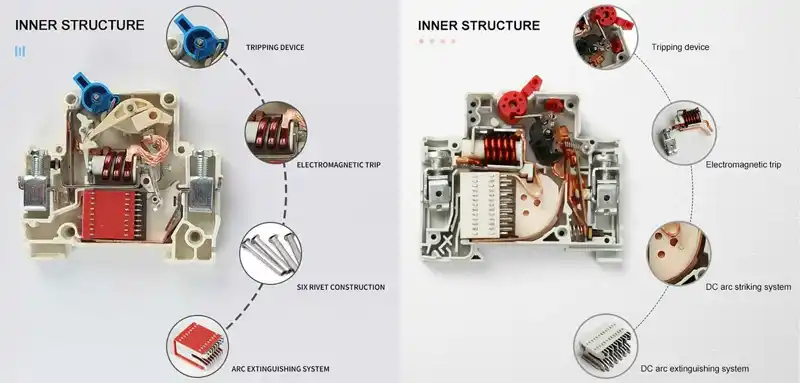
Mis on alalisvoolu ja vahelduvvoolu kaitselülitid?
Alalisvoolu kaitselülitite määratlus
Alalisvoolukaitselüliti on seade, mis kaitseb seadmeid alalisvooluga juhusliku kokkupuute tagajärjel tekkivate kahjustuste eest. See on oluline ohutusmehhanism elektrisüsteemides. Alalisvoolukaitselülitid on spetsiaalselt loodud alalisvoolusüsteemide ainulaadsete väljakutsete lahendamiseks, kus elekter voolab pidevalt ühes suunas.
Alalisvoolusüsteemide põhiomadused:
- Vool voolab ühes, konstantses suunas
- Pinge püsib stabiilne (ei vaheldu)
- Levinud päikesepaneelides, akudes ja elektriautodes
- Nõuab spetsiaalseid katkestamistehnikaid
Vahelduvvoolu kaitselülitite määratlus
Vahelduvvoolukaitselüliti on ülekoormuse kaitseseade, mis töötab vahelduvvooluga. See vool muudab suunda mitu korda sekundis – 50 või 60 korda, olenevalt elektrivõrgu sagedusest.
Kliimaseadmete põhiomadused:
- Vool muudab suunda 50–60 korda sekundis
- Pinge ületab nulli kaks korda tsükli jooksul
- Standard elamu- ja ärihoonetes
- Lihtsam katkestada loomulike nullpunktide ületamise tõttu
Alalisvoolu ja vahelduvvoolu kaitselülitite kriitilised erinevused
Kaare kustutamine: põhiline erinevus
Erinevalt vahelduvvoolust ei läbi alalisvool loomulikult nullpunkti, mistõttu on kaare katkestamine ja kustutamine raskem. Seetõttu vajavad alalisvoolukaitselülitid kaare tõhusaks kustutamiseks keerukamat konstruktsiooni.
Vahelduvvoolu kaare kustumine:
- Kuna vahelduvvoolu pinge vaheldub positiivse ja negatiivse vahel, on igas tsüklis kaks punkti, kus pinge on null. Kui kontaktid eralduvad ja tekib kaar, kaob kaar 1/120 sekundi jooksul.
- Looduslikud nullpunktid aitavad vooluringi katkestada
- Lihtsamad sisekujundusnõuded
Alalisvoolu kaare kustumine:
- Alalisvoolu korral, kus pinge on pidev, on elektrikaar püsiv ja katkestuskindlam. Sel põhjusel peavad alalisvoolukaitselülitid sisaldama täiendavaid kaarekustutusmeetmeid: neil on tavaliselt mehhanism elektrikaare pikendamiseks ja hajutamiseks, et lihtsustada katkestust.
