Introduction
In electrical systems, and particularly in solar photovoltaic (PV) installations, understanding the differences between distribution boxes and combiner boxes is crucial. Both play significant roles but are tailored for distinct functionalities. This blog will explore what each box does, their components, applications, and key differences.
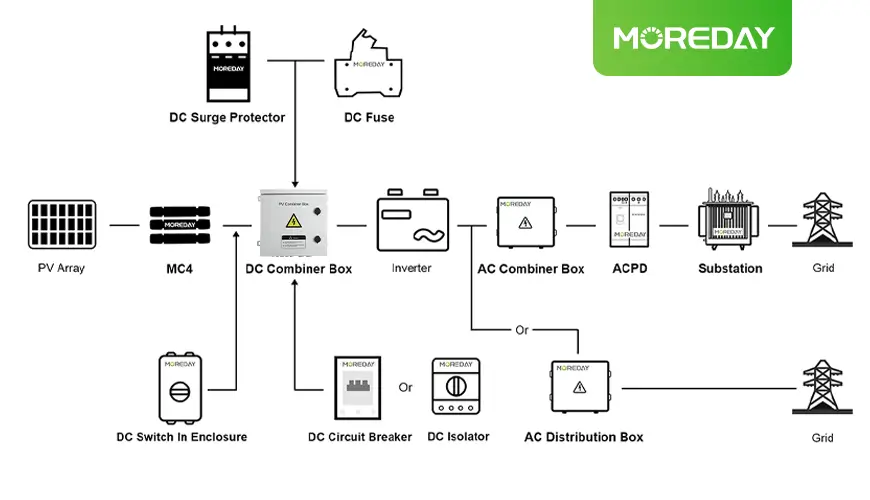
Credit to Moreday
Understanding Distribution Boxes
A distribution box is a central point for distributing electrical power from a single source to multiple circuits. It ensures safe power management and includes protective elements such as circuit breakers or fuses to guard against overloads. Here’s a closer look at their features and applications:
Functionality
Distribution boxes are designed to distribute electrical power to various circuits within a building or facility, providing protection against faults to ensure safe operation.
Components
A typical distribution box contains:
- Circuit Breakers: Protect each circuit against overloads and short circuits.
- Fuses: Offer additional protection by breaking the circuit under fault conditions.
- Surge Protection Devices: Safeguard against voltage spikes.
Applications
These boxes are widely used in:
- Residential Settings: Manage household electrical systems safely.
- Commercial Settings: Distribute power efficiently in office buildings and retail environments.
- Industrial Settings: Ensure proper power management for heavy machinery and equipment.
Design
Distribution boxes are designed for both indoor and outdoor use, with weatherproof enclosures for outdoor applications to withstand various environmental conditions.
Understanding Combiner Boxes
A combiner box is specifically used in solar energy systems to consolidate outputs from multiple solar panels or inverters into a single output. This simplifies wiring and enhances overall system safety. Key features include:
Functionality
Combiner boxes combine the DC or AC outputs of several solar panels or inverters into one output line, which is then fed into an inverter or the grid.
Components
A typical combiner box includes:
- Fuses or Circuit Breakers: Provide protection for each input string.
- Surge Protection Devices: Protect against voltage spikes.
- Monitoring Equipment: Sometimes included to track performance.
Applications
Primarily used in solar PV systems, combiner boxes are essential for managing and organizing multiple strings of solar panels efficiently and safely.
Design
Combiner boxes are often designed to be weather-resistant, with an IP65 rating or higher, making them suitable for outdoor conditions where solar panels are typically installed.
Comparing Distribution Boxes and Combiner Boxes
| Aspect | Distribution Box | Combiner Box |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Distributes electrical power to multiple circuits | Combines outputs from multiple solar panels or inverters into a single line |
| Typical Components | Circuit breakers, fuses, surge protection devices | Fuses or circuit breakers for each string, surge protection, sometimes monitoring equipment |
| Usage Context | Used in general electrical systems across residential, commercial, and industrial settings | Specifically used in solar photovoltaic systems to streamline and secure the wiring process |
| Protection Mechanism | Protects against overloads to individual circuits | Protects against overcurrent and surges in solar panel installations |
| Installation Location | Suitable for indoor and outdoor installations, often weatherproof for outdoor use | Primarily installed outdoors near solar panel arrays, designed to withstand environmental challenges |
Installation Complexity Comparison
When comparing distribution boxes and combiner boxes, installation complexity is an important factor to consider. Here’s a breakdown of the installation considerations for each:
- Distribution Box Installation:
- Generally simpler to install due to standardized components and wiring methods
- Typically installed indoors, often in utility rooms or basements
- Requires proper grounding and adherence to local electrical codes
- May need professional installation depending on the complexity of the electrical system
- Combiner Box Installation:
- More complex installation process, especially in large-scale solar systems
- Often installed outdoors, requiring weather-resistant enclosures
- Involves connecting multiple solar panel strings, which can be intricate
- Requires careful planning of wire routing and management
- May include additional components like surge protection devices or monitoring systems
- Shared Considerations:
- Both require proper labeling of circuits for easy identification and maintenance
- Installation complexity increases with system size for both types of boxes
- Proper ventilation is crucial to prevent overheating, especially for combiner boxes in solar installations
- Impact on Overall System:
- Combiner boxes can significantly reduce wiring complexity in solar installations, potentially lowering overall installation costs
- Distribution boxes simplify future expansions of electrical systems in buildings
- Both types of boxes contribute to system efficiency and safety when installed correctly
While distribution boxes are generally more straightforward to install in traditional electrical systems, combiner boxes require more specialized knowledge due to their role in solar power systems. The installation complexity of combiner boxes is offset by their ability to streamline large-scale solar installations and improve system performance
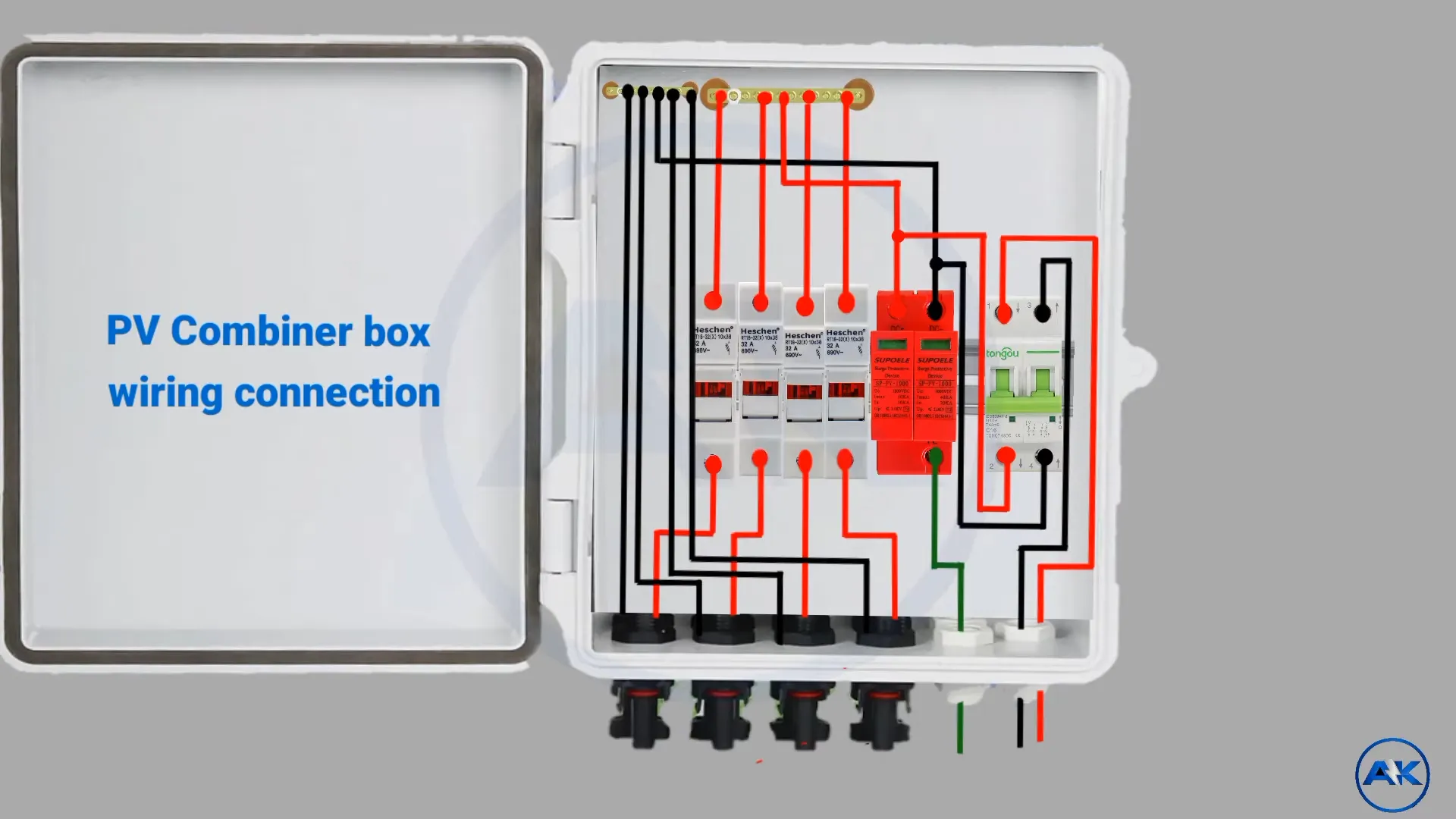
Combiner Boxes Wire Connection
Explore More: https://viox.com/solar-combiner-box-wiring-diagram/
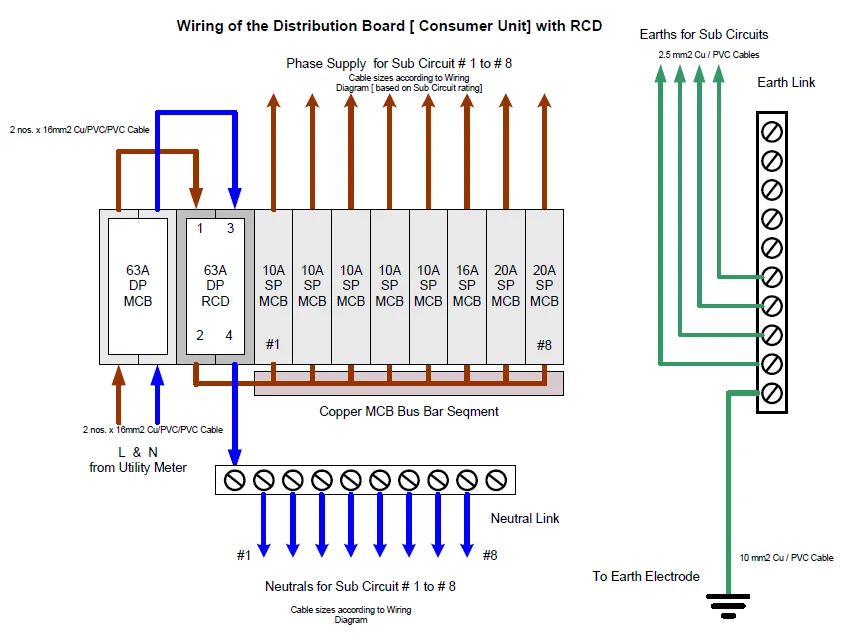
Distribution Boxes Wire Diagram
Explore More:https://viox.com/distribution-box-and-selection-guide/
Conclusion
In summary, while both distribution boxes and combiner boxes are vital for managing electrical connections, their roles differ significantly. Distribution boxes are designed to distribute power safely across various circuits in general electrical systems, whereas combiner boxes are specialized for aggregating outputs from solar panels before sending them to an inverter. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the appropriate device based on the specific requirements of an electrical installation, especially in solar PV systems. For tailored advice and optimal selection, consulting with professionals is recommended.