante un cortocircuito, tale interruttore automatico non può interrompere il guasto in modo sicuro. L'interruttore automatico potrebbe esplodere (sì, letteralmente) o fallire catastroficamente.
Soluzione: Calcolare la corrente di cortocircuito disponibile per il vostro sistema. Per i sistemi a batteria, utilizzare la specifica di scarica massima del produttore. Selezionare interruttori automatici con capacità di interruzione superiore alla vostra corrente di guasto.
Errore #4: Dimenticare la riduzione della potenza in base alla temperatura
Le scatole di combinazione solari spesso raggiungono i 60-70 °C alla luce diretta del sole. Il vostro interruttore automatico “50A” potrebbe essere omologato solo per una capacità effettiva di 36A a quella temperatura.
Soluzione: Sovradimensionare l'interruttore automatico per tenere conto della riduzione della potenza in base alla temperatura oppure migliorare la ventilazione nel vostro involucro. Alcuni installatori utilizzano scatole di combinazione termicamente isolate con ventilazione forzata per mantenere le temperature più vicine a 40 °C.
Il futuro: Interruttori automatici CC intelligenti
Ecco qualcosa che la maggior parte degli ingegneri non ha ancora realizzato: stiamo entrando nell'era degli interruttori automatici a stato solido e i sistemi CC ne beneficeranno per primi.
Gli interruttori elettromeccanici tradizionali si basano sulla separazione fisica dei contatti. Gli interruttori a stato solido utilizzano semiconduttori di potenza (MOSFET o IGBT) per interrompere elettronicamente la corrente: nessuna parte mobile, nessun arco, nessuna saldatura dei contatti.
Per i sistemi CA, gli interruttori a stato solido sono un optional. Per i sistemi CC? Sono rivoluzionari.
Un interruttore CC a stato solido può interrompere un guasto a 600 V, 100 A in meno di 1 millisecondo, 100 volte più velocemente degli interruttori elettromeccanici. Nessun arco, nessun calore, nessuna erosione dei contatti. Possono eseguire milioni di cicli senza degradazione. Possono implementare algoritmi di protezione avanzati, comunicare lo stato sulle reti e adattare le curve di intervento alle condizioni del sistema.
Lo svantaggio? Costo. Un interruttore CC a stato solido potrebbe costare tra i 300 e gli 800 € rispetto agli 80-120 € per un elettromeccanico. Ma per le applicazioni critiche, come l'accumulo di batterie su scala industriale, i data center, i sistemi militari, tale prezzo è giustificato dall'affidabilità e dalle prestazioni.
La certificazione UL 489 ora copre gli interruttori automatici a stato solido, quindi vedremo una maggiore adozione man mano che i costi diminuiscono. Entro 5-10 anni, prevedo che lo stato solido diventerà lo standard per i sistemi CC superiori a 200 V.
La conclusione
La differenza fondamentale tra gli interruttori CC e CA si riduce a un fatto spietato: La corrente CC non vuole fermarsi.
La corrente CA attraversa naturalmente lo zero 120 volte al secondo, dando un aiuto agli interruttori. La corrente CC scorre continuamente, combattendo ogni tentativo di interromperla. Tale resistenza all'interruzione plasma tutto: dalla progettazione interna dell'interruttore ai criteri di selezione, al costo, ai requisiti del codice.
Quando si sceglie l'interruttore giusto per la propria applicazione, non si sta semplicemente spuntando una casella su un progetto elettrico. Si sta costruendo l'ultima linea di difesa tra il normale funzionamento e un guasto catastrofico. Tale difesa deve corrispondere alla fisica del tipo di corrente.
Utilizzare interruttori CC per sistemi CC. Utilizzare interruttori CA per sistemi CA. Non applicare mai in modo incrociato.
Se si sta progettando un sistema fotovoltaico solare, un'installazione di accumulo di batterie, un'infrastruttura di ricarica per veicoli elettrici o qualsiasi applicazione CC, investire negli interruttori con classificazione CC corretta con un'adeguata capacità di interruzione. Se si lavora con impianti elettrici standard per edifici, alimentazione di rete o controllo di motori CA, utilizzare interruttori CA progettati per tale scopo.
E se si è mai tentati di sostituire l'uno con l'altro per risparmiare 50 €? Ricordarsi dei contatti saldati, della fattura di riparazione da 40.000 € e della settimana di inattività.
⚡ Per gli interruttori CC e CA VIOX progettati per applicazioni solari, a batteria e industriali, contattare il nostro team tecnico per una guida alla selezione specifica per l'applicazione e soluzioni certificate UL 489.