- Nõuab magnetilisi väljapuhumismähiseid või spetsiaalset kontaktgeomeetriat
- Keerulisem ja kallim ehitus
Pinge ja voolutugevuse taluvusvõime
Siin on tabel, mis näitab alalisvoolu- ja vahelduvvoolukaitselülitite peamisi tehnilisi erinevusi:
| Funktsioon | Alalisvoolu kaitselülitid | Vahelduvvoolu kaitselülitid |
|---|---|---|
| Kaare väljasuremine | Spetsialiseeritud alalisvoolu jaoks: Võrreldes traditsiooniliste vahelduvvoolukaitselülititega on neil rohkem eeliseid alalisvoolukaaride käsitlemisel ja need suudavad kaare tõhusalt kustutada. | Loomulik nullpunkti ületamise abi |
| Pingeklassid | Alalisvoolu pinge võib elamutes ulatuda kuni 600 volti ja ärihoonetes 1000 või 1500 volti. | Standardsed 120 V, 240 V, 480 V nimiväärtused |
| Kontakt disain | Alalisvoolu jaoks on kaks ja vahelduvvoolu jaoks kolm peamist kontakti. | Kolm peamist kontakti kliimaseadmete jaoks |
| Hinnapunkt | Kõrgem hind: Alalisvoolukaitselülitite erilise disaini ja materjalinõuete tõttu on nende hinnad tavaliselt kõrgemad kui traditsioonilistel vahelduvvoolukaitselülititel. | Madalam hind lihtsama disaini tõttu |
| Suuruse nõuded | Suur suurus: Mõned alalisvoolukaitselülitite tüübid võivad olla suuremad ja hõivata rohkem paigaldusruumi oma kaare kustutamise ja soojuse hajutamise nõuete tõttu. | Kompaktsed standardsuurused |
Ohutusstandardid ja sertifikaadid
UL 489 standardid:
See standard hõlmab seadmeid, mille nimipinge on 1000 volti vahelduvvoolu ja 1500 volti alalisvoolu või vähem ning voolutugevus 6000 amprit või vähem. Nii alalis- kui ka vahelduvvoolukaitselülitid peavad läbima ranged ohutustestid, kuid UL 489 sertifikaat on kaitselülitite kõrgeim ohutusstandard. See on spetsiaalselt loodud haru-/eraldiseisva vooluahela kaitsmiseks.
Rakendused: millal kasutada alalisvoolu ja vahelduvvoolu kaitselüliteid
Alalisvoolu kaitselüliti rakendused
Päikeseenergia süsteemid:
- Alalisvoolukaitselülitid on eriti olulised olukordades, kus on kõrged ohutus- ja töökindlusnõuded, näiteks fotogalvaanilise energia tootmisel.
- NEC-i koodide kohaselt nõutav päikeseenergia ja salvestusprojektide puhul
- Päikesepaneelide stringide kõrgepinge käsitsemine
Elektrisõidukite laadimine:
- Elektrisõidukid (EV-d): Nõutakse kompaktseid ja suure jõudlusega kaitselüliteid, mis on võimelised taluma suuri alalisvoolusid
- Kiirlaadimisjaamade jaoks kriitilise tähtsusega
- Aku kaitse elektriautosüsteemides
Aku salvestussüsteemid:
- Alalisvoolukaitselülititel on oluline roll akupankade, päikesepaneelide massiivide, inverterite ja muu kaitsmisel.
- Vältige liitiumakude termilist läbimurret
- Hädavajalik võrguväliste elektrisüsteemide jaoks
Tööstus- ja raudteerakendused:
- Tööstus- ja raudteerakendused: vajavad suure lahutusvõimega tugevaid kaitselüliteid
- Mootori juhtimine alalisvooluajamisüsteemides
- Rasketehnika kaitse
Vahelduvvoolu kaitselüliti rakendused
Elamu- ja ärihooned:
- Vahelduvvoolukaitselülitid on levinud võrku ühendatud elektrisüsteemides
- Standard kodudes ja kontorites
- Kaitske kodumasinaid ja valgustusahelaid
Võrguga ühendatud süsteemid:
- Peamise elektripaneeli kaitse
- Toite- ja haruahela kaitse
- Tööstusmootorite juhtimine (vahelduvvoolumootorid)
Kuidas valida õige kaitselüliti
Alalisvoolu kaitselüliti valikukriteeriumid
1. Pingereitingu valik:
Kaitselüliti peaks olema nimipinge poolest sobiv päikesepaneelide või paneelide rea maksimaalsele pingele. Näiteks 12 V alalisvoolu kaitselüliti, 24 V alalisvoolu kaitselüliti ja muud sellised.
⚠️ Ohutushoiatus: Kasutage alati kaitselülitit, mis on spetsiaalselt ette nähtud alalispinge ja -voolu jaoks. Valige kaitselüliti, mille pinge nimiväärtus on võrdne või suurem teie süsteemi maksimaalsest alalispingest.
2. Voolutugevuse arvutamine:
Kaitselüliti peaks olema nimiväärtusega maksimaalsele voolule, mida päikesepaneel või paneelide jada suudab normaalsetes töötingimustes genereerida. Näiteks: 100 amprit alalisvoolukaitselüliti, 100 A alalisvoolukaitselüliti, 200 amprit alalisvoolukaitselüliti, 250 A alalisvoolukaitselüliti ja teised.
3. Katkestusvõime nõuded:
Lahutusvõime on maksimaalne vool, mille kaitselüliti suudab ohutult ja kahjustusteta välja lülitada. See on eriti oluline akusüsteemide puhul, kus lühisvoolud võivad olla äärmiselt suured.
Pinge katkestusvõime
Siin on tabel, mis näitab tüüpilisi alalisvoolukaitselülitite katkestusvõimeid:
| Süsteemi pinge | Tüüpiline katkestusvõime | Üldised rakendused |
|---|---|---|
| 12 V alalisvool | 5000A @12V | Autod, haagissuvilad, väikesed päikesepaneelid |
| 24V DC | 3000A @ 24V | Merendus, telekommunikatsioon |
| 48 V alalisvool | 1500A @ 42V | Andmekeskused, telekommunikatsioon |
| 125 V alalisvool | 10 000–25 000 A | Tööstussüsteemid |
| 600 V alalisvool | 14 000–65 000 A | Suured päikesepaneelid |
Vahelduvvoolu kaitselüliti valikukriteeriumid
1. Standardpinge reitingud:
- 120V elamute valgustuse ja pistikupesade jaoks
- 240 V suurtele kodumasinatele ja HVAC-seadmetele
- 480 V äri- ja tööstusrakenduste jaoks
2. Praegune reitingu valem:
Arvutage NEC nõuete kohaselt eeldatava koormusvoolu 125% põhjal:
Kaitselüliti reiting = koormusvool × 1,25
3. Katkestav võimsus:
- Elamumajandus: tüüpiline 10 000 AIC
- Kommertskasutus: 22 000–65 000 AIC-d
- Tööstus: kuni 200 000 AIC-d suure rikkesagedusega rakenduste jaoks
Kood nõuetele Vastavuse ja Tööohutuse Nõuded
Riikliku elektriseadustiku (NEC) nõuded
Alalisvooluahela nõuded:
HOONETE SEES peavad PV-süsteemide alalisvooluahelad, mille pinge ületab 30 volti või 8 amprit, olema paigutatud metallkaablikanalitesse või standardile 250.118(10) vastavatesse MC-tüüpi metallkestaga kaablitesse või metallkorpustesse.
Pinge piirangud:
Ühe- ja kahepereelamute puhul on endiselt piiratud 600 V alalisvoolu vooluringid ja teiste hoonete puhul on endiselt piiratud 1000 V alalisvoolu vooluringid.
Nõutav märgistus:
Järgmised PV-süsteemi alalisvooluahela juhtmeid sisaldavad juhtmestikumeetodid ja -ümbrised tuleb tähistada püsivalt kinnitatud siltidega, millel on kiri PHOTOVOLTAIC POWER ALLIKAS või SOLAR PV DC CIRCUIT.
Professionaalse paigalduse nõuded
🔧 Eksperdi nipp: Kõrged paigaldusnõuded: Kuna alalisvoolukaitselülitid käitlevad alalisvoolu, on nende paigaldus- ja juhtmestikunõuded kõrged, eriti kõrgepingerakendustes, mis nõuab professionaalset paigaldus- ja hoolduspersonali.
UL-i nimekirja nõuded:
- Kõik kaitselülitid peavad olema UL-sertifikaadiga
- UL 489 seadmeid hinnatakse ja need on loetletud kasutamiseks eraldiseisva tootena.
- Sobitage kaitselülitite nimiväärtused konkreetsete rakendustega
Tüüpiliste probleemide lahendamine
Alalisvoolusüsteemi probleemid
Kaarkeevituse efekt:
Kui alalisvoolukaitselüliti ei suuda kaarlahendust korralikult katkestada, võivad kontaktid kokku keevitada. See ohtlik seisund nõuab viivitamatut professionaalset sekkumist.
Pingereitingu mittevastavused:
80 V alalisvoolukaitselüliti kasutamine 48 V alalisvoolusüsteemis ei pruugi olla piisav, kuna päikesepaneelide avatud vooluringi pinge (Voc) võib enne temperatuurikorrektsiooni olla üle 88 V alalisvoolu.
Kliimaseadme probleemid
Häiriv väljalülitus:
Sageli põhjustatud ülekoormatud vooluringidest või suure käivitusvooluga seadmetest. Lahendus: uuendage võimsama kaitselüliti vastu või vähendage vooluringi koormust.
Halva kontaktiga seotud probleemid:
Niiskes keskkonnas on kaitselülititele soovitatav spetsiaalne niiskustöötlus. See töötlus aitab vältida hallitust ja/või seeni, mis võivad seadet korrodeerida.
Keskkonnaalased kaalutlused
Temperatuuri mõjud
Kõrge temperatuuriga rakendused:
Kui temperatuuril üle 104 °F (40 °C) kasutatakse standardseid termomagnetilisi kaitselüliteid, tuleb kaitselüliti nimiväärtust vähendada või see vastavalt keskkonnale ümber kalibreerida.
IP-reitingu nõuded
Välistingimustes paigaldamiseks valige sobiva IP-kaitseastmega kaitselülitid:
- IP65Tolmukindel ja veekindel
- IP67Veekindel ja sobib kasutamiseks karmides keskkondades
- NEMA 4XKorrosioonikindel merendusrakenduste jaoks
Kiire valiku juhend
Päikeseenergia süsteemide jaoks
- Vajalikud alalisvoolukaitselülitid päikesepaneelide stringide jaoks
- Pinge nimiväärtus ≥ süsteemi maksimaalne tühikäigupinge
- Voolutugevus = 125% paneeli maksimaalsest väljundvõimsusest
- Täiustatud tehnoloogia kasutamisel peab tahkislülitite puhul vastama UL 489I sertifitseerimisnõuetele
Elamute rakenduste jaoks
- Vahelduvvoolukaitselülitid kõigi majapidamisvooluringide jaoks
- Standardsed 120V/240V nimivoolud
- AFCI/GFCI kaitse seal, kus kood seda nõuab
- Soovitatav on professionaalne paigaldus
Elektriautode laadimiseks
- Alalisvoolukaitselülitid aku kaitsmiseks
- Vahelduvvoolukaitselülitid laadimisjaama toiteks
- Nõutav suur katkestusvõime
- Temperatuuri alandamine võib olla vajalik
Korduma Kippuvad Küsimused
K: Kas ma saan alalisvoolusüsteemis kasutada vahelduvvoolu kaitselülitit?
A: Vahelduvvoolukaitselüliti kasutamine alalisvoolusüsteemis võib kujutada endast ohutusriski ega pruugi rikkevoolusid tõhusalt katkestada. Ohutuse ja nõuetekohase töö tagamiseks kasutage alati konkreetse süsteemi jaoks sobivat tüüpi kaitselülitit.
K: Miks on alalisvoolu kaitselülitid kallimad kui vahelduvvoolu kaitselülitid?
A: Alalisvoolukaitselülitite erilise konstruktsiooni ja materjalinõuete tõttu on nende hinnad tavaliselt kõrgemad kui traditsioonilistel vahelduvvoolukaitselülititel. Keerulised kaarekustutusmehhanismid ja spetsiaalsed materjalid suurendavad tootmiskulusid.
K: Millised pingereitingud on alalisvoolukaitselülititele saadaval?
A: Alalisvoolukaitselülitid on saadaval erinevates nimivooludes alates 12 V autotööstusele kuni 1500 volti alalisvoolu või vähem tööstus- ja päikeseenergia rakenduste jaoks.
K: Kas alalisvoolukaitselülitite paigaldamiseks on vaja eriväljaõpet?
V: Jah, eriti kõrgepinge rakenduste puhul. Kõrged paigaldusnõuded: Kuna alalisvoolukaitselülitid taluvad alalisvoolu, on nende paigaldus- ja juhtmestikunõuded kõrged, eriti kõrgepinge rakendustes, mis nõuab professionaalset paigaldus- ja hoolduspersonali.
K: Kuidas arvutada oma päikesesüsteemi jaoks õige suurusega alalisvoolukaitselüliti?
A: Kaitselüliti peaks olema nimiväärtusega maksimaalsele voolule, mida päikesepaneel või paneelide jada suudab normaalsetes töötingimustes genereerida. Kasutage tootja spetsifikatsioone ja rakendage NEC 125% nimivõimsuse vähendamise tegurit.
K: Mis vahe on UL 489 ja UL 1077 hinnangutel?
A: UL 489 sertifikaat on kaitselülitite kõrgeim ohutusstandard. See on spetsiaalselt loodud harukontori/eraldiseisva vooluahela kaitsmiseks, samas kui UL 1077 hõlmab seadmete sees kasutatavaid lisakaitsmeid.
K: Kas üks kaitselüliti saab töötada nii vahelduv- kui ka alalisvoolurakendustes?
A: c3controls seeria 1100 UL 489 harukaitselülitid ja UL 1077 lisakaitsmed sobivad nii vahelduvvoolu- kui ka alalisvooluahelatele. Tööpinged on aga väga erinevad. Saadaval on spetsiaalsed kahe nimipingega kaitselülitid, millel on vahelduvvoolu ja alalisvoolu jaoks oluliselt erinevad pinged.
K: Mis juhtub, kui ma kasutan valet tüüpi kaitselülitit?
A: Vale tüüpi kaitselüliti kasutamine võib põhjustada rikkevoolude katkestamata jätmise, potentsiaalse tuleohu, eeskirjade rikkumise ja seadmete kahjustumise. Ohutuse ja vooluahela usaldusväärse kaitse tagamiseks on ülioluline kasutada konkreetse elektrisüsteemi jaoks õiget tüüpi kaitselülitit.
Professionaalsed soovitused
⚡ Esmajärjekorras ohutus: Ärge kunagi proovige vahelduvvoolu- ja alalisvoolukaitselüliteid omavahel vahetada. Kaare kustumise ja vooluomaduste põhimõttelised erinevused muudavad selle äärmiselt ohtlikuks.
🔍 Koodide järgimine: Kontrollige alati oma rakenduse jaoks kohalikke elektrieeskirju ja NEC-i nõudeid. Alalisvoolusüsteemidel on juhtmete kaitsmise ja märgistamise osas erinõuded.
🛠️ Professionaalne paigaldus: Üle 50 V alalisvoolusüsteemide või mis tahes ärirakenduste puhul kaasake kvalifitseeritud elektrik, kes tunneb alalisvoolusüsteemi nõudeid.
📋 Dokumentatsioon: Ohutuse ja garantii tagamiseks pidage kaitselülitite spetsifikatsioonide, paigalduskuupäevade ja katsetulemuste kohta üksikasjalikke andmeid.
Alalisvoolu- ja vahelduvvoolu kaitselülitite oluliste erinevuste mõistmine tagab ohutud ja eeskirjadele vastavad elektripaigaldised. Olenemata sellest, kas projekteerite päikeseenergia süsteemi, uuendate elamute vooluringe või planeerite tööstusrakendusi, on õige kaitselüliti tüübi ja nimivõimsuse valimine seadmete kaitse ja inimeste ohutuse tagamiseks hädavajalik.
Keeruliste paigalduste või kaitselüliti valiku kahtluse korral konsulteerige alati kvalifitseeritud elektrikutega, kes mõistavad teie rakenduse erinõudeid ja kohalikke elektrieeskirju.
Seotud
Miks me kasutame kodus vahelduvvoolu, mitte alalisvoolu
Päikese-, aku- ja elektriautosüsteemide alalisvoolukaitselülitite praktiline juhend