Domande Frequenti
D: Posso utilizzare un interruttore automatico CA in un sistema CC?
R: No. L'utilizzo di un interruttore CA in un sistema CC è pericoloso e potrebbe non interrompere efficacemente le correnti di guasto. Gli interruttori CA si basano sugli attraversamenti dello zero naturali nella corrente alternata per estinguere gli archi. La corrente CC non ha attraversamenti dello zero, quindi l'arco si mantiene, saldando potenzialmente i contatti insieme. Utilizzare sempre interruttori con classificazione CC per i sistemi CC.
D: Perché gli interruttori automatici CC sono più costosi degli interruttori automatici CA?
R: Gli interruttori CC richiedono meccanismi interni più complessi per superare il problema dell'attraversamento dello zero. Hanno bisogno di bobine di soffiaggio magnetiche, disposizioni di contatti multiple, scivoli di arco specializzati con dozzine di piastre e materiali di contatto premium come leghe di argento-tungsteno. Questa ulteriore complessità aumenta i costi di produzione di 5-8 volte rispetto agli interruttori CA.
D: Quali sono i valori di tensione disponibili per gli interruttori automatici CC?
R: Gli interruttori CC variano da 12 V (applicazioni automobilistiche) a 1.500 V CC (solare industriale e su larga scala). Le classificazioni comuni includono 12 V, 24 V, 48 V, 80 V, 125 V, 250 V, 600 V e 1.000 V CC. Per il solare residenziale, il massimo è in genere 600 V CC secondo i requisiti NEC.
D: Ho bisogno di una formazione specifica per installare gli interruttori automatici CC?
R: Sì, soprattutto per i sistemi superiori a 50 V CC o per le applicazioni commerciali. I sistemi CC hanno requisiti di sicurezza unici, tra cui il percorso dei cavi, l'etichettatura, l'arresto rapido e la protezione contro i guasti a terra. Le installazioni CC ad alta tensione (superiori a 600 V) richiedono professionisti elettrici qualificati che abbiano familiarità con l'articolo 690 e l'articolo 706 del NEC.
D: Come posso calcolare la dimensione corretta dell'interruttore CC per il mio impianto solare?
R: Utilizzare la corrente di cortocircuito (Isc) dalla scheda tecnica del pannello solare e moltiplicarla per 1,25 secondo NEC 690.8. Per la classificazione della tensione, calcolare la tensione a circuito aperto (Voc) corretta in base alla temperatura alla temperatura prevista più fredda. Arrotondare sempre alla successiva classificazione standard dell'interruttore. Tenere conto della riduzione della temperatura se la scatola di combinazione funziona a una temperatura superiore a 40 °C.
D: Qual è la differenza tra le classificazioni UL 489 e UL 1077?
R: UL 489 è lo standard di sicurezza più elevato per la protezione dei circuiti derivati: questi interruttori possono essere utilizzati come dispositivi di protezione autonomi nel sistema elettrico. UL 1077 copre i protettori supplementari progettati per l'uso solo all'interno delle apparecchiature, non per la protezione dei circuiti derivati. Per i sistemi solari, a batteria e elettrici per edifici, specificare sempre interruttori con classificazione UL 489.
D: Un unico interruttore automatico può funzionare sia per applicazioni CA che CC?
R: Alcuni interruttori hanno una doppia classificazione sia per CA che per CC, ma le classificazioni di tensione e corrente differiscono in modo significativo tra le due applicazioni. Un interruttore potrebbe essere classificato 240 V CA / 125 V CC, il che significa che può gestire una tensione CA più elevata ma solo una tensione CC inferiore a causa delle sfide di estinzione dell'arco. Verificare sempre sia le classificazioni CA che CC se si utilizza un interruttore a doppia classificazione e non superare mai nessuna delle due classificazioni.
D: Cosa succede se utilizzo il tipo sbagliato di interruttore automatico?
R: L'utilizzo del tipo di interruttore errato può comportare il mancato intervento in caso di correnti di guasto (con conseguenti rischi di incendio), l'effetto di saldatura ad arco (i contatti si fondono insieme in modo permanente), danni alle apparecchiature, violazioni del codice e potenziali lesioni. Nello scenario di apertura di questo articolo, l'utilizzo di un interruttore CA in un sistema CC ha causato danni per 40.000 €. La corretta selezione dell'interruttore è assolutamente fondamentale per la sicurezza e una protezione affidabile